- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Determination of Boron Content Using a Simple and Rapid Miniaturized Curcumin Assay
Published: Vol 8, Iss 2, Jan 20, 2018 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2703 Views: 8690
Reviewed by: Kyoko MIWAMagdalena MigockaAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Efficient Generation of Genome-wide Libraries for Protein–ligand Screens Using Gibson Assembly
Tamara Sternlieb [...] Igor Cestari
Nov 20, 2022 3433 Views

Purification of Human Cytoplasmic Actins From Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Brian K. Haarer [...] Jessica L. Henty-Ridilla
Dec 5, 2023 1745 Views

CAPS-Based SNP Genotyping for Nitrogen-Response Phenotypes in Maize Hybrids
Jannis Jacobs [...] Peter K. Lundquist
Dec 20, 2025 543 Views
Abstract
To determine boron quantity in soil, water and biological samples, several protocols are available. Colorimetric assays are the simplest and cheapest methods which can be used to determine boron concentration. However, published protocols do not give straightforward guidance for beginners to adopt these protocols for routine use in the laboratory. Based on a previously published available procedure, we present a detailed and modified version of a curcumin based colorimetric protocol to determine boron concentration extracted from any sample. Our modified protocol is able to determine up to 0.2 nmole of Boron in a sample volume of 300 µl.
Keywords: BoronBackground
Boron (B) can be quantified using spectrometric and colorimetric methods. Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) is the most sensitive method currently available having a detection limit of 0.01 mg/L (Kmiecik et al., 2016) but requires a sample volume of 5 ml. However, this technique requires sophisticated and expensive equipment which is not affordable for smaller laboratories. Alternatively, colorimetric based assays using curcumin or Azomethine-H dyes can be used for the routine analysis of boron in all laboratories with access to a spectrophotometer that can measure absorbance at 550 nm. Bingham (1982) reported that the curcumin assay is more efficient than the Azomethine-H based assay. Therefore, we present a modified version of simple and rapid curcumin assay to quantify B based on a protocol originally published by Wimmer and Goldbach (1999). We have used this protocol to determine the intracellular boron in yeast cells and Arabidopsis protoplasts. Additionally, this protocol can be used to study the uptake, root to shoot translocation-mechanisms of Boron in plants.
Materials and Reagents
Note: As boron leaches from lab glassware, all chemicals should be prepared in plastic bottles.
- Falcon tubes (15 ml and 50 ml) (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 62.547.254 )
- 1.5 ml tubes
- Pipette tips
- 96-Well UV Microplate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 8404 )
- Boric acid (H3BO3) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 15663 )
- 0.1 N hydrochloric acid (HCl)
- 2-Ethyl-1,3-hexanediol (Acros Organics, catalog number: 118512500 )
- Chloroform (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 10122190 )
- Concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 10294300 )
- Concentrated acetic acid (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 10304980 )
- Curcumin (Alfa Aesar, catalog number: B21573 )
- Methyl-Isobutyl-Ketone (MIBK) (Avantor Performance Materials, MACRON, catalog number: 6247-04 )
- Extraction solution (see Recipes)
- Acid mixture (see Recipes)
- Curcumin solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Centrifuge
- Chemical fume hood
- Pipette
- Microplate reader (BMG LABTECH, model: CLARIOstar )
Procedure
- Harvest the yeast/protoplasts samples in a 50 ml Falcon tube by centrifugation at 4,000 x g (for yeast)/100 x g (for protoplast) for 5 min. Wash the pellet with 25 ml ice cold water to remove boric acid from the pellet. Resuspend the pellet in 400 µl of Milli-Q water in a 1.5 ml tube. Heat the samples at 90 °C for 30 min and vortex to release intracellular B into solution. Centrifuge at maximum speed for 2 min at room temperature and collect 300 µl of supernatant for B quantification.
For detailed boron uptake assay in yeast, users may refer to Takano et al., 2002 ; and to process the protoplasts from plant tissue please refer to Yoo et al., 2007.
Note: We recommend that users test the assay with their own buffers/solvents if they do not use water to solubilise their samples.
- Prepare standards containing 0, 0.02, 0.05, 0.10, 0.19, 0.39, 0.77 mg boric acid/L using Milli-Q water in a 15 ml Falcon tube (refer to Table 1).
