- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Experimental Liver Fibrosis and Intrasplenic Transplantation of CD45+ Bone Marrow Cells
Published: Vol 6, Iss 20, Oct 20, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1972 Views: 14805
Reviewed by: Anonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Murine Hair Follicle Derived Stem Cell Transplantation onto the Cornea Using a Fibrin Carrier
Mindy Call [...] Ursula Schlӧtzer-Schrehardt
May 20, 2018 6631 Views

Determining Bone-forming Ability and Frequency of Skeletal Stem Cells by Kidney Capsule Transplantation and Limiting Dilution Assay
Hitoshi Uchida [...] Wei Hsu
Mar 20, 2023 1721 Views
Abstract
Liver fibrosis results from the excessive collagen deposition (collagen scar) by activated hepatic stellate cells (HpSCs), leading to the inhibition of normal liver regeneration and function. Fibrogenesis is a complex mechanism involving both the synthesis and degradation of matrix proteins by different cell types, mainly macrophages in the liver. Carbon tetrachloride-induced fibrosis (CCl4) and cirrhosis is one of the oldest, simplest and probably the most widely used toxin-based experimental model for the induction of fibrosis. Here we have explained experimental animal model of liver fibrosis using CCl4, injecting twice a week for a period of 8 weeks. In these fibrotic mice, bone marrow (BM) derived CD45+ cells were transplanted via intrasplenic route after 8 weeks of CCl4 injection, and half of the CCl4 dose was continued till the end of the experiment to know the effect of transplanted cells on liver fibrosis and regeneration. So far, crude bone marrow (BM) cells or mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have been used for the treatment of liver fibrosis. Low survival rate, less fibrolytic and profibrogenic properties of MSCs remain the major concerns for inadequate recovery of liver from fibrosis. This led us to investigate BM cells devoid of mesenchymal lineage that is CD45+ cells for the antifibrotic effect as this population consisting of mononuclear cells which are the precursor of macrophages and may involve in the scar degradation process. Cells transplantation can be followed in different ways like intrasplenic infusion, tail vein injection and ectopic cell transplantation in experimental animal models. The survival of the cells after ectopic transplantation is less when compared to tail vein and intrasplenic infusion. Intrasplenic route of transplantation is effective in engraftment and long term survival of the donor cells especially in case of liver disease models. This protocol describes fibrosis mouse model development, intrasplenic route of cell transplantation and tracking of the donor cells after transplantation.
Keywords: Bone Marrow CellsMaterials and Reagents
- Falcon tubes
15 ml (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 352097 )
50 ml (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 352070 ) - Culture discs (Corning, catalog number: 430167 )
- Pipettes tips (Eppendorf, catalog number: 022491954 )
- Surgical glass slides (Thickness: 1.45 mm; 75 x 25 mm & 76 x 26 mm) (Polar Industrial, catalog number: Blue Star PIC 2 )
- BD tuberculin syringe 1 ml (BD, catalog number: 309623 )
- Cell strainer (40 μm) (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 352340 )
- Petri plates (30 mm, 100 mm)
- Six- to eight-week-old male C57BL/6J (THE JACKSON LABORATORY, catalog number: 000664-C57BL/6J )
- Enhanced green fluorescence protein (eGFP) transgenic mice [C57BL/6-Tg(UBC-GFP)30Scha/J] (THE JACKSON LABORATORY, catalog number: 004353 )
- Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 319961 )
- Mineral oil (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M8410 )
- CO2 gas
- Formalin (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: SF98-4 )
- Iso-propyl alcohol (Thermo Fisher Scintific, catalog number: A416S-4 )
- Xylene (Thermo Fisher Scintific, catalog number: X3S )
- Paraffin wax (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 107151 )
- Picrosirus Red Staining Kit (Polysciences, catalog number: 24901-250 )
- Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 12100-046 )
- FCS
- Phosphate buffer saline (PBS) (HiMedia Laboratories, catalog number: TS1099 )
- Anti-CD45 APC (affymetrix, eBioscience, catalog number: 17-0451 )
- 70% ethanol
- Ketamin (nirlife healthcare, catalog number: Ketamin )
- Xylazine (INDIAN IMMUNOLOGICALS, catalog number: 21 )
- 10% formalin saline solution
- PBS
- Sucrose (Thermo Fisher Scintific, catalog number: S5 )
- Poly-L-lysine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P4707 )
- Nail polish
- Ketamine
- Xylazine
- Triton X-100 (HiMedia Laboratories, catalog number: 9002-93-1 )
- Bovine serum albumin (BSA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A9418 )
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Biological Industries, catalog number: 04121-1A)
- DAPI
- Isotype mouse IgG (Jackson ImmunoResearch, catalog number: 015-000-003 )
- Isotype goat IgG (Jackson ImmunoResearch, catalog number: 005-000-003 )
- Anti-GFP antibody (Takara Bio, catalog number: 632381 )
- Anti-Albumin antibody (Bethyl Laboratories, catalog number: A90-134B )
- Alexa Fluor donkey anti-mouse 488 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Invitrogen, catalog number: A-21202 )
