- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Mapping RNA Sequences that Contact Viral Capsid Proteins in Virions
Published: Vol 7, Iss 14, Jul 20, 2017 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2398 Views: 8853
Reviewed by: Longping Victor TseWeiyan JiaAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Production and Purification of Cell Culture–generated Hepatitis B Virus by Transient Transfection and Density Gradient
Asako Murayama [...] Takanobu Kato
Jul 20, 2023 1899 Views

Flotation Assay With Fluorescence Readout to Study Membrane Association of the Enteroviral Peripheral Membrane Protein 2C
Kasturika Shankar [...] Lars-Anders Carlson
Apr 5, 2025 1608 Views

Detection and Analysis of S-Acylated Proteins via Acyl Resin–Assisted Capture (Acyl-RAC)
Dina A. Abdulrahman and Michael Veit
Apr 5, 2025 1834 Views
Abstract
We have adapted the methodology of CLIP-seq (Crosslinking-Immunoprecipitation and DNA Sequencing) to map the segments of encapsidated RNAs that contact the protein shells of virions. Results from the protocol report on the RNA sequences that contact the viral capsid.
Keywords: Protein-RNA interactionBackground
Positive-sense RNA viruses include pathogens of all life forms. Viruses with icosahedral shapes have the viral coat proteins form a protective shell around the RNA genome (Stockley et al., 2013). In the phage MS2 and the plant-infecting Brome mosaic virus (BMV), the coat protein preferentially contacts specific RNA sequences (Ni et al., 2013; Hoover et al., 2016; Rolfsson et al., 2016). These contacts could regulate the timing of RNA release during infection, viral gene expression, and viral RNA replication (Hoover et al., 2016). Identification of the capsid-RNA interactions could thus provide insights into the regulations of viral infection and provide means to inhibit viral infection. With this in mind, we have developed a method to identify the capsid-RNA contacts in purified virions using a combination of UV crosslinking, RNA fragmentation, selective precipitation of the coat protein, and next-generation sequencing of the cDNAs made from RNA fragments. The protocol below was developed for BMV virions.
Materials and Reagents
Note: All solutions should be made using sterile water with resistivity of better than 18.3 MΩ and analytical grade reagents.
- Pipette tips (Corning, catalog number: 4154 )
- 6-well clear polystyrene flat-bottomed tissue culture plate (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 351146 )
- Polyallomer centrifuge tubes (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 344060 )
- Polypropylene microcentrifuge tubes and tips that are certified to be Ribonuclease free
- iBlotTM PVDF membrane (0.2 μm) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: IB401001 )
- Razor blade (GEM, catalog number: RB-GEM-080014 )
- 0.22 μm filter (EMD Millipore, catalog number: SCGPU05RE )
- Zymo RNA Clean & Concentrator (ZYMO RESEARCH, catalog number: R1015 )
- BMV virions purified using cesium chloride density gradients and suspended in SAMA buffer
Note: High purity BMV virions can be obtained as described in Vaughan et al. (2014). The virions are kept in an acidic buffer because pH affects the swelling of the BMV virions and can change the CP-RNA interaction. - 10x Fragmentation Reagent and Stop Solution: 200 mM EDTA (pH 8.0) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: AM8740 )
- PierceTM Protein A/G magnetic beads (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 88847 )
- Anti-BMV CP antibody
Note: This is a polyclonal antiserum we generated in rabbits immunized with highly purified BMV capsid protein. - NuPAGE® Novex® 4-12% Bis-Tris Gel, NuPAGE® MES-SDS running buffer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: NP0321BOX )
- 1x MES SDS running buffer
- Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 10010023 )
- 0.1% Ponceau-S (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P3504 )
- Protease K (Fungal) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 25530015 )
- T4 Polynucleotide Kinase (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0201L )
- Small RNA kit (Illumina, catalog number: RS-200-0036 )
- 1.8x SPRI beads (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 41105518 )
- SPRIselect reagent (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: B23317 )
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) (Avantor Performance Materials, Macron, catalog number: 7680 )
