- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Isolation of Highly Pure Primary Mouse Alveolar Epithelial Type II Cells by Flow Cytometric Cell Sorting
Published: Vol 6, Iss 22, Nov 20, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2013 Views: 27599
Reviewed by: Fanglian HeHongwei HanAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Identification and Sorting of Adipose Inflammatory and Metabolically Activated Macrophages in Diet-Induced Obesity
Dan Wu [...] Weidong Wang
Oct 20, 2025 2233 Views

Selective Enrichment and Identification of Cerebrospinal Fluid-Contacting Neurons In Vitro via PKD2L1 Promoter-Driven Lentiviral System
Wei Tan [...] Qing Li
Nov 20, 2025 1335 Views

Revisiting Primary Microglia Isolation Protocol: An Improved Method for Microglia Extraction
Jianwei Li [...] Guohui Lu
Dec 5, 2025 1460 Views
Abstract
In this protocol, we describe the method for isolating highly pure primary alveolar epithelial type II (ATII) cells from lungs of naïve mice. The method combines negative selection for a variety of lineage markers along with positive selection for EpCAM, a pan-epithelial cell marker. This method yields 2-3 x 106 ATII cells per mouse lung. The cell preps are highly pure and viable and can be used for genomic or proteomic analyses or cultured ex vivo to understand their roles in various biological processes.
Background
The internal surfaces of lungs are lined by epithelial cells, the type of epithelial cell varying morphologically and functionally with the location within the lung. ATII cells are one of the two types of epithelial cells that line the alveolar walls and have been described to play critical roles in surfactant synthesis and secretion. They are also part of the first line of defense within the lung and are involved in initiating and modulating immune responses during pulmonary infection or allergy. They are also thought to act as progenitor cells in the distal lung with proliferative capacity and the ability to repair the epithelium after injury. Available methods of ATII isolation did not yield cell preps that were more than 80-85% pure, making them unsuitable for reliable analyses of mRNA and protein expression. The method described here is an improvement over prior methods and yields mouse primary ATII cell preps with the highest purity that can thus be reliably used for expression analyses. For further discussion on the method, we refer the reader to the original publication from where this protocol originates (Sinha et al., 2016).
Materials and Reagents
- C57BL/6 mice (Charles River Laboratories, strain code: 027)
- 2,2,2-tribromoethanol (Avertin) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T48402 )
- tert-Amyl alcohol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 240486 )
- 70% ethanol (Decon Labs, catalog number: V1401 )
- 1 ml slip-tip syringe (important to not use a Luer-LokTM tip syringe) (BD, catalog number: 309659 )
- 10 ml syringe (BD, Luer-LokTM, catalog number: 309604 )
- 25 G x 5/8 inch needle (BD, catalog number: 305122 )
- 20 G x 1.16 inch angiocatheter (BD, AngiocathTM, catalog number: 381134 )
- Surgical silk suture 3-0 (Henry Schein, catalog number: 100-7842 )
- 70 μm cell strainer (Corning, catalog number: 431751 )
- 40 μm cell strainer (Corning, catalog number: 352340 )
- 20 μm nylon mesh (Spectrum, catalog number: 146510 )
- Kimwipes (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 06-666A )
- 5 ml polypropylene tubes (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 352063 )
- 15 ml tubes (Corning, catalog number: 430052 )
- 50 ml conical tube (Corning, catalog number: 430290 )
- Non TC-treated 10 cm Petri dish (Corning, catalog number: 430591 )
- D-PBS (without Ca2+ and Mg2+, no phenol) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 14190250 )
- 0.5 M EDTA, pH 8.0 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 15575020 )
- Dispase II (neutral protease, grade II) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 4942078001 )
- Low melting point agarose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A9419 )
- DMEM (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 11965-092 )
- Penicillin-streptomycin (10,000 U/ml) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 15140122 )
- 1 M HEPES (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 15630080 )
- ACK lysis buffer (Lonza, catalog number: 10-548E )
- Biotinylated anti-mouse CD45, clone 30-F11, 0.5 mg/ml (Affymetrix, eBioscience, catalog number: 13-0451-85 )
- Biotinylated anti-mouse CD16/32, clone 2.4G2, 0.5 mg/ml (BD, PharmingenTM, catalog number: 553143 )
- Biotinylated anti-mouse CD31, clone MEC13.3, 0.5 mg/ml (Biolegend, catalog number: 102504 )
- Biotinylated anti-mouse TER119, clone TER119, 0.5 mg/ml (Affymetrix, eBioscience, catalog number: 13-5921-85 )
- Biotinylated anti-mouse Integrin β4, clone 346-11A, 0.5 mg/ml (Biolegend, catalog number: 12603 )
- Anti-mouse EpCAM-APC, clone G8.8, 0.2 mg/ml (Affymetrix, eBioscience, catalog number: 17-5791-82 )
- Dynabeads® MyOneTM streptavidin T1 magnetic beads (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 65601 )
- Streptavidin-PE, 0.5 mg/ml (BD, PharmingenTM, catalog number: 554061 )
- Rabbit anti-pro-SP-C, polyclonal serum (EMD Millipore, catalog number: AB3786 )
- DNase I (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D5025 )
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 26140 )
- DAPI (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Molecular ProbesTM, catalog number: D1306 )
- Avertin solution (100% stock working solution) (see Recipes)
- Avertin solution (2.5% stock working solution) (see Recipes)
- Dispase solution (see Recipes)
- 1% Low melting agarose (see Recipes)
- Complete DMEM (see Recipes)
- DNase I solution (see Recipes)
- Sort buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Fine-tipped small scissors (Roboz surgical instrument company, catalog number: RS-5910 )
- Fine forceps (Roboz surgical instrument company, catalog number: RS-5211 )
- Horizontal platform orbital rocker (VWR, catalog number: 40000-300 )
- Tube rotator (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 400110Q )
- Orbital incubator-shaker (VWR, catalog number: 10027-214 )
- Biosafety cabinet (VWR, catalog number: 89413-126 )
- Stratalinker (Stratagene, model: 1800 )
- DynaMagTM-2 magnetic separator (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 12321D )
- FACS Aria cell sorter (BD, model: BD FACSARIA III )
Software
- FACS Diva (BD Biosciences)
- FlowJo (TreeStar)
Procedure
Note: Mice should be cared for and used in accordance with national and institutional policies. All protocols must be approved by the institutional animal committee. In our case, all procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at the University of California San Francisco.