- Alexa Fluor donkey anti-goat 594 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Invitrogen, catalog number: 11058 )
- Antifade (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Molecular probesTM,catalog number: P36961 )
- Ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) (HiMedia Laboratories, catalog number: TC092 )
- Potassium chloride (KCl) (Thermo Fisher Scintific, catalog number: 13305 )
- Potassium dihydrogen ortho phosphate (KH2PO4) (Central Drug House, catalog number: 029608 )
- Disodium hydrogen phosphate (Na2HPO4) (Thermo Fisher Scintific, catalog number: S379 )
- Glocose (Thermo Fisher Scintific, catalog number: D16 )
- Gelatin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G9664 )
- Phenol red (Thermo Fisher Scintific, catalog number: P7410 )
- Magnesium chloride hexahydrate (MgCl2·6H2O) (Sigma-aldrich, catalog number: M2670 )
- Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate (MgSO4·7H2O) (Sigma-aldrich, catalog number: 230391 )
- Calcium chloride (CaCl2) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C5670 )
- Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S5761 )
- Tissue freezing media (Leica Biosystems Nussloch, catalog number: 14020108926 )
- CCl4 dose preparation (see Recipes)
- Gey’s solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Tissue processing cassettes
- Oven (Scientific Systems Company)
- Pure paraffin wax container
- Embedding machine
- Laminar flow (Esco Micro Pte, model: AC2-2E9 )
- Scissors (2)
- Blunt forceps (2)
- Surgical blades with scalpel
- Hemostatic forceps
- Suture threads
- Suture needle
- Dissecting board
- FACS AriaTM III (BD, model: BD FACSARIA III )
- Incubator (SHEL LAB, model: SCO5A )
- Pipets (Eppendorf)
- Glows (SAFEMAX)
- Centrifuge (Eppendorf, model: 5810R )
- Cryotome (Thermo Fisher Scientific, model: CryoStar NX50 Cryostat )
- Ultra-Thin semiautomatic microtome (Histo Line Laboratories, model: MRS 3500 )
Software
- Adobe Photoshop
Procedure
- Experimental liver fibrosis model
- Development of fibrosis mouse model
- A liver fibrosis model was established in C57Bl6/J mice by repeated injection of CCl4 (0.8 ml/kg body weight) in mineral oil, twice a week, for a period of 8 weeks (16 doses) via intraperitoneal injection as shown in the Figure 1.
- CD45+ cells were isolated from eGFP transgenic mice and transplanted through intrasplenic route.
- After 3 days of transplantation, CCl4 dose was reduced to half and continued till the end of experiment to avoid spontaneous regression of the fibrosis.
- After 4 weeks of transplantation, mice were sacrificed in excess CO2 gas, serum samples were stored for liver function tests, and liver tissue was fixed in 10% formalin saline for 48-72 h for histological analyses.
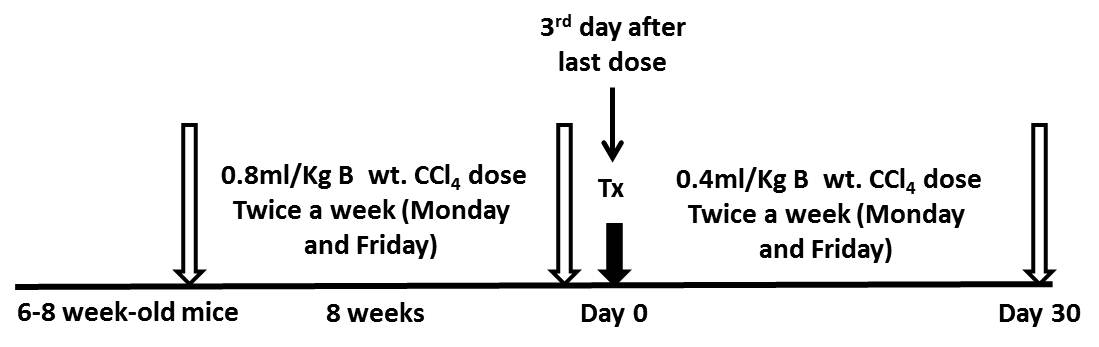
Figure 1. A schematic diagram with timeline and doses for fibrosis model development. B wt. - Body weight; Tx - Transplantation.
- A liver fibrosis model was established in C57Bl6/J mice by repeated injection of CCl4 (0.8 ml/kg body weight) in mineral oil, twice a week, for a period of 8 weeks (16 doses) via intraperitoneal injection as shown in the Figure 1.
- Tissue processing for paraffin sectioning
- Take fixed tissues, put in the tissue processing cassettes and label properly as per experiment with the help of a pencil.
- Dehydrate them with series of isopropyl alcohol gradations (30%, 50%, 70%, 90% and 100% for 30 min intervals in each step).
- Place the tissues in 1:1 isopropyl alcohol and xylene for 30 min.
- Place in pure xylene for 1 h.
- All tissue cassettes dipped in 1:1 xylene and paraffin wax solution for 30 min in 60 °C oven.
- Place the cassettes in pure paraffin wax container 1, then 2 and 3 for 1 h at each step in 60 °C oven.
- Then embed in the steel or plastic molds with the help of embedding machine. These blocks can be used forever if stored properly in room temperature.
- Then cut 5 µm sections into the floater bath (45-50 °C) and take on to the poly-lysine coated slides. Air dry completely in room temperature and use for staining (cut sections can be stored for 2-3 months if stored properly, otherwise loss of antigenicity occurs and is not good for immunohistochemistry).
- Take fixed tissues, put in the tissue processing cassettes and label properly as per experiment with the help of a pencil.
- Measurement of fibrosis
- Fibrosis can be measured by Picrosirus red staining. Cut sections are rehydrated, processed for Picrosirus staining as per the protocol provided by the kit manufacturer.
- After staining with picrosirus red, fibrosis is determined by using Ishak et al. (1995) scoring system or METAVIR (Group FMCS, 1994) scoring system (Table 1). The representative images of liver sections stained with Picrosirus stain are shown in Figure 2.
Note: Fibrosis can be measured by many ways by different staining techniques such as Masson’s trichrome staining, Picrosirus red staining, collagen staining with antibodies etc. In addition, percentage of collagen proportionate area in the Picrosirus stained sections using NIH ImageJ software or quantitative estimation of hydroxyproline in liver tissue by calorimetric methods can be followed to measure the extent of fibrosis.
