- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Quantification of Trypanosoma cruzi in Tissue and Trypanosoma cruzi Killing Assay
Published: Vol 7, Iss 22, Nov 20, 2017 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2613 Views: 8196
Reviewed by: Alexandros AlexandratosAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

A Participant-Derived Xenograft Mouse Model to Decode Autologous Mechanisms of HIV Control and Evaluate Immunotherapies
Emma Falling Iversen [...] R. Brad Jones
Apr 5, 2025 2555 Views

PBMC-Humanized Mouse Model for Multiple Sclerosis: Studying Immune Changes and CNS Involvement
Anastasia Dagkonaki [...] Lesley Probert
May 20, 2025 4045 Views

Isolation and Imaging of Microvessels From Brain Tissue
Josephine K. Buff [...] Sophia M. Shi
Aug 5, 2025 2698 Views
Abstract
Infection with Trypanosoma cruzi causes Chagas disease. The methods provided here allow for the quantification of T. cruzi in the liver, heart, and blood of intraperitoneally-infected mice and analysis of the killing activity of the cells infected with T. cruzi in vitro.
Keywords: Trypanosoma cruziBackground
Chagas disease, characterized by chronic cardiomyopathy, is caused by infection with the intracellular protozoan parasite Trypanosoma cruzi (Bonney et al., 2015). Approximately 20 million people in Latin America suffer from Chagas disease (Ribeiro et al., 2012; Flavia Nardy et al., 2015), and it has become a global health issue owing to the migration of infected individuals (Andrade et al., 2014; Garcia et al., 2015; Requena-Mendez et al., 2015). Several drugs, such as nifurtimox and benznidazole, have been developed for treating Chagas disease. However, these drugs need to be taken for several months and severe side effects have been reported (Viotti et al., 2009). A major aim of treatment is to inhibit T. cruzi transmission via blood as well as prevent the development of heart failure. Thus, the protocol for quantification of T. cruzi and the T. cruzi killing assay presented here might aid the development of novel diagnostic methods and therapeutic strategies for Chagas disease.
Part I: Quantification of T. cruzi in tissue
The following protocol (Kitada et al., 2017) was partially modified from the previously described methods (Cencig et al., 2011; Caldas et al., 2012).
Materials and Reagents
- Pipette tips (Labcon, catalog numbers: 1093-260-000 , 1045-260-000 , 1036-260-000 )
- 15 cm culture dishes (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 150468 )
- Blood collection tubes CAPIJECT (Terumo, catalog number: CJ-NA )
- 10 cm Petri dishes (Sansyo, catalog number: 36-3406 )
- 1.5 ml microtubes (FUKAEKASEI and WATSON, catalog number: 131-415C )
- Disposal hemocytometer (All-Biz, catalog number: 4109:37650 )
- 8-week-old male and female C57BL/6 mice (Japan SLC)
- LLC-MK2 cells (Rhesus monkey kidney epithelial cells) gifted by Professor S. Hamano (Institute of Tropical Medicine, Nagasaki University), which are also available at ATCC. Information regarding the LLC-MK2 cells is available at https://www.atcc.org/en/Products/Cells_and_Microorganisms/By_Tissue/Kidney/CCL-7.aspx#documentation
- Trypanosoma cruzi Tulahuen strain (gifted by professor S. Hamano (Institute of Tropical medicine, Nagasaki University))
- 10 mg/ml Proteinase K (Merck, catalog number: 124568 )
- Phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1) (NACALAI TESQUE, catalog number: 25970-56 )
- Chloroform (JUNSEI CHEMICAL, catalog number: 28560-0330 )
- 2-Propanol (JUNSEI CHEMICAL, catalog number: 64605-0330 )
- 70% ethanol (JUNSEI CHEMICAL, catalog number: 17065-0382 )
