- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
ER Microsome Preparation and Subsequent IAA Quantification in Maize Coleoptile and Primary Root Tissue
Published: Vol 6, Iss 9, May 5, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1805 Views: 11373
Reviewed by: Samik BhattacharyaLaura ZaninAgnieszka Zienkiewicz

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Optimized Isolation of Lysosome-Related Organelles from Stationary Phase and Iron-Overloaded Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Cells
Jiling Li and Huan Long
Nov 20, 2024 1787 Views

Isolation and Biophysical Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles From Hairy Root Cultures
Marisa Conte [...] Alfredo Ambrosone
Mar 5, 2025 2255 Views

Rapid Miniprep of Intact Chloroplasts from Arabidopsis thaliana Leaves
Brenda A. Carranza-Correa [...] Manuel Gutiérrez-Aguilar
May 20, 2025 2684 Views
Abstract
Auxin is a major growth hormone in plants and the first plant hormone to be discovered and studied (Darwin and Darwin, 1880). The auxin molecule in plants was first identified as indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) by Kögl et al. (1934). Active research over nearly a decade has shed light on many of the molecular mechanisms of its action but the complexity and redundancy of the auxin biosynthetic network raises questions about control of this system. We have shown that some enzymes involved in the YUCCA-route of auxin biosynthesis are not cytosolic but localised to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in both Arabidopsis thaliana (YUCCA4.2) (Kriechbaumer et al., 2012) as well as Zea mays (ZmTAR1 and ZmSPI) (Kriechbaumer et al., 2015). This is raising the intriguing possibility of subcellular compartmentation of auxin biosynthesis. To show that maize auxin biosynthesis indeed can take place in microsomal as well as cytosolic cellular fractions from maize seedlings we applied the protocol described here: Microsomes are being isolated from maize coleoptile and primary root tissue, enzyme assays with microsomal and cytosolic fractions using either tryptophan (Trp) or indole- -3pyruvic acid (IPyA) as a substrate are carried out and the auxin IAA is extracted and quantified.
Keywords: MaizeMaterials and Reagents
- Pipettes (1 ml, 200 µl and 10 µl) (Gilson Scientific Ltd., catalog number: F123602 , F123601 and F144802 )
- Eppendorf tubes (2 ml) (Eppendorf AG, catalog number: 0030120094 )
- Eppendorf conical tubes (50 ml) (Eppendorf AG, catalog number: 0030122178 )
- 0.45 µm syringe filters (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F8273 )
- Cheese cloth (DUTSCHER SCIENTIFIC, catalog number: 789056 )
- Ice box and ice
- Liquid nitrogen
- Triethanolamine-acetic acid (TEA-HOAc) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 90278 )
- Potassium acetate (KOAc) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P1190 )
- Magnesium acetate [Mg(OAc)2] (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M5661 )
- Sucrose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S0389 )
- DL-Dithiothreitol (DTT) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 43815 )
- Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: E5391 )
- Tris-Hydrochloride (Tris-HCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 252859 )
- β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate disodium salt (NADPH) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 93205 )
- Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F6625 )
- Indole-3-pyruvic acid (IPyA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: I7017 )
- Tryptophan (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T0254 )
- Ethyl acetate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 270989 )
- Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S7795 )
- Distilled water
- Ethyl acetate for HPLC (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 650528 )
- Acetic acid for HPLC (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A6283 )
- Methanol for HPLC (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 34860 )
- Stock solutions (see Recipes)
- Buffers (see Recipes)
- Buffers for microsome extraction (Buffer 1, Buffer 2, Buffer 3 and Buffer 4)
- Buffers for HPLC analysis
- Buffers for microsome extraction (Buffer 1, Buffer 2, Buffer 3 and Buffer 4)
Equipment
- Porcelain mortar & pestle (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z247464 and Z247502 )
- Glass bottles for buffers (100 ml, 250 ml and 500 ml) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z305170 , Z305189 and Z305197 )
- Refrigerated table centrifuge (Eppendorf AG, model: 5430R )
- Ultracentrifuge with swing-out rotor SW41 (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 331362 )
- Ultracentrifuge corex tubes (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 331372 )
- Glass rod and a 2 ml Potter–Elvehjem homogenizer (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P7734-1EA )
- water bath (37 °C) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, model: TSGP02 )
- Speed-vac (LABCONCO, catalog number: 7810016 )
- Nanodrop ND-2000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 13400504 )
- High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) (600E multisolvent delivery system) (WATERS, catalog number: 720000699EN )
- Reverse phase column (Apollo C18) (250 mm x 4.6 mm, 5 μm) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GraceTM, catalog number: 5126767 )
- UV monitor 486 (WATERS) and a fluorescence monitor 470 (WATERS)
Procedure
- Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) microsome preparation
- All steps are carried out on ice or at 4 °C unless indicated otherwise.