- Mouse dissection
- Sacrifice mice using an approved inhaled or injectable anesthetic overdose procedure. We sacrificed mice by i.p. injection of 1 ml of 2.5% avertin per mouse.
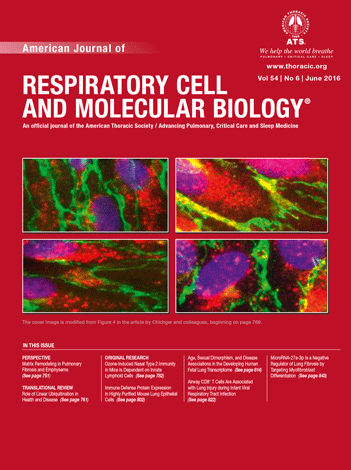
Note: Both CO2 asphyxiation and cervical dislocation are incompatible for the purposes of this protocol. Unlike anesthetic overdose, CO2 asphyxiation stops the heart from beating which then reduces perfusion quality later in the protocol. Cervical dislocation destroys structures in the neck region which are required intact for this protocol. - Pin mouse down onto dissecting tray. With the help of a suture loop (Figure 1A) around the front incisors, immobilize the head (Figure 1B). Spray the ventral surface with 70% ethanol.
Note: Immobilizing the head helps with tracheal cannulation and dispase infusion steps later. - Cut open the fur, then cut open the peritoneum along the midline. Cut through the rib cage along the midline (Figure 1C) except the top part, which houses large blood vessels.
Note: Take care to avoid nicking large blood vessels, the lungs or heart. The success of the following steps depends on the integrity of the above structures. - Hold the rib cage with forceps and snip away the diaphragm from the place it attaches to the rib cage (Figure 1D). Then cut up on two sides of the midline to remove the sternum and expose the heart and lungs (Figure 1E).
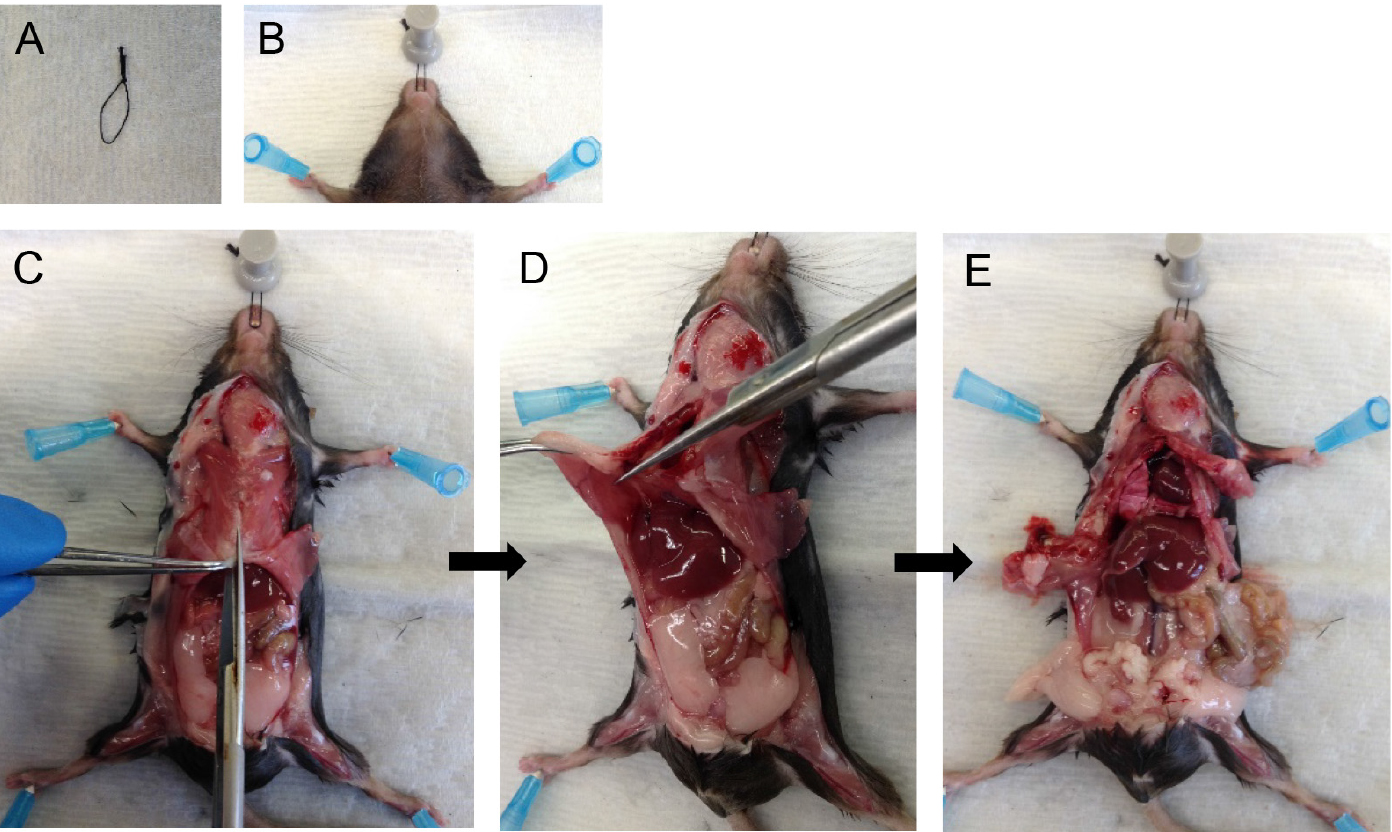
Figure 1. Mouse dissection steps. Immobilize the head of the mouse (A-B) and dissect the rib cage and diaphragm to expose lungs and heart (C-E).
