- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Quantitative Determination of Ascorbate from the Green Alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by HPLC
Published: Vol 6, Iss 24, Dec 20, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2067 Views: 8879
Reviewed by: Maria SinetovaClaudia CatalanottiAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

A Quick Method to Quantify Iron in Arabidopsis Seedlings
Chandan Kumar Gautam [...] Wolfgang Schmidt
Mar 5, 2022 3920 Views

Isolation of Intact Vacuoles from Arabidopsis Root Protoplasts and Elemental Analysis
Chuanfeng Ju [...] Zhenqian Zhang
Mar 5, 2023 2035 Views

High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Quantification of Glyphosate, Aminomethylphosphonic Acid, and Ascorbate in Culture Medium and Microalgal Cells
Juan Manuel Ostera [...] Gabriela Malanga
Apr 5, 2025 1171 Views
Abstract
Ascorbate (Asc, also called vitamin C) is of vital importance to the cellular functions of both animals and plants. During evolution, Asc has become one of the most abundant metabolites in seed plants; however, Asc contents in cyanobacteria, green algae and bryophytes are very low. Here we describe a sensitive and reliable HPLC method for the quantitative determination of cellular Asc content in the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.
Keywords: AscorbateBackground
Previous protocols for the determination of cellular Asc content were developed for higher plants, of which the amounts of cellular Asc are high enough for the analysis. Those protocols are not suitable for green algae, since both the amounts of the plant material and the levels of the cellular Asc are usually limited. Therefore, there was a need to develop a novel method with sensitivity improved to the µM range to measure the cellular Asc in green algae.
Materials and Reagents
- 15-ml conical centrifuge tubes (Corning, Falcon®)
- Polypropylene microcentrifuge tubes of 1.5 ml (Eppendorf)
- 0.3 ml polypropylene chromatographic vials (Focus Technology, model: VP91 ) with polypropylene cap and PTFE/silicone septa (Focus Technology, model: SC9291 )
- 4 mm hydrophilic PTFE syringe filter with a 0.22 µm pore size (Nantong Filterbio Membrane, catalog number: FBS4PTFE022L )
- 47 mm hydrophilic PTFE membrane with a 0.45 µm pore size (Nantong Filterbio Membrane, catalog number: FBM047PTFE045L )
- Glass beads 212-300 µm (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G9143-250G )
- 1 ml disposable polypropylene syringe (B. Braun Medical, catalog number: 9166017V )
- Millex-GS 33 mm sterile syringe filter with a 0.22 µm pore size (EMD Millipore, catalog number: SLGS033SS )
- Milli-Q water
- Liquid nitrogen
- Tris-(2-carboxyethyl)-phosphine hydrochloride (TCEP) (Carl Roth, catalog number: HN95.2 )
- Potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4) (Carl Roth, catalog number: 3904.1 )
- Orthophosphoric acid (H3PO4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: W290017 )
- EDTA (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: EDS-100G )
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Duchefa Biochemie, catalog number: S0520.1000 )
- Potassium chloride (KCl) (Duchefa Biochemie, catalog number: P0515.1000 )
- Di-sodium hydrogen phosphate (Na2HPO4) (Carl Roth, catalog number: P030.2 )
- Magnesium chloride hexahydrate (MgCl2·6H2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M2393-100g )
- Calcium chloride dihydrate (CaCl2·2H2O) (Duchefa Biochemie, catalog number: C0504.1000 )
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 258148-2.5L-D )
- Sodium L-Asc (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 4034-100G )
- Acetonitrile HPLC gradient grade (VWR, HiPerSolv Chromanorm®, catalog number: 83639.320 )
- Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (see Recipes)
- Extraction buffer (see Recipes)
- HPLC mobile phase A (see Recipes)
- HPLC mobile phase B (see Recipes)
- Sodium L-Asc standard solutions (see Recipes)
Equipment
- ScepterTM handheld automated cell counter (EMD Millipore, catalog number: PHCC00000 )
- ScepterTM Sensors – 40 µm (EMD Millipore, catalog number: PHCC40050 )
- Refrigerated table centrifuge and microcentrifuge
- HPLC system (Shimadzu Scientific Instruments) equipped with:
- LC pump (Shimadzu Scientific Instruments, model: LC-20AD )
- Thermostated autosampler (Shimadzu Scientific Instruments, model: SIL-20AC )
- Photo Diode Array detector (Shimadzu Scientific Instruments, model: SPD-M30A )
- Column oven (Shimadzu Scientific Instruments, model: CTO-20AC )
- Synergy hydro 4u Hydro – RP 80 Å 250 x 4.6 mm (Phenomenex, catalog number: 00G-4375-E0 ) directly mounted with a guard column AQ C18 4.0 x 3.0 mm (Phenomenex, catalog number: KJ0-4282 )
Software
- LabSolution (Shimadzu Scientific Instruments)
Procedure
- Sample preparation
- Prepare liquid Chlamydomonas cultures and collect 1 ml sample when the cultures are in the exponential growth phase. Mix the sample with 19 ml of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Use a Scepter cell counter to determine cell number and cell volume by following the instructions displayed on the screen. Briefly, depress the plunger, submerge the tip, and release the plunger to soak up 50 μl liquid culture into the tip. The Scepter cell counter detects each cell passing through the orifice of the tip, calculates cell density, and displays a histogram of cell diameter or volume on the screen (Johnston, 2010).