- TE buffer solution (pH 8.0) (NACALAI TESQUE, catalog number: 32739-31 )
- Go Taq qPCR Master Mix (Promega, catalog number: A6002 )
- RPMI 1640 (NACALAI TESQUE, catalog number: 30264-56 )
- Primers (Invitrogen custom DNA primers)
T. cruzi specific primers (Tc1), 5’-cgagctgttgcccacacgggtgct-3’ and 5’-cctccaagcagcggatagttcagg-3’ (Cencig et al., 2011); and TNF-α DNA primers, 5’-tccctctcatcagttctatggccca-3’ and 5’-cagcaagcatctatgcacttagacccc-3’ (Caldas et al., 2012)
- Lysis buffer (see Recipes)
- Tris-HCl (NACALAI TESQUE, catalog number: 35434-21 )
- Ethylenediaminetetraacetate acid (EDTA) (NACALAI TESQUE, catalog number: 06894-14 )
- Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 311-90271 )
- Potassium chloride (NaCl) (JUNSEI CHEMICAL, catalog number: 19015-0350 )
- Tris-HCl (NACALAI TESQUE, catalog number: 35434-21 )
- RPMI 1640 culture medium (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Pipettes (Nichiryo, catalog numbers: 00-NPX2-1000 , 00-NPX2-200 , 00-NPX2-20 , 00-NPX2-2 )
- Forceps (Hammacher, catalog number: HSC_553-11 )
- Microbalance (Chyo Balance, model: JPN-200W )
- Scissor (Fine Science Tools, catalog number: 91460-11 )
- Shaking incubator (TAITEC, model: BR-43FM MR )
- Centrifuge (TOMY SEIKO, model: MX-200 )
- Vortex
- Real-Time PCR thermal cycler: Step One PlusTM system Real-Time PCR System (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Applied BiosystemsTM, model: StepOnePlusTM, catalog number: 4376600 )
- Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, model: NanoDropTM 2000 )
Procedure
- T. cruzi preparation
- 5 x 105-1 x 106 LLC-MK2 cells are seeded into a 15 cm culture dish on day 1 before infection.
- The LLC-MK2 cells seeded in step A1 are infected with 2 x 106 T. cruzi strain Tulahuen (MOI = 2).
- Change the culture medium (20 ml) every 3 days. In Figure 1A, amastigotes are shown in T. cruzi-infected cells (Panel A), which differentiate into the infective form trypomastigotes (Panel B) that are released into the culture medium.
- After 7 days of infection, trypomastigotes in the culture supernatants are counted microscopically (Figure 1). Approximately 2 x 107 trypomastigotes are obtained.
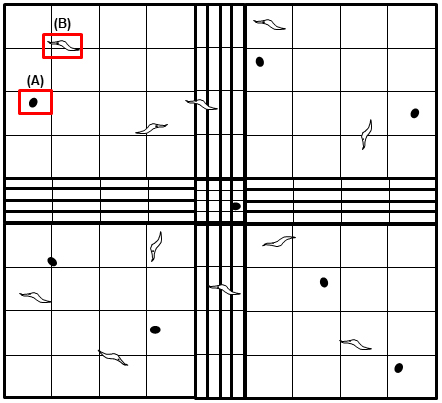
Figure 1. Schematic of T. cruzi in a hemocytometer. A. Amastigotes; B. Trypomastigotes.
- 5 x 105-1 x 106 LLC-MK2 cells are seeded into a 15 cm culture dish on day 1 before infection.
- Preparation of tissue standards and quantitative PCR
- Collect the liver and heart from a non-infected mouse into a 15 cm Petri dish and collect the blood (more than 200 μl) in a CAPIJECT tube.
- Cut the heart and liver into small pieces by scissor and add 1 x 106 T. cruzi trypomastigotes to 30 mg heart, 30 mg liver, or 200 μl blood from a non-infected C57BL/6 mouse in a 1.5 ml microtube.
- Add 500 μl lysis buffer (see Recipes) and 5 μl of 10 mg/ml Proteinase K and incubate at 55 °C in a shaking incubator (shaking speed: 110 times/min) for 18 h.
- Centrifuge at 13,000 x g for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Transfer the supernatant to a fresh 1.5 ml microtube.
- Add 500 μl phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1) and mix the contents of the microtube using a vortex.
- Centrifuge at 13,000 x g for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Transfer the upper layer to a fresh 1.5 ml microtube.
- Add 500 μl chloroform and mix the contents of the microtube using a vortex.
- Centrifuge at 13,000 x g for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Transfer the upper layer to a fresh 1.5 ml microtube.
- Add 500 μl 2-propanol and mix the contents of the microtube using a vortex.