Table1. The Ishak scoring and the METAVIR scoring system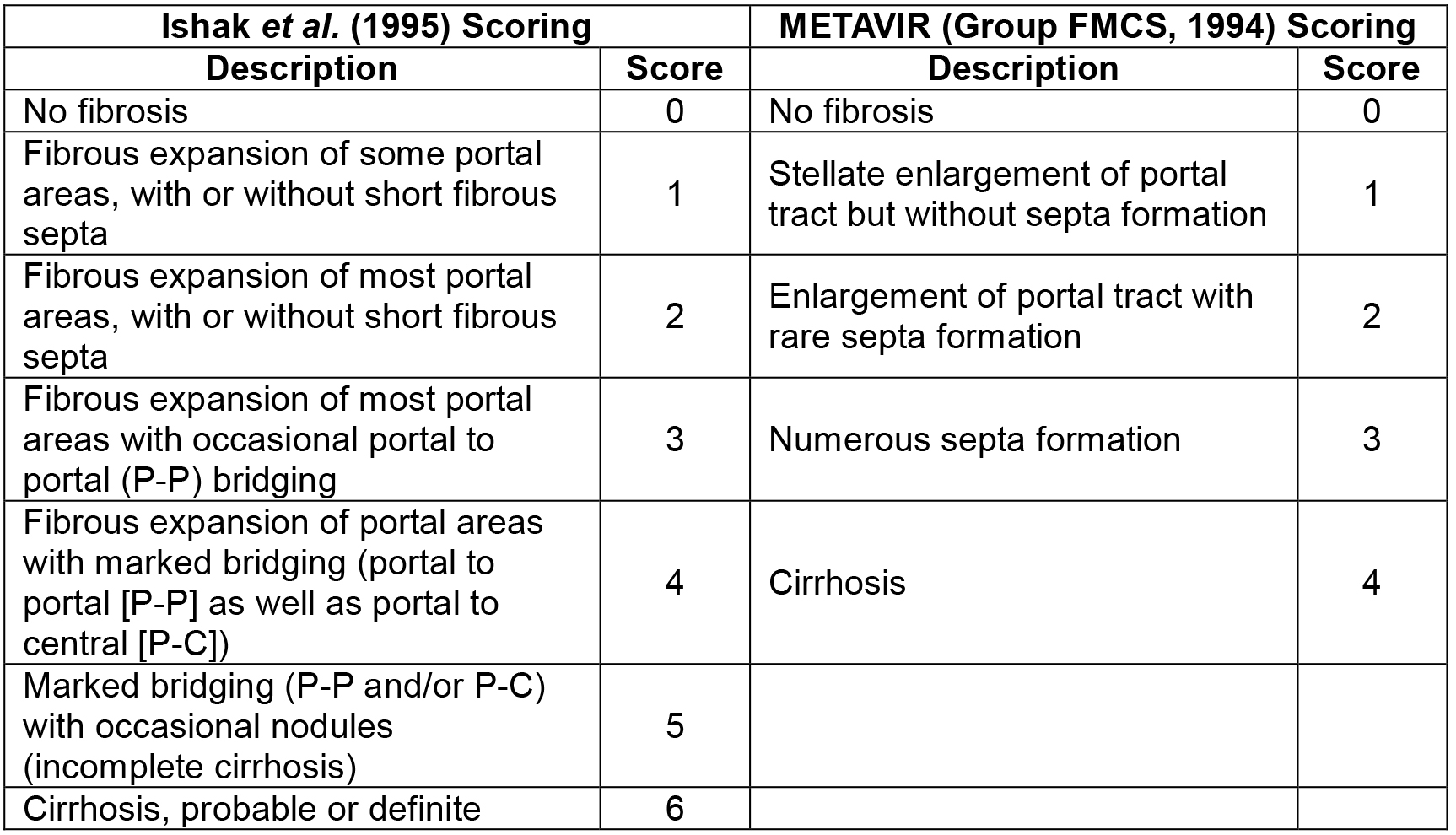
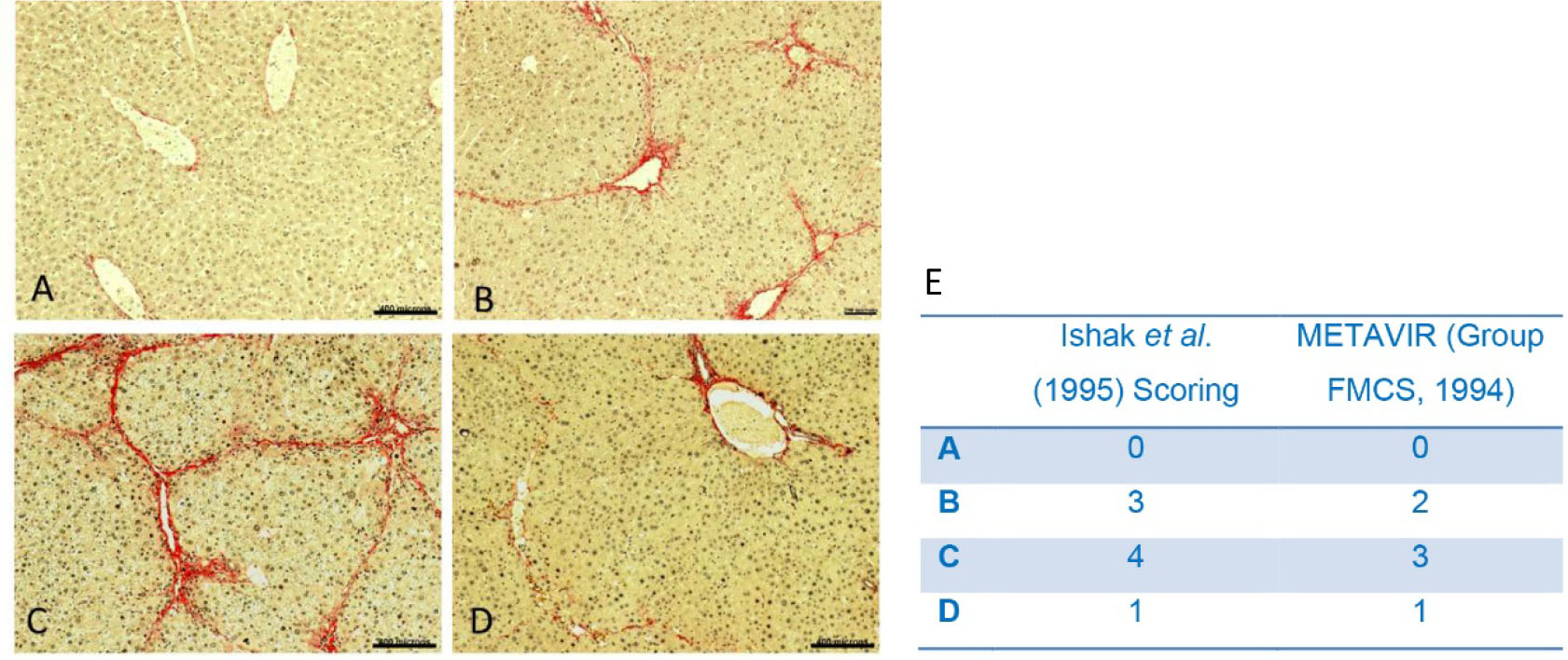
Figure 2. Pathological changes of liver in the presence of CCl4. A. No CCl4 dose; B. CCl4 (0.8 ml/kg body weight) in mineral oil, twice a week, for a period of 4 weeks and harvested 3 days after last dose; C. CCl4 (0.8 ml/kg body weight) in mineral oil, twice a week, for a period of 8 weeks and half of CCl4 dose (0.4 ml/Kg body weight, twice a week) was continued till the end of experiment (further 4 weeks); D. CCl4 (0.8 ml/kg body weight) in mineral oil, twice a week, for a period of 8 weeks and dose was stopped for further 4 weeks then harvested (score 1). Scale bars A, C, D = 400 µm, B = 200 µm (100x). E. Ishak and METAVIR scoring system of the representative images A, B, C and D.
- Fibrosis can be measured by Picrosirus red staining. Cut sections are rehydrated, processed for Picrosirus staining as per the protocol provided by the kit manufacturer.
- Development of fibrosis mouse model
- Bone marrow CD45+ cells isolation
- Six to eight weeks old eGFP transgenic mice are sacrificed by inhaling excess CO2 and then dipped in 70% isopropyl alcohol for 1 min to avoid contamination from the skin.
- The mouse is taken to laminar hood and placed on the dissecting board.
- Cut the skin at the middle of the trunk towards and along the two sides of the tail with the help of a pair of scissors so that it will be easy to pull the skin towards the claws and claws dissected out at the ankle joints along with the peeled skin. Then hind limbs are dissected out at the connection between hind limb and trunk.
- Muscles, ligaments and tendons are carefully disassociated from the tibias and femurs using sterile surgical scalpel and also scrubbed to remove the residual tissue parts.
- Tibias and femurs are separated by bending in opposite direction and transferred to a 30 mm Petri plate containing DMEM with 3% FCS.
- Repeat the steps B4 and B5 for other hind limb.
- The bone is held with a sterile forceps and tip of two ends excised using a micro-dissecting scissors.
