- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Analysis of Telomeric G-overhangs by in-Gel Hybridization
(*contributed equally to this work) Published: Vol 6, Iss 7, Apr 5, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1775 Views: 9094
Reviewed by: Tie LiuShyam SolankiTzvetina Brumbarova

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

A Novel Gene Stacking Method in Plant Transformation Utilizing Split Selectable Markers
Guoliang Yuan [...] Xiaohan Yang
Feb 20, 2025 1969 Views

Optimized Protocol for DNA Extraction in Three Theobroma Species
Angie F. Riascos-España [...] Pedro A. Velasquez-Vasconez
May 5, 2025 2050 Views

CAPS-Based SNP Genotyping for Nitrogen-Response Phenotypes in Maize Hybrids
Jannis Jacobs [...] Peter K. Lundquist
Dec 20, 2025 543 Views
Abstract
Telomeric DNA in majority of eukaryotes consists of an array of TG-rich tandem repeats. The TG-rich DNA strand is oriented with its 3’ end towards chromosome termini and is usually longer than its complementary CA-rich strand, thus forming 3’ single stranded overhang (G-overhang). G-overhangs arise from incomplete replication of chromosome termini by the lagging strand mechanism and post-replicative nucleolytic processing. The G-overhang is important for telomere protection as it serves as a binding platform for specific proteins and is required for t-loop formation. Hence, structure of telomeric G-overhang is an important indicator of telomere maintenance and functionality. Here we describe a method for analysis of G-overhangs in a model plant Arabidopsis thaliana by in-gel hybridization technique. This method allows relative quantification of the amount of single stranded telomeric DNA. Short telomeric probes are radioactively labeled and hybridized to DNA under non-denaturing conditions to specifically detect ssDNA. Total telomeric DNA can be measured using denaturing conditions in the same gel and this procedure usually follows the non-denaturing in-gel hybridization. Terminal nature of the ssDNA is verified by exonuclease treatment. This technique was originally developed in yeast and now is used as a major tool for G-overhang analysis in a variety of organisms ranging from human to plants.
Keywords: TelomereMaterials and Reagents
- Plastic wrap (common food wrap or FisherbrandTM Clear Plastic Wrap) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 22-305654 )
- Whatman® papers (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 3030917 )
- GeneJET Plant Genomic DNA Purification Kit (Life Technologies, catalog number: K0792 )
Note: Currently, it is “Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: K0792”. - T4 DNA polymerase (NEB, catalog number: M0203S )
- NEB buffer #2 (NEB, catalog number: B7002S )
- dNTPs (Life Technologies, catalog number: R0181 )
Note: Currently, it is “Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: R0181”. - Isopropanol
- Absolute ethanol (EtOH)
- HindIII (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: ER0501 )
- 3 M NaOAc (pH 5.2)
- DNA Gel Loading Dye (6x) (Life Technologies, catalog number: R0611 )
Note: Currently, it is “Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: R0611”. - PeqGold Universal agarose (VWR, catalog number: 732-2789 )
- Ethidium Bromide (EtBr) solution (1%) (Applichem, catalog number: A1152 )
- T4 polynucleotide kinase (PNK) (10 U/µl) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: EK0031 )
- Custom oligonucleotide probe, (TA3C3)4 or (TA3C3)3 (10 pmol/µl) (Sigma-Aldrich)
- γ32P-ATP (> 6,000 Ci/mmol) (HARTMANN ANALYTIC GmbH, catalog number: SRP-501 )
- QIAquick Nucleotide Removal Kit (QIAGEN, catalog number: 28304 )
- Tris
- Acetic acid
- EDTA (pH 8.0)
- NaCl
- Sodium citrate (pH 7.0)
- SDS
- Na-phosphate buffer (pH 7.2)
- BSA
- Tris-Cl (pH 8)
- 1x TAE (see Recipes)
- 20x SSC (see Recipes)
- Hybridisation buffer (see Recipes)
- Wash solution-1 (see Recipes)
- Wash solution-2 (see Recipes)
- Denaturation solution (see Recipes)
- Neutralization solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- EppendorfTM ThermoMixerTM C
- Centrifuge (Eppendorf AG)
- Horizontal Midi Gel Electrophoresis system (PerfectBlue Gel System Midi S, Peqlab)
- Gel DocTM XR+ System (Bio-Rad Laboratories)
- Gel dryer (Bio-Rad Laboratories, model: 583 )
- Imaging plate (Fujifilm, catalog number: BAS-IP MS 2025 )
Note: Currently, it is “GE Healthcare, catalog number: BAS-IP MS 2025”. - Vacuum pump (Gardner Denver Thomas GmbH, ILMVAC, catalog number: 412711 )
- Water bath with shaking
- Pharos FX Plus Molecular Imager (Bio-Rad Laboratories)
- PC with an image analysis software (e.g., Image Lab from Bio-Rad Laboratories)
Software
- Image Lab 5.1 (Bio-Rad Laboratories) (freely available at http://www.bio-rad.com/en-us/product/image-lab-software)
Procedure
- Non-denaturing in-gel hybridization
- Genomic DNA was prepared using standard procedures. DNA was prepared as method described in Kazda et al. (2012) or using GeneJET Plant Genomic DNA Purification Kit. When 2x CTAB DNA extraction procedure (Borevitz et al., 2003) was used, incubation was done at 55 °C (for 1 h) instead of 65 °C to reduce a risk of DNA melting.