- Centrifuge at 13,000 x g for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Aspirate the supernatant and wash the pellet in 500 μl 70% ethanol gently.
- Centrifuge at 5,500 x g for 5 min at 4 °C.
- Aspirate the supernatant and air dry for 10 min.
- Dissolve the DNA pellet in TE buffer solution (pH 8.0) and measure the concentration of DNA to generate 25 μg/ml tissue DNA.
- DNA from the tissue spiked with T. cruzi is sequentially 10-fold diluted with 25 μg/ml DNA from the tissues without T. cruzi (Figure 2). The prepared standards contain DNA from 103-10-2 parasites per 50 ng of total DNA. A standard curve to determine the amounts of T. cruzi DNA in the tissues from mice infected with T. cruzi is generated using these standards. The pipet tips should be changed in between each dilution.
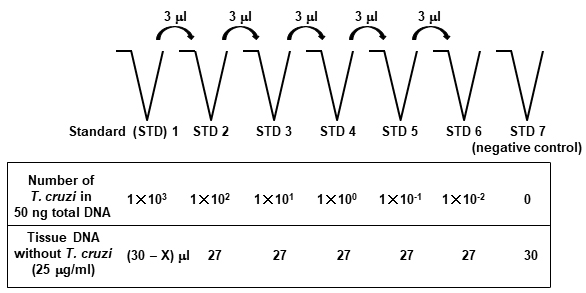
Figure 2. Scheme of the protocol to generate the standards to quantify T. cruzi in tissue
- For a standard curve to evaluate the amount of TNF-α DNA, 25 mg/ml tissue DNA containing 1 x 103 T. cruzi (STD1), as prepared above, is subsequently 10-fold diluted with distilled water or TE buffer (Figure 3). Internal control ‘TNF-α DNA’ is used to normalize the amount of tissue being analyzed in each PCR reaction (Cummings and Tarleton, 2003; Caldas et al., 2012). The pipet tips should be changed in between each dilution.
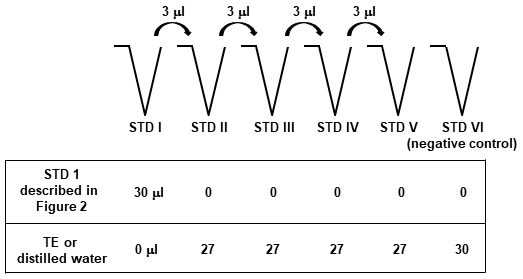
Figure 3. Scheme of the protocol to prepare the standards to quantify tissue TNF-α DNA
- Generation of T. cruzi and TNF-α standard calibration curve by qPCR (Figures 4A and 4B)
- Mix following components
10 μl of Go Taq qPCR Master Mix
1 μl of 10 μM T. cruzi specific primers (Tc1) or TNF-α DNA primers
2 μl of DNA standards for T. cruzi (Figure 2) or TNF-α DNA (Figure 3)
7 μl of double distilled water
- Amplification protocol
95 °C for 10 min, and 40 cycles of 94 °C for 15 sec and 64.3 °C for 1 min.
Fluorescent emission (520 nm) is measured at the end of the elongation step. A melting curve phase program is applied with a continuous fluorescent measurement between 65 °C and 95 °C. Each DNA sample is quantified in duplicate from two independent qPCR runs.
Figure 4. Standard curve generated with DNA from the livers of non-infected mice spiked with or without T. cruzi trypomastigotes. A and B. A 10-fold dilution series prepared as described above was amplified with primers specific to T. cruzi DNA (A) or murine TNF-α DNA (B). The standard curves were generated from the linear region of each sample application curve.
- Mix following components
- Collect the liver and heart from a non-infected mouse into a 15 cm Petri dish and collect the blood (more than 200 μl) in a CAPIJECT tube.
- Quantification of T. cruzi DNA in the tissues from T. cruzi-infected mice
- The mice (at least 5 mice) are injected intraperitoneally with 250 μl PBS including 5 x 102 T. cruzi trypomastigotes prepared as in steps A1-A4.
- At 20 and 30 days after infection, the heart, liver, and blood are collected from mice.
- 30 mg heart or liver, or 200 μl blood, are incubated with 500 μl lysis buffer/5 μl 10 mg/ml Proteinase K at 55 °C in a shaking incubator (110 min-1) for 18 h.
