- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Muscle Histology Characterization Using H&E Staining and Muscle Fiber Type Classification Using Immunofluorescence Staining
Published: Vol 7, Iss 10, May 20, 2017 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2279 Views: 35185
Reviewed by: Antoine de MorreeJalaj GuptaAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Systematic Analysis of Smooth Muscle and Cartilage Ring Formation during Mouse Tracheal Tubulogenesis
Haoyu Wu [...] Wenguang Yin
Jul 5, 2023 1534 Views

Protocol for the Implantation of Scaffolds in a Humanized Mouse Cutaneous Excisional Wound Healing Model
Dina Gadalla [...] David G. Lott
Sep 20, 2024 1452 Views

Dissection and Whole-Mount Immunofluorescent Staining of Mouse Hind Paw Muscles for Neuromuscular Junction Analysis
Rebecca L. Simkin [...] James N. Sleigh
May 20, 2025 3913 Views
Abstract
Muscle function is determined by its structure and fiber type composition. Here we describe a protocol to examine muscle histology and myofiber types using hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and immunofluorescence staining, respectively. H&E stain nucleus in blue and cytoplasm in red, therefore allowing for morphological analyses, such as myofiber diameter, the presence of degenerated and regenerated myofibers, and adipocytes and fibrotic cells. Muscle fibers in adult skeletal muscles of rodents are classified into 4 subtypes based on the expression of myosin heavy chain proteins: Myh7 (type I fiber), Myh2 (type IIA fiber), Myh1 (type IIX fiber), Myh4 (type IIB fiber). A panel of monoclonal antibodies can be used to specifically label these muscle fiber subtypes. These protocols are commonly used in the study of muscle development, growth and regeneration (for example: Wang et al., 2015; Nie et al., 2016; Yue et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2017).
Keywords: Skeletal muscleBackground
Skeletal muscle is composed of myocytes, adipocytes, fibroblasts and other cell types. Multinuclear myocytes, the main composition of skeletal muscle, are also called myofibers (muscle fibers). Investigation of muscle histology is a routine approach to study muscle function. Generally, the diameter of muscle fiber and the extent of adipocytes and fibrotic area are associated with muscle strength (Yue et al., 2016). In addition, the presence of central nucleated muscle fibers serves as a surrogate indicator of newly regenerated muscle fibers during muscle regeneration (Wang et al., 2017). Based on the differential metabolic traits and the expression of myosin heavy chain (MyHC) subtypes, myofibers are classified into four types (I, IIa, IIx and IIb). The analysis of myofiber composition is helpful for studying muscle metabolic and contractile functions (Schiaffino and Reggiani, 2011).
Materials and Reagents
- Clips (Universal, catalog number: UNV11240 )
- Kimwipes (KCWW, Kimberly-Clark, catalog number: 34155 )
- T-pin (Business Source, catalog number: 32351 )
- Blade (Crescent Manufacturing, catalog number: 7223 )
- Positive charged microscope slides (IMEB, catalog number: B-8255 )
- Cover slides (IMEB, catalog number: CG1-2450 )
- Adult mice
Note: DBA/2J female mice at 6 weeks were used to show the dissection of muscles. C57BL/6 male mice at 2-month old and 1-year old were used to do stainings in this protocol, but male or female mice of other genetic backgrounds or strains, at different ages can be used. - Tissue-Tek OCT compound (Sakura, catalog number: 4583 )
- 2-methylbutane (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: O3551-4 )
- Dry ice (Purdue Lilly Stores, Local dry ice supplier)
- Ethanol (Decon Labs, catalog number: V1001 )
- Xylene (Avantor® Performance Materials, Macron, catalog number: 8668 )
- Xylene-based mounting medium (Source Mount, catalog number: 9277722 )
- Primary antibodies
Dystrophin (Abcam, catalog number: ab15277 )
Myh2 MyHC-2A (2F7), Myh4 MyHC-2B (10F5) and Myh7 MyHC-1 (BA-F8) are from Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank (DSHB). We are using the concentrate 0.1 ml products - Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (pH 7.4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P3813 )
