- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Detection of Reactive Oxygen Species in Oryza sativa L. (Rice)
Published: Vol 6, Iss 24, Dec 20, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2061 Views: 23842
Reviewed by: Pooja SaxenaAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

A Quick Method to Quantify Iron in Arabidopsis Seedlings
Chandan Kumar Gautam [...] Wolfgang Schmidt
Mar 5, 2022 3929 Views

Isolation of Intact Vacuoles from Arabidopsis Root Protoplasts and Elemental Analysis
Chuanfeng Ju [...] Zhenqian Zhang
Mar 5, 2023 2048 Views

High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Quantification of Glyphosate, Aminomethylphosphonic Acid, and Ascorbate in Culture Medium and Microalgal Cells
Juan Manuel Ostera [...] Gabriela Malanga
Apr 5, 2025 1178 Views
Abstract
Superoxide ions (O2-) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) are the reactive oxygen species (ROS) that play a significant role in regulation of many plant processes. The level of O2- ions is determined qualitatively using nitrobluetetrazolium (NBT) assay while the H2O2 is qualitatively estimated using 3,3-diaminobenzidine (DAB) and 2’,7’-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (H2DCFDA) assay. Further the aqueous content of H2O2 is estimated quantitatively using ferrous oxidation-xylenol orange (FOX) assay.
Keywords: RiceBackground
Superoxide ions (O2-) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) are the vital reactive oxygen molecules that play a central role in many processes involved in plant growth and development including abiotic stress tolerance. To get better insights into the ROS mediated regulation of these processes, qualitative and quantitative estimation of different types of ROS is of significant importance. O2- is produced by the transfer of electrons from NADPH to oxygen (O2) mediated by the NADPH oxidase enzyme system. These ions are estimated in rice seedlings using NBT assay which is based upon the principle of reduction of yellow coloured NBT into dark blue coloured insoluble formazan by O2- (Kaur et al., 2016).
H2O2 is another reactive oxygen molecule that acts as an important signaling molecule regulating different plant processes. The content of H2O2 is estimated qualitatively in rice seedlings using DAB and H2DCFDA assay (Kaur et al., 2016). DAB assay is based upon the principle of formation of deep brown polymerization product on the reaction of DAB with H2O2 while H2DCFDA assay is based upon the principle of fluorescent microscopy. When non fluorescent H2DCFDA binds to ROS (predominantly H2O2), it gets converted into highly fluorescent 2’,7’-dichlorofluorescein (DCF). DCF gives a green coloured fluorescence when excited with a laser beam of excitation 488 nm using confocal microscope. Further, the quantitative measurement of aqueous H2O2 is carried out using ferrous oxidation-xylenol orange (FOX) method (Kaur et al., 2016). FOX assay is based upon the principle of oxidation of ferrous ions by H2O2 to ferric ions. Ferric ions then bind with xylenol orange to give a coloured complex having absorption maxima at 560 nm.
Materials and Reagents
- Petri dish (35 mm) (Tarsons, catalog number: 460035 )
- Microscopic glass slides
- Glue or nail enamel
- Whatman filter paper No.1 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 09-805 )
- Amber Eppendorf (Capacity: 2 ml) (Tarsons, catalog number: 500013 )
- Glass tubes
- Tubes (Capacity:15 ml and 50 ml) (Tarsons, catalog numbers: 546021 [15 ml]; 546041 [50 ml])
- Disposable cuvettes (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z330361 )
Note: This product has been discontinued. - Leaf of 14 days old fresh rice seedlings
- Tri-sodium citrate dihydrate (HiMedia Laboratories, catalog number: RM1415 )
- Glycerol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G5516 )
- Absolute ethanol