- Negative control was generated by removing terminal G-overhangs with T4 DNA polymerase that has a strong 3’ exonuclease activity on ssDNA. Genomic DNA (2 µg) was treated with 30U of T4 DNA polymerase in presence of 0.1 mM dNTPs in total reaction volume of 200 µl of 1x NEB buffer #2. Reaction was incubated for 30 min at 37 °C. DNA was precipitated with 200 µl isopropanol, centrifuged 30 min at max speed at RT and washed with 70% EtOH. Resuspension of dry DNA was carried out at 37 °C in 175 µl dH2O. Samples were processed immediately.
- Samples and their T4 DNA polymerase pretreated negative controls (2 µg each) were digested with 50 U of HindIII in total reaction volume of 200 µl of 1x Buffer R. Reaction was incubated overnight at 37 °C. DNA was precipitated with 20 µl of 3 M NaAc (pH 5.2) and 200 µl of isopropanol, centrifuged 30 min at max speed at RT and washed with 70% EtOH. Resuspension of dry DNA was carried out at 37 °C in 20-25 µl dH2O. Samples were stored at -20 °C or processed immediately and 4-5 µl of DNA Gel Loading Dye (6x) was added.
- Digested DNA was separated using agarose gel electrophoresis. Gel was prepared in 1x TAE at a final concentration of 0.9% agarose. Samples were loaded and separated at 25 V for 15 h. DNA was stained by ethidium bromide. Gel was soaked in 200 ml of 2x SSC with 20 µl of 1% ethidium bromide at RT for 30 min while shaking.
- DNA was visualized by UV and picture was acquired using Gel DocTM XR+ System (Figure 1). Attention was paid that lanes were not over saturated (Figure 2, for accurate signal quantification).
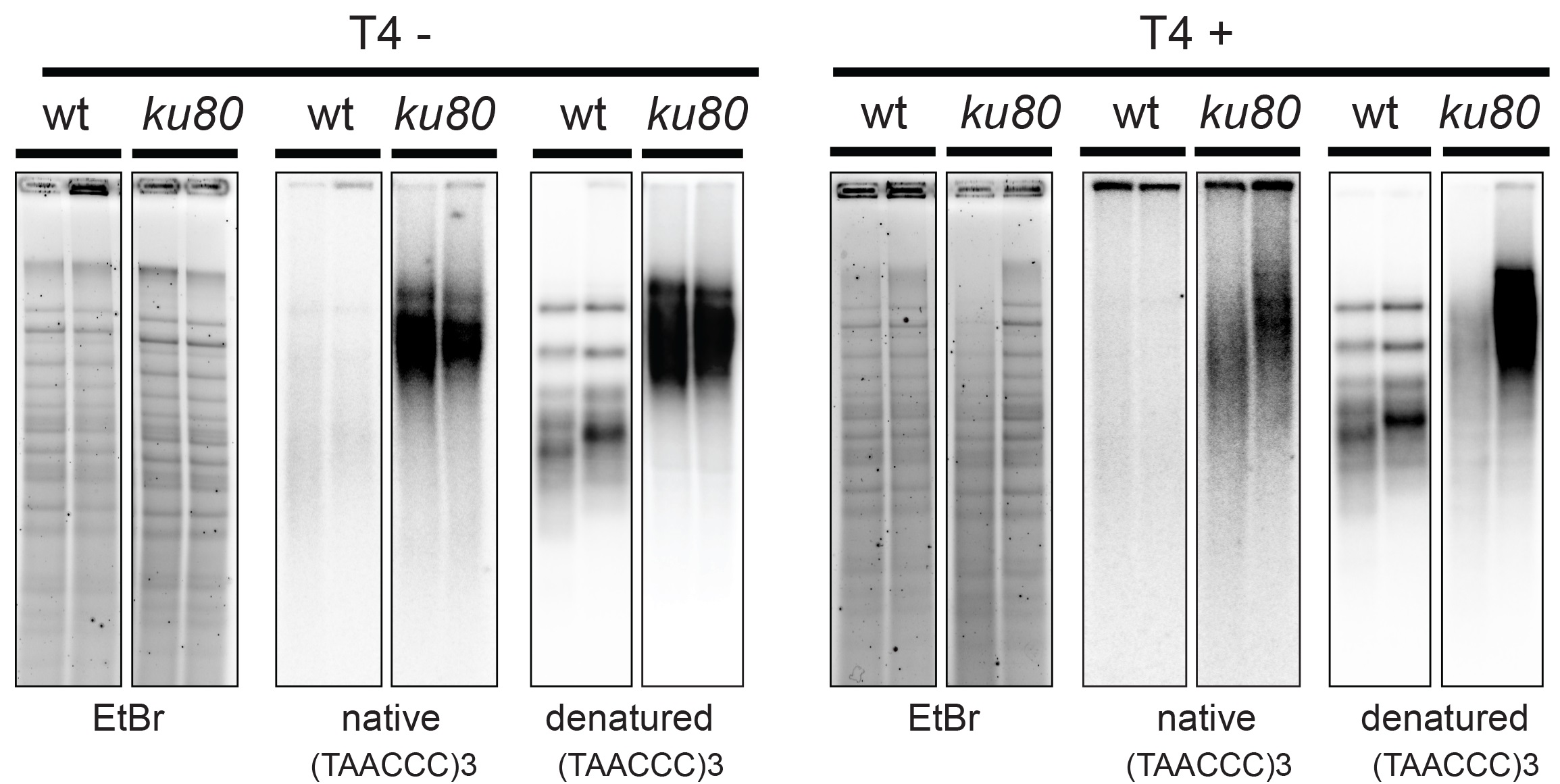
Figure 1. In-gel hybridization analysis of wild type and ku80 mutant A. thaliana. The digested DNA of two biological replicates of wild type (wt) and mutant (ku80) was separated on an agarose gel and hybridized with a radioactively labeled (TAAACCC) 3 probe first under native and then under denaturing conditions (left panel). The same procedure was used for T4 treated samples (right panel).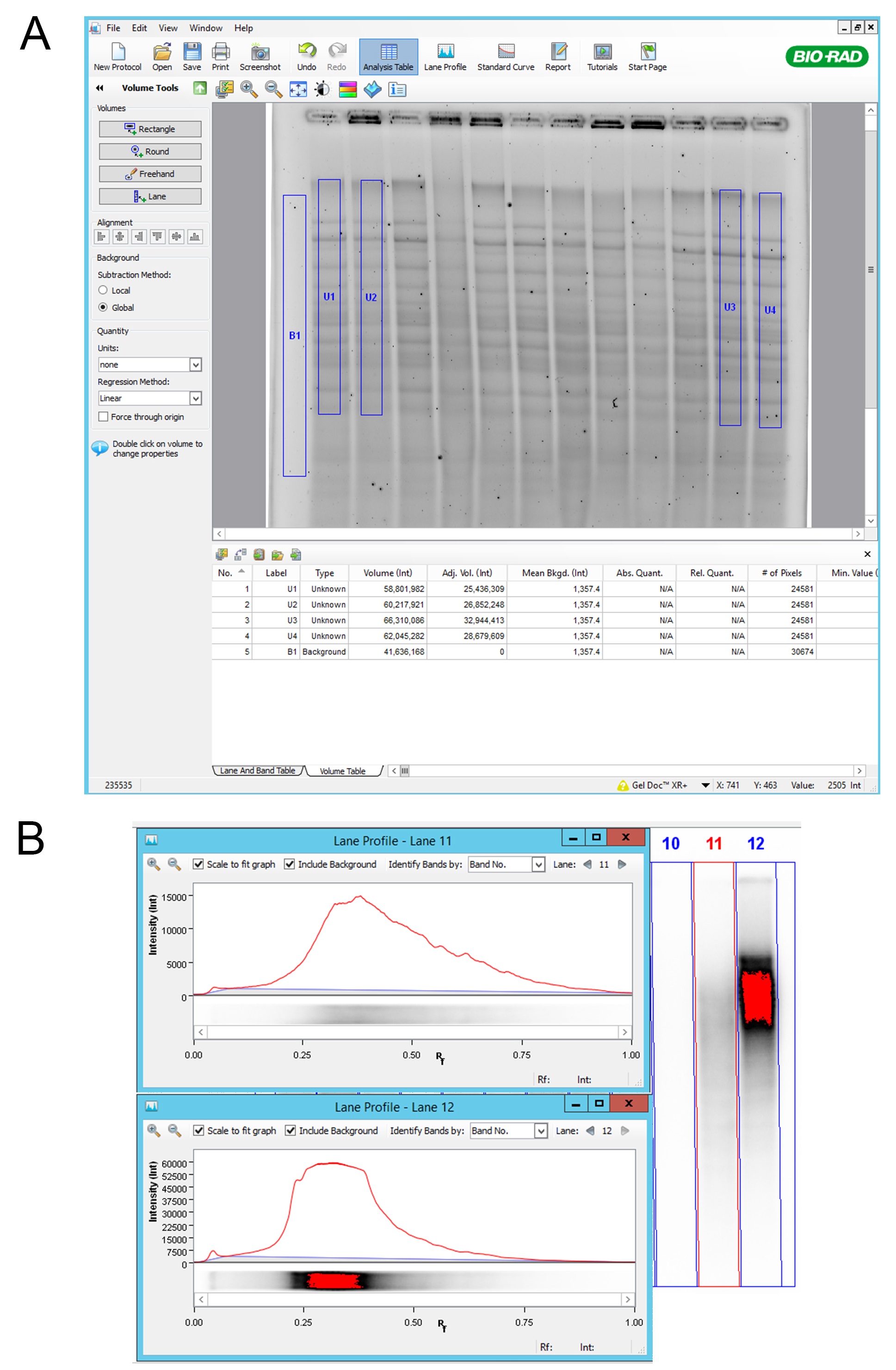
Figure 2. Volume analysis using Image Lab 5.1 software. A. “Rectangle”; Using “Rectangle” function in “Volume Tools”, we selected relevant lane area and background. Background subtraction was set to Global and “Adj. Vol.” values were exported for further analysis; B. Lane profile; Attention was paid that lanes were not showing the signal saturation. Saturation of the signal can be seen as red color in lane 12. In the lane profile we can see flattening of the signal peak where we cannot fully observe the total amount of the signal. - Agarose gel was dried using a gel drier. Gel was sandwiched between two Whatman papers and dried in a gel drier under vacuum at RT for 10 min per side. Gel was processed immediately.
- For G-overhang detection, 10 pmol of (TA3C3) 4 or (TA3C3) 3 oligonucleotide probe resuspended in dH2O was labeled in presence of 5 µl of γ-32P-ATP (> 6,000 Ci/mmol) using 10 U T4 PNK in total reaction volume of 20 µl of 1x PNK A Buffer. Reaction was incubated at 37 °C for 30 min and purified with QIAquick nucleotide removal kit according to manufacturer´s instructions.
- Dried gel was prehybridized in 50 ml hybridization buffer (in a plastic container) in 50 °C water bath with shaking (35 rpm) for 1-2 h. A heavy item was used to fix the container on the bottom of the water bath, so it does not float. Entire volume of purified probe was added and hybridized overnight at 50 °C in the water bath with shaking (35 rpm).