- HT1 buffer (Component of the NexSeq 500 kit) (Illumina, catalog number: FC-404-2005 )
- Sodium acetate, Na(OAc) (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 106268 )
- Magnesium acetate tetrahydrate, Mg(OAc)2·4H2O (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M0631 )
- Glacial acetic acid (EMD Millipore, catalog number: AX0073-9 )
- Ethanol, absolute (Decon Labs, catalog number: 2716 )
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S7653 )
- Tris base (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T6066 )
- Tween 20 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P1379 )
- Sodium dodecyl sulfate, sodium salt (SDS) (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 7910-OP )
- Glycerol (VWR, BDH®, catalog number: BDH1172 )
- Bromophenol blue (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: B0126 )
- Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP120 )
- SAMA buffer (see Recipes)
- 3 M sodium acetate (pH 5.2) (see Recipes)
- IP binding buffer (see Recipes)
- IP wash buffer (see Recipes)
- 4x Laemmli sample buffer (see Recipes)
- PK buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Ultraviolet Cross-linker (UVP, model: CL-1000 , catalog number: 95-0174-01)
- Beckman Coulter Ultima Max-XP ultracentrifuge (Beckman Coulter, model: OptimaTM Max-XP , catalog number: 393315)
- DynaMag-2 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 12321D )
- SureLock X Mini-gel electrophoresis system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: El0001 )
- iBlot® Dry Blotting System (Thermo Fisher Scientific, model: iBlotTM 2, catalog number: IB21001 )
- Agilent 2200 Tape station (Agilent Technology, model: Agilent 2200 )
- Miseq or NexSeq500 (Illumina, model: NexSeqTM 500 )
Software
- Mapping program: bowtie2 ver. 2.2.6
- Graphing program: JBrowse ver. 1.12.1
Procedure
- UV crosslinking
- Add 400 µl of 100 µg/ml each of purified BMV virions into 3 wells of a 6-well cell culture plate. Incubated the plate on ice for at least 5 min. Place the plate without the cover in the crosslinking machine and irradiate three times at 254 nm to 400 mJ/cm2 (Figure 1). Between irradiations, agitate the samples with gently tapping the plate to mix the samples and incubate the plate on ice for 3 min to prevent the samples from overheating. Repeat the irradiation, agitation, and incubation on ice two more times.
Notes:- BMV virions are purified to homogeneity using cesium chloride density gradients as described in Ni et al., 2014. The concentration of the purified virion was determined in Ni et al., 2014.
- The dose of irradiation that provided optimal crosslinking of the BMV virion RNAs was determined empirically by sequencing the RNA fragments processed through the protocol. The same conditions were also successfully used for crosslinking of bacteriophage MS2 RNA (Rolfsson et al., 2016). Nonetheless, it is quite likely that modifications in the crosslinking time should be empirically determined for other virions.

Figure 1. Location of the plate containing BMV virions in the UV crosslinker
- BMV virions are purified to homogeneity using cesium chloride density gradients as described in Ni et al., 2014. The concentration of the purified virion was determined in Ni et al., 2014.
- For a negative control, repeat step A1, but do not irradiate the virions. This control reaction can be processed in parallel with the irradiated virion.
- Harvest and pool the irradiated virion solutions into a small polyallomer centrifuge tube and centrifuge at 150,000 x g for 30 min using a preparative ultracentrifuge. Resuspend the virion pellet in 150 µl 100 mM Tris (pH 7.0).
- Add 15 µl of RNA Fragmentation Reagent, mix and incubate at 70 °C for 15 min.
Note: We have empirically examined several combinations of ribonucleases and observed more bias in the cleavage of the RNAs. Zinc-induced cleavage of the RNA produced more random cleavage of the RNA, is easier to use, and is easily removed during the processing of the samples. For BMV, the conditions used will fragment the BMV RNA to ~50-nt in length (Figure 2). During the fragmentation step, the pH of the solution and the incubation at 70 °C will cause the BMV virion to dissociate and denature. The virion solution should become cloudy soon after incubation. With other virions, it will be important to try different conditions to identify those that can generate relatively short RNA fragments. - Add 15 µl 0.2 M EDTA (pH 8.0), mix and incubate on ice for 10 min to stop the reaction.
