- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Sterol Analysis in Kluyveromyces lactis
Published: Vol 7, Iss 17, Sep 5, 2017 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2527 Views: 7789
Reviewed by: Yanjie LiPierre-Damien DenechaudAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Metabolite and Fatty Acid Analysis of Yeast Cells and Culture Supernatants
Liwei Chen and Wei Ning Chen
Sep 5, 2014 17849 Views

Tracking Lipid Transfer by Fatty Acid Isotopolog Profiling from Host Plants to Arbuscular Mycorrhiza Fungi
Andreas Keymer [...] Caroline Gutjahr
Apr 5, 2018 9255 Views
Abstract
Sterols are essential lipids of most eukaryotic cells with multiple functions (structural, regulatory and developmental). Sterol profile of yeast cells is often determined during the studies of ergosterol synthesis mutants used to uncover a number of functions for various sterols in yeast cells. Molecular studies of ergosterol biosynthesis have been also employed to identify essential steps in the pathway against which antifungals might be developed. We present here a protocol for the isolation of non-saponifiable lipids (sterols) from Kluyveromyces lactis yeast cells and a chromatographic method for quantitative analysis of sterols in lipid extracts (HPLC) that can be performed in laboratories with standard equipment.
Keywords: Ergosterol biosynthesisBackground
Ergosterol, the primary membrane sterol found in yeast cells, serves a structural role in cellular membranes similar to that of cholesterol in mammalian systems. Sterols have been shown to be responsible for a number of important physical characteristics of membranes by affecting rigidity, fluidity and permeability of membranes. Through their interactions with phospholipids and sphingolipids, sterols are proposed to maintain the lateral heterogeneity of the protein and lipid distribution in the plasma membrane because of their putative role in inducing microdomains called lipid rafts (Dupont et al., 2011; Souza et al., 2011). Sterol biosynthesis in yeast is an energy-expensive, multistep aerobic process, requiring heme and molecular oxygen. Ergosterol and its biosynthetic steps are the major targets for antifungal compounds which have minor effects on cholesterol synthesis of the host organism (Daum et al., 1998). Both ergosterol and some of its biosynthetic intermediates (squalene, 7-dehydrocholesterol) belong to chemicals with a direct positive appeal to people. Therefore a simple and reliable method for sterol isolation is highly rewarding (Valachovic and Hapala, 2017). In this protocol, we describe the analytical method for sterol isolation used for determination of sterol profile in yeast cells.
Materials and Reagents
- Pipette tips (Eppendorf, GBO)
- Inoculation loop
- 15-ml polypropylene centrifuge tubes (Corning, catalog number: 430791 )
- Acid-washed glass beads, diameter 0.45 mm (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G8772 ) (see Note 1)
- Glass Pasteur pipette (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z628018 )
- 20 ml Pyrex® glass tubes with Teflon cups (Corning) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z653527) (see Note 1)
Manufacturer: Pyrex, catalog number: 1622/10M . - Kluyveromyces lactis yeast strain to be analysed
- n-Hexane (anhydrous 95%) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 439177 ) (see Note 1)
- HPLC standard ergosterol (purity ≥ 95%) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 45480 ); 0.3 mg/ml stock solution in methanol
- Yeast extract (Biolife Italiana, catalog number: 4122202 )
- Bacto peptone (Biolife Italiana, catalog number: 4122592 )
- D-Glucose (Biolife Italiana, catalog number: 4125012 )
- Potassium hydroxide (KOH) pellets (Merck, catalog number: 1050331000 )
- Methanol (CHROMASOLVTM for HPLC, ≥ 99.9%) (Honeywell, catalog number: 24229 )
- Water (CHROMASOLV® Plus, for HPLC) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V270733 )
Note: This product has been discontinued. - YEPD rich growth medium (see Recipes)
- Methanolic KOH solution (60% KOH, 50% methanol) (see Note 2 and Recipes)
Equipment
- Pipettes (Eppendorf, HTL)
- Incubation shaker Multitron Standard (Infors HT, Bottmingen, Switzerland)
- Haemocytometer
- Centrifuge 5804R (Eppendorf, model: 5804 R )
- High speed Vortex-Genie 2 (Scientific Industries, model: Digital Vortex-Genie 2 , catalog number: SI-A246)
- Automatic sampler (Shimadzu Scientific Instruments, model: SIL-20AC )
- HPLC instrument (Shimadzu Scientific Instruments, model: Prominence 20A ) equipped with reversed phase C18 column (Ascentis® Express C18, particle size 5 μm, column size 3 x 150 mm, Supelco), UV-Vis detector (Shimadzu Scientific Instruments, model: SPD-20A )
- FastPrep® cell homogenize (MP Biomedicals, model: FastPrep®-24, catalog number: 116004500 )
Procedure
- Use an inoculation loop to transfer a tip of a single colony from an agar plate into 100 ml of sterile liquid YEPD medium (see Recipes). Incubate the culture in a shaker at 150 rpm at 28 °C to reach the exponential phase (1 x 107 cells/ml). Monitor the cell density by counting the cell number in a haemocytometer.