Table1. Boric acid standards presented in different units
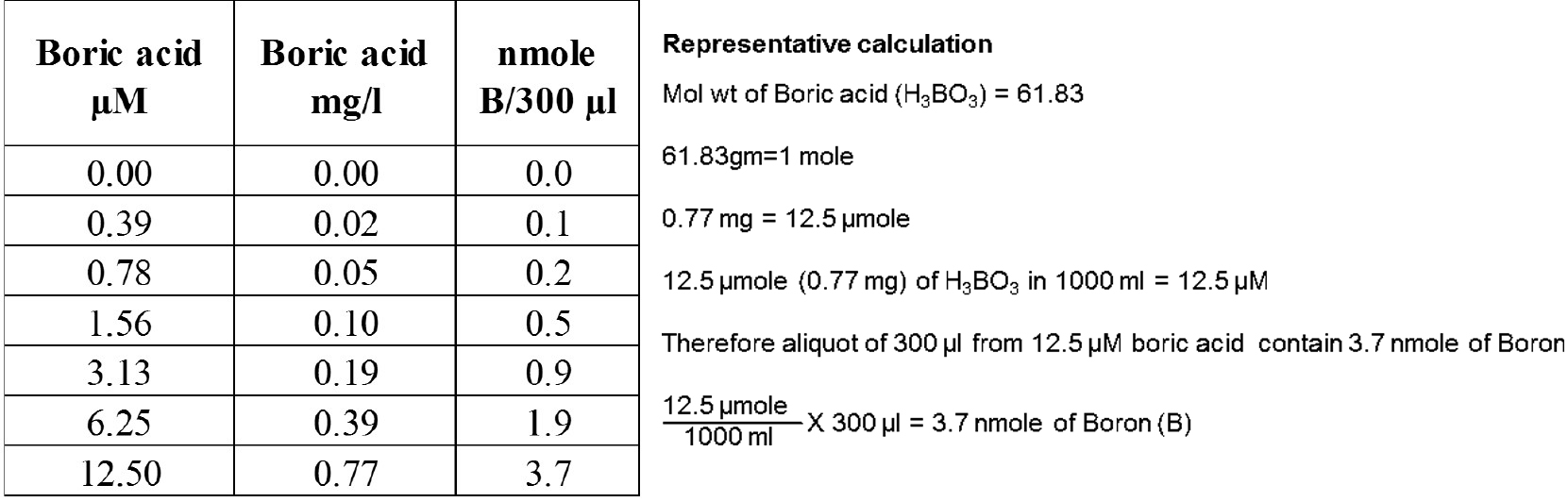
- Aliquot 300 µl (which is equivalent to 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 0.9, 1.9, 3.7 nmole B) of each standard and samples into 1.5 ml tubes.
- Acidify the samples and standards by adding 100 µl of 0.1 N HCl. Mix well by vortex and incubate for 5 min at room temperature.
Note: From Step 3 onwards perform all the reactions in chemical fume hood.
- Add 70 µl extraction solution (see Recipes), mix vigorously by vortexing for 30 sec. After 2 min, repeat the vortex for another 30 sec.
- Centrifuge the samples at 15,000 x g speed for 5 min to facilitate clear separation of organic phase.
- Pipette 50 µl of lower organic phase (Figure 1A) into a new 1.5 ml tube containing 200 µl of acid mix (see Recipes) and mix well by vortexing.
Notes:- Be aware that the lower phase contains chloroform and that chloroform leaks out from plastic pipette tips. To avoid pipetting errors, make sure that the tip is tightly attached to pipette and transfer liquids quickly.
- The mixture of sulphuric acid and acetic acid is a viscous solution. Therefore, care must be taken while pipetting to avoid pipetting errors and hazards to users from corrosive solutions. We recommend cutting the tip of the 1 ml tip and pipette slowly in a fume hood.