- Gel was removed from the hybridization solution and rinsed with wash solution-1 briefly, followed by two additional washes with wash solution-1 at RT, 35 rpm shaking for one hour. Later two washes with wash solution-2 at 38 °C, 35 rpm shaking for one hour was given.
- Gel was dried at RT between Whatman papers in gel drier under vacuum. Attention was paid not to over dry the gel (maximum 1 min drying time in total).
- Gel was wrapped in plastic wrap and exposed to imaging plate without a delay for up to 3 days at 4 °C to avoid contamination. Freezing and thawing causes gel to become brittle and was avoided.
- Signal was detected on Pharos FX (Figure 1).
- Genomic DNA was prepared using standard procedures. DNA was prepared as method described in Kazda et al. (2012) or using GeneJET Plant Genomic DNA Purification Kit. When 2x CTAB DNA extraction procedure (Borevitz et al., 2003) was used, incubation was done at 55 °C (for 1 h) instead of 65 °C to reduce a risk of DNA melting.
- Denaturing in-gel hybridization
This procedure usually follows the non-denaturing in-gel hybridization to detect total telomeric DNA in analyzed samples.- Gel was unwrapped and DNA was denatured by soaking and rocking gel lightly in denaturing solution (100-200 ml) for 30 min at RT (35 rpm).
- Denaturing solution was removed and gel was rinsed with dH2O prior to adding neutralization solution (100-200 ml) for 15 min at RT.
- Equilibration was done in 100-200 ml of 5x SSC for 15 min at RT and gel was prehybridized in 50 ml hybridization solution for 1 h as indicated previously.
- Hybridization was done overnight with the same probe and conditions as was used for the non-denaturing in-gel hybridization.
- Washing and exposure were done as for the non-denaturing in-gel hybridization. Shorter exposure (1 d) is usually sufficient for detecting strong signal (Figure 1).
- Gel was unwrapped and DNA was denatured by soaking and rocking gel lightly in denaturing solution (100-200 ml) for 30 min at RT (35 rpm).
- Signal calculation by “Image Lab 5.1” software
The G-overhang signal from samples is normalized to DNA loading determined by ethidium bromide staining, and calculated by subtracting corresponding negative control pretreated with T4 DNA polymerase.- EtBr gel (loading control)
- “Volume tools” “Rectangle” was used for quantification.
- Selected area. Always the same rectangle was used for all lanes (first rectangle was copied and pasted). The area was selected in a way that the whole lane is covered as best as possible. However, the area around the lanes was not included in the rectangle (Figure 2A).
- Selected background. The “Global” subtraction method was used and the rectangle was also used for this purpose (Figure 2A).
- Selected area. Always the same rectangle was used for all lanes (first rectangle was copied and pasted). The area was selected in a way that the whole lane is covered as best as possible. However, the area around the lanes was not included in the rectangle (Figure 2A).
- “Analysis table” was used.
- Values were copied to clip board and transferred to excel. Attention was paid to decimal point. Adjusted values “Adj. Vol.” were used (values corrected for background by the software Figure 2A).
- Ratio was calculated (highest value “wt_high” was set to 1, other value “mut” - was corrected, Figure 3A).
X= EtBr (“Adj. Vol.”) / EtBr (highest “Adj. Vol.”)
e.g. wt_high=5,000 and mut=3,000 -> Xmut= 3,000/5,000= 0.6
-> Xwt= 5,000/5,000= 1.0
- Values were copied to clip board and transferred to excel. Attention was paid to decimal point. Adjusted values “Adj. Vol.” were used (values corrected for background by the software Figure 2A).
- “Volume tools” “Rectangle” was used for quantification.
- Native gel (G-overhang signal)
- Volume analysis was done as previously.
- Adjusted values were corrected for loading (T4 untreated and T4 treated samples, Figure 3A).
Y= native (“Adj. Vol.”) / X
e.g. mut= 4,500 and Xmut= 0.6 -> Ymut= 4,500/0.6= 7,500
wt = 5,000 and Xwt=1.0 -> Ywt= 5,000/ 1.0= 5,000 - Values were corrected for T4 treatment. Values were subtracted from T4 treated sample.