- Mounting medium for immunostaining (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: S3023 )
- Nail polish (Crystal clear) (Sally Hansen, catalog number: 004677963 )
- Secondary antibodies
Goat anti-Mouse IgG1, Alexa Fluor 568 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Invitrogen, catalog number: A-21124 )
Goat anti-Mouse IgG1, Alexa Fluor 488 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Invitrogen, catalog number: A-21121 )
Goat anti-Mouse IgG2b, Alexa Fluor 568 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Invitrogen, catalog number: A-21144 )
Goat anti-Mouse IgG2b, Alexa Fluor 647 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Invitrogen, catalog number: A-21242 )
Goat anti-Mouse IgM, Alexa Fluor 488 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Invitrogen, catalog number: A-21042 )
Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L), Alexa Fluor 647 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Invitrogen, catalog number: A-21245 ) - Hematoxylin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H9627 )
- Potassium alum (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 237086 )
- Sodium iodate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S4007 )
- Glacial acetic acid (Avantor® Performance Materials, Macron, catalog number: V193 )
- Glycerol (Avantor® Performance Materials, Macron, catalog number: 5092 )
- Eosin Y (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, catalog number: sc-203734 )
- Goat serum (Jackson ImmunoResearch, catalog number: 005-000-121 )
- Bovine serum albumin (BSA) (Gemini Bio-Products, catalog number: 700-105P )
- Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: X100 )
- Sodium azide (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: S2271 )
- Hematoxylin solution (see Recipes)
- Eosin Y solution (see Recipes)
- Blocking buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Embedding molds (Structure Probe, SPI Supplies, catalog number: 2449M-AB )
- Cold-resistant beaker (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z155519 )
- -80 °C freezer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, model: FormaTM 8600 Series )
- Leica CM1850 cryostat (Leica Biosystems, model: CM1850 )
- Staining jar (BRAND, catalog number: 472800 )
- Fume hood (Fisher Scientific, model: Fisher Hamilton SafeAire )
- 14.0 MP digital USB microscope camera (OMAX Microscope, catalog number: A35140U3 )
- Leica DMI 6000B fluorescent microscope (Leica Microsystems, model: DMI 6000 B )
- Lumen 200 fluorescence illumination system (Prior Scientific, model: Lumen 200 )
- Coolsnap HQ CCD camera (Photometrics, model: Coolsnap HQ )
- Liquid blocker (Ted Pella, catalog number: 22309 )
- Dissecting scissors, 10 cm, straight (WPI, catalog number: 14393-G )
- Vannas scissors, 8 cm, straight (WPI, catalog number: 14003-G )
- Tweezer, 4.25”, straight (Excelta, catalog number: 5-S-SE )
- Tweezer, 4.75”, straight (Excelta, catalog number: 3-S-SE )
Software
- Photoshop software (e.g., Photoshop CC)
Procedure
- Dissection of muscles
- Tools used to dissect muscles of mice are shown in Figure 1A. Video 1 shows how to dissect muscles from a mouse.
- Position the mouse supine on a dissection board (Styrofoam board) and secure the leg with a T-pin (Figure 1B).
- Peel off the leg skin to expose the hind limb muscles. Expose tendons of tibialis anterior (TA) muscle and extensor digitorum longus (EDL) muscle (Figure 1B).
- Gently remove the fascia covering the TA muscle.
- Cut the distal TA tendon and use it to peel off the TA muscle. Carefully remove the TA muscle at its proximal attachment (Figure 1C).
- After removing the TA muscle, cut distal EDL muscle and peel off the EDL muscle. Carefully cut the proximal EDL tendon and remove the EDL muscle. To dissect soleus muscle (SOL), position the mouse prone on a dissection board and secure the leg with a T-pin (Figure 1D).
- Cut the tendon of gastrocnemius (GA) muscle and use it to peel off the GA muscle till the exposure of a SOL tendon (Figure 1E).
- Cut the SOL tendon and use it to peel off the SOL muscle (Figure 1F).