- Pre-cool all buffers, tubes etc. used in the procedure.
- 5 g of maize coleoptile or primary root tissue (4 d after germination) are ground to fine powder in liquid nitrogen using a pre-cooled mortar and pestle.
- The powder is then homogenized in 4 ml of ice-cold buffer 1 and transferred into a 50 ml falcon tube.
- 4 ml of ice-cold buffer 2 are added to the tube and the suspension was incubated on ice for 10 min. Then the homogenate is centrifuged at 1,000 x g for 10 min at 4 °C. The resulting supernatant is poured over 4 layers of cheese cloth into a fresh falcon tube. At this step, the resulting extract is considered total plant extract for later enzymatic assays. The extract is centrifuged again at 4,500 x g for 25 min at 4 °C.
- Prepare ultracentrifuge corex tubes with a 4 ml sucrose cushion (buffer 3) on the bottom.
- The 8 ml of plant suspension is layered on top of the sucrose cushion by slightly angling the tube and carefully and slowly pipetting the suspension at the side of the tube. The tube is centrifuged for 90 min at 93,000 x g (ultracentrifuge with swing-out rotor SW41).
- The resulting pellet is removed from the ultracentrifuge tube if necessary with 20 μl of buffer 4 and transferred to a 2 ml Potter–Elvehjem homogenizer. The supernatant is kept and used as cytosolic extract in later IAA quantifications.
- The final pellet was resuspended in 200 μl of buffer 4 using a glass rod and a 2 ml Potter-Elvehjem homogenizer. Protein content was measured using a Nanodrop. Freshly prepared microsomes were used for enzymatic assays straight away.
- This part of the procedure will take between 3 and 4 h depending on sample size.
- All steps are carried out on ice or at 4 °C unless indicated otherwise.
- Microsomal enzymatic tests
- The YUCCA-route of auxin biosynthesis is a two-step process (Figure 1): In maize TAR-proteins [Tryptophan Aminotransferase of Arabidopsis-related proteins; ZmTAR1 (Chourey et al., 2010), ZmVT2 (Phillips et al., 2011), and ZmTAR3 (ZmAlliin1; Bernardi et al., 2012)] are converting tryptophan (Trp) to indole-3-pyruvic acid (IPyA) which is then converted by YUCCA proteins to IAA [ZmYUC1 and ZmSPI1 (Phillips et al., 2011)]. It was shown that ZmYUC1 and ZmVT2 are localized in the cytosol, whereas ZmSPI1, ZmTAR1 and ZmTAR3 are localized to the ER (Kriechbaumer et al., 2015).