- Harvest the cells by centrifugation at 3,000 x g for 5 min at room temperature (RT) and discard the supernatant.
- Wash the cell pellets with deionized water (RT) and harvest the cells by centrifugation (3,000 x g, 5 min, RT).
- Resuspend the cell pellets in deionized water (RT) to a concentration of 1 x 109 cells in 1 ml of water. Transfer 1 ml of cell suspension into a new polypropylene 15 ml tube.
- Add 1 ml of sterile glass beads to the tube and cool 3 min on ice.
- Break the pre-cooled cells in vortex 6 x 60 sec at 2,500 rpm with 1 min cooling on ice between the breaking runs (see Note 2).
- Transfer broken cell suspension (without any glass beads) with glass Pasteur pipette to 20 ml Pyrex glass tube with Teflon cup.
- Add 3 ml of methanolic KOH solution and incubate for 2 h at 70 °C (see Notes 3 and 4).
- Cool the mixture, add 3 ml of n-hexane and mix well (10 sec) on a vortex mixer.
- Separate the organic and water phases at RT by centrifugation for 5 min at 3,000 x g.
- Transfer the upper organic phase with glass Pasteur pipette to a clean Pyrex glass tube with Teflon cup.
- Re-extract the water phase with 3 ml of n-hexane, collect the upper phase separated by centrifugation (5 min, 3,000 x g, RT) and join both organic phases.
- Evaporate n-hexane from the joined organic phases under the stream of nitrogen going into the tube for 10 min at RT, 3 bar.
- For HPLC analysis of non-saponifiable lipids (sterols), dissolve dry lipid extract equivalent of 1 x 109 cells in 1 ml of solvent (e.g., n-hexane or acetone) (see Note 5).
- Load 10 μl aliquot on the C18 column using automatic sampler. Ergosterol is separated with 95% methanol and 5% water as the mobile phase, flow 0.8 ml/min. Column temperature is set to 25 °C (see Note 6).
- Ergosterol is detected using UV-Vis detector at 280 nm.
Data analysis
The peak identity was determined from the retention times of ergosterol standard and from characteristic spectra (Figure 1). The quantity of sterols could be calculated from calibration curves constructed for individual standards used.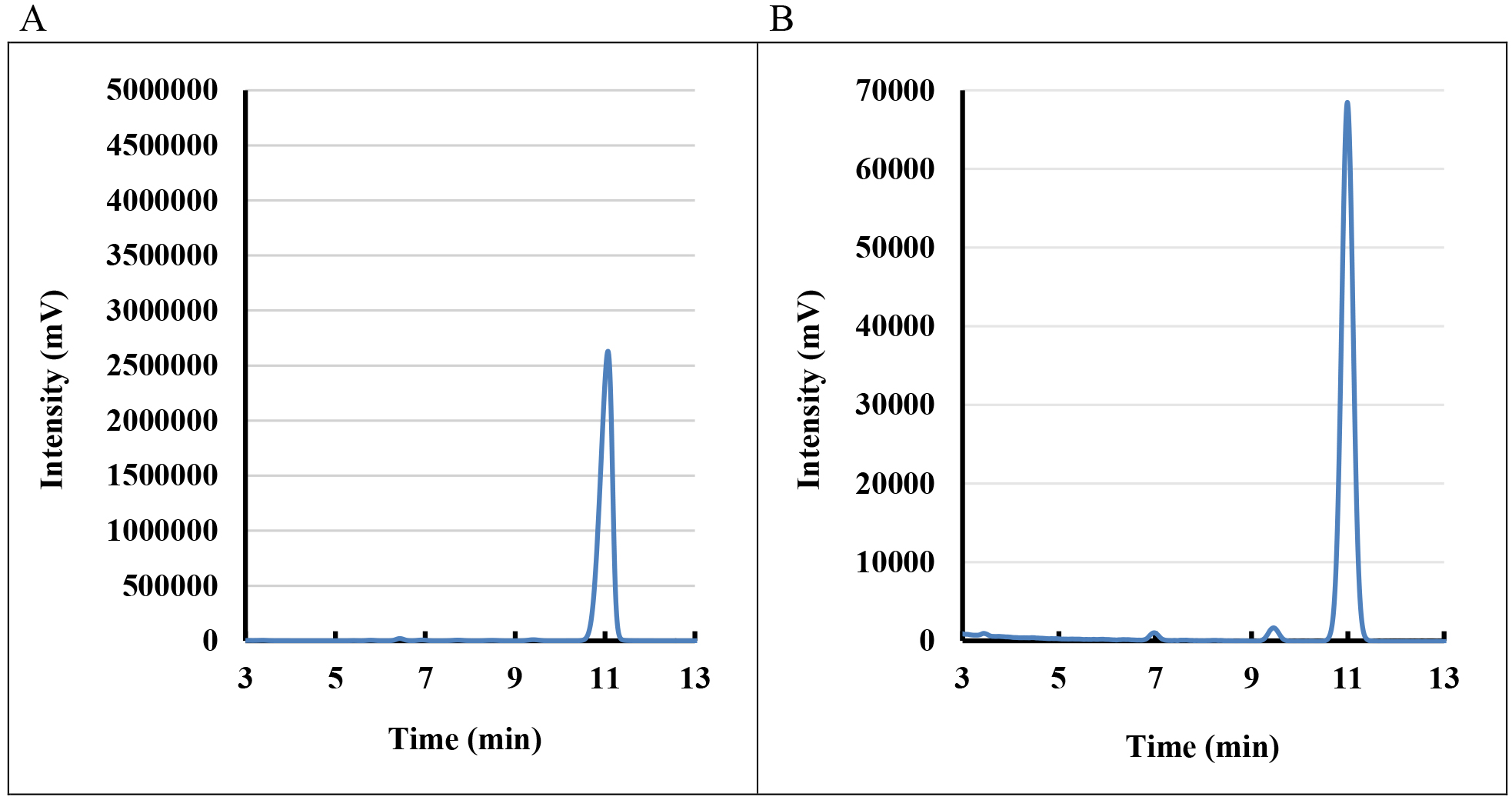
Figure 1. Chromatogram of sterols (A) Standard ergosterol (0.8 mmol/L) and (B) Sterol profile of K. lactis cells (ergosterol represents more than 80% of total amount of yeast sterols)
Notes
- All organic solvents used in lipid extraction should be of highest purity. Plastic material must not be used during the extraction procedure (with exception of the cell breaking step). Organic solvents release additives from the plastics which might interfere with subsequent analysis. Glass and Teflon® materials should be used throughout the procedure.