- BD tuberculin syringe with needle containing DMEM is inserted into the cut tip of the bone and slowly flushed through bone cavity into a 50 ml Falcon tube which is already containing 5 ml of DMEM with 3% FCS. Repeat twice from both ends of the bone or until the bone becomes white.
- Repeat steps B7 and B8 for all pieces of bones. The entire procedure for isolation of cells is depicted in Figure 3.
Note: Bone marrow cells are isolated in two stage process. In the first stage, cells are removed from tibia and femurs by flushing with medium. The firmly adhered cells (mostly stromal cells and primitive stem cells) of the endosteal region are recovered in the second stage by digesting the crushed bone with collagenase type IV (0.03%) and dispase enzyme (2 U/ml).By performing these two stage yield a higher number of cells (Baligar et al., 2016). - Centrifuge at 259 x g for 5 min and supernatant is discarded.
- Erythrocytes are lysed by treatment with Gey’s solution as follows, 5 ml of Gey’s solution is added per mouse bone marrow cells pellet and gently suspend with the help of a pipet tip for 90 sec, and then PBS is added up to 50 ml to dilute the Gey’s solution.
Note: Gey’s treatment is used to lyse RBCs. The time of treatment is important because inadequate treatment period made lead to improper lysis of RBC. If treatment period is exceeded above permitted, it may kill the target cells. Use 5 ml of reagent per mouse bone marrow. After bone marrow flushing, wash with media and add 5 ml (In case of more number of cells are harvested from 2 or 3 mice, accordingly Falcon tube number is increased) on the cells pellet, mix gently with the pipettes for exactly 90 sec. Immediately dilute with 45 ml of PBS and spin down (259 x g for 5 min) then wash with media. - Centrifuge at 259 x g for 5 min and supernatant is discarded and pellet is washed in medium.
- Filter cell suspension through a 40 µm cell strainer.
- Then count the cells by using hemocytometer and used for anti-CD45 antibody staining.