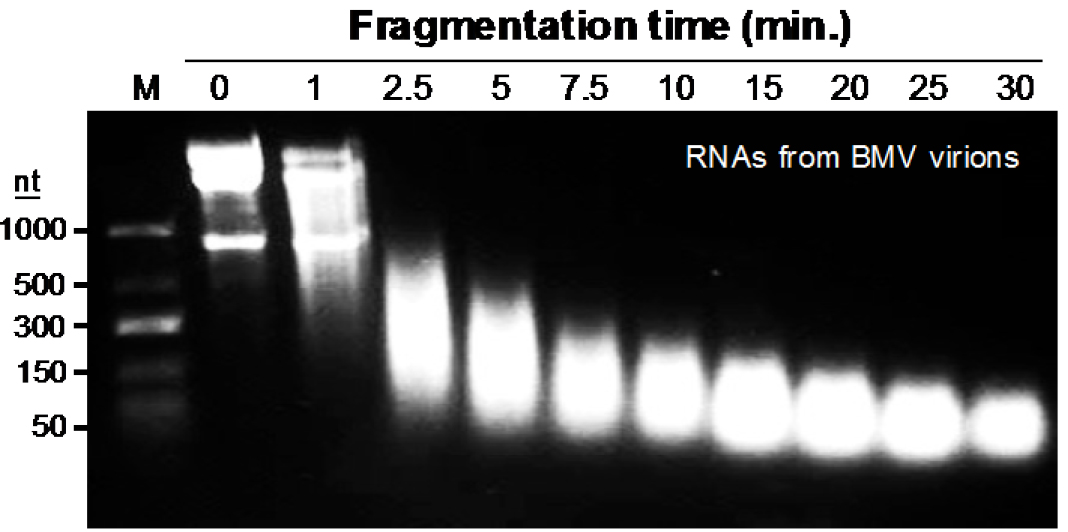
Figure 2. Time-dependent fragmentation of RNAs from UV-crosslinked BMV virions. The image shown is from ethidium bromide-stained agarose gel containing 100 μg BMV virions that were resuspended in 150 μl Tris buffer (pH: 7.0) containing 10 Mm ZnCl2, and heated at 70 °C to fragment BMV RNA for the time indicated in the gel image.
- Add 400 µl of 100 µg/ml each of purified BMV virions into 3 wells of a 6-well cell culture plate. Incubated the plate on ice for at least 5 min. Place the plate without the cover in the crosslinking machine and irradiate three times at 254 nm to 400 mJ/cm2 (Figure 1). Between irradiations, agitate the samples with gently tapping the plate to mix the samples and incubate the plate on ice for 3 min to prevent the samples from overheating. Repeat the irradiation, agitation, and incubation on ice two more times.
- Immunoprecipitation and RNA extraction
- Add 50 µl of the Pierce Protein A/G magnetic beads suspension into a 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tube. Add 1 ml of ice-cold IP binding buffer (see Recipes), mix, and then concentrate the beads by placing the tube against the magnetic tube holder. The beads should be concentrated on the side of the microcentrifuge tube. Use a pipette to remove the supernatant. Repeat the washing of the beads.
- Resuspend beads in 100 µl ice-cold IP binding buffer, add the anti-BMV CP antibody and the crosslinked CP-RNA solution from step A5 and place the tube to mix on a rocking platform set at 50 rpm at 4 °C for 2 h.
- Collect the beads and co-precipitated protein using a magnetic tube holder. Remove the supernatant. Add 1 ml ice-cold IP binding buffer to wash the beads four times, each time collect the beads using Magnastrip and remove the supernatant.
- Remove final wash solution, add 100 µl of Laemmli sample buffer (see Recipes) to the beads, mix and heat at 95 °C for 2 min, load up to 30 µl samples on precast 4-12% Bis-Tris gel, and run the gel for 1 h at 150 V in 1x MES SDS running buffer.
- Transfer protein-RNA complexes from the gel to a PVDF membrane using a wet transfer apparatus (Bio-Rad Laboratories). Transfer should be at 100 V for 2.5 h.
Note: Transferring the protein from the denaturing PAGE to the PVDF membrane will help to remove non-covalently bound RNA fragments, and will decrease the background. - Rinse the membrane with sterile PBS buffer twice, stain with 0.1% Ponceau-S for 10 min. then rinse the membrane with sterile PBS twice to remove excess dye. Cut out the portion of the membrane at ca. 3-4 mm above the BMV CP band using a new razor blade (Figure 3). Transfer the membrane slice that contains the CP and crosslinked RNA fragments into a 1.5 ml sterile microcentrifuge tube, rinse with sterile PBS twice.