- DNA from the tissues isolated from T. cruzi-infected mice is extracted as described above (steps B4-B17).
- Normalize the T. cruzi DNA loads in the tissues.
To normalize the amount of tissue analyzed in each PCR reaction, the murine TNF-α DNA is used to correct for intra-sample variation in the initiation sample amount, sample loading, and DNA recovery (Cummings and Tarleton, 2003). The T. cruzi DNA value and TNF-α DNA value are calculated automatically by plotting the Ct values against each standard of known concentration shown in Figure 4. Normalization of the T. cruzi DNA value = (T. cruzi DNA value/TNF-α DNA value) x 10, where 10 corresponds to the expected value for TNF-α from 30 mg heart/liver or 200 μl blood (Caldas et al., 2012).
- The mice (at least 5 mice) are injected intraperitoneally with 250 μl PBS including 5 x 102 T. cruzi trypomastigotes prepared as in steps A1-A4.
Part II: T. cruzi killing assay
Materials and Reagents
- Pipette tips (Labcon, catalog numbers: 1093-260-000 , 1045-260-000 , 1036-260-000 )
- 10 ml syringe (Terumo, catalog number: SS-10SZP )
- 26 G needle (Terumo, catalog number: NN2613S )
- Cell strainer 40 μm nylon (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 352340 )
- 50 ml tube (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 339652 )
- 10 cm culture dishes (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 150466 )
- Scraper (Corning, catalog number: 3008 )
- 24-well plates (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 142475 )
- Glass coverslip (13 mm) (Matsunami Glass, catalog number: C013001 )
- Slide glass (MUTO PURE CHEMICALS, catalog number: 110510 )
- Disposal hemocytometer (All-Biz, catalog number: 4109:37650 )
- 6 cm Petri dishes (AS ONE, catalog number: 1-8549-02 )
- 8-week-old male and female C57BL/6 mice (Japan SLC)
- Trypanosoma cruzi Tulahuen strain (gifted by professor S. Hamano, Institute of Tropical Medicine, Nagasaki University)
- ISOFLURANE Inhalation Solution (Pfizer)
- 70% ethanol (JUNSEI CHEMICAL, catalog number: 17065-0382 )
- HBSS (NACALAI TESQUE, catalog number: 17460-15 )
- 1x phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (NACALAI TESQUE, catalog number: 14249-24 )
- GM-CSF (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 077-04674 )
- 0.25% trypsin (NACALAI TESQUE, catalog number: 35555-54 ) containing 0.02% EDTA (NACALAI TESQUE, catalog number: 06894-14 )
- IFN-γ (PeproTech, catalog number: 315-05 )
- 4% paraformaldehyde (NACALAI TESQUE, catalog number: 09154-85 )
- Diff-Quik (Sysmex, catalog number: 16920 )
- RPMI 1640 (NACALAI TESQUE, catalog number: 30264-56 )
- ACK lysing buffer (pH 7.2–7.4) (see Recipes)
- RPMI 1640 culture medium (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Pipettes (Nichiryo, catalog numbers: 00-NPX2-1000 , 00-NPX2-200 , 00-NPX2-20 , 00-NPX2-2 )
- Scissors (MIZUHO, catalog number: 09-207-00 )
- Forceps (Hammacher, catalog number: HSC_553-11 )
- Microscope (Olympus, model: CX31 )
- Handheld tally counter (Line Seiki, catalog number: H-102 )
- Centrifuge (TOMY SEIKO, model: AX-310 )
Procedure
- Preparation of bone marrow-derived macrophages
Note: The following protocol referred to a previous report (Weischenfeldt and Porse, 2008).- Euthanize mice with isoflurane inhalation solution.
- Sterilize the hind legs and abdomen with 70% ethanol.
- Make an incision in the midline of the abdomen.
- Clip outward to expose the hind legs.
- Remove all muscle from the bone using scissors and cut off the bones at the root of the femurs.
- After cutting the bone at both lower extremities, separate the femur and tibia by cutting at the knee joint in a Petri dish.
- Flush the bones with HBSS using a 10 ml syringe and a 26 G needle.
- Pass the bone marrow cells through a cell strainer in 50 ml tubes.