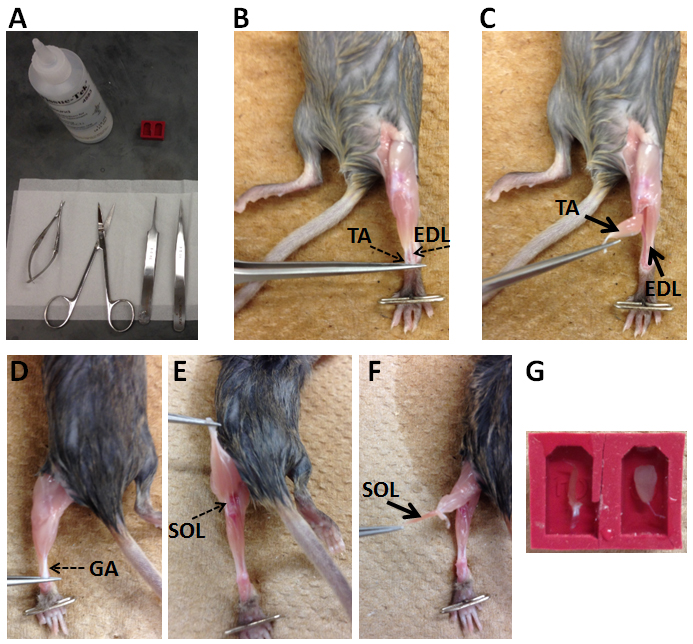
Figure 1. Procedure of dissection muscles from a mouse. A. Tools used to dissect muscles; B-F. Key steps for muscle dissection; G. Illustration of how muscles are placed in embedding molds with O.C.T. compound. SOL is in the left mold and TA is in the right mold. Video 1. Dissection of skeletal muscles from a mouse
Video 1. Dissection of skeletal muscles from a mouse - Tools used to dissect muscles of mice are shown in Figure 1A. Video 1 shows how to dissect muscles from a mouse.
- Embedding of muscle
- After dissection, skeletal muscles (e.g., tibialis anterior, soleus, extensor digitorum longus) are embedded in embedding molds (e.g., SPI Supplies) with minimum amount of Tissue-Tek O.C.T. compound possible to cover the muscles (Figure 1G).
- Place a cold-resistant beaker of 2-methylbutane into a slurry of dry ice and ethanol (pure), which allows fast cooling to -78 °C. When the correct temperature is attained, no bubble will appear after putting a piece of dry ice into the 2-methylbutane.
- Freeze the embedded muscle by placing it into the cooled 2-methylbutane for 5 min and then transfer the muscle sample to a -80 °C freezer for storage.
- After dissection, skeletal muscles (e.g., tibialis anterior, soleus, extensor digitorum longus) are embedded in embedding molds (e.g., SPI Supplies) with minimum amount of Tissue-Tek O.C.T. compound possible to cover the muscles (Figure 1G).
- Cryosectioning
- Before cryosectioning, the cryostat with the blade is pre-cooled to -22 ± 2 °C. Samples are placed in cryostat for at least 20 min for thermal equilibration. Attach the sample on the round metallic holders of the cryostat with Tissue-Tek O.C.T.
- Make 10 µm-thick sections and collect them on room temperature positive charged microscope slides and then store the slides in a slide box in a -80 °C freezer. These slides can be processed further for H&E staining or immunostaining.
- Before cryosectioning, the cryostat with the blade is pre-cooled to -22 ± 2 °C. Samples are placed in cryostat for at least 20 min for thermal equilibration. Attach the sample on the round metallic holders of the cryostat with Tissue-Tek O.C.T.
- H&E staining
- Bring the slides from the -80 °C freezer to room temperature.
- Incubate the slides with hematoxylin solution in a staining jar for 10 min to stain the nuclei.
- Transfer the slides to a staining jar with running water (tap water is fine) till the water is clear.
- Transfer the slides to a staining jar with Eosin solution for 3 min.
- Successively transfer the slides into staining jars with 70% ethanol for 20 sec, 90% ethanol for 20 sec, 100% ethanol for 1 min and xylene for 3 min.
- Take out slides from xylene and place the slides in a fume hood till the slides are dry.
- Mount the slides with xylene-based mounting media and cover with cover slides. Clips are used to press the slides to squeeze bubbles.
- Store the slides at room temperature.
- Hematoxylin and Eosin-stained images were captured with a 14.0 MP digital microscope camera which is attached via a c-mount to the side port of a Leica DMI 6000B microscope.
- Bring the slides from the -80 °C freezer to room temperature.
- Immunostaining with MyHC antibodies
- Bring the slides from the -80 °C freezer to room temperature and surround the sections with a liquid blocker (Ted Pella) to limit the usage of the incubation solutions.
- Place the slides in a wet chamber (Note 5) and block the sections with blocking buffer for at least 30 min at room temperature. For the immunostaining with MyHC antibodies from DSHB, do not fix samples or sections with fixative solution (this is specifically for the MyHC antibodies).
- Dilute primary antibodies with blocking buffer. Myh2, Myh4 and Myh7 antibodies are diluted at a ratio 1:300. Dystrophin antibody is diluted at a ratio 1:1,000. Remove blocking buffer from the sections and add diluted primary antibodies on sections. Place the slides in a wet chamber overnight at 4 °C.