- Due to a rigid cell wall it is essential to break yeast cells for efficient extraction of lipids. FastPrep® cell homogenizer is recommended (e.g., MP Biomedicals). 2 x 45 sec breaking intervals with 5 min cooling on ice between the subsequent runs is recommended.
- To prepare 10 ml of methanolic KOH solution it is recommended to dissolve 6 g of KOH pellets in 5 ml in methanol mixed with 2.5 ml water. When KOH is fully dissolved, final volume should be adjusted to 10 ml with water. As the reaction is strongly exothermic special care should be taken during preparation of the solution.
- Efficiency of neutral lipid hydrolysis depends on the quality of methanolic KOH mixture. It is strongly recommended to use freshly prepared solution.
- Due to high volatility of the solvents, lipid extracts are always dried under the stream of nitrogen and dissolved in an exact volume of the solvent immediately before chromatographic analysis.
- Sterols present in the non-saponifiable lipid extracts originate from the free sterol fraction and from hydrolysed steryl ester fraction. If HPLC analysis is not used for preparative purification, column temperature can be increased to 40 °C to speed up the separation process.
- The HPLC-UV method proposed here may be useful for the sterol analysis in various yeasts and possibly for other types of sample (Valachovic and Hapala, 2017). Using standards of other sterols e.g., lanosterol, squalene, zymosterol, it is possible to determine their quantity in the sample.
Recipes
- YEPD rich growth medium
2% D-glucose
1% yeast extract
2% Bacto peptone - Methanolic KOH solution (60% KOH, 50% methanol)
6 g KOH pellets
5 ml methanol
H2O (distilled H2O) up to 10 ml
Acknowledgments
This protocol was adapted from Valachovic and Hapala (2017) and used in our previous studies (Goffa et al., 2014; Konecna et al., 2016). This work was supported by the Slovak Research and Development Agency grant APVV-0282-10 and VEGA 2/0111/15.
References
- Daum, G., Lees, N. D., Bard, M. and Dickson, R. (1998). Biochemistry, cell biology and molecular biology of lipids of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 14(16): 1471-1510.
- Dupont, S., Beney, L., Ferreira, T. and Gervais, P. (2011). Nature of sterols affects plasma membrane behavior and yeast survival during dehydration. Biochim Biophys Acta 1808(6): 1520-1528.
- Goffa, E., Balazfyova, Z., Toth Hervay, N., Simova, Z., Balazova, M., Griac, P. and Gbelska, Y. (2014). Isolation and functional analysis of the KlPDR16 gene. FEMS Yeast Res 14(2): 337-345.
- Konecna, A., Toth Hervay, N., Valachovic, M. and Gbelska, Y. (2016). ERG6 gene deletion modifies Kluyveromyces lactis susceptibility to various growth inhibitors. Yeast 33(12): 621-632.
- Souza, C. M., Schwabe, T. M., Pichler, H., Ploier, B., Leitner, E., Guan, X. L., Wenk, M. R., Riezman, I. and Riezman, H. (2011). A stable yeast strain efficiently producing cholesterol instead of ergosterol is functional for tryptophan uptake, but not weak organic acid resistance. Metab Eng 13(5): 555-569.
- Valachovic, M. and Hapala, I. (2017). Biosynthetic approaches to squalene production: The case of yeast. Methods Mol Biol 1494: 95-106.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Gbelska, Y., Toth Hervay, N., Morvova, M. and Konecna, A. (2017). Sterol Analysis in Kluyveromyces lactis. Bio-protocol 7(17): e2527. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2527.
Category
Microbiology > Microbial metabolism > Lipid
Biochemistry > Lipid > Lipid measurement
Biochemistry > Lipid > Lipid isolation
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