- Based on the calculated cell density, harvest 2 x 106 cells, place it in a 15-ml conical centrifuge tube and centrifuge it at 12,000 x g for 1 min at room temperature.
- Gently re-suspend the pelleted cells in 1 ml Milli-Q water and repeat the centrifugation step.
- Discard the supernatant and freeze the pellet in liquid nitrogen. The samples can be stored at -80 °C for several months.
- Add 200 µl of extraction buffer to the frozen pellet and mix it by vigorous shaking. The extraction buffer contains TCEP to keep Asc in the reduced form.
- Transfer the resuspended cells into a 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tube containing 100 µl glass beads and vortex at maximum speed for 30 sec. Incubate the sample at room temperature for two minutes (during which the sample becomes brownish), then place it on ice.
- Centrifuge the sample at 19,000 x g at 4 °C for 30 min.
- Collect 120 µl of the supernatant (without stirring up the pellet) and filter it into chromatographic vials using 4 mm hydrophilic PTFE syringe filters with a pore size of 0.22 µm. The samples are stable for 24 h at 4 °C and can be stored at -80 °C for several months; however, freeze-thaw cycles should be avoided.
- Prepare liquid Chlamydomonas cultures and collect 1 ml sample when the cultures are in the exponential growth phase. Mix the sample with 19 ml of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Use a Scepter cell counter to determine cell number and cell volume by following the instructions displayed on the screen. Briefly, depress the plunger, submerge the tip, and release the plunger to soak up 50 μl liquid culture into the tip. The Scepter cell counter detects each cell passing through the orifice of the tip, calculates cell density, and displays a histogram of cell diameter or volume on the screen (Johnston, 2010).
- Determination of Asc concentration by HPLC (see Nováková et al., 2008a for theoretical basics)
- Ascorbate can be efficiently separated chromatographically using a Synergy hydro 4u Hydro – RP 80 Å 250 x 4.6 mm column. Attach the column fitted with a suitable guard column (AQ C18 4.0 x 3.0 mm) to the HPLC. Equilibrate the column with mobile phase A for at least 30 min at a flow rate of 1 ml/min.
- Set the tray temperature of the autosampler at 4 °C and the column oven temperature at 20 °C.
- While waiting for the temperature and baseline to stabilize, prepare the sample sequence table. Insert the chromatographic vials containing the samples into the tray of the autosampler.
- Inject 20 µl sample. For the elution of Asc, use an isocratic mobile phase of 50 mM KH2PO4 (pH 2.5, adjusted with orthophosphoric acid) for 5 min at a flow rate of 1 ml/min then apply a short acetonitrile (mobile phase B) gradient from 0% to 30% between 3.5 and 6 min to elute the less polar components from the column. Between 8 and 9 min decrease the percentage of mobile phase B to 0% and equilibrate the column to the mobile phase A for an additional 9 min. The total running time is 18 min.
- Record the signal between 190 and 500 nm at a sampling frequency of 4 Hz and 1,024 spectral resolution with a slit set to 8 nm. The Asc peak appears at approximately 5.1 min with an absorption maximum at around 244 nm.
- Ascorbate can be efficiently separated chromatographically using a Synergy hydro 4u Hydro – RP 80 Å 250 x 4.6 mm column. Attach the column fitted with a suitable guard column (AQ C18 4.0 x 3.0 mm) to the HPLC. Equilibrate the column with mobile phase A for at least 30 min at a flow rate of 1 ml/min.
Data analysis
- Prepare a two-fold serial dilution between 0.2 and 50 µM Asc dissolved in the extraction buffer. Determine the peak areas of Asc in the HPLC chromatograms by the LabSolution software (Shimadzu Scientific Instruments) and use linear fitting to obtain a calibration curve (Figure 1).