- Sacrifice mice using an approved inhaled or injectable anesthetic overdose procedure. We sacrificed mice by i.p. injection of 1 ml of 2.5% avertin per mouse.
- Cardiac perfusion
Note: A video of cardiac perfusion has been provided for the user (Video 1).- Snip the inferior vena cava (IVC) and aorta near the kidneys to exsanguinate the mouse.
Note: Quickly proceed to perfusion as clots start to form as soon as the mouse starts bleeding, which drastically reduces the quality of perfusion. - Take a D-PBS-filled 10 ml syringe attached to a 25 G x 5/8 inch needle and insert the needle into the right ventricle (Figure 2A), aiming in the direction of the pulmonary artery (Figure 2B). Gently push the plunger of the syringe to perfuse the lungs with 5 ml of D-PBS.
Notes: - You should see perfusate flowing out from the snip made in the IVC/aorta. With good perfusion, the lungs should turn white in color.
- Perfusion with plain D-PBS instead of D-PBS-EDTA is critical as EDTA inhibits dispase enzyme action downstream.
- You can hold the tip of the heart with forceps to prevent the needle from sliding out (Figure 2A).
- At the end of the perfusion, cut the heart away (Figure 2C).
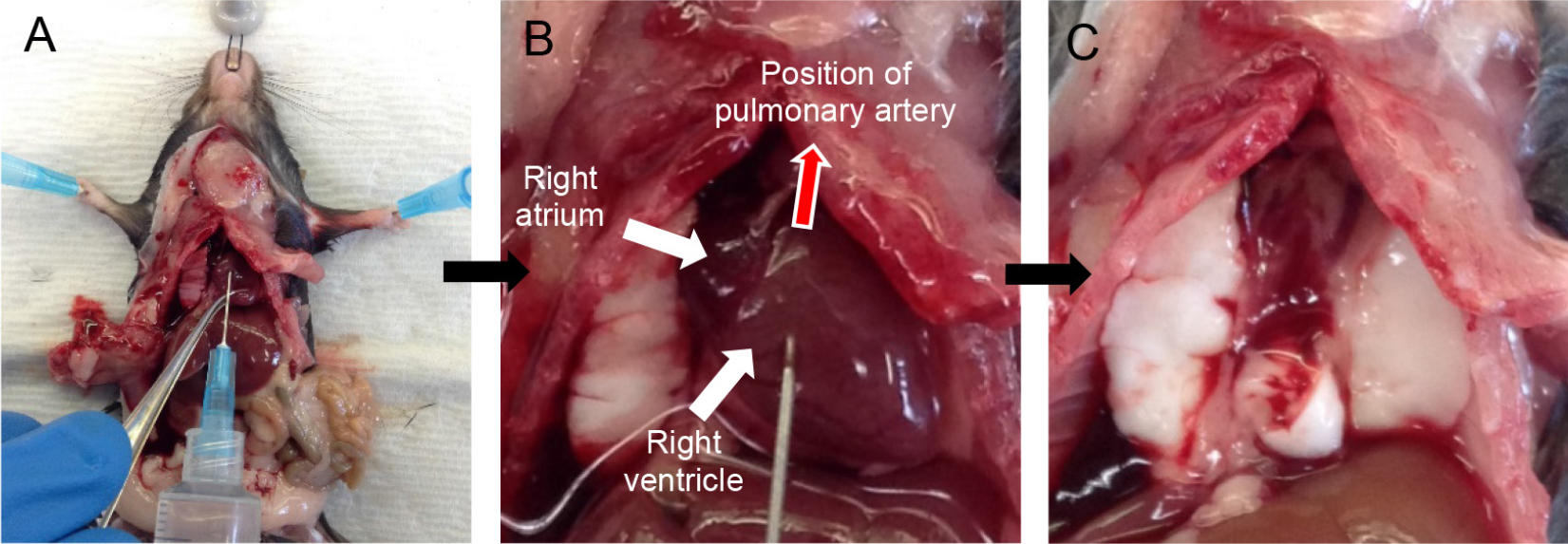
Figure 2. Cardiac perfusion of the lungs via right ventricle. Snip the IVC and insert needle into the right ventricle (A) pointing in the direction of the pulmonary artery (B). Lungs after perfusion with 5 ml DPBS (heart removed) (C).
Video 1. Cardiac perfusion of mouse lungs via the right ventricle
- Snip the inferior vena cava (IVC) and aorta near the kidneys to exsanguinate the mouse.
- Tracheal cannulation
- Flip the dissection board such that the head of the mouse is closer to you.
Note: This makes tracheal cannulation, dispase infusion and downstream manipulations much easier. - Grab the two lobes of the salivary glands with fine forceps and gently pull them apart (Figures 3A and 3B).
Note: The trachea lies just below the salivary glands. - Expose the trachea by snipping the tissue covering it with fine-tipped small scissors.
- With the help of fine forceps, loop the trachea with surgical suture and make a loose knot (Figure 3C).
- With fine-tipped scissors, make a small nick on the ventral surface of the trachea.
Note: The nick should be just big enough to pass the sheath of the 20 G angiocatheter, which serves well as a tracheal cannula (Figure 3D). - Slide the sheath of the 20 G angiocatheter into the trachea and secure in place by tightening the suture knot around it (Figure 3E).
