- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Liquid Luminescent DNA-precipitation Assay
Published: Vol 6, Iss 10, May 20, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1812 Views: 8779
Reviewed by: Jia LiGriselda Zuccarino-CataniaAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Working on transcription factors requires studying interactions between protein and DNA. After identification of putative binding-sequences and motifs, Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) experiment is classically used to determine specific interactions of proteins and nucleic acids. This lengthy process is rather heavy-handed because of radioisotopically labeled DNA and autoradiographic visualization that are required for the experiments.
Liquid luminescent DNA precipitation assay provides rapid, reliable and quantitative results concerning protein-DNA interactions. This protein-DNA binding assay is based on solution hybridization between Digoxigenin-labeled (DIG) DNA and glutathione S-transferase (GST)-fused DNA binding protein bound to Glutathione Sepharose 4B beads (Figure 1), without electrophoresis (Toshiharu et al., 2008). Digoxigenin is a steroid found in plants. It is increasingly used as a label for nonradioactive detection of nucleic acids and proteins.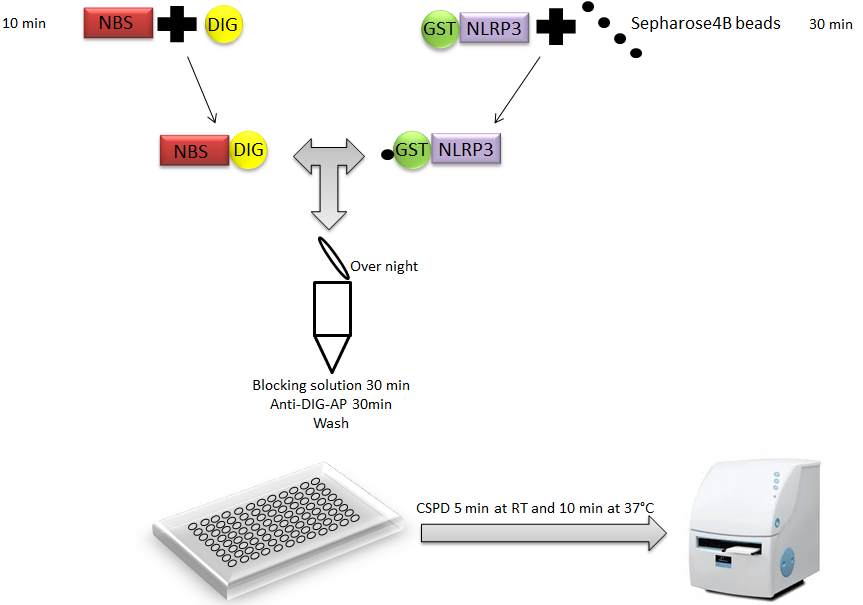
Figure 1. Representation of liquid chemiluminescent DNA pull-down assay. A Glutathione S-transferase (GST)-fused NLRP3 (GST-NLRP3) bound to Glutathione Sepharose 4B beads is incubated with a DIG-labeled double-stranded DNA fragment containing putative NLRP3 Binding Site (NBS) in protein-DNA binding buffer. After extensive washing, protein-DNA binding on beads is detected using anti-DIG antibody conjugated to alkaline phosphatase, which is measured by a chemiluminescent reaction using a luminometer Disodium 3-(4-methoxyspiro {1,2-dioxetane-3,2′-(5′-chloro) tricyclo [3.3.1.13, 7] decan}-4-yl) phenyl phosphate(CSPD).
Here, we described how we used this technique to demonstrate the interaction between NLRP3 protein and its DNA binding site (Bruchard et al., 2015).