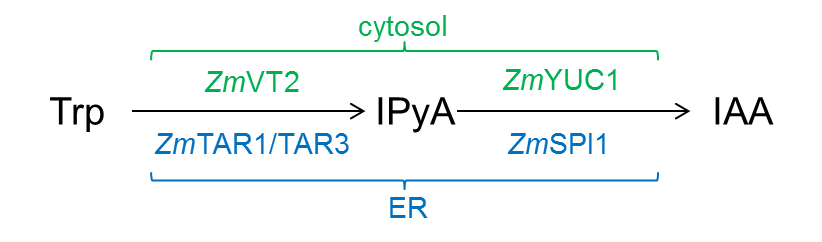
Figure1. YUCCA-route of auxin biosynthesis in maize. Cytosolic enzymes are labeled in green, ER-localised enzymes in blue. - Enzymatic activity tests (100 μl total volume) with microsomal and cytosolic fractions were carried out in the following manner:
20 μl of microsomal or cytosolic extract or total plant extract (see step A5)
1 mM NADPH
100 μM FAD
100 μM IPyA or Trp (depending on experimental interest)
100 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) up to a total volume of 100 μl
Mixed carefully in 2 ml Eppendorf tubes
Note: For this the 100 mM Tris-HCl should be pipetted first, followed by the plant extract and then FAD. The reaction time is started with the addition of the substrate (IPyA or Trp).
The assays were incubated for 1 h in a 37 °C water bath and snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen straight after the incubation time. - For comparison enzymatic tests were also performed with the cytosolic fraction and total plant extract.
- At this stage the assays can be stored at -20 °C before the IAA analysis is carried out.
- The YUCCA-route of auxin biosynthesis is a two-step process (Figure 1): In maize TAR-proteins [Tryptophan Aminotransferase of Arabidopsis-related proteins; ZmTAR1 (Chourey et al., 2010), ZmVT2 (Phillips et al., 2011), and ZmTAR3 (ZmAlliin1; Bernardi et al., 2012)] are converting tryptophan (Trp) to indole-3-pyruvic acid (IPyA) which is then converted by YUCCA proteins to IAA [ZmYUC1 and ZmSPI1 (Phillips et al., 2011)]. It was shown that ZmYUC1 and ZmVT2 are localized in the cytosol, whereas ZmSPI1, ZmTAR1 and ZmTAR3 are localized to the ER (Kriechbaumer et al., 2015).
- IAA extraction and quantification
- IAA is extracted by ethyl acetate phase separation (Park et al., 2003; Kriechbaumer et al., 2007) (Figure 2) from the enzyme assays prepared in section B. The whole sample of each assay is used for this procedure.
- For this the pH of sample is adjusted higher than 9.5 with 1 M Na2CO3, and the sample is then extracted with 400 μl of ethyl acetate.
- The aqueous lower phase is recovered and 200 μl of water are added.
- The partitioning procedure is repeated recover the aqueous phase again.
- The aqueous phases from both partitioning steps are combined.
- The collected aqueous phase is acidified with acetic acid to a pH below 2.5 and partitioned twice with addition of 400 μl of ethyl acetate for each step.
- The organic phases are collected and the liquid evaporated using a speed-vac (pre-set settings with room temperature). Evaporation will take around two hours but the sample should be checked from time to time.
- The dried substances are re-dissolved in 100% methanol and can be stored at -20 °C before further analysis if necessary.
- For this the pH of sample is adjusted higher than 9.5 with 1 M Na2CO3, and the sample is then extracted with 400 μl of ethyl acetate.
- The IAA extraction can take up to 5 h depending on sample size and evaporation time in the speed-vac.