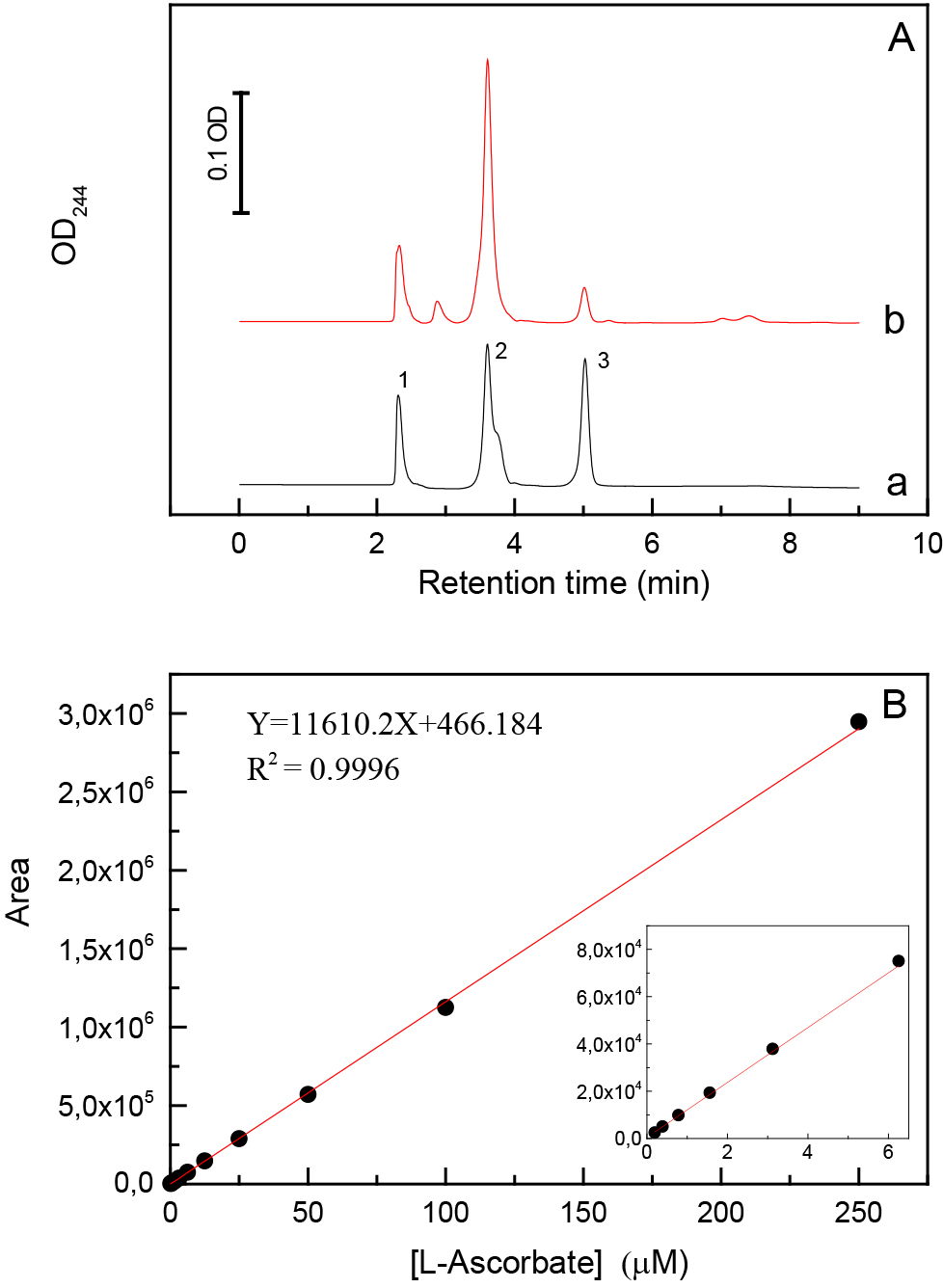
Figure 1. Typical HPLC chromatograms recorded at 244 nm and a calibration curve for the determination of L-Asc concentration. A. Chromatographic profiles of (a) 62.5 µM L-Asc dissolved in extraction buffer (95% orthophosphoric acid, 2 mM EDTA, 10 mM TCEP, pH 2.5) and (b) C. reinhardtii cell extract. The identified peaks are (1) orthophosphoric acid; (2) EDTA; (3) L-Asc. B. Calibration curve for the determination of L-Asc concentration calculated based on linear fitting of the peak areas and using 1/area weighting. The LOD and LOQ values are 0.2 and 1.5 µM, respectively. - Calculate the cellular Asc concentration using the following formula:
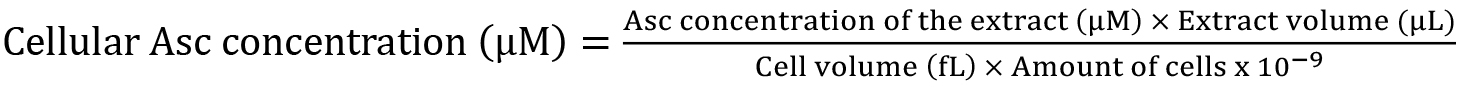
Notes
- The average cell volume for C. reinhardtii is about 200 fl. The typical Asc concentration of CC124 C. reinhardtii cells grown in liquid Tris-acetate-phosphate medium for three days at approximately 80 µmole photons m-2 s-1 is about 40 µM. The cellular Asc content, however, strongly depends on the algal strain, the growth medium, the age of the cultures, growth light and stress conditions (Nagy et al., 2016; Vidal-Meireles et al., unpublished).
