- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
In vitro Dephosphorylation Assay of c-Myc
Published: Vol 7, Iss 2, Jan 20, 2017 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2011 Views: 9142
Reviewed by: HongLok LungGabriel O. FerreroJianwei Sun

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Endo-1,4-β-D-xylanase Assay Using Azo-Xylan and Variants Thereof
Luca Bombardi [...] Salvatore Fusco
Apr 20, 2025 1917 Views

Activation of X-Succinate Synthases for Fumarate Hydroalkylation Using an In Vitro Activation Method
Anshika Vats [...] Mary C. Andorfer
Jun 20, 2025 2510 Views

An Optimized Enzyme-Coupled Spectrophotometric Method for Measuring Pyruvate Kinase Kinetics
Saurabh Upadhyay
Aug 20, 2025 2442 Views
Abstract
This protocol describes experimental procedures for in vitro dephosphorylation assay of human protein c-Myc. This protocol can be adapted to detect phosphatase activity of other Ser/Thr phosphatases.
Keywords: DephosphorylationBackground
Carboxy-terminal domain RNA polymerase II polypeptide A small phosphatase 1 (SCP1, also known as CTDSP1 or NLI-IF) belongs to the FCP/SCP phosphatase family and was originally reported to dephosphorylate the C-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase II (Yeo et al., 2003). Smad2, 3 (Wrighton et al., 2006), Snail (Wu et al., 2009), PML (Lin et al., 2014), and c-Myc (Wang et al., 2016) have also been identified as substrates of SCP1.
Materials and Reagents
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf tubes
- 50 ml tube
- 100 mm dish
- E. coli cells
- HKE293T cell
- HA-c-Myc plasmid
- LB medium
- IPTG
- Glutathione sepharose 4B (GE Healthcare, catalog number: 17075601 )
- Glycerol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G5516 )
- PierceTM BCA Protein Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 23225 )
- Lipofectamine 2000
- c-Myc antibody (Abcam, catalog number: ab32072 )
- Protein A/G beads (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, catalog number: sc-2003 )
- BSA
- Coomassie blue R250 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 27816 )
- c-Myc Ser62 phosphorylation antibody ([Abnova, catalog number: MAB6763 ] or [Abcam, catalog number: ab78318 ])
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 221465 )
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S7653 )
- Potassium chloride (KCl)
- Disodium hydrogen phosphate (Na2HPO4)
- Potassium phosphate monobasic (KH2PO4)
- Tris base (C4H11NO3) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T1503 )
- EDTA (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: E5134 )
- Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: X100 )
- Phenylmethanesμlfonyl fluoride (PMSF) (C7H7FO2S) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P7626 )
- cOmplete protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 04693116001 )
- Dithiothreitol (DTT) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D0632 )
- PhosSTOP tablet (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 04906845001 )
- β-mercaptoethanol
- Bromophenol blue
- Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)
- Magnesium chloride (MgCl2) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 449172 )
- L-Glutathione reduced (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G4251 )
- Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (see Recipes)
- IP lysis buffer (see Recipes)
- Phosphatase reaction buffer (see Recipes)
- 5x SDS loading dye (see Recipes)
- GST elution buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 250 ml flask
- Shaker
- Cell scraper
- Incubator
- Centrifuges
Procedure
- Heterologous expression and purification of phosphatase
- Inoculate a single colony of E. coli cells containing the GST-vector, GST-SCP1-WT (wild type) or GST-SCP1-DN (dominant-negative) plasmid into 10 ml LB medium and grow overnight (ON) at 37 °C.
- Transfer 2 ml of ON culture to a 250 ml flask containing 48 ml of LB medium.
- Incubate at 37 °C in a shaker at 200 rpm until OD600 reaches to 0.5. Induce with IPTG at a final concentration of 1 mM for 4 h.
- Transfer the cell culture into a 50 ml tube.
- Spin down at room temperature for 5 min, 3,000 x g to collect cells.
- Discard supernatant, wash the cell pellet once with 1x PBS.
- Resuspend the cell pellet in 500 μl IP lysis buffer without phosSTOP and then put the 50 ml tube on ice for 30 min. Vortex for 15 sec every 10 min.