- CD45+ cells are sorted by using FACS AriaIII (70 mm nozzal) technique. Here, we used FACS AriaIII for the CD45 positive cells sorting by labeling with anti-CD45 APC antibody surface antigen (Baligar et al., 2016).
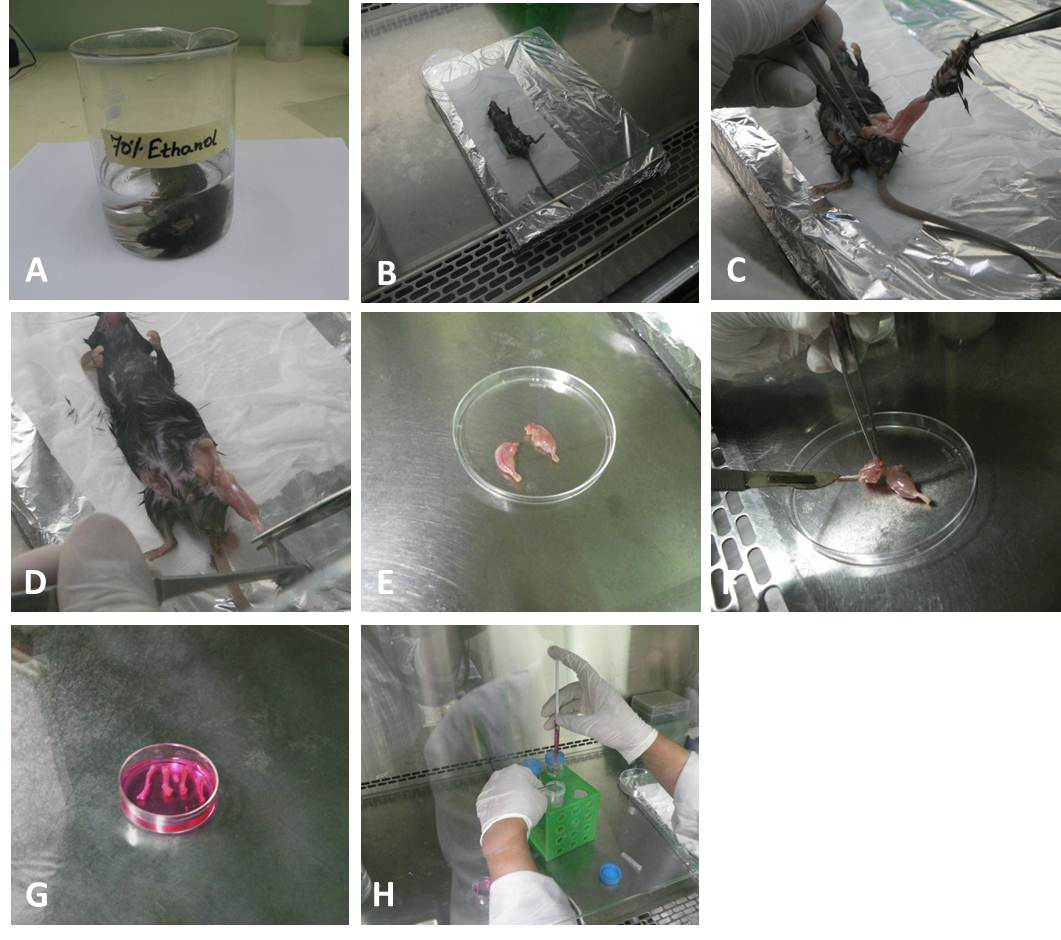

Figure 3. Isolation of BM stem cells from femur and tibia. A. The sacrificed mouse is dipped in 70% (v/v) ethanol for 1-2 min. B. Mouse is taken in side a biosafety cabinet hood and placed on a dissecting board. C. Carefully skin is removed. D. Claws dissected out at the ankle joints. E. Skin removed legs kept in 100 mm sterile Petri plate. F. Muscles, ligaments, and tendons are removed. G. Tibias and femurs are dissected and kept in complete media. H. BD tuberculin syringe needle is introduced into bone cavity and slowly flush the marrow out into the 50 ml Falcon tube containing 5-10 ml of complete media. The bone cavities are washed twice from both ends again until the bones became whitish.
- Six to eight weeks old eGFP transgenic mice are sacrificed by inhaling excess CO2 and then dipped in 70% isopropyl alcohol for 1 min to avoid contamination from the skin.
- Cell transplantation
- Before transplantation, all surgical materials, suture tread, suture needle, cotton should be autoclaved and arranged in the laminar hood. Pre-arrange a separate suture thread of approximately 10 cm long for the ligation of spleen.
- Anesthetize the animals with ketamine (100 mg/kg body weight) and xylazine (10 mg/kg body weight) by intraperitonial injection.
- Turn the animal left side and shave an area of 2-3 cm2 underneath the caudal rib (Figure 4A).
- Disinfect the shaved areas with 70% isopropyl alcohol.
- Incise the skin below the most caudal rib for 0.5 cm at the dorsoventral side using scissors (Video 1).
- Lift the spleen carefully with the help of small blunt end forceps (Video 1).
- Place the pre-arranged ligation over the spleen and loosely ligate at the tip around the spleen without holding the adipose tissue (do not pull the spleen) as shown in the Figure 4B (Video 1).
- Insert the syringe loaded with cells at the tip of spleen before the knot and after passing the needle tighten the knot to avoid the back flow (Avoid the perforation of the spleen and subsequent leakage. Figure 4D, Video 1).
- Slowly infuse cell suspension (50-80 μl) over 1-2 min until it is completely injected (cells are infused gently to avoid choking of the vain as shown in Video 1).
- Don’t remove the needle immediately after infusion; wait for 2-3 min to avoid back flow (Video 1).