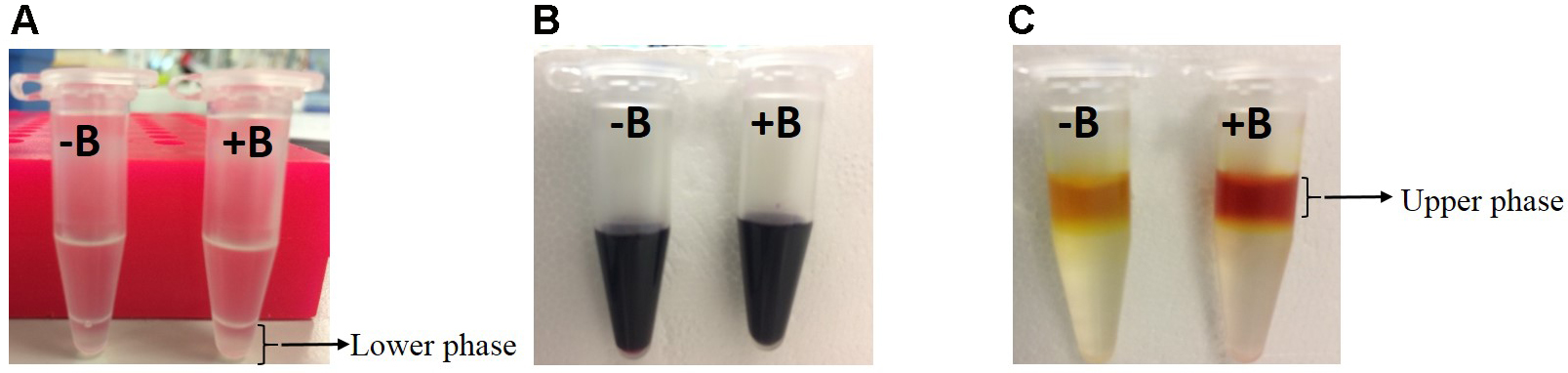
Figure 1. Steps showing phase separation and colour development in the absence (-B) or presence (+B) of boron
- Be aware that the lower phase contains chloroform and that chloroform leaks out from plastic pipette tips. To avoid pipetting errors, make sure that the tip is tightly attached to pipette and transfer liquids quickly.
- Add 250 µl of curcumin solution (see Recipes) and shake well until it forms homogenous dark purple colour (Figure 1B).
- Centrifuge the tubes at 15,000 x g for 1 min and incubate the reaction mixture at room temperature for 1 h.
- After 1 h, stop the reaction by adding 500 µl of Milli-Q water and mix well by inverting the tubes.
- Centrifuge the tubes at 15,000 x g for 1 min to facilitate clear phase separation.
- Carefully pipette 200 µl of upper phase (Figure 1C) into a 96-well UV Microplate and measure the absorbance at 550 nm using a microplate reader.
Note: Chloroform in the reaction mixture melts many types of plastic microplates and interferes in absorbance reading. Therefore, it is very important to use microplates resistant to organic solvents (for example, Thermo ScientificTM 96-Well UV Microplate or a quartz microplate).
- Plot the absorbance against the quantity of B and prepare the calibration curve as shown in Figure 2. To obtain calibration curve, plot the absorbance values (A550 nm) against the quantity of boron (nmole B) using a spreadsheet (left panel of Figure 2).
Note: Jennings et al., 2007 have used both curcumin method and ICP-MS to quantify boron in yeast cells. They found that using the two methods the results were indistinguishable.
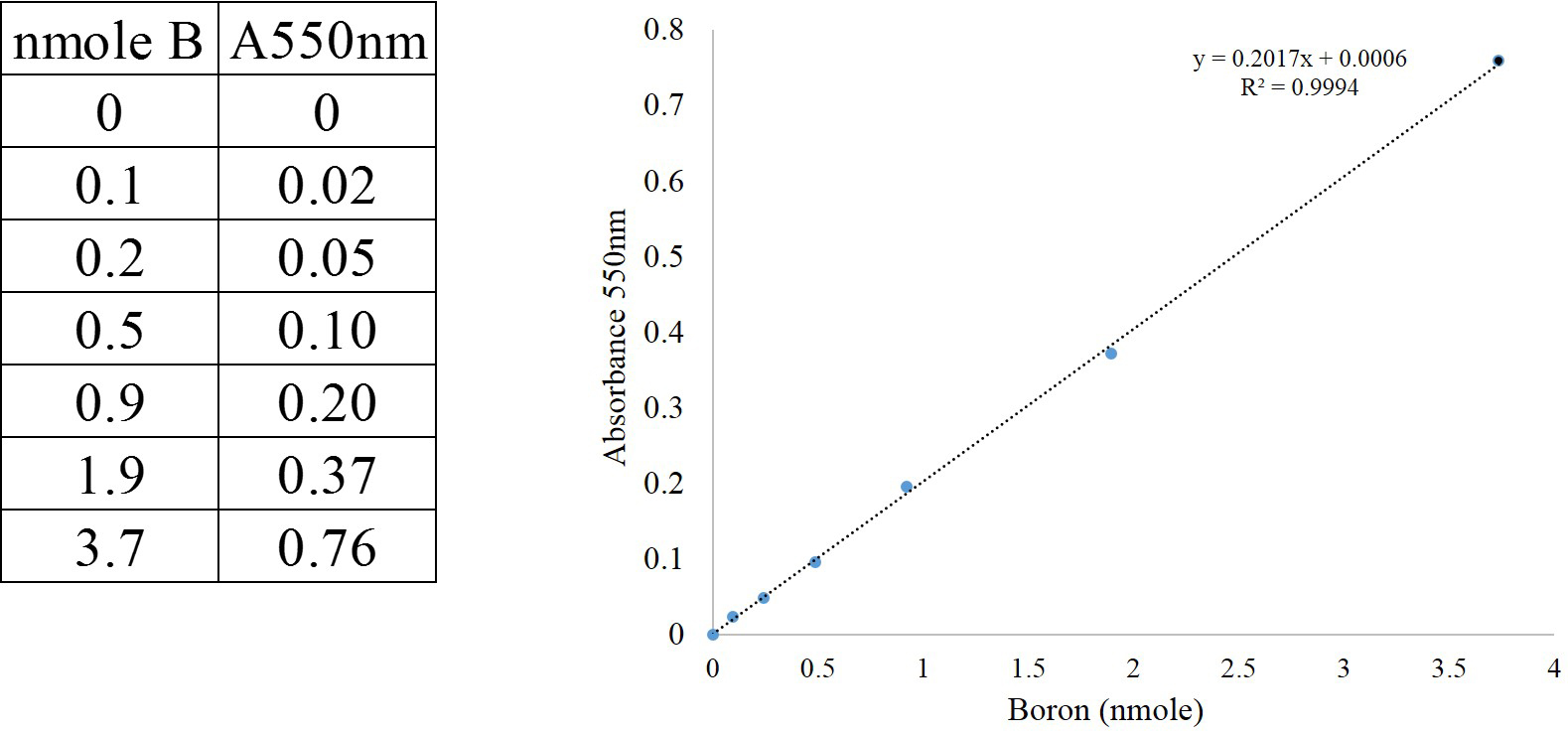
Figure 2. Calibration curve for the determination of boron concentration. Absorbance measured at 550 nm (A550 nm).
- Use the obtained calibration curve to determine the quantity of B in unknown samples.
Recipes
Note: Every time make fresh solutions in a falcon tube.
- Extraction solution
Dissolve 2-ethyl-1,3-hexanediol 10% (v/v) in chloroform
- Acid mixture
Mix sulphuric acid (conc.) and acetic acid (conc.) in 1:1 (v/v) ratio in a Falcon tube
- Curcumin solution