Materials and Reagents
- BL21 bacteria (DE3) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM)
- pGEX-4T-1 vector (Addgene, catalog number: 27458001 )
- GST fusion NLRP3 protein
- Glutathione sepharose 4B (GE Healthcare, catalog number: 17-0756-01 )
- Potassium chloride (KCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9541 )
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S7653 )
- Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), pH 8 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: E9884 )
- Dithiothreitol (DTT) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D0632 )
- Glycerol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G5516 )
- Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T9284 )
- Double-stranded oligonucleotides containing the putative binding sequence (Life Technologies)
- DIG gel shift kit (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 03353591910 )
- Disodium 3-(4-methoxyspiro {1, 2-dioxetane-3, 2′-(5′-chloro) tricyclo [3.3.1.13,7] decan}-4-yl) phenyl phosphate (CSPD) (chemiluminescent substrate)
Note: It is included in DIG gel shift kit. - DNAse/RNase free water (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 11538646 )
- Tris-HCl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T5941 )
- Binding buffer (see Recipes)
- Washing buffer (see Recipes)
- Maleic acid buffer (see Recipes)
- 10x blocking solution (see Recipes)
- Detection buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- End-over-end rotator
- PerkinElmer Envision Plate Reader (PerkinElmer Inc., catalog number: 2104-0010A )
Procedure
GST fusion NLRP3 proteins were previously produced in BL21 bacteria. GST alone was used as a control. Briefly, classical cloning method was used to insert GST-NLRP3 sequence in pGEX-4T-1 vector. BL21 were transformed by a heat shock according to supplier’s instructions. 24 h later bacteria were lysate with 1% Triton X-100 solution.
- Day 1
Binding of GST-fusion protein and Glutathione Sepharose 4B beads- Glutathione Sepharose 4B was washed twice with 5 ml binding buffer and centrifuged at 500 x g for 5 min at room temperature.
- GST-fused proteins were purified with Glutathione Sepharose 4B. Three ml of bacteria lysate obtained after BL21 sonication were added to the prepared Glutathione Sepharose 4B in a final volume of 30 ml of binding buffer, and incubated for 30 min at room temperature with gentle agitation. Protein/Glutathione Sepharose 4B complexes were isolated by centrifugation at 500 x g for 5 min at room temperature and washed with 5 ml binding buffer. Centrifugation at 500 x g for 5 min allowed collecting Protein/Glutathione Sepharose 4B complexes.
DNA labeling reaction
The NLRP3-binding sequence (NBS) (5′-TCTGTTTTGGGAGGCAGAGCTTTGTTTCTATG-3′) was labeled with Digoxigenin through the use of a DIG Gel Shift Kit but Liquid chemiluminescent DNA pull-down assays can also be performed using biotinylated DNA. - Double-stranded oligonucleotides were diluted to 10 ng/µl with DNAse/RNase free water.
- Put the tubes containing 100 ng of double-strand DNA (10 µl) on ice and add 4 µl labeling buffer, 5 mM CoCl2-solution, 0.05 mM DIG-ddUTP solution and 200 U Terminal transferase. Mix by pipetting up and down.
- The tubes were centrifuged and incubated for 15 min at 37 °C in a dry block heater and put immediately on ice after this incubation.
- The reaction was stopped with 2 µl EDTA.
- DNA was then diluted to 4 ng/µl by adding 3 µl of water (DNAse/RNAse free).
Protein-DNA binding reaction - 2 µg of GST-proteins bound to Glutathione Sepharose 4B beads were incubated with 20 fmol DIG-labeled double-stranded DNA fragments in protein-DNA binding buffer from the DIG Gel Shift Kit in a final volume of 20 µl overnight at room temperature.
- Glutathione Sepharose 4B was washed twice with 5 ml binding buffer and centrifuged at 500 x g for 5 min at room temperature.
- Day 2
- GST-fused proteins bound to DNA were washed three times with 1 ml Washing Buffer from the kit and centrifuged each time at 500 x g for 5 min at room temperature.
- Then the beads were incubated in 500 µl 1x blocking solution (dilution of 10x blocking solution in maleic acid buffer) for 30 min at room temperature.
- GST-fused proteins bound to DNA were incubated with anti-DIG Fab fragments conjugated with 75 mU/ml alkaline phosphatase (from DIG gel shit kit) for 30 min at room temperature in 1x blocking solution.
- GST-fused proteins bound to DNA are washed twice with 5 ml Washing Buffer.
- After washes, the complexes were transferred in detection buffer to 96-well plates and were incubated for 5 min at room temperature with 1 μg/ml 3-(4-methoxyspiro {1,2-dioxetane-3,2′-(5′-chloro) tricyclo [3.3.1.13,7] decan}-4-yl) phenyl phosphate (CSPD) , followed by incubation for 10 min at 37 °C.
- Light emission was measured using a PerkinElmer Envision Plate Reader. Light detection was performed during 1 sec per well.
