- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Positional Analysis of Fatty Acids in Phospholipids by PLA2 Treatment
Published: Vol 6, Iss 12, Jun 20, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1850 Views: 7617
Reviewed by: Marisa RosaAgnieszka ZienkiewiczAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Sorghum bicolor Extracellular Vesicle Isolation, Labeling, and Correlative Light and Electron Microscopy
Deji Adekanye [...] Jeffrey L. Caplan
Oct 5, 2024 2108 Views

A New Approach to Detect and Semi-quantify All Molecular Species and Classes of Anionic Phospholipids Simultaneously in Plant Samples
Manon Genva [...] Laetitia Fouillen
Apr 20, 2025 1719 Views

PhosphoLIMBO: An Easy and Efficient Protocol to Separate and Analyze Phospholipids by HPTLC From Plant Material
Louise Fougère [...] Yohann Boutté
Sep 5, 2025 1334 Views
Abstract
Plant phospholipids can be produced in the endoplasmic reticulum or plastids. Lipids from different sources can be distinguished by the fatty acid profile, in terms of the preferred fatty acid species esterified to the sn-1 or sn-2 position of the glycerol backbone (Ohlrogge and Browse, 1995). This protocol is used to determine the fatty acid profile in total plant phospholipids by the treatment of sn-2 specific phospholipase A2 (PLA2).
Keywords: LipidomicsMaterials and Reagents
- Glass tubes [PYREXTM screw cap culture tubes with PTFE lined phenolic caps (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Fisher ScientificTM, catalog number: 14-932H )]
- Pipette 100-1,000 µl (Eppendorf Research 2100)
- AxygenTM 1,000 µl universal pipette tips (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Fisher ScientificTM, catalog number: 14-222-690 )
- Total plant lipids
Note: Extracted by the method described in the companion lipid extraction and profiling protocol by the same authors (Liu and Wang, 2016) and the original publication (Welti et al., 2002) - Chloroform (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: C607 )
- PLA2 from honey bee venom (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9279 )
Note: Dissolved in reaction buffer to 1 unit/µl before use. - Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S7653 )
- Nitrogen gas
- HEPES (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H3375 )
- Calcium chloride (CaCl2) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C8106 )
- Magnesium chloride hexahydrate (MgCl2·6H2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M2670 )
- Methanol (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Fisher ScientificTM, catalog number: A456 )
- Reaction buffer (see Recipes)
- NaCl solution (see Recipes)
- Extraction solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Nitrogen evaporator N-EVAP (Meyer Organomation, model: 111 )
- Ultrasonic processor with probe, work at 30% power (GEX 130PB) or similar equipment [e.g., ultrasonic processor, (Cole-parmer, model: EW-04714-51 )]
- Incubator (Thermo Fisher Scientific, model: Isotemp 537D ) or similar equipment [e.g., microbiological incubators (Thermo Fisher Scientific, IsotempTM, catalog number: 15-103-0513 )]
Procedure
- Total plant lipids were reconstituted by chloroform and the amount of lipids corresponding to 0.2 mg dry weight were aliquoted in glass tubes. Same amount of untreated lipid samples will be used as controls in step 9.
- Lipids were dried in the nitrogen evaporator thoroughly (>30 min), mild heating (<50 °C) may be used to accelerate the process.
- Dried lipids were hydrated in 500 µl reaction buffer at room temperature for >10 min, followed by sonication (30% power, on ice) to disperse the lipids uniformly.
- 10 units (10 µl) of PLA2 were added to the reaction, mixed by vortex. The reaction mixtures were incubated at 37 °C for 2 h to completely digest phospholipids.
- 500 µl of 500 mM NaCl was added to the mixture to facilitate phase separation. 2 ml extraction solution was added and vortexed to terminate the reaction and extract lipids.
- Centrifuge at ~200 x g for 10 min. Transfer the bottom (organic) phase to another glass tube.
- Add 1 ml chloroform and repeat step 6, twice for complete extraction.
- Dry extracted lipids under nitrogen gas, reconstitute the lipids in 50 µl chloroform.
- Use total lipids corresponding to 0.2 mg dry weight as control, profile both digested and undigested lipids in mass spectrometry as described in the companion lipid extraction and profiling protocol by the same authors (Liu and Wang, 2016). Three or more biological repeats are recommended and Student’s t-test is used for statistical analysis. Compare regular lipids in undigested samples and lysolipids in digested samples to determine position/composition of fatty acid in different lipid classes. For more quantitative results and more phospholipids classes besides phosphatidylcholine (PC) and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), lipid samples can first be resolved by thin layer chromatography (TLC) (Refer to the method in Liu et al., 2015) and each lipid/lysolipid spot can be quantified by transmethylation and GC analysis (Politz et al., 2013).