Note: Do not slide the cannula too far down the trachea to avoid the cannula rupturing the airways at the point of bifurcation of the trachea into the two main extra-pulmonary bronchi or alternatively the cannula entering one of those bronchi, which will prevent all the lung lobes from being infused with dispase later on.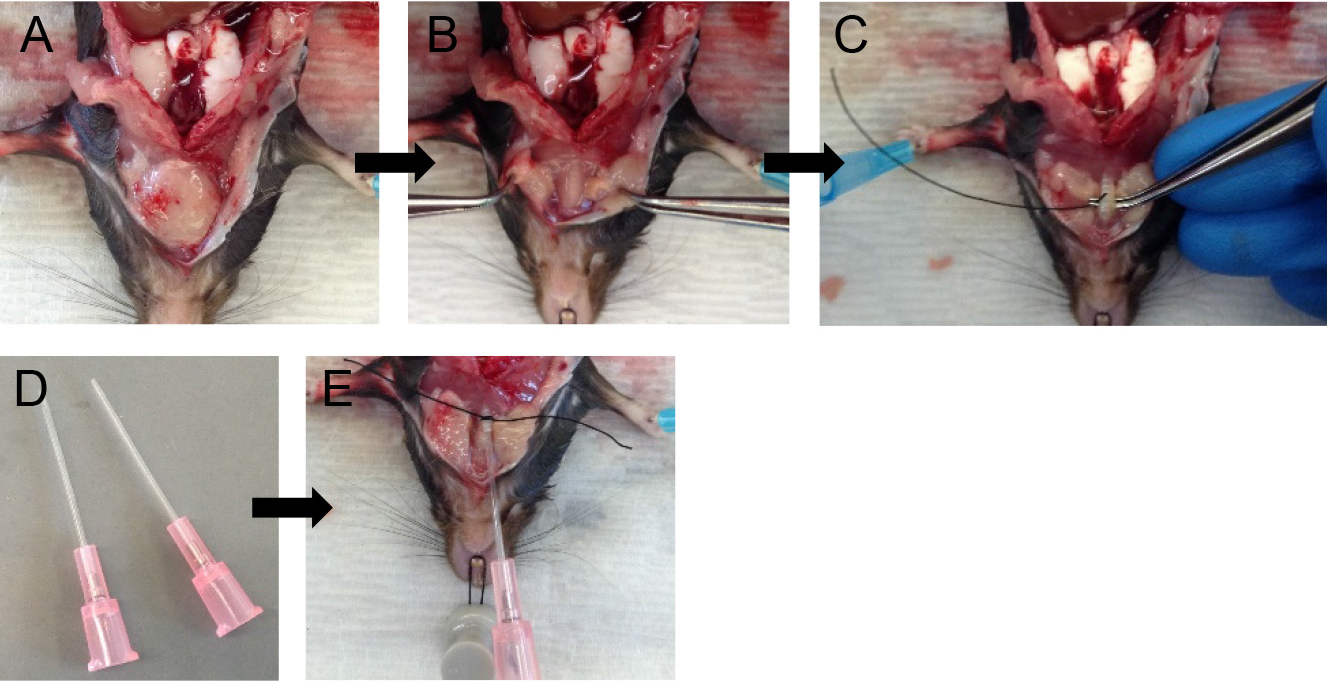
Figure 3. Tracheal cannulation. Tease apart salivary glands (A-B) and expose the trachea. Loop the trachea with suture (C), insert cannula and secure in place (D-E).
- Flip the dissection board such that the head of the mouse is closer to you.
- Dispase and agarose infusions
- Fill a slip-tip 1 ml syringe to maximal capacity with dispase (see Recipes).
- Attach the syringe to the tracheal cannula and slowly inject the full volume of dispase in the syringe. Leave the syringe in place for ~45 sec to allow the dispase to distribute throughout the lungs without allowing it to spill back out (Figure 4A).
Note: You should see all the lung lobes inflate. If that is not the case, see tip under tracheal cannulation above. - Fill another 1 ml slip-tip syringe with 0.6 ml of lukewarm (i.e., 42-45 °C) 1% low-melt agarose (see Recipes).
- Remove the syringe with dispase and quickly attach the agarose-containing syringe to the catheter.
Note: Switching of the syringes should be done rapidly to minimize back flow and leakage of dispase. Having a slip-tip, instead of a Luer-Lok tip syringe greatly helps with speed at this step. - Inject the agarose gently into the lungs, leave the syringe in place and cover the lungs with crushed ice for 2 min to allow for the agarose to solidify (Figure 4B).
Rationale: The agarose pushes the enzyme further into the alveolar spaces, effectively plugs the airways and prevents club cells from digesting off the airways and ultimately contaminating the ATII epithelial preparation. - Loosen the suture knot and slide the syringe and cannula out.