Dissolve curcumin (2 mg/ml) powder in MIBK (Methyl-Isobutyl-Ketone)
Acknowledgments
This protocol is adapted from the original paper by Wimmer and Goldbach (1999). This work is supported by Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) grant (BB/N017765/1), United Kingdom. Authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bingham, F. T. (1982). Boron. In: Page, A. L. (Ed.). Methods of soil analysis Part-2 chemical and mineralogical properties. American Society of Agronomy pp: 431-448.
- Jennings, M. L., Howren, T. R., Cui, J., Winters, M. and Hannigan, R. (2007). Transport and regulatory characteristics of the yeast bicarbonate transporter homolog Bor1p. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 293(1): C468-76.
- Kmiecik, E., Tomaszewska, B., Wator, K. and Bodzek, M. (2016). Selected problems with boron determination in water treatment processes. Part I: comparison of the reference methods for ICP-MS and ICP-OES determinations. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23(12): 11658-11667.
- Takano, J., Noguchi, K., Yasumori, M., Kobayashi, M., Gajdos, Z., Miwa, K., Hayashi, H., Yoneyama, T. and Fujiwara, T. (2002). Arabidopsis boron transporter for xylem loading. Nature 420(6913): 337-40.
- Yoo, S. D., Cho, Y. H. and Sheen, J. (2007). Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts: a versatile cell system for transient gene expression analysis. Nat Protoc 2(7): 1565-72.
- Wimmer, M. A. and Goldbach, H. E. (1999). A miniaturized curcumin method for the determination of boron in solutions and biological samples. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 162: 15-18.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2018 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
TC, M. and Jones, A. M. E. (2018). Determination of Boron Content Using a Simple and Rapid Miniaturized Curcumin Assay. Bio-protocol 8(2): e2703. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2703.
Category
Plant Science > Plant physiology > Nutrition
Microbiology > Heterologous expression system > Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Biochemistry > Other compound > Boron
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