- The extraction buffer contains TCEP, which keeps Asc in the more stable reduced form; therefore, by the method described above, the total cellular Asc concentration (dehydroascorbate + Asc) is determined. However, if there is a need to determine the amount of dehydroascorbate within the cell, omit TCEP from the extraction buffer. In this case, however, the samples should be processed and measured within less than 2 h, and cannot be frozen. Dehydroascorbate does not absorb at 244 nm, thus the ratio of Asc to dehydroascorbate is calculated based on the difference in absorption at 244 nm in the presence or absence of TCEP.
Recipes
- Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, 1 L; based on Chazotte, 2012)
8 g NaCl
0.2 g KCl
1.44 g Na2HPO4
0.24 g KH2PO4
0.1 g MgCl2·6H2O
Milli-Q water
Dissolve the salts in Milli-Q water and adjust the pH to 7.2 with HCl
Complete the volume to 990 ml by adding Milli-Q water and dispense the solution into aliquots Sterilize the solution by autoclaving for 20 min at 121 °C, 15 psi on liquid cycle
Dissolve 0.133 g CaCl2·2H2O in 10 ml of Milli-Q water, filter-sterilize it and add it to the solution after autoclaving
Store the sterile PBS at room temperature - Extraction buffer (100 ml; based on Nováková et al., 2008b)
74.448 mg EDTA
286.65 mg TCEP
Milli-Q water
Dissolve the salts completely in Milli-Q water
Add 5 ml of 98% orthophosphoric acid
Dispense the solution into aliquots, and store at -80 °C until use - HPLC mobile phase A (1 L)
6.8045 g KH2PO4
Milli-Q water
Adjust the pH to 2.5 with 98% orthophosphoric acid
Filter the solution using 0.45 µm hydrophilic PTFE membrane
Note: This solution must be freshly prepared. - HPLC mobile phase B (1 L)
100% acetonitrile
Degas by sonication for 20 min at room temperature - Sodium L-Asc standard solutions
Dissolve 49.5 mg sodium L-Asc in 1 ml of extraction buffer to obtain a 50 mM sodium L-Asc solution
Dilute 10 µl aliquot in 10 ml extraction buffer
Prepare a two-fold dilution series from this 50 µM stock solution down to 0.2 µM
Note: This solution must be freshly prepared.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Lendület/Momentum Programme of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences (LP-2014/19) and the National, Research and Development Office (research grant NN114524).
References
- Chazotte, B. (2012). Labeling Golgi with fluorescent ceramides. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2012(8).
- Johnston, G. (2010). Automated handheld instrument improves counting precision across multiple cell lines. BioTechniques 48: 325-327
- Nagy, V., Vidal-Meireles, A., Tengölics, R., Rákhely, G., Garab, G., Kovács, L. and Tóth, S. Z. (2016). Ascorbate accumulation during sulphur deprivation and its effects on photosystem II activity and H2 production of the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Cell Environ 39(7): 1460-1472.
- Nováková, L., Solich, P. and Solichová, D. (2008a). HPLC methods for simultaneous determination of ascorbic and dehydroascorbic acids. Trends Anal Chem 27: 942-958.
- Nováková, L., Solichová, D., Pavlovičová, S. and Solich, P. (2008b). Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography method for the determination of ascorbic acid. J Sep Sci 31(9): 1634-1644.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Kovács, L., Vidal-Meireles, A., Nagy, V. and Tóth, S. Z. (2016). Quantitative Determination of Ascorbate from the Green Alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by HPLC. Bio-protocol 6(24): e2067. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2067.
Category
Plant Science > Plant biochemistry > Other compound
Biochemistry > Other compound > Ascorbate
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link