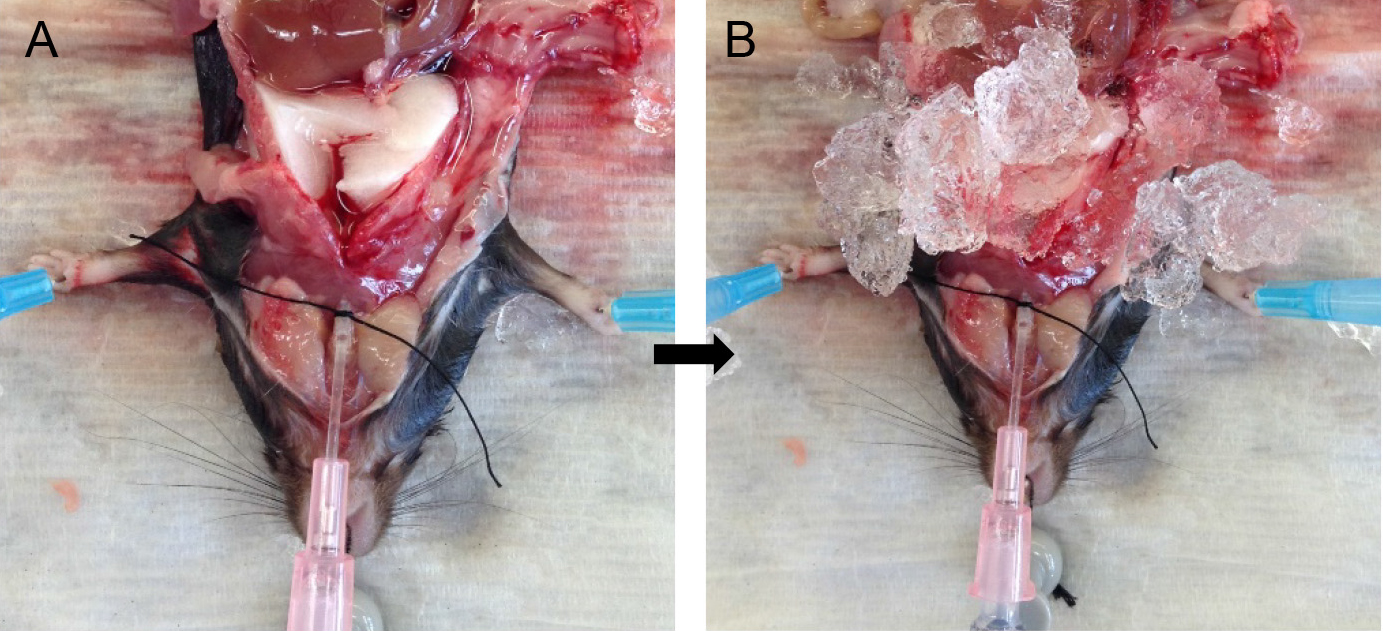
Figure 4. Infusions of dispase followed by agarose. Inject dispase into lungs followed by agarose solution (A) and cover lungs with ice (B) for solidification of agarose.
- Fill a slip-tip 1 ml syringe to maximal capacity with dispase (see Recipes).
- Dispase digestion
- Carefully dissect out the lungs from the thoracic cavity by grasping the trachea with forceps, then snipping down behind the lungs while gently pulling the lungs away. Avoid nicking the lungs.
- Rinse the lungs with D-PBS in a Petri dish till there is no more blood contaminating the outside surface of the lungs (Figure 5A). Dab away excess D-PBS with Kim wipes.
- Cut away individual lung lobes while excluding extra-pulmonary airways and other tissues (Figure 5B). Drop the lobes in a 50 ml conical tube containing 0.5 ml of dispase (Figure 5C).
Note: Do not nick or chop the lung lobes. The lobes need to be kept intact for selective and efficient release of ATII cells. Chopping up will cause release of contaminating cell types from the airways. - Incubate for 45 min at room temperature (RT) on a rocker at 150 rpm.
Notes: - Digestion should not be done at 37 °C as increased dispase activity at 37 °C release many more types and numbers of contaminating stromal cells from the lungs which is undesirable. At RT, the digestion preferentially releases ATII cells.
- Rocking helps with digestion but the exact speed of rocking is not critical. In winter months, if the laboratory temperature drops significantly lower than 25 °C, a forced-air incubator-shaker set to 25 °C can be used as an alternative as low temperatures lead to poor lung tissue digestion.
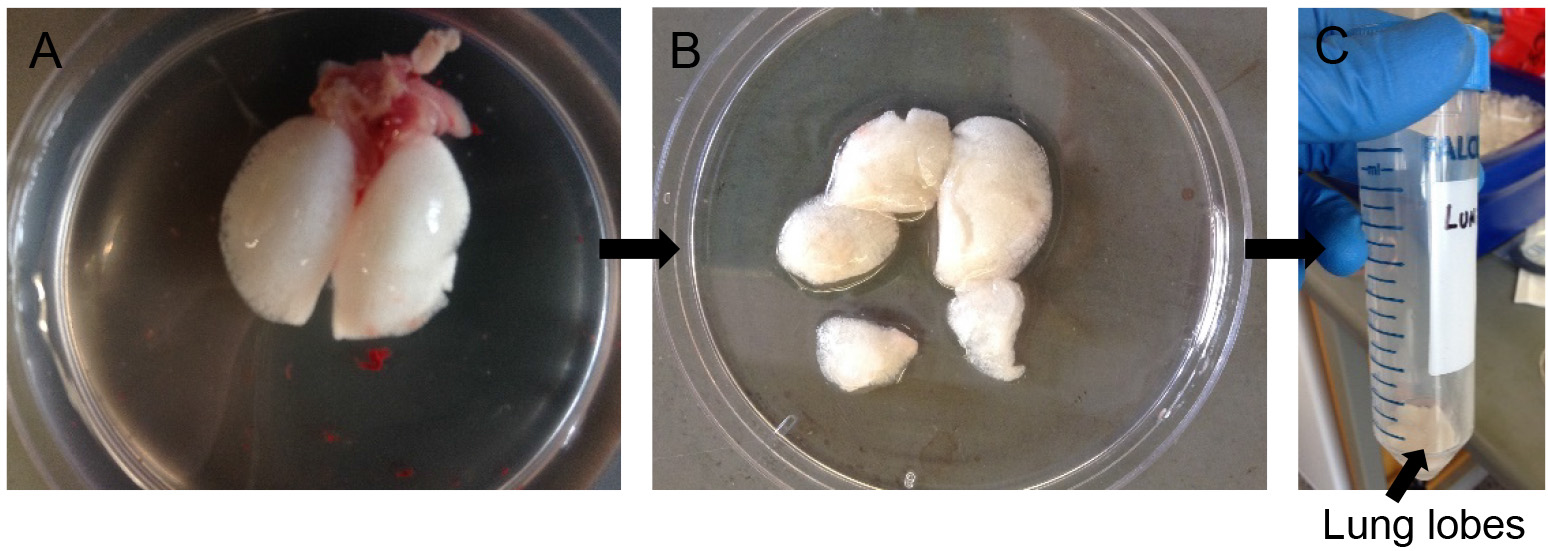
Figure 5. Dispase digestion. Rinse lung lobes in DPBS (A), snip away individual lobes leaving out airways (B) and transfer to 50 ml conical with more dispase for digestion (C).