- Activated charcoal (HiMedia Laboratories, catalog number: PCT1001 )
- Trichloroacetic acid (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T6399 )
- Liquid nitrogen
- 30 % hydrogen peroxide solution (H2O2) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H1009 )
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl) (Molychem, catalog number: 23540 )
- Diaminobenzidine (DAB) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D8001 )
- Nitrobluetetrazolium (NBT) (HiMedia Laboratories, catalog number: MB107 )
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 1310-73-2 )
- 2’,7’-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (H2DCFDA) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Molecular ProbesTM, catalog number: D399 )
- Dimethyl sulphoxide (Minimum assay: 99.0%) (S D Fine-Chem, catalog number: 38216 )
- Ammonium ferrous sulfate (HiMedia Laboratories, catalog number: GRM1026 )
- Sulfuric acid (HiMedia Laboratories, catalog number: AS016 )
- Xylenol orange (LobaChemie, catalog number: 06507 )
- Methanol (HPLC grade) (Minimum Assay: 99.7%) (HiMedia Laboratories, catalog number: AS061 )
- Butylated hydroxytoluene (HiMedia Laboratories, catalog number: GRM797 )
- NBT solution (see Recipes)
- DAB solution (see Recipes)
- H2DCFDA solution (see Recipes)
- Ferrous oxidation-xylenol orange (FOX) reagent (see Recipes)
- Standard H2O2 solutions (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Pipette (Corning, model: Lambda Plus)
- Vacuum infiltration equipment (Dessicator connected to vacuum pump) (Vacuum pump: Rocker 300 , Rocker Scientific, model: Rocker 300]; Dessicator vacuum: tarsons 403010 [Tarsons, model: 403010 ] )
- Water bath (Polyscience, model: WB02S )
- Stereomicroscope (Olympus, model: SZ61 )
- Confocal microscope (Nikon A1R, Laser scanning confocal microscope system)
- Centrifuge (REMI, model: C-24 PLUS )
- Spectrophotometer (PerkinElmer, model: Lambda 25 )
Note: This product has been discontinued. - Weighing balance (Citizen Scale, model: CY220 )
- pH meter (Systronics, model: µ361 )
- Pestle mortar
Procedure
- NBT assay (For detection of O2-) (Video 1)Video 1. Procedure for qualitative estimation of superoxide ions (O2-) using NBT assay in rice
- Cut the second leaf of rice seedlings at the base of stem into small pieces (approximately 1 cm) (Figure 1).
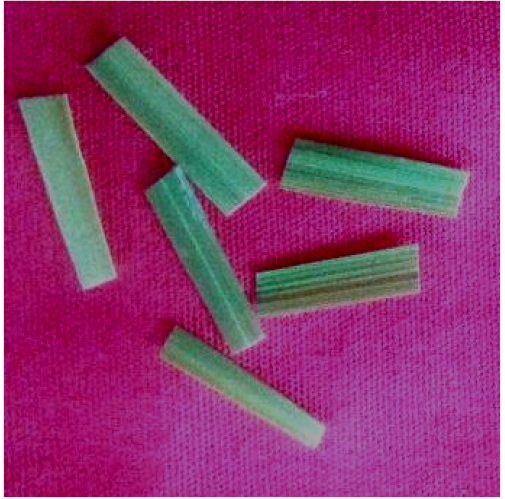

Figure 1. Pieces of rice seedlings approximately 1 cm in length - Dip the cut pieces immediately into 6 mM NBT solution (2 ml) prepared in sodium citrate (pH 6.0) in a Petri dish (35 mm) using a tweezer.
- Vacuum infiltrate the dipped samples for 10 min at 60 KPa pressure and then incubate at room temperature for 10 min under room light.
Note: If vacuum infiltration unit is not available, dip and incubate the samples for 8 h at room temperature under light. - After incubation, dip the samples in absolute ethanol and then keep them in a water bath (100 °C) till the chlorophyll is removed from the samples completely (usually occurs in 2 h) (Figure 2).
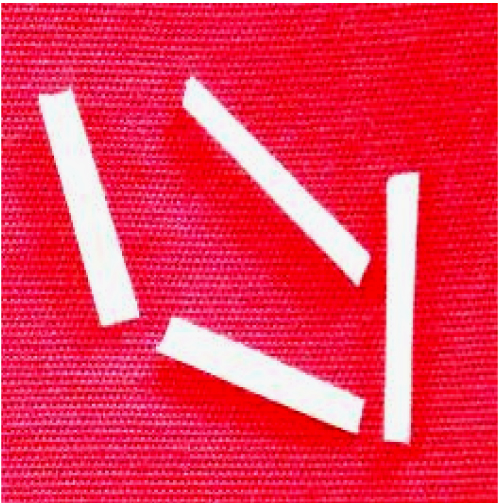

Figure 2. Pieces of rice seedlings approximately 1 cm in length after removal of chlorophyll
- Cool and dip the samples in 20% glycerol.
- Capture the images using a stereomicroscope by keeping the samples on a slide.
- Appearance of dark blue colour indicates the presence of O2- (Figure 3).
- Cut the second leaf of rice seedlings at the base of stem into small pieces (approximately 1 cm) (Figure 1).
- DAB assay (For detection of H2O2)
- Cut the second leaf of rice seedlings at the base of stem into small pieces (approximately 1 cm).
- Dip the cut pieces immediately into DAB solution (1 mg/ml) prepared in double distilled water (2 ml) (pH = 3.8) in a Petri dish (35 mm) using tweezers.
- Vacuum infiltrate the dipped samples for 10 min at 60 KPa pressure and then incubate at room temperature for 10 min under room light.