- Dilute secondary antibodies with PBS at a ratio 1:1,000. Incubate secondary antibodies with sections for 30 min to 1 h at room temperature. Slides are placed in a wet chamber.
- Wash the slides with PBS for 5 times. Before mounting the slides, remove PBS as much as possible, but keep sections wet.
- Mount the slides with immunostaining mounting media and cover with cover slides. Clips are used to press the slides to squeeze bubbles. Seal the slides with clear nail polish.
- Store the slides at 4 °C.
- Fluorescent images were captured using the Leica DMI 6000B fluorescent microscope.
- Bring the slides from the -80 °C freezer to room temperature and surround the sections with a liquid blocker (Ted Pella) to limit the usage of the incubation solutions.
Data analysis
- H&E staining of Tibialis anterior muscle sections
Cardiotoxin (CTX) was injected into tibialis anterior (TA) muscles of 1-year old male mice to induce muscle damage which was followed by muscle regeneration. Two weeks after CTX injection, TA muscles were processed for cryosection and H&E staining (Figure 2). Most myofibers had central nuclei, indicative of muscle regeneration (Figure 2). Adipocytes and degenerated myofibers were found in TA muscle sections (Figure 2).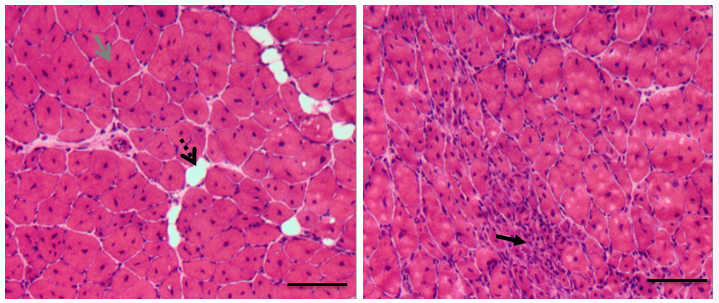
Figure 2. H&E staining of regenerated TA muscles isolated from 1-year old mice. Re/degenerated myofibers and adipocytes are indicated by different arrows. Scale bars = 100 µm.
- Immunostaining of myofiber types
SOL muscles and TA muscles of 2-month old male mice were processed for immunostaining of myosin heavy chain (MyHC). For SOL muscles, we used Myh2, Myh7 and Dystrophin primary antibodies to stain Type IIa, Type I myofibers and sarcolemma, respectively. Goat anti-Mouse IgG1-488, Goat anti-Mouse IgG2b-568 and Goat anti-Rabbit IgG-647 secondary antibodies were used to distinguish Myh2, Myh7 and Dystrophin primary antibodies, respectively. SOL muscle is ‘slow’ muscle which contains Type I (Red), Type IIa (Green) and Type IIx (Black) myofibers (Figure 3).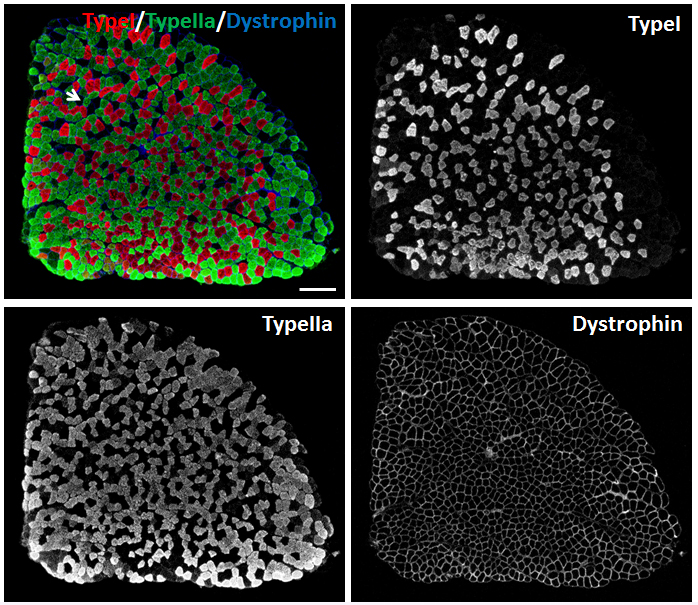
Figure 3. Immunostaining of myofibers in SOL muscles of 2-month old male mice. Myh2, Myh7 and Dystrophin primary antibodies were used to stain Type IIa (Green), Type I (Red) myofibers and sarcolemma (Blue), respectively. Unlabeled myofibers (Black) are presumed to be Type IIx myofibers. One Type IIx myofiber is indicated by the arrow. Scale bar = 200 µm.