- Spin at 20,000 x g for 10 min at 4 °C. Collect the supernatant into a new Eppendorf tube.
- Prepare a 50% (v/v) slurry of glutathione sepharose 4B in lysis buffer, and add 50 μl of slurry to the supernatant. Rotate for 1 h at 4 °C.
- Collect the beads by spinning at 1,000 x g for 1 min at 4 °C. Discard the supernatant and wash the beads 3 times with 1x PBS. Store in 1 beads volume of PBS supplemented with 10% glycerol at 4 °C if not going on to the next step immediately.
- To elute GST protein from beads, add 1 bead volume of GST elution buffer, vortex for 10 min at 4 °C. Collect supernatant, repeat one more time, and combine the supernatants. Use BCA Protein Assay Kit to quantify the concentration of protein.
- Expression and purification of phosphorylated c-Myc
- Transfect HKE293T cells (at a density of 1.5 x 106 in a 100 mm dish) with 5 µg of HA-c-Myc plasmid using Lipofectamine 2000.
- Harvest the cells in 1 ml of 1x PBS by using a cell scraper after a 36-48 h incubation.
- Collect the cell pellet by spinning at 1,000 x g for 1 min at 4 °C.
- Discard the supernatant, and lyse the cells in 500 µl lysis buffer on ice for 30 min.
- Collect the lysate by spinning at 12,000 x g for 15 min at 4 °C, and then transfer the cell lysate into a new Eppendorf tube.
- Use 1 μg of c-Myc antibody to immunoprecipitate HA-c-Myc protein from 1 mg/500 μl HEK293T cell lysate. Gently rotate for 1 h at 4 °C.
- Wash protein A/G beads 3 times with IP lysis buffer. Add 30 μl (60 μl 50% slurry) to the cell lysate (step 2d) and rotate for 1 h at 4 °C.
- Collect the beads by spinning at 1,000 x g for 1 min at 4 °C. Wash 3 times with 0.5 ml ice-cold IP lysis buffer.
- Store the beads in 1 bead volume of PBS supplemented with 10% glycerol on ice before use.
- Pick 5 µl solution and 1 µg BSA to run SDS-PAGE gel, and stain the gel with Coomassie blue, using 1 µg BSA as control, to determine HA-c-Myc immunocomplex concentration.
- Dephosphorylation assay
- Add the 0.1 µg HA-c-Myc, with 0.5 μg of bacterially-expressed GST-vector, GST-SCP1-WT (wild-type) or GST-SCP1-DN (dominant-negative) in 50 μl phosphatase buffer.
- Incubate the mixture at 37 °C for 30 min.
- Add 1 bead volume of 2x SDS loading buffer into the mixture. Stop the phosphatase reaction by heating at 100 °C for 5 min.
- Half of each sample is fractioned by SDS-PAGE and detect phosphatase on the gel by Coomassie blue staining (Simpson, 2010).
- The other half of each sample is used to detect the phosphorylation status of c-MYC at Ser62 by Western blotting using anti-pSer62 antibody.
- After phosphorylation detection, strip the membrane using 0.8 N NaOH for 30 sec. Detect total c-Myc protein substrate with anti-c-Myc antibody.