- Centrifuge at 240 x g for 5 min at 4 °C.
- Aspirate the supernatant and add 1 ml ACK lysing buffer (see Recipes) for the lysis of red blood cells at room temperature.
- After 3 min, add 9 ml cold PBS.
- Centrifuge at 240 x g for 5 min at 4 °C.
- Aspirate the supernatant.
- Culture 2 x 107 bone marrow cells isolated from the lower extremities of a mouse in 10 ml RPMI 1640 culture medium (see Recipes) supplemented with 10 ng/ml GM-CSF in a 10 cm culture dish.
- Wash the cells with PBS twice every 2 days and add fresh RPMI 1640 culture medium with 10 ng/ml GM-CSF.
- After 6 days, aspirate the supernatant and add 10 ml PBS.
- Aspirate the PBS and add 1 ml 0.25% trypsin containing 0.02% EDTA. Incubate at 37 °C for 5 min.
- Add 10 ml RPMI 1640 culture medium and scrape the cells with a scraper.
- Collect the cells in RPMI 1640 culture medium into 50 ml tubes.
- Centrifuge at 240 x g for 5 min at 4 °C.
- Aspirate the supernatant.
- Place the glass coverslips, sterilized by autoclave treatment, into the wells of a 24-well plate.
- Plate 5 x 104 bone marrow-derived macrophages on glass coverslips with 500 μl RPMI 1640 culture medium containing 10 ng/ml GM-CSF.
- After 18 h, bone marrow-derived macrophages are used in the T. cruzi killing assay.
- Euthanize mice with isoflurane inhalation solution.
- T. cruzi killing assay
- Bone marrow-derived macrophages prepared as in steps A23-A25 are cultured with 500 μl RPMI 1640 culture medium for 18 h in the presence of 0, 1, 10, or 100 ng/ml IFN-γ, which enhances parasite-killing activity in phagocytic cells.
- Aspirate the supernatant and wash with 500 μl PBS five times.
- Add 500 μl RPMI 1640 culture medium with 10 ng/ml GM-CSF.
- Infect 5 x 104 T. cruzi trypomastigotes with macrophages for 6 h (MOI = 1).
- After washing with 500 μl PBS three times, add 500 μl RPMI 1640 culture medium with 10 ng/ml GM-CSF and culture for 72 h.
- Aspirate the culture medium and wash with 500 μl PBS.
- Fix cells with 500 μl 4% paraformaldehyde and incubate for 10 min at room temperature.
- To visualize intracellular amastigotes, stain the cells using Diff-Quik kit.
- Apply a coverslip onto a slide glass using forceps.
- Count the number of intracellular amastigotes (Figure 5) under a microscope.

Figure 5. The intracellular parasites. Bone marrow-derived macrophages infected with T. cruzi for 6 h in the presence or absence of IFN-γ were rigorously washed and cultured for 72 h. The cells were fixed and stained with Diff-Quik. Original magnification, 400x. * Indicates nucleus. An arrowhead indicates amastigotes.
- The intracellular parasite numbers in 200 macrophages are counted under a light microscope (Figure 6).
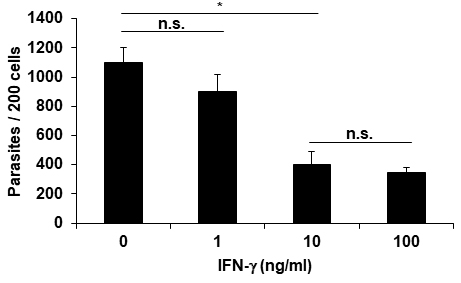
Figure 6. The number of intracellular amastigotes. The number of parasites per 200 macrophages. Graph represents the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05. Differences between the control and experimental groups were evaluated using Student’s t-test. Differences of P < 0.05 were considered significant.
- Bone marrow-derived macrophages prepared as in steps A23-A25 are cultured with 500 μl RPMI 1640 culture medium for 18 h in the presence of 0, 1, 10, or 100 ng/ml IFN-γ, which enhances parasite-killing activity in phagocytic cells.