- Then remove the needle and set the ligation tight for 2-3 min (Video 1).
- Remove the thread and relocate the spleen in the cavity.
Note: Steps C9-C12 are the critical steps, as cells should be infused very slowly to avoid choking of the vein. After passing all cell suspension, don’t remove the needle suddenly, if you remove suddenly there will be chance getting back flow of cells as well as bleeding. Therefore, at least keep needle inside the spleen at least 2-4 min so that pressure in the spleen is released and clotting will occur at the site of puncture. The remove the needle slowly followed by slight tightening of the knot for at least 1-2 min. it wills also aid back flow and clotting at puncture site. Then slowly remove knot make sure that there should not be a back flow of any fluid. - Close the abdominal peritoneum and then skin with the degradable sterile suture separately.
- Rehydrate the animal with subcutaneous injection of 1 ml of sterile saline solution (5 ml/100 g body weight Figure 4E).
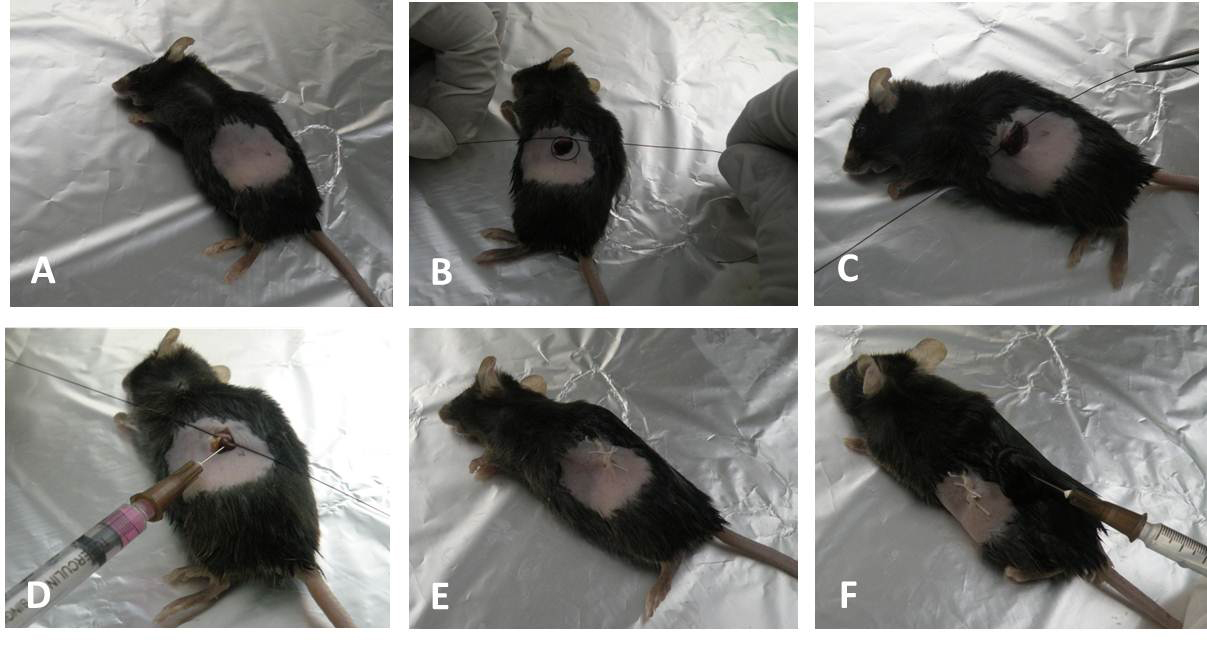
Figure 4. Intrasplenic transplantation of the stem cells. A. Turn the animal left side and shave an area underneath the caudal rib. B. and C. Exposure of the spleen and ligation with the thread. D. Insertion of the needle into the spleen then tightens the thread and infuse cells into spleen. E. Close the peritoneum and skin with suture. F. Rehydration by subcutaneous injection of saline after surgery.Video 1. Showing intrasplenic transplantation of cells (steps C5-C11) - Avoid postoperative analgesia to minimize the potential fulminate liver failure.
- Keep the animals into a pre-warmed cage immediately after surgery and allow free access to water and food. Then shift cages in the animal rack for follow-up.
- Before transplantation, all surgical materials, suture tread, suture needle, cotton should be autoclaved and arranged in the laminar hood. Pre-arrange a separate suture thread of approximately 10 cm long for the ligation of spleen.
- Detection of transplanted cells by Immunohistochemical technique (IHC)
- After 30 days of transplantation, sacrifice mice by inhaling excess CO2.
- Remove the liver using a scissors.
- Dissect the liver lobe into pieces and fix a part of the lobe in 4% paraformaldehyde (cryosections) and a part in 10% formalin saline solution (Paraffin sections).
Note: Generally, cryosections are good for Immunohistochemistry (IHC) when compared to paraffin sections. However, cryosections may not give clear morphology than paraffin sections. In paraffin sections for IHC, it requires additional step of antigen retrieval at high degree temperature (85-95 °C). It is also possible that some of the antigens may lose during paraffin processing. Considering all these, this protocol used cryosections for the IHC and paraffin sections for picrosirus red staining. - Prepare the cryosections after fixing for 2-3 days. The fixed tissue washed in PBS and keep in 30% sucrose solution for overnight (6-7 h) to get integrity of the sections.
- Then tissue is embedded in the tissue freezing medium for solidifying in cryochamber (cryo bar temp approx. -35 °C to -40 °C).
- Cut the section at 5 µm thickness and mount on the pre coated slides.
- Wash the slides and make border around the each section with the help of nail polish so that antibody should not move out of the sections.