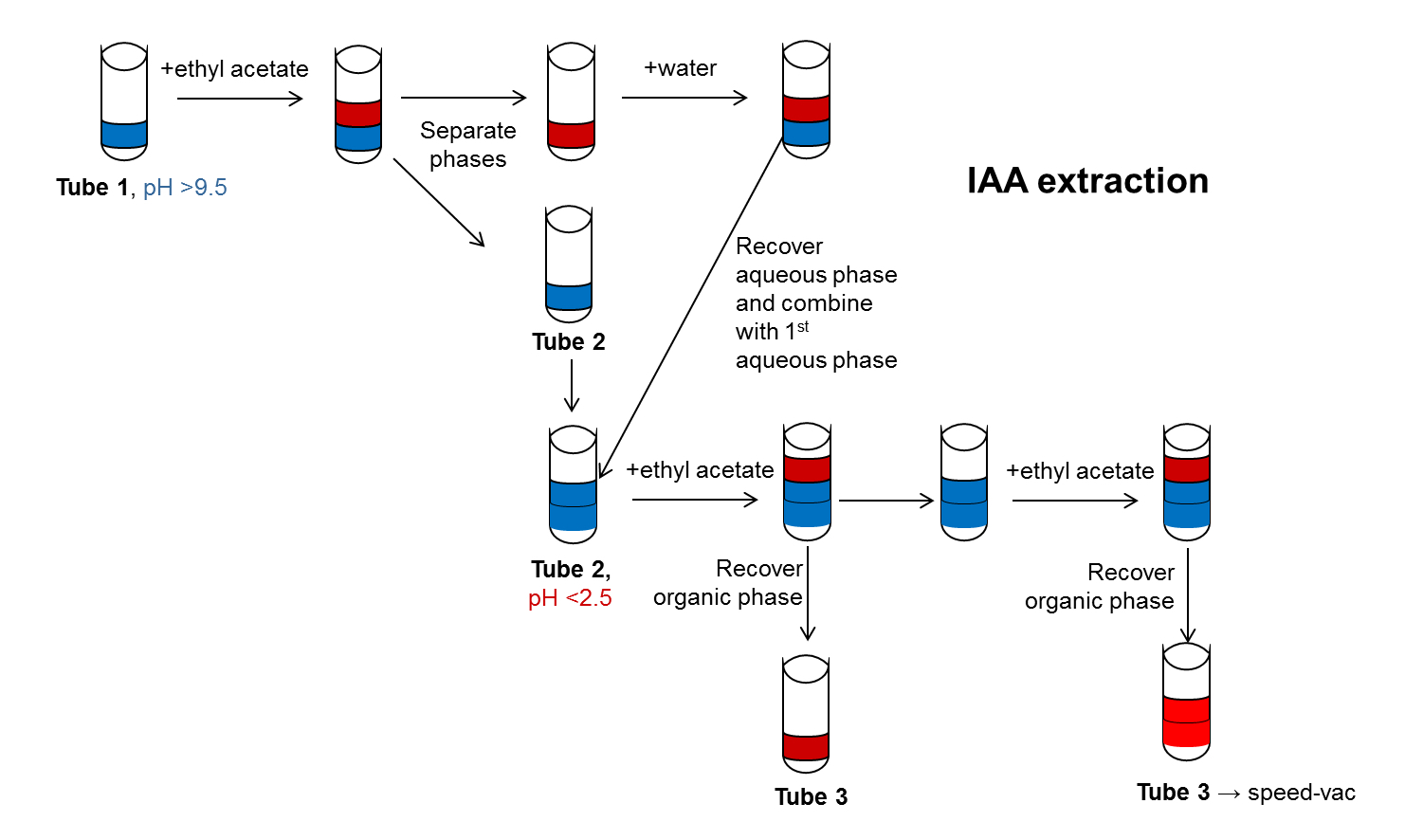
Figure 2. Schematic representation of IAA extraction using ethyl acetate phase separation. The steps for IAA extraction by ethyl acetate phase separation are shown in this diagram. The Water phase is shown in blue, the organic phase in red. pH adjustments are indicated as well as changes in Eppendorf tubes. - IAA is then analysed via high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with a reverse phase column.
- For this the HPLC system is run in an isocratic flow of 0.8 ml min-1 with a 40:60 mixture of buffer A (10% methanol, 0.3% acetate) and buffer B (90% methanol, 0.3% acetate). Peaks were identified by comparison with the standard substances with respect to retention time and UV spectrum using both a UV monitor and a fluorescence monitor.
- The amount of IAA in each sample was calculated using the volume of the IAA-peak and compare it with the volume of IAA peaks resulting from IAA standards with known amounts. This will give the amount of IAA per sample. The protein amount in microsomal, cytosolic and total protein fractions is determined by measuring absorbance at 280 nm by an UV-Vis Spectrophotometer (e.g., by Nanodrop Instrument ND-2000). With this data the amount of IAA per µg protein can be calculated (Figure 4).