Recipes
- Lysis buffer
100 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.5)
5 mM EDTA
0.2% SDS
200 mM NaCl
- RPMI 1640 culture medium
10% fetal bovine serum
100 μg/ml streptomycin, 100 U/ml penicillin
100 μM 2-mercaptoethanol
- ACK lysing buffer (pH 7.2-7.4)
0.15 M NH4Cl
1 mM KHCO3
0.1 mM EDTA
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan, and the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (to K.T. and H. K.), and by the Ichiro Kanehara Foundation and the Kurata Memorial Hitachi Science and Technology Foundation (to H.K.). The protocols provided here were partially modified from previously described methods by S. Cencing et al. (2011) and S. Caldas et al. (2012) (Quantification of T. cruzi) and by J. Weischenfeldt and B. Porse (2008) (Preparation of bone marrow-derived macrophages). We thank Kate Fox, DPhil, from Edanz Group (www.edanzediting.com/ac) for editing a draft of this manuscript. The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
References
- Andrade, D. V., Gollob, K. J. and Dutra, W. O. (2014). Acute chagas disease: new global challenges for an old neglected disease. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 8(7): e3010.
- Bonney, K. M., Taylor, J. M., Thorp, E. B., Epting, C. L. and Engman, D. M. (2015). Depletion of regulatory T cells decreases cardiac parasitosis and inflammation in experimental Chagas disease. Parasitol Res 114(3): 1167-1178.
- Caldas, S., Caldas, I. S., Diniz Lde, F., Lima, W. G., Oliveira Rde, P., Cecilio, A. B., Ribeiro, I., Talvani, A. and Bahia, M. T. (2012). Real-time PCR strategy for parasite quantification in blood and tissue samples of experimental Trypanosoma cruzi infection. Acta Trop 123(3): 170-177.
- Cencig, S., Coltel, N., Truyens, C. and Carlier, Y. (2011). Parasitic loads in tissues of mice infected with Trypanosoma cruzi and treated with AmBisome. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 5(6): e1216.
- Cummings, K. L. and Tarleton, R. L. (2003). Rapid quantitation of Trypanosoma cruzi in host tissue by real-time PCR. Mol Biochem Parasitol 129(1): 53-59.
- Flavia Nardy, A., Freire-de-Lima, C. G. and Morrot, A. (2015). Immune evasion strategies of Trypanosoma cruzi. J Immunol Res 2015: 178947.
- Garcia, M. N., Woc-Colburn, L., Aguilar, D., Hotez, P. J. and Murray, K. O. (2015). Historical perspectives on the epidemiology of human Chagas disease in Texas and recommendations for enhanced understanding of clinical Chagas disease in the Southern United States. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 9(11): e0003981.
- Kitada, S., Kayama, H., Okuzaki, D., Koga, R., Kobayashi, M., Arima, Y., Kumanogoh, A., Murakami, M., Ikawa, M. and Takeda, K. (2017). BATF2 inhibits immunopathological Th17 responses by suppressing Il23a expression during Trypanosoma cruzi infection. J Exp Med 214(5): 1313-1331.
- Requena-Mendez, A., Aldasoro, E., de Lazzari, E., Sicuri, E., Brown, M., Moore, D. A., Gascon, J. and Munoz, J. (2015). Prevalence of Chagas disease in Latin-American migrants living in Europe: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 9(2): e0003540.
- Ribeiro, A. L., Nunes, M. P., Teixeira, M. M. and Rocha, M. O. (2012). Diagnosis and management of Chagas disease and cardiomyopathy. Nat Rev Cardiol 9(10): 576-589.
- Viotti, R., Vigliano, C., Lococo, B., Alvarez, M. G., Petti, M., Bertocchi, G. and Armenti, A. (2009). Side effects of benznidazole as treatment in chronic Chagas disease: fears and realities. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 7(2): 157-163.
- Weischenfeldt, J. and Porse, B. (2008). Bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMM): Isolation and applications. CSH Protoc 2008: pdb prot5080.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Kayama, H., Kitada, S. and Takeda, K. (2017). Quantification of Trypanosoma cruzi in Tissue and Trypanosoma cruzi Killing Assay. Bio-protocol 7(22): e2613. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2613.
Category
Microbiology > Antimicrobial assay > Killing assay
Immunology > Animal model > Mouse
Cell Biology > Tissue analysis > Tissue isolation
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