For TA muscles, we used Myh2, Myh4 and Myh7 primary antibodies to stain Type IIa, Type IIb and Type I myofibers, respectively. Goat anti-Mouse IgG1-568, Goat anti-Mouse IgM-488, and Goat anti-Mouse IgG2b-647 secondary antibodies were used to distinguish Myh2, Myh4 and Myh7 primary antibodies, respectively. TA muscle is ‘fast’ muscle which is dominated by Type IIa (Red), Type IIx (Black) and Type IIb (Green) myofibers (Figure 4). Few Type I myofibers exist in TA muscles (Figure 4).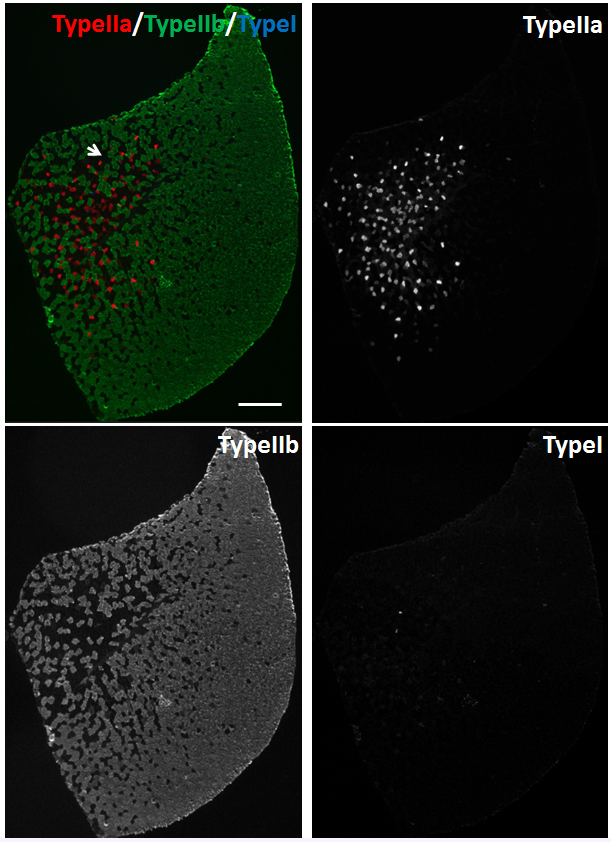
Figure 4. Immunostaining of myofibers in TA muscles of 2-month old male mice. Myh2, Myh4 and Myh7 primary antibodies were used to stain Type IIa (Red), Type IIb (Green) and Type I (Blue) myofibers, respectively. Unlabeled myofibers (Black) are presumed to be Type IIx myofibers. One Type IIx myofiber is indicated by the arrow. Scale bar = 500 µm.
The numbers of myofibers are counted with Photoshop software (we use Photoshop CC, but any version of Photoshop containing the Count Tool works). For example, when counting different types of myofibers in a SOL muscle section, first, open image in Photoshop CC (Figure 5A). Next, choose Image > Analysis > Count Tool (Figure 5A). Next, choose Red and Blue channels (bottom right corner) to show Type I myofibers and sarcolemma (Figure 5B). A number will appear in a myofiber when you click the myofiber. Total number can be found in the Counts bar (top left corner, oval labeled, Figure 5B). After counting Type I myofibers, choose Green and Blue channels to count Type IIa myofibers. At last, choose Red, Green and Blue channels, myofibers without Red or Green labelling are Type IIx myofibers.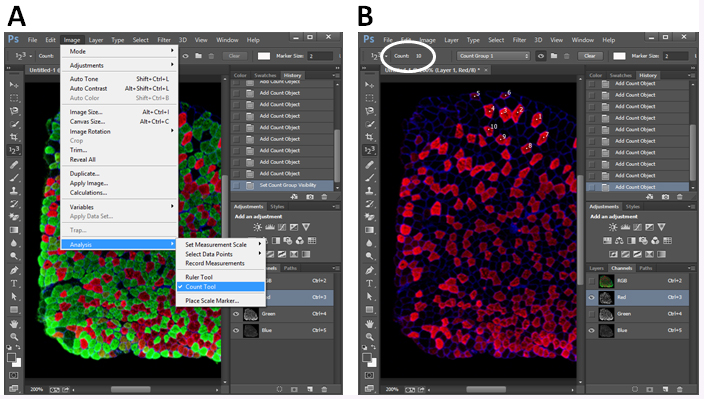
Figure 5. Illustration of myofiber counting in Photoshop CC. A. Open Count Tool in Photoshop CC; B. Choose a type of myofiber and count the number by clicking the myofiber. The total number is shown in the Count bar (oval highlighted).