- Carefully dissect out the lungs from the thoracic cavity by grasping the trachea with forceps, then snipping down behind the lungs while gently pulling the lungs away. Avoid nicking the lungs.
- Preparation of single cell prep
- Decant digested lungs from the 50 ml conical into a 10 cm Petri dish (Figure 6A). Add 7 ml of complete DMEM and 10 μl of DNase (see Recipes).
Note: Without DNase, the cells will be very sticky and clump together, which eventually lowers cell yield at the end. - Gently tease the lung parenchyma away from the large airways using sharp tweezers. Avoid teasing near large airways (Figures 6B and 6C).
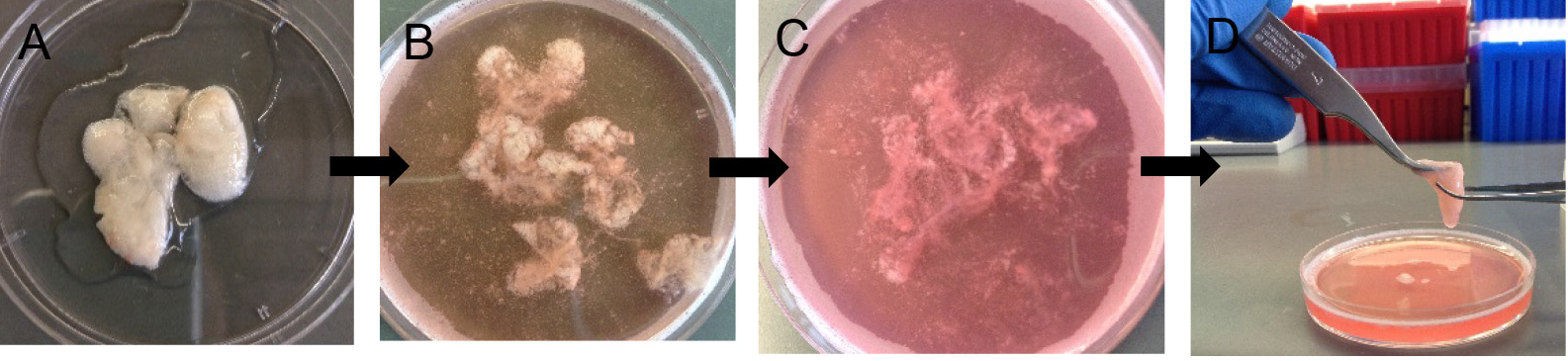
Figure 6. Preparation of crude lung single cell suspension. After 45 min digestion (A), gently tease lung parenchyma with fine forceps (B-D) to release more cells into suspension. - Rock the Petri dish in a horizontal plane at 60 rpm for another 10 min at RT to allow more cell release.
Note: Rocking helps with digestion but the exact speed of rocking is not critical. - Use two fine forceps to keep the digested lung tissue in a compact mass and repeatedly move one pair of forceps down the tissue mass to release more cells (Figure 6D).
- Discard the airways and serially strain the lung crude single cell prep through a 70 μm, 40 μm and 20 μm* strainers.
Notes: - At the end of each straining step, rinse the Petri dish or 50 ml conical and strainer with 2 ml complete DMEM and pool with cell suspension to maximize cell recovery.
- *On the assembly of 20 μm strainers: To prepare your own 20 μm strainers (not available commercially), cut out the base from a 50 ml conical and also cut out a hole in the cap (Figure 7A) using a sharp blade and caution. Cut a square from the 20 μm nylon mesh sheet and cover the top of the cut 50 ml conical (Figure 7B). Screw the nylon mesh in place with the help of the cut cap (Figures 7C and 7D). To strain cells, place strainer cap side down on top of a fresh 50 ml conical. If the isolated cells will be cultured ex vivo, the 20 μm strainer can be sterilized prior to use with 120 Joules/meter2 dose of UV light delivered using a Stratalinker model 1800. Please note that the nylon mesh is not autoclavable.
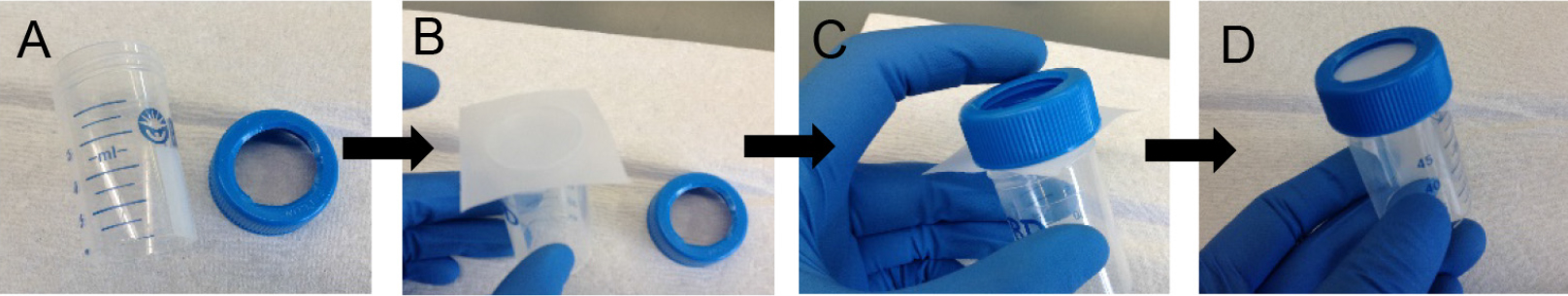
Figure 7. Assembly of 20 μm strainer. Using a cut 50 ml conical (A) and a square piece of 20 μm nylon mesh (B), assemble the strainer (C-D). - Count cells. At this step, the cell yield is ~25-35 million cells per mouse lung.
- Spin cells down at 300 x g, 10 min, 4 °C.