Note: If vacuum infiltration unit is not available, dip and incubate the samples for 8 h at room temperature under light. - After incubation, dip the samples in the absolute ethanol and then keep them in a water bath (100 °C) till the chlorophyll is removed from the samples completely (usually occurs in 2 h).
- Cool and dip the samples in 20% glycerol.
- Capture the images using a stereo microscope by keeping the samples on a slide.
- Appearance of brown coloured product indicates the presence of H2O2 (Figure 4).
- Cut the second leaf of rice seedlings at the base of stem into small pieces (approximately 1 cm).
- H2DCFDA assay (For detection of H2O2)
- Cut the second leaf of rice seedlings at the base of stem into small pieces (approximately 1 cm).
- Dip the cut pieces immediately into 10 µM H2DCFDA solution in a Petri dish (35 mm) using tweezers.
- Vacuum infiltrate the dipped samples for 5 min at 60 KPa pressure and then incubate at room temperature for 10 min in the dark.
Note: If vacuum infiltration unit is not available, dip the samples for 2 h at room temperature. - After incubation, wash the samples three times properly with autoclaved double distilled water.
- Dip the samples in 20% glycerol after washing.
- For confocal analysis, put the sample on a slide and fix a thin cover slip over it using nail enamel or glue.
- Observe the samples under a confocal microscope using laser beam of wavelength of excitation 488 nm.
- Green fluorescence indicates the presence of H2O2 and red represents the autofluorescence of chlorophyll.
- Cut the second leaf of rice seedlings at the base of stem into small pieces (approximately 1 cm).
- Quantification of aqueous H2O2 content
- Homogenize 0.5 g fresh seedlings in activated charcoal (0.1 g) prepared in 5 ml of 5% trichloroacetic acid using a pestle and mortar with liquid nitrogen.
- Filter the homogenate using a Whatman filter (No.1) and collect the filtrate in 2 ml amber Eppendorf tubes (H2O2 is light sensitive).
- Centrifuge the filtrate at 5,000 x g for 10 min in the tubes.