Note: The membrane slices can be stored at -80 °C until use. - Add 200 µl of 1 mg/ml Proteinase K diluted in the PK buffer (see Recipes) to the membrane slice. Incubate at 37 °C for 1 h with occasional mixing to digest the CP.
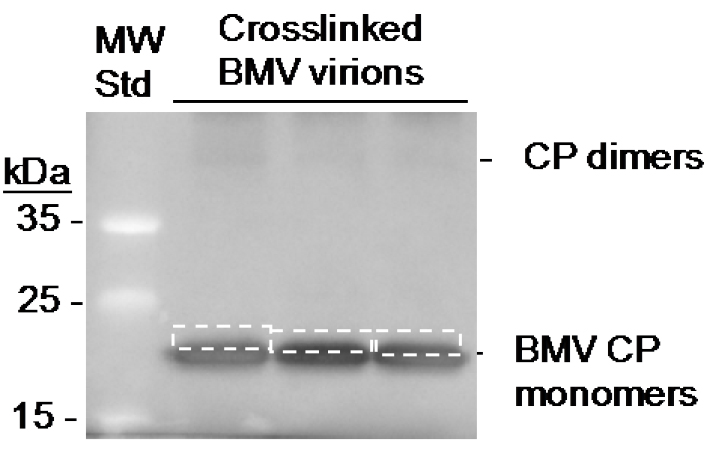
Figure 3. Location of the RNA excised from crosslinked BMV coat protein. The image is of the membrane following Western blot transfer. The boxes with dashed lines denote the area of the membrane excise with a razor blade.
- Add 50 µl of the Pierce Protein A/G magnetic beads suspension into a 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tube. Add 1 ml of ice-cold IP binding buffer (see Recipes), mix, and then concentrate the beads by placing the tube against the magnetic tube holder. The beads should be concentrated on the side of the microcentrifuge tube. Use a pipette to remove the supernatant. Repeat the washing of the beads.
- cDNA library construction and Illumina DNA sequencing
- Apply the solution from step B7 that contains eluted RNA fragments to a Zymo RNA Clean & Concentrator column. Elute the RNA using 35 µl elution buffer from the kit.
- Add 5 µl of 10x PNK buffer and 50 U of the PNK enzyme and 5 µl of 10 mM ATP. Incubate the mixture at 37 °C for 30 min.
Note: The PNK adds a 5’-phosphate to the RNAs to enable the addition of oligonucleotides adaptors needed for library construction. - Transfer the RNA to a fresh Zymo RNA Clean & Concentrator column and elute the RNA in 7 µl elution buffer from the kit. Analyze 2 µl of the eluant on an Agilent High-sensitivity RNA TapeStation tape to determine the RNA concentration.
- Use a volume of remaining eluant that contains between 200 ng to 1 µg of the eluted RNA to construct a cDNA library using an Illumina Small RNA kit. Construction of the library as per the manufacturer’s instruction using 11 to 15 cycles of DNA amplification, with the cycle number being dependent on the mass of the RNA present.
- Estimate the concentration of the libraries using the Agilent High-sensitivity DNA TapeStation.
- Pool the libraries then clean and concentrate the pool using a 1.8x ratio of SPRIselect beads (Beckman Coulter) and eluted in 22 µl.
Note: In the TapeStation, the libraries of DNA fragments are separated by electrophoresis from the adaptors, the primer dimers and other DNA molecules generated during the amplification process. The DNAs of lengths expected to have adaptors flanking the cDNA are excised and eluted. - The libraries (5 µl with ca. 500 ng of each library) were denatured with 5 µl of 0.2 N NaOH for 5 min, then neutralized with 985 µl of the HT1 buffer provided by Illumina. 5 µl of the 200 mM Tris pH 7.5 was added to supplement the buffering capacity of the HT1 buffer.
Note: Given the small sizes of viral genomes, multiple viral libraries can be a small percentage of an Illumina sequencing run. Even 1% of the sample on a run can still result in several hundred thousand reads for each of the libraries. - The Illumina NextSeq500 run was performed by members of the Indiana University CGB staff using a 75-High output flow cell designated for an 80-bp read.
- Apply the solution from step B7 that contains eluted RNA fragments to a Zymo RNA Clean & Concentrator column. Elute the RNA using 35 µl elution buffer from the kit.