Representative data
Representative data from Liu et al., 2015 (Figure 1). Total lipids were digested by PLA2, followed by analysis of PC and LysoPC by mass spectrometry. The increase of LPC16 in digested sample and increase of PC34 in undigested samples in RNAi lines compared with WT are similar, suggesting the increased PC34 in RNAi lines have C16 fatty acid esterified to the sn-1 position, which originates from the eukaryotic pathway.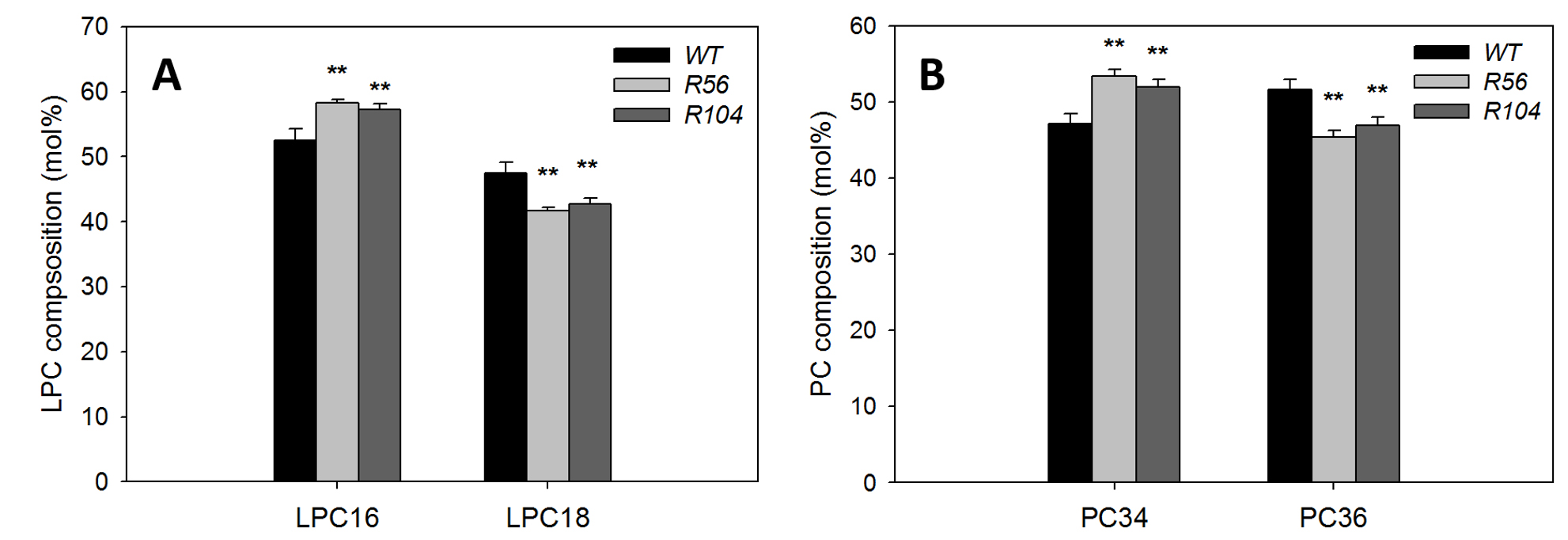
Figure 1. Analysis of fatty acyl chain position/composition in phosphatidylcholine (PC). A. Content of LysoPC with C16 and C18 fatty acids after PLA2 treatments of lipids from two AAPT RNAi lines and WT plants. B. Content of PC with C34 and C36 fatty acids without PLA2 treatments of lipids from two AAPT RNAi lines and WT plants. * and ** mark differences between WT and mutant at P < 0.05 and at P < 0.01, respectively based on Student’s t-test. Values are means ± SD (n = 3).
Recipes
- Reaction buffer
100 mM HEPES, pH 7.4
10 mM CaCl2
10 mM MgCl2
Note: Stable in room temperature. - NaCl solution
500 mM NaCl
Note: Stable in room temperature. - Extraction solution
66.7% (v/v) Chloroform
33.3% (v/v) Methanol
Note: made before use
Acknowledgments
This protocol is adapted from the work of Williams et al., 1995. Work was supported by the National Institute of Food and Agriculture Grant 2016-67013-24429 and the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Grant DE-AR0000202.
References
- Liu, Y. and Wang, X. (2016). Extraction and profiling of plant polar glycerol lipids. Bio-protocol 6(12): e1849.
- Liu, Y., Wang, G. and Wang, X. (2015). Role of aminoalcoholphosphotransferases 1 and 2 in phospholipid homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 27(5): 1512-1528.
- Ohlrogge, J. and Browse, J. (1995). Lipid biosynthesis. Plant Cell 7(7): 957-970.
- Politz, M., Lennen, R. and Pfleger, B. (2013). Quantification of bacterial fatty acids by extraction and methylation. Bio-protocol 3(21): e950.
- Williams, J. P., Khan, M. U. and Wong, D. (1995). A simple technique for the analysis of positional distribution of fatty acids on di- and triacylglycerols using lipase and phospholipase A2. J Lipid Res 36(6): 1407-1412.
- Welti, R., Li, W., Li, M., Sang, Y., Biesiada, H., Zhou, H. E., Rajashekar, C. B., Williams, T. D. and Wang, X. (2002). Profiling membrane lipids in plant stress responses. Role of phospholipase D alpha in freezing-induced lipid changes in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 277(35): 31994-32002.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Liu, Y. and Wang, X. (2016). Positional Analysis of Fatty Acids in Phospholipids by PLA2 Treatment. Bio-protocol 6(12): e1850. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1850.
Category
Biochemistry > Lipid > Lipid measurement
Plant Science > Plant biochemistry > Lipid
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link