Optional: If the pellet shows presence of RBCs, gently resuspend pellet in 5 μl DNase and 2 ml ACK lysis buffer. Place on ice for 2 min. Make up volume to 10 ml with complete DMEM and spin cells down at 300 x g, 10 min, 4 °C. - Resuspend cell pellet in 5 μl DNase and 500 μl complete DMEM.
- Decant digested lungs from the 50 ml conical into a 10 cm Petri dish (Figure 6A). Add 7 ml of complete DMEM and 10 μl of DNase (see Recipes).
- Magnetic enrichment of ATII cells
- Stain with biotinylated antibodies against lineage (Lin) markers – add 5 μl of each of the following biotinylated antibodies to single cells (from one lung) suspended in 500 μl of complete DMEM and 5 μl of DNase: anti-CD45, anti-CD16/32, anti-CD31, anti-Ter119, anti-integrin β4.
Rationale: The above antibody cocktail will mark hematopoietic cells (CD45 positive), alveolar macrophages (CD45 positive and CD16/32 positive), endothelial cells (CD31 positive), erythroid cells (Ter119 positive), club cells (integrin β4 positive) and distal lung progenitor cells (integrin β4 positive) for depletion.
Note: The above antibody amounts are optimal when isolating ATII cells from naïve mice lungs. When isolating ATII cells from inflamed lungs with increased numbers of inflammatory cell infiltrates, the amounts of antibodies against lineage markers can be increased at this magnetic depletion step. The user should optimize this based on their mouse model and needs. - Incubate for 45-60 min on ice with intermittent mixing by gentle flicking of the cells.
- While the cells are incubating with the antibodies, prepare the magnetic beads for use (2.5 µl SA MyOne T1 beads/1 x 106 cells). Wash the beads with 1 ml D-PBS twice to remove azide. Collect beads in the DynaMag-2 magnetic separator.
- At the end of the antibody incubation, wash the cells once in 10 ml complete DMEM (spin at 300 x g, 10 min, 4 °C) and resuspend in 500 μl complete DMEM and 5 μl DNase. Transfer cells to 1.5 ml tube with the appropriate number of washed beads. Incubate in the cold room for 30 min on a tube rotator to prevent the beads from settling to the bottom.
- Magnetic separation – Place the 1.5 ml tube with bead-bound cells in the magnetic separator for 2 min. Lineage positive cells will get stuck to the tube wall. Gently pipette out unattached cells and place into a fresh 1.5 ml tube. Place the fresh tube in the magnetic and repeat magnetic depletion for a total of 3 times.
- Stain with biotinylated antibodies against lineage (Lin) markers – add 5 μl of each of the following biotinylated antibodies to single cells (from one lung) suspended in 500 μl of complete DMEM and 5 μl of DNase: anti-CD45, anti-CD16/32, anti-CD31, anti-Ter119, anti-integrin β4.
- Cell sorting
- Transfer magnetically enriched ATII cells to a 5 ml FACS tube.
- Re-stain cells for lineage markers using biotinylated antibodies exactly as before.
- Wash cells as before with complete DMEM and resuspend in 500 μl complete DMEM and 5 μl of DNase.
- Add 1 μl of streptavidin-PE (to place all the lineage marker positive cells in the PE channel) and 5 μl of EpCAM-APC (to stain all epithelial cells). Incubate for 45-60 min on ice in the dark with intermittent mixing by gentle flicking of the cells.
- Wash cells with 10 ml sort buffer (see Recipes) once and resuspend at 5 x 106 cells/ml in sort buffer with DAPI (0.5 μg/ml) for FACS sorting. Strain cells through a 40 μm strainer to avoid any cell clumps that might clog the cell sorter.
- Set up the FACS Aria cell sorter for sorting using a 100 μm nozzle. Set up compensation using single color controls.
Note: Please note that covering these aspects in detail is beyond the scope of this protocol. A new user can perhaps get help of a flow cytometry core operator for detailed instructions on cell sorting depending on the sorter available to the user. - Sort FSChi SSChi, singlet, DAPI- live, Lin- EpCAM+ cells (Figure 8), which are ATII cells, into 15 ml tubes containing 5 ml of ice-cold complete DMEM. Typically, this protocol yields 2-3 x 106 highly pure (98-99%) and highly viable (97-98%) ATII cells per lung from a naïve mouse.
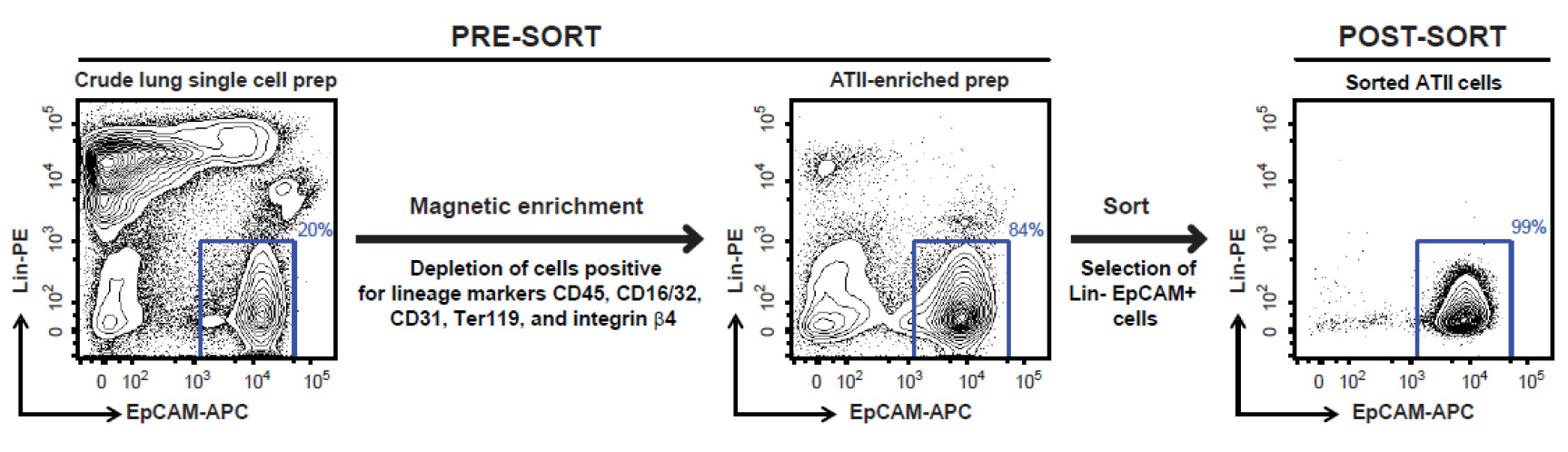
Figure 8. FACS sorting strategy for isolating highly pure murine ATII cells. Shown are representative flow cytometric plots of lung cells collected before and after magnetic enrichment, and after sorting. Displayed on the y-axis is staining for Lin markers (CD45, CD16/32, CD31, Ter119 and integrin β4) while the x-axis shows EpCAM staining. Events displayed on the plots are DAPI negative single cells. A gate around Lin- EpCAM+ cells, as shown above, is used to sort the cells.