Data analysis
- Trim and quality-filter the reads using Trimmomatic ver. 0.33, with a minimal cutoff score of 20 (Bolger et al., 2014). Reads shorter than 20 nucleotides post trimming were excluded.
- Map the reads to corresponding reference sequences using the computer program Bowtie2 ver 2.2.6 (Langmead and Salzberg, 2012) with default mapping parameter values. For each read, only the best alignments, as defined by least edit distance, were used.
- Display the number of reads spanning each base position of the reference sequence on JBrowse ver. 1.12.1 as BigWig tracks (Skinner et al., 2009).
Notes
While this protocol has been optimized for the analysis of the RNAs that bind to the BMV capsid, the protocol can be directly adapted to map the virions of interest. The key will be the availability of highly pure virions and an antibody that can efficiently precipitate the capsid protein of interest. The construction of cDNA libraries, nex-gen DNA sequencing and data analysis can be performed in facilities that specialize in genomic analysis.
Recipes
- SAMA buffer
50 mM Na(OAc)
8 mM Mg(OAc)2, pH 5.5 - 3 M sodium acetate (pH 5.2)
Dissolve 12.3 g sodium acetate in 30 ml H2O
Adjust pH to 5.2 with glacial acetic acid
Add H2O to 50 ml
Filter with a device containing 0.22 μm filter
Store at room temperature - IP binding buffer*
150 mM NaCl
25 mM Tris (pH 7.2)
0.05% Tween 20 - IP wash buffer*
500 mM NaCl
25 mM Tris (pH 7.2)
0.05% Tween-20*Note: For convenience, make 20x stocks of the buffers and dilute with sterile water to 1x for use.
- 4x Laemmli sample buffer
8% SDS
40% glycerol
240 mM Tris (pH 6.8)
0.04% bromophenol blue - PK buffer
50 mM Tris (pH 7.5)
75 mM NaCl
6.3 mM EDTA
1% SDS
Acknowledgments
This protocol was established in the work supported by grant NIH 1R01AI090280 to CK. This protocol was adapted from the work of Ni et al. (2013) and Hoover et al. (2016) and unpublished results of E. Chuang. We thank A. Kao for photography used in this protocol.
References
- Bolger, A. M., Lohse, M. and Usadel, B. (2014). Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30(15): 2114-2120.
- Hoover, H. S., Wang, J. C., Middleton, S., Ni, P., Zlotnick, A., Vaughan, R. C. and Kao, C. C. (2016). Phosphorylation of the brome mosaic virus capsid regulates the timing of viral infection. J Virol 90(17): 7748-7760.
- Langmead, B. and Salzberg, S. L. (2012). Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods 9(4): 357-359.
- Ni, P., Vaughan, R. C., Tragesser, B., Hoover, H. and Kao, C. C. (2013). The plant host can affect the encapsidation of brome mosaic virus (BMV) RNA: BMV virions are surprisingly heterogeneous. J Mol Biol 426(5): 1061-1076.
- Rolfsson, O., Middleton, S., Manfield, I. W., White, S. J., Fan, B., Vaughan, R., Ranson, N. A., Dykeman, E., Twarock, R., Ford, J., Kao, C. C. and Stockley, P. G. (2016). Direct evidence for packaging signal-mediated assembly of bacteriophage MS2. J Mol Biol 428(2 Pt B): 431-448.
- Skinner, M. E., Uzilov, A. V., Stein, L. D., Mungall, C. J. and Holmes, I. H. (2009). JBrowse: a next-generation genome brower. Genome Res 19(9): 1630-1638.
- Stockley, P. G, Ranson, N. A. and Twarock, R. (2013). A new paradigm for the roles of the genome in ssRNA viruses. Future Virol 8: 531-543.
- Vaughan, R., Tragesser, B., Ni, P., Ma, X., Dragnea, B. and Kao, C. C. (2014). The tripartite virions of the brome mosaic virus have distinct physical properties that affect the timing of the infection process. J Virol 88(11): 6483-6491.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Kao, C. C., Chuang, E., Ford, J., Huang, J., Podicheti, R. and Rusch, D. B. (2017). Mapping RNA Sequences that Contact Viral Capsid Proteins in Virions. Bio-protocol 7(14): e2398. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2398.
Category
Microbiology > Microbial biochemistry > RNA
Microbiology > Microbial biochemistry > Protein
Biochemistry > RNA > RNA-protein interaction
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