Note: Either centrifuge the filtrate from one sample in two 2 ml Eppendorf tubes and then pool the supernatant together or use a 5 ml amber Eppendorf tube. - Collect 0.2 ml of the supernatant in a glass tube and add 1 ml FOX reagent to it.
- Mix the reaction mix properly and incubate at room temperature for 15 min.
- Estimate the content of aqueous H2O2 by recording the absorbance at 560 nm using a disposable plastic cuvette and calculate the concentration using a standard curve.
- The concentration is calculated using the beer-lambert law, i.e.
A = ε x b x c
Where,
A = absorbance,
ε is the wavelength-dependent molar absorptivity coefficient,
b = path length,
c = concentration. - For the standard curve preparation, take 0.2 ml of different concentrations of H2O2, add 1 ml of FOX reagent and proceed as similar to the samples (see Recipe 5).
Note: The absorbance should be taken at 560 nm wavelength.
- Homogenize 0.5 g fresh seedlings in activated charcoal (0.1 g) prepared in 5 ml of 5% trichloroacetic acid using a pestle and mortar with liquid nitrogen.
Data analysis
- NBT assay
Observation: Appearance of dark blue colour indicates presence of O2- (Figure 3).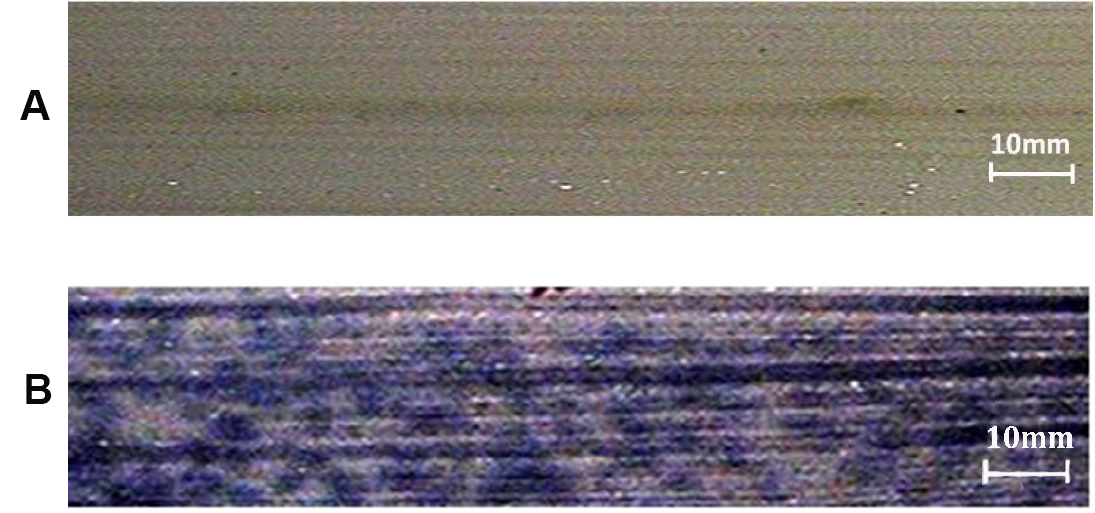
Figure 3. Stereomicroscope image of NBT assay of rice leaf showing the presence of superoxide ions (O2-) indicated by presence of blue coloured formazan. A. Negative control; B. Rice sample showing the presence of superoxide ions (O2-). - DAB assay
Observation: Appearance of brown coloured product indicates presence of H2O2 (Figure 4).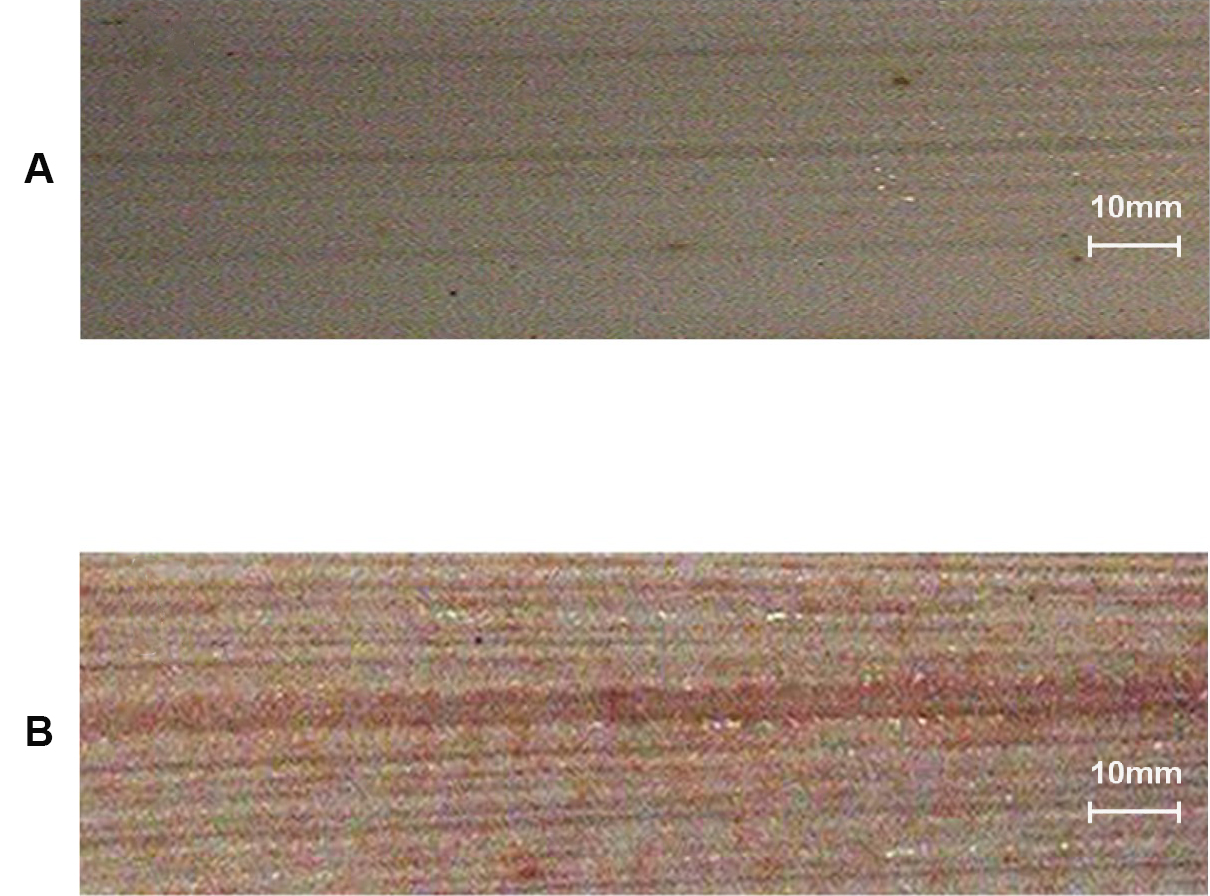
Figure 4. Stereomicroscope image of DAB assay of rice leaf showing the presence of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) indicated by presence of brown coloured product. A. Negative control; B. Rice sample showing the presence of Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). - H2DCFDA assay
Observation: Green fluorescence indicates presence of H2O2 and red signifies autofluorescence of chlorophyll (Figure 5).