- GST-fused proteins bound to DNA were washed three times with 1 ml Washing Buffer from the kit and centrifuged each time at 500 x g for 5 min at room temperature.
Representative data
The emission signal from all the reagents mixed together without DNA-DIG was used for normalization and data are presented as arbitrary units. All experimental conditions were tested with GST-NLRP3 and GST alone. Double strand DNA labeled without DIG was tested alone and used as a competitor (Figure 2).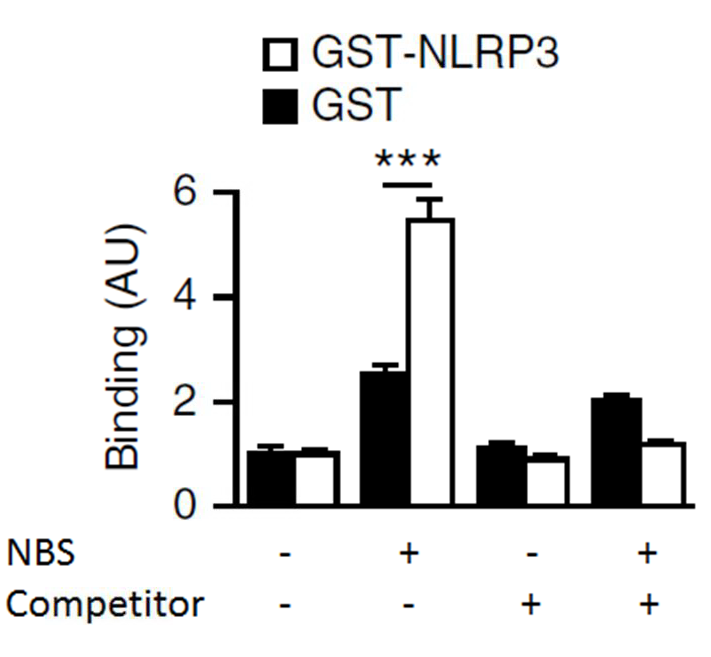
Figure 2. Representative data of liquid chemiluminescent DNA pull-down assay. Light emission was measured from the liquid chemiluminescent DNA pull-down assay to indicate binding. The histograms indicate relative light emission (arbritary units, AU). Glutathione S-transferase (GST)-NLRP3 was incubated with Digoxigenin (DIG)-labeled NBS with or without Competitor (non labelled NBS). Data are shown as means ± SEM.
Recipes
- Binding buffer
75 mM KCl
50 mM NaCl
1 mM EDTA
1 mM DTT
10% glycerol
0.1% Triton X-100 - Washing buffer
0.1 M maleic acid
0.15 M NaCl (pH 7.5)
0.3% (v/v) Tween 20 - Maleic acid buffer
0.1 M maleic acid
0.15 M NaCl
Adjust with NaOH to pH 7.5 - 10x blocking solution
10% (w/v) blocking reagent in maleic acid buffer - Detection buffer
0.1 M Tris-HCl
0.1 M NaCl (pH 9.5)
Acknowledgments
This protocol is adapted from Toshiharu et al. (2008). This project was supported by the French National Research Agency (“Investissements d’Avenir” program; ANR-11-LABX-0021), the Ligue nationale contre le cancer (F. G. and F. V.), the Institut National du Cancer (F. G.), Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (F. G).
References
- Bruchard, M., Rebe, C., Derangere, V., Togbe, D., Ryffel, B., Boidot, R., Humblin, E., Hamman, A., Chalmin, F., Berger, H., Chevriaux, A., Limagne, E., Apetoh, L., Vegran, F. and Ghiringhelli, F. (2015). The receptor NLRP3 is a transcriptional regulator of TH2 differentiation. Nat Immunol 16(8): 859-870.
- Iwasaki, T., Miyazaki, W., Rokutanda, N. and Koibuchi, N. (2008). Liquid chemiluminescent DNA pull-down assay to measure nuclear receptor-DNA binding in solution. Biotechniques 45(4): 445-448.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Végran, F., Bruchard, M., Derangère, V. and Ghiringhelli, F. (2016). Liquid Luminescent DNA-precipitation Assay. Bio-protocol 6(10): e1812. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1812.
Category
Cell Biology > Cell-based analysis > Protein-DNA interactions
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link