- Permeabilize the sections with 0.1% of Triton X-100 for 15 min (3 changes at 5 min intervals).
- Block the sections with the serum or with general blocking solution 3% BSA for 1 h.
- Place primary antibody against eGFP (mouse monoclonal dilution 1:200) and incubate for 2 h. And also keep another section for isotype control for the primary antibody so that the testing antibody will not show any non-specific binding.
- Wash with PBST (PBS containing 0.01% Triton X-100) 3 times.
- Put Secondary Alexa Fluor-conjugated anti-mouse 488 (1:400 dilutions - depending on the source) and incubate for 1 h.
- Then wash as step D11.
- Add DAPI 1:1,000 dilution for 10 min and wash one with PBS.
- Mount with Antifade and seal with nail polish. Then observe in fluorescent microscope.
- First, adjust the IgG-isotype control, increase the exposure time till no background colour is seen even in high exposure.
- Then adjust test slide and set the exposure time, capture the Images (Figure 5).
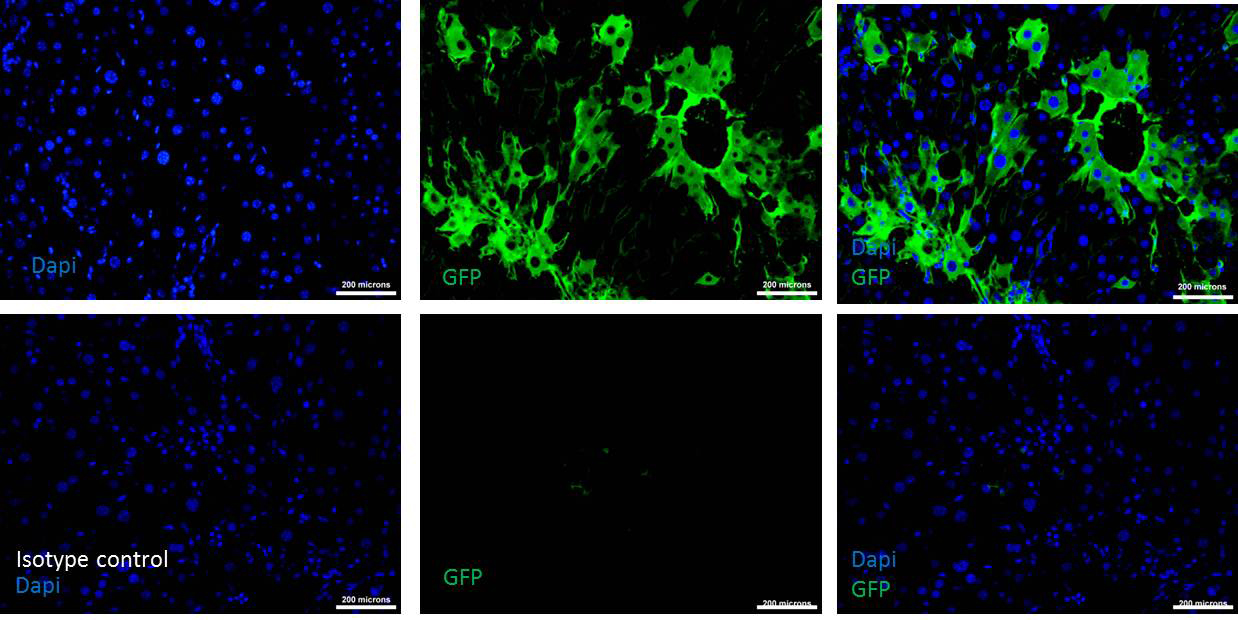
Figure 5. Donor cells engraftment after 30 days of transplantation. Upper row shows the immunohistochemistry of transplanted liver tissue section stained with DAPI and GFP antibody indicating the presence of donor cells (See merged photo of DAPI and GFP at the upper right). Lower row is the Isotype control for the same tissue sections showing the absence of non-specific binding of the GFP antibody (See the merged photo of DAPI and GFP at the lower right). Scale bars = 200 µm (200x). - After 30 days of transplantation, sacrifice mice by inhaling excess CO2.
- Detection of the fate of donor cells
- Follow ‘D’ till step D9, mix appropriately diluted primary antibodies against eGFP (raised in mouse monoclonal) and albumin (raided in goat polyclonal). Don’t forget to make IgG-isotype control.
- Follow step D11.
- Add secondary antibody AF anti-mouse 488 (1:400 dilutions - depending up on the source) and AF anti-goat 594 (1:400 dilutions - depending up on the source for 1 h)
- Then wash as step D11, and follow steps D14-D17. Take separate images of blue (DAPI), green (eGFP) and red (albumin) channel images, then merge them by using Adobe Photoshop or similar program (Figure 6).