Figure 5. Confocal H2DCFDA staining images. 1. Red colour indicates chlorophyll; 2. Green colour indicates ROS predominantly hydrogen peroxide; 3. Overlay of ROS and chlorophyll.
Notes
- DAB will dissolve in double distilled water only at acidic pH (pH = 3.8), so set the pH of water with HCl before adding DAB. It will take a little longer for dissolution.
- During H2DCFDA assay, samples should be minimally exposed to light.
- After H2DCFDA exposure, proceed immediately for confocal microscopy.
- All solutions for aqueous hydrogen peroxide estimation should be prepared fresh and should be used within 2 h.
Recipes
- NBT solution
6 mM NBT prepared in 10 mM of sodium citrate (pH = 6)
Adjust the pH using either 1 N HCl or 1 N NaOH - DAB solution
1 mg/ml DAB solution prepared in autoclaved double distilled water (pH = 3.8)
Adjust the pH using 1 N HCl - H2DCFDA solution
Prepare 10 mM of H2DCFDA in dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO)
Dilute it to 10 µM using autoclaved double distilled water - Ferrous oxidation-xylenol orange (FOX) reagent (see Table 1)
Prepare the following stock solutions:
Reagent a: 25 mM ammonium ferrous sulfate prepared in 2.5 M sulfuric acid
Reagent b: 0.25 M xylenol orange prepared in HPLC-grade methanol
Reagent c: 9.69 mg of butylated hydroxytoluene prepared in 90 ml of HPLC-grade methanol
Table 1. Preparation of FOX reagentStock Solutions Volume Reagent a 1 ml Reagent b 50 µl Reagent c 90 ml Autoclaved double distilled water 8.95 ml Total 100 ml - Standard H2O2 solutions
- 5 % trichloroacetic acid (TCA) solution
Dissolve 5 g of TCA in 100 ml of autoclaved double distilled water - 100 µM H2O2 stock solution in 5% trichloroacetic acid
- Standard H2O2 solutions (see Table 2)
Notes:- Different concentrations of H2O2 should be prepared in 5% trichloroacetic acid.
- The range of concentrations to be used for preparing standard curve depends upon the range of hydrogen peroxide content present in the given sample.
Table 2. Preparation of standard H2O2 solutionsConcentration
of H2O2 (in µM)Volume of H2O2 to be
used from stock (in µl)Volume of TCA to be used
from stock (in µl)FOX reagent
(in ml)BLANK 0 200 1 10 20 180 1 20 40 160 1 30 60 140 1 40 80 120 1 50 100 100 1 60 120 80 1 70 140 60 1 80 160 40 1 90 180 20 1 100 200 0 1 - Different concentrations of H2O2 should be prepared in 5% trichloroacetic acid.
- 5 % trichloroacetic acid (TCA) solution
Acknowledgments
This protocol has been adopted and modified from DeLong et al. (2003), Kristiasen et al. (2009) and Wu et al. (2010). Authors acknowledge the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India for financial support (Project No. BT/PR13965/BRB/10/883/2010).
References
- DeLong, J. M., Prange, R. K., Hodges, D. M., Forney, C. F., Bishop, M. C. and Quilliam, M. (2002). Using a modified ferrous oxidation-xylenol orange (FOX) assay for detection of lipid hydroperoxides in plant tissue. J Agr Food Chem 50(2): 248-254.
- Kaur, N., Dhawan, M., Sharma, I. and Pati, P. K. (2016). Interdependency of reactive oxygen species generating and scavenging system in salt sensitive and salt tolerant cultivars of rice. BMC Plant Biol 16(1): 131.
- Kristiansen, K. A., Jensen, P. E., Moller, I. M. and Schulz, A. (2009). Monitoring reactive oxygen species formation and localisation in living cells by use of the fluorescent probe CM-H(2)DCFDA and confocal laser microscopy. Physiol Plant 136(4): 369-383.
- Wu, G. L., Cui, J., Tao, L. and Yang, H. (2010). Fluroxypyr triggers oxidative damage by producing superoxide and hydrogen peroxide in rice (Oryza sativa). Ecotoxicology 19(1): 124-132.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Kaur, N., Sharma, I., Kirat, K. and Pati, P. K. (2016). Detection of Reactive Oxygen Species in Oryza sativa L. (Rice). Bio-protocol 6(24): e2061. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2061.
Category
Plant Science > Plant biochemistry > Other compound
Biochemistry > Other compound > Reactive oxygen species
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