- Transfer magnetically enriched ATII cells to a 5 ml FACS tube.
Data analysis
- At the end of cell sorting, rerun sorted cells through the FACS Aria to check for purity. We have routinely observed that the sorted cells are 98-99% Lin- EpCAM+ and 97-98% viable (Figure 8).
- Optional: Purity can also be assessed by the expression of pro-SP-C, which is a specific marker for ATII cells. About 30,000 sorted cells can be cytospun and then stained for pro-SP-C to check for purity (Figure 9). Alternatively, ~200,000-500,000 cells can be saved for intracellular staining for pro-SP-C using standard intracellular flow cytometry methods. The previous method allows visualization of cell morphology – pro-SP-C staining is found in the cytoplasm and is granular in appearance (Figure 9, inset). The latter method yields superior quantitation of ATII prep purity. We routinely found that our sorted cells were 98-99% pro-SP-C+. For more details, please refer to the original publication (Sinha et al., 2016).

Figure 9. Purity of sorted ATII cells. Cells from (A) crude lung digest and (B) ATII cells after FACS sorting were spun onto slides and stained for pro-SP-C, a specific ATII marker, to assess purity. - Isolated ATII cells can be used for different purposes. For RT-PCR analysis, sorted cells can be pelleted and subsequently lysed in lysis buffer for RNA isolation (as per your choice of RNA isolation method). For protein expression analysis by Western blotting, wash the cells once with 10 ml of D-PBS to remove serum proteins – this wash step is critical to avoid serum proteins from interfering with your Western blotting. Spin down cells and resuspend pellet in lysis buffer supplemented with protease inhibitor cocktail (as per your choice of protein extraction method). Alternatively, cell pellets can be snap frozen and stored in liquid nitrogen till the RNA or protein extraction step. For ex vivo culture, these cells can be grown on matrigel or fibronectin-coated surfaces or in other ways depending on your experimental question.
Notes
- If the isolated cells need to be cultured, all steps must be carried out in a biosafety cabinet and usual sterile procedures should be followed. Dissection instruments must be autoclaved.
- It is recommended that a new user unfamiliar with the techniques practice and gain some technical experience with each step prior to attempting the full protocol for isolation. This will increase the chances of a successful isolation.
- The protocol is fairly long. Depending on the number of mice to be sacrificed and the desired yield of ATII cells, the full procedure could take 7-8 h.
Recipes
- 100% avertin stock solution
10 g 2,2,2-tribromoethanol
10 ml tert-amyl alcohol
Dissolve by heating and stirring
Solution is light sensitive; keep covered in foil and store at 4 °C - 2.5% avertin working solution
Prepare a 2.5% avertin working solution by diluting the 100% stock 1:40 in DPBS or isotonic saline
e.g., 1 ml of 100% avertin stock plus 39 ml DPBS. Filter working solution with 0.22 µm strainer
Solution is light sensitive; keep covered in foil and store at 4 °C
Note: Label container with the date of dilution and use within 30 days of that date. - Dispase solution
50 U/ml in D-PBS
Reconstitute an entire 1 g vial at once
Store aliquots at -20 °C
Note: Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles; thaw on ice prior to use. - Low melting agarose (1%)
50 mg in 5 ml water
Using a boiling water bath, boil agarose till clear
Ready to use when lukewarm to touch (about 42-45 °C)
Prepare fresh - Complete DMEM (DMEM with 10% FBS, Pen-Strep, 10 mM HEPES)
500 ml DMEM
50 ml heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum
5 ml Pen-Strep (10,000 U/ml)
5 ml of 1 M HEPES
Prepare in a biosafety cabinet under sterile conditions; store at 4 °C; maintain sterility - DNase I solution
5,000 Kunitz U/ml in D-PBS
Store aliquots at -20 °C
Note: Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles; thaw on ice prior to use. - Sort buffer (D-PBS with 2% FBS, 1 mM EDTA)
500 ml D-PBS (without Ca2+ and Mg2+)
10 ml heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum
1 ml of 0.5 M EDTA
Prepare in a biosafety cabinet under sterile conditions; store at 4 °C; maintain sterility
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the US National Institutes of Health (AI65495 and AI68150 to C.A.L.). Thanks to Pooja Mehta and James Mueller for help with pictures and video. This protocol was adapted from Sinha et al. (2016).
References
- Sinha, M. and Lowell, C. A. (2016). Immune defense protein expression in highly purified mouse lung epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 54(6): 802-813.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Sinha, M. and Lowell, C. A. (2016). Isolation of Highly Pure Primary Mouse Alveolar Epithelial Type II Cells by Flow Cytometric Cell Sorting. Bio-protocol 6(22): e2013. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2013.
Category
Immunology > Immune cell isolation > Maintenance and differentiation
Immunology > Immune cell staining > Flow cytometry
Cell Biology > Cell isolation and culture > Cell isolation
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link