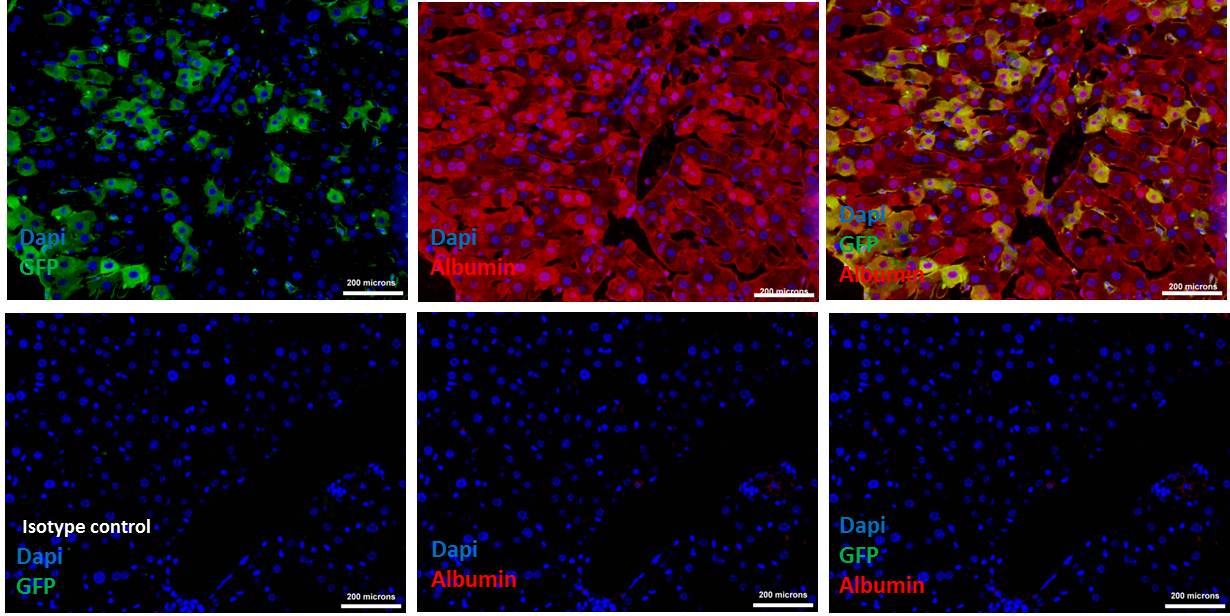
Figure 6. Donor cells (eGFP) differentiated into hepatocytes, expressing albumin. Upper row shows the Immunohistochemistry of transplanted liver tissue section double stained with GFP and albumin antibodies indicating the presence of donor cells that expressing albumin (See merged photo of DAPI, GFP and albumin at the upper right). Lower row is the Isotype control for the same tissue sections showing the absence of non-specific binding of the GFP and albumin antibodies (See the merged photo of DAPI and GFP at the lower right). Scale bars = 200 µm (200x). - Follow ‘D’ till step D9, mix appropriately diluted primary antibodies against eGFP (raised in mouse monoclonal) and albumin (raided in goat polyclonal). Don’t forget to make IgG-isotype control.
Data analysis
Data analysis has been reported as mean ± SEM. Student’s t-test was carried out to calculate the significance. The number of mice used for different experiments for creation of fibrosis model and intraspleenic transplantation is presented in the original publication (Baligar et al., 2016).
Notes
- During creation of the fibrotic model, strictly follow regular intervals of CCl4 treatment, that is twice a week till the end of the experiment.
- Continue CCl4 dose (half) even after the cell transplantation till the end of the experiment, otherwise recovery of live due to cell transplantation will be confused with spontaneous regression of fibrosis after discontinuation of CCl4 injection.
- Intrasplenic transplantation needs one more person to help during spleen knot and cells infusion.
- Avoid more pulling of the spleen, as it is connected with fat and blood vessels.
- Don’t remove the needle suddenly after cells infusion is completed. It helps to prevent back flow of cells.
- Don’t remove the knot suddenly after removing the needle. It helps to avoid back flow.
Recipes
- CCl4 dose preparation
1 ml CCl4
5 ml mineral oil
Notes: - Take CCl4 oil with the help of glass pipette (use pipette man) and add to the 5 ml mineral oil which was taken in the glass vial. Then mix gently.
- Don’t use plastic pipettes or vials.
- Gey’s solution
- Solution A
3.5 g NH4Cl
0.185 g KCl
0.15 g Na2HPO4
0.012 g KH2PO4
0.5 g glucose
2.5 g gelatin
0.005% phenol red
100 ml Milli Q water
Note: Autoclave and store at 4 °C. - Solution B
0.42 g MgCl2·6H2O
0.14 g MgSO4·7H2O
0.34 g CaCl2
100 ml Milli Q water
Note: Autoclave and store at 4 °C. - Solution C
2.25 g NaHCO3
100 ml Milli Q water
Note: Do not autoclave, syringe filter and store at 4 °C.
Autoclave solution A and B, then mix 20 ml of A, 5 ml of B and 5 ml of C (syringe filtered).
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India for generous support in the Center for Molecular Medicine programme.
References
- Baligar, P., Mukherjee, S., Kochat, V., Rastogi, A. and Mukhopadhyay, A. (2016). Molecular and cellular functions distinguish superior therapeutic efficiency of bone marrow CD45 cells over mesenchymal stem cells in liver cirrhosis. Stem Cells 34(1): 135-147.
- Chang, M. L., Yeh, C. T., Chang, P. Y. and Chen, J. C. (2005). Comparison of murine cirrhosis models induced by hepatotoxin administration and common bile duct ligation. World J Gastroenterol 11(27): 4167-4172.
- Group FMCS. (1994). Intraobserver and interobserver variations in liver biopsy interpretation in patients with chronic hepatitis C. The French METAVIR Cooperative Study Group. Hepatology 20(1 Pt 1): 15-20.
- Ishak, K., Baptista, A., Bianchi, L., Callea, F., De Groote, J., Gudat, F., Denk, H., Desmet, V., Korb, G., MacSween, R. N., Phillips, M.J., Portmann, B.G., Poulsen, H., Scheuer, P.J., Scheuer, M. and Thaler, H. (1995). Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis. J Hepatol 22(6): 696-699.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Baligar, P., Pokhrel, S. and Mukhopadhyay, A. (2016). Experimental Liver Fibrosis and Intrasplenic Transplantation of CD45+ Bone Marrow Cells. Bio-protocol 6(20): e1972. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1972.
Category
Stem Cell > Adult stem cell > Cell transplantation
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link