Data analysis
HA-c-Myc purified from HEK293T cells was incubated with purified GST, GST-SCP1-WT, and GST-SCP1-DN proteins at 37 °C for 30 min. The immunoprecipitates are analyzed using anti-pSer62, anti-c-Myc, or anti-GST antibodies. SCP1 dephosphorylates c-Myc at Ser62 in vitro, analyzed using Western blotting.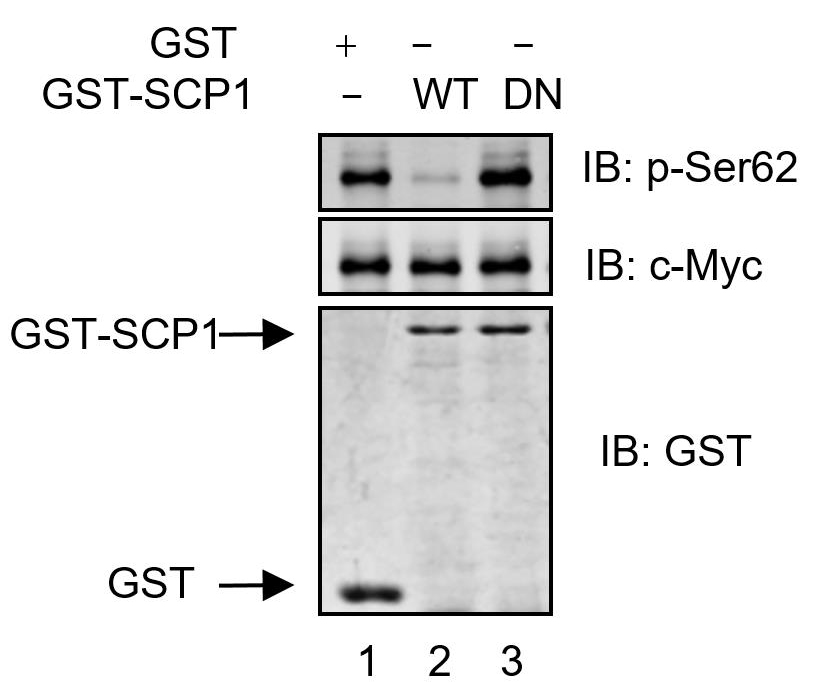
Figure 1. SCP1 dephosphorylates c-Myc at Ser62 in vitro (Wang et al., 2016)
Recipes
- Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)
137 mM NaCl
2.7 mM KCl
10 mM Na2HPO4
1.8 mM KH2PO4
Adjust the pH to 7.4 - IP lysis buffer
50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5
150 mM NaCl
0.5 mM EDTA
0.5% Triton X-100
Add 1 mM PMSF, Roche cOmplete protease inhibitor cocktail and phosSTOP tablet before use
Adjust NaCl concentration or/and Triton X-100 level to obtain optimum condition for different phosphatases and different antibodies - Phosphatase reaction buffer
50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 6.8
150 mM NaCl
1 mM EDTA, pH 8.0
10 mM DTT without phosphatase inhibitors - 5x SDS loading buffer
5% β-mercaptoethanol
0.02% bromophenol blue
30% glycerol
10% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)
250 mM Tris-Cl, pH 6.8 - GST elution buffer
3.4 mM reduced dry glutathione
50 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (31501141).
References
- Lin, Y. C., Lu, L. T., Chen, H. Y., Duan, X., Lin, X., Feng, X. H., Tang, M. J. and Chen, R. H. (2014). SCP phosphatases suppress renal cell carcinoma by stabilizing PML and inhibiting mTOR/HIF signaling. Cancer Res 74(23): 6935-6946.
- Simpson, R. J. (2010). Rapid Coomassie blue staining of protein gels. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2010(4): pdb prot5413.
- Wang, W., Liao, P., Shen, M., Chen, T., Chen, Y., Li, Y., Lin, X., Ge, X. and Wang, P. (2016). SCP1 regulates c-Myc stability and functions through dephosphorylating c-Myc Ser62. Oncogene 35(4): 491-500.
- Wrighton, K. H., Willis, D., Long, J., Liu, F., Lin, X. and Feng, X. H. (2006). Small C-terminal domain phosphatases dephosphorylate the regulatory linker regions of Smad2 and Smad3 to enhance transforming growth factor-beta signaling. J Biol Chem 281(50): 38365-38375.
- Wu, Y., Evers, B. M. and Zhou, B. P. (2009). Small C-terminal domain phosphatase enhances snail activity through dephosphorylation. J Biol Chem 284(1): 640-648.
- Yeo, M., Lin, P. S., Dahmus, M. E. and Gill, G. N. (2003). A novel RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain phosphatase that preferentially dephosphorylates serine 5. J Biol Chem 278(28): 26078-26085.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Liao, P., Wang, W. and Ge, X. (2017). In vitro Dephosphorylation Assay of c-Myc. Bio-protocol 7(2): e2011. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2011.
Category
Cancer Biology > Cancer biochemistry > Protein
Biochemistry > Protein > Activity
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