- IAA is extracted by ethyl acetate phase separation (Park et al., 2003; Kriechbaumer et al., 2007) (Figure 2) from the enzyme assays prepared in section B. The whole sample of each assay is used for this procedure.
Representative data
To check for the purity of the microsomal fraction both the microsomal as well as the cytosolic fraction were probed with an anti-ZmNIT antibody detecting cytosolic nitrilases (Figure 3). This antibody was shown to detect the maize nitrilases 1 and 2 protein very specifically in various tissues in the range of ng mg-1 of total protein (Park et al., 2003; Kriechbaumer et al., 2007). The nitrilase band was only detectable in the cytosolic fraction indicating a rather pure microsomal fraction.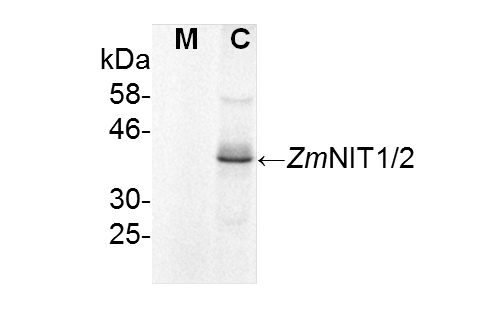
Figure 3. Immunoblot analysis for purity of microsomal fractions. Microsomal (M) and cytosolic (C) fractions were tested for nitrilase proteins using immunoblot analysis. 100 μg of protein from each fraction were probed with anti-ZmNIT1 antibodies (1:400) recognizing the cytosolic maize nitrilases 1 and 2. (Kriechbaumer et al., 2015).
Representative data for the conversion of tryptophan to IAA in maize coleoptiles and primary root is shown in Figure 4 [data from Kriechbaumer et al. (2015)].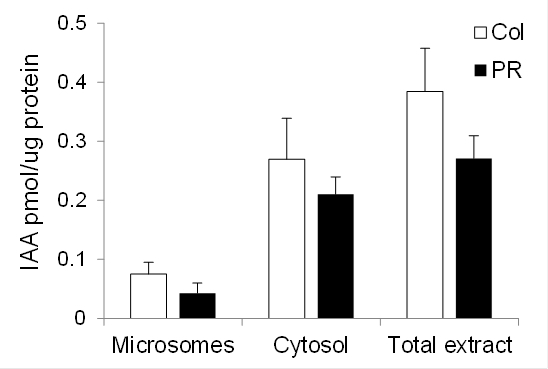
Figure 4. Auxin biosynthetic capacity in maize. Enzymatic conversion of tryptophan to IAA by microsomal (Microsomes) fractions, cytosolic (Cytosol) fractions, or total plant extract from maize coleoptiles (Col, white bars) and primary roots (PR, black bars) 4 d after germination. Standard errors are indicated. n = 2 (two biological samples with three technical replicates each).
Notes
- Collect plant material straight into a chilled falcon tube that is kept on ice and try to collect the material as quickly as possible.
- Pre-chill tubes, glassware, buffers, centrifuges etc and keep your samples on ice as much as possible.
- Where possible timewise freshly prepared microsomes should be used for enzyme assays. Freezing in 20% glycerol for later assays is possible but not recommended.
- Assays can be performed with any HPLC system (e.g., Dionex, Beckman…)
- It is advisable to at least confirm some data points using mass spectrometry to be sure that the correct molecule is being quantified.