Notes
- Thermal equilibration is indispensable before cryosectioning.
- The H&E staining protocol is generated based on our daily practice. It is not necessary to fix the sections before the hematoxylin staining. In addition, the ‘Blueing’ procedure is not required after the hematoxylin staining.
- In the immunostaining using MyHC antibodies from DSHB, avoid fixation of the sections. Fixation disrupts the binding of antibody to myosin heavy chain.
- The Abcam Dystrophin antibody works well in fixed and non-fixed sections.
- The wet chamber is made by placing several wet papers in a slide box (Figure 6). Place a slide in a wet chamber as it is shown in Figure 6.

Figure 6. Setup of a wet chamber and placement of a slide in a wet chamber
Recipes
- Hematoxylin solution
6 g hematoxylin
100 ml ethanol
150 g potassium alum
2,000 ml double-distilled H2O
1.2 g sodium iodate
120 ml glacial acetic acid
900 ml glycerol
Dissolve the hematoxylin in ethanol, and the potassium alum in distilled water. After that, mix them with glycerol, and add sodium iodate and glacial acetic acid at last. Store hematoxylin solution at room temperature - Eosin Y solution
2 g Eosin Y
40 ml double-distilled H2O
760 ml 95% ethanol
4 ml glacial acetic acid
Dissolve Eosin Y in double-distilled H2O. Then add 95% ethanol, and mix. While working in a fume hood, add glacial acetic acid and mix well. Store covered at room temperature - Blocking buffer
5% goat serum
2% BSA
0.2% Triton X-100
0.1% sodium azide
200 ml blocking buffer is prepared with PBS containing 10 ml goat serum, 4 g BSA, 4 ml 10% Triton X-100 and 0.2 g sodium azide. Aliquot and store at -20 °C
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the US National Institutes of Health (R01AR071649 to S.K.).
References
- Nie, Y., Sato, Y., Wang, C., Yue, F., Kuang, S. and Gavin, T. P. (2016). Impaired exercise tolerance, mitochondrial biogenesis, and muscle fiber maintenance in miR-133a-deficient mice. FASEB J 30(11): 3745-3758.
- Schiaffino, S. and Reggiani, C. (2011). Fiber types in mammalian skeletal muscles. Physiol Rev 91(4): 1447-1531.
- Wang, C., Wang, M., Arrington, J., Shan, T., Yue, F., Nie, Y., Tao, W. A. and Kuang, S. (2017). Ascl2 inhibits myogenesis by antagonizing the transcriptional activity of myogenic regulatory factors. Development 144(2): 235-247.
- Wang, J. H., Wang, Q. J., Wang, C., Reinholt, B., Grant, A. L., Gerrard, D. E. and Kuang, S. (2015). Heterogeneous activation of a slow myosin gene in proliferating myoblasts and differentiated single myofibers. Dev Biol 402(1): 72-80.
- Yue, F., Bi, P., Wang, C., Li, J., Liu, X. and Kuang, S. (2016). Conditional loss of Pten in myogenic progenitors leads to postnatal skeletal muscle hypertrophy but age-dependent exhaustion of satellite cells. Cell Rep 17(9): 2340-2353.
Article Information
Copyright
Wang et al. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0).
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Wang, C., Yue, F. and Kuang, S. (2017). Muscle Histology Characterization Using H&E Staining and Muscle Fiber Type Classification Using Immunofluorescence Staining. Bio-protocol 7(10): e2279. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2279.
- Bi, P., Yue, F., Sato, Y., Wirbisky, S., Liu, W., Shan, T., Wen, Y., Zhou, D., Freeman, J. and Kuang, S. (2016). Stage-specific effects of Notch activation during skeletal myogenesis. Elife 5.
Category
Neuroscience > Peripheral nervous system > Skeletal muscle
Cell Biology > Tissue analysis > Tissue staining
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