Recipes
- Stock solutions
1 M TEA-HOAc (pH 7.5)
1 M KOAc (pH 7.5)
0.1 M Mg(OAc)2
1 M sucrose
1 M DTT
0.5 M EDTA
1 M Tris-HCl (pH 8.0)
1 M Na2CO3
0.1 M NADPH
0.1 M FAD
0.1 M IPyA
0.1 M Trp - Buffers
Note: Filter buffers 1-4 through 0.45 µm syringe filters. Add DTT from 1M stock fresh prior to use.- Buffers for microsome extraction
- Buffer 1
25 mM TEA-HOAc (pH 7.5)
50 mM KOAc (pH 7.5)
5 mM Mg(OAc)2
0.25 M sucrose
4 mM DTT - Buffer 2
100 mM TEA-HOAc (pH 7.5)
20 mM EDTA - Buffer 3
25 mM TEA-HOAc (pH 7.5)
25 mM KOAc (pH 7.5)
2 mM Mg(OAc)2
0.5 M sucrose
4 mM DTT - Buffer 4
25 mM TEA-HOAc (pH 7.5)
0.25 M sucrose
1 mM DTT
- Buffer 1
- Buffers for HPLC analysis
Buffer A: 10% methanol, 0.3% acetate
Buffer B: 90% methanol, 0.3% acetate
- Buffers for microsome extraction
Acknowledgments
This protocol was adapted from Kriechbaumer et al. (2015). This work was supported by a research scholarship from the Korean Federation of Science and Technology Societies (KOFST) awarded to Dr Verena Kriechbaumer and the British Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (grant No. BB/J004987/1 research grant awarded to Prof Chris Hawes.
References
- Abell, B. M., Holbrook, L. A., Abenes, M., Murphy, D. J., Hills, M. J. and Moloney, M. M. (1997). Role of the proline knot motif in oleosin endoplasmic reticulum topology and oil body targeting. Plant Cell 9(8): 1481-1493.
- Bernardi, J., Lanubile, A., Li, Q. B., Kumar, D., Kladnik, A., Cook, S. D., Ross, J. J., Marocco, A. and Chourey, P. S. (2012). Impaired auxin biosynthesis in the defective endosperm18 mutant is due to mutational loss of expression in the ZmYuc1 gene encoding endosperm-specific YUCCA1 protein in maize. Plant Physiol 160(3): 1318-1328.
- Chourey, P. S., Li, Q. B. and Kumar, D. (2010). Sugar-hormone cross-talk in seed development: two redundant pathways of IAA biosynthesis are regulated differentially in the invertase-deficient miniature1 (mn1) seed mutant in maize. Mol Plant 3(6): 1026-1036.
- Darwin, C. and Darwin, F. (1880). The power of movement in plants. John Murray.
- Kögl, F., Haagen-Smit, A. J. and Erxleben, H. (1934). Über ein neues Auxin (Heteroauxin) aus Harn. 11. Mitteilung über pflanzliche Wachstumsstoffe. Hoppe-Seyler’s Zeitschrift für Physiologisch Chemie 228: 90-103.
- Kriechbaumer, V., Park, W. J., Piotrowski, M., Meeley, R. B., Gierl, A. and Glawischnig, E. (2007). Maize nitrilases have a dual role in auxin homeostasis and beta-cyanoalanine hydrolysis. J Exp Bot 58(15-16): 4225-4233.
- Kriechbaumer, V., Seo, H., Park, W. J. and Hawes, C. (2015). Endoplasmic reticulum localization and activity of maize auxin biosynthetic enzymes. J Exp Bot 66(19): 6009-6020.
- Park, W. J., Kriechbaumer, V., Moller, A., Piotrowski, M., Meeley, R. B., Gierl, A. and Glawischnig, E. (2003). The Nitrilase ZmNIT2 converts indole-3-acetonitrile to indole-3-acetic acid. Plant Physiol 133(2): 794-802.
- Phillips, K. A., Skirpan, A. L., Liu, X., Christensen, A., Slewinski, T. L., Hudson, C., Barazesh, S., Cohen, J. D., Malcomber, S. and McSteen, P. (2011). Vanishing tassel2 encodes a grass-specific tryptophan aminotransferase required for vegetative and reproductive development in maize. Plant Cell 23(2): 550-566.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Kriechbaumer, V. (2016). ER Microsome Preparation and Subsequent IAA Quantification in Maize Coleoptile and Primary Root Tissue. Bio-protocol 6(9): e1805. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1805.
Category
Plant Science > Plant cell biology > Organelle isolation
Cell Biology > Organelle isolation > Microsome
Plant Science > Plant biochemistry > Plant hormone
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