Z= Y(T4-) – Y(T4+)
e.g. Ymut= 7,500 and Ymut_T4= 1,200 -> Zmut= 6,300
Ywt= 5,000 and Ywt_T4= 1,000 -> Zwt= 4,000
- Volume analysis was done as previously.
- Ratio calculation (set highest wild type control sample “highest wt” to 1, Figure 3A).
A= Z / Z(highest wt)
e.g. Zwt= 4,000 and Zmut= 6,300 -> Amut= 6,300/4,000= 1,575
-> Awt= 1.0 - Graphical representation
Relative values from the point 3 are used to present the result of the analysis in a graph (Figure 3B).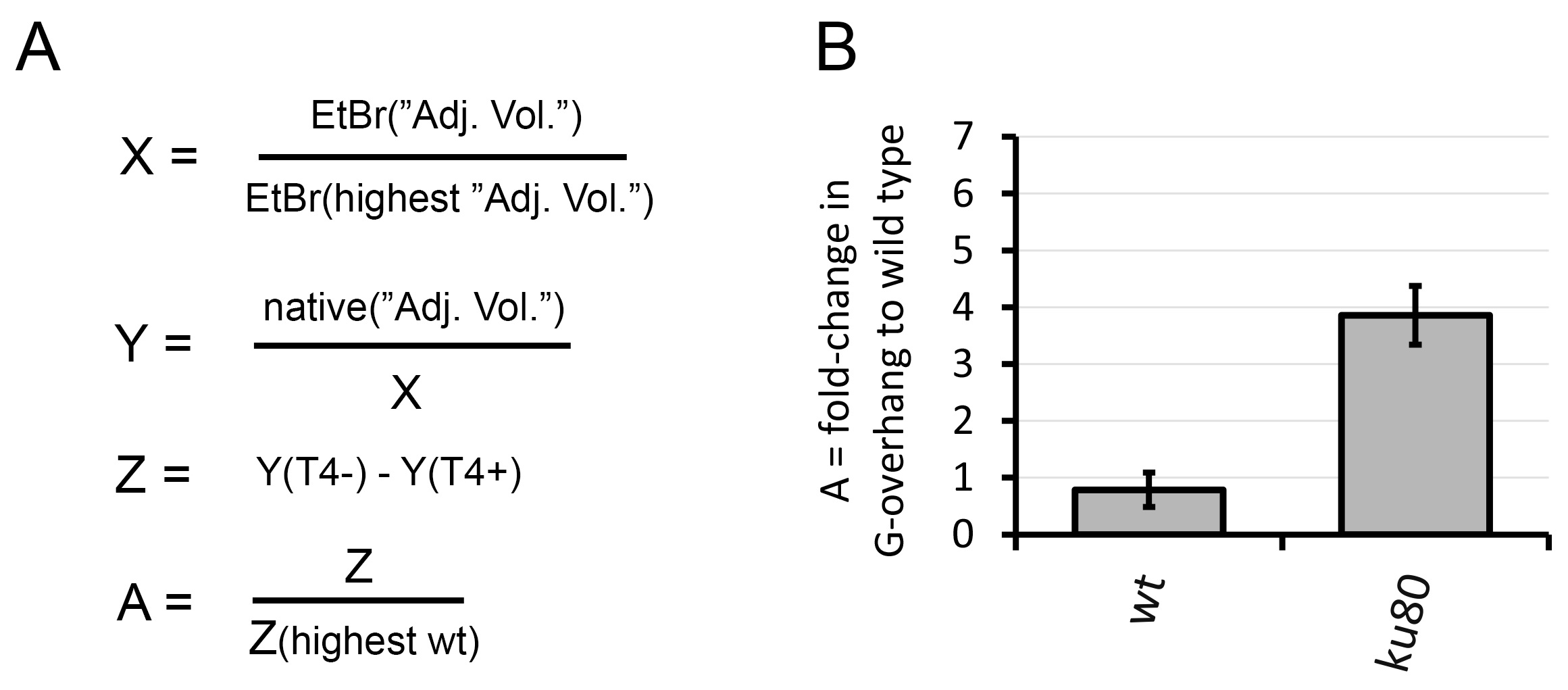
Figure 3. Graphical representation of the In-gel hybridization analysis. A. Signal calculation; Signal from the EtBr gel was used to create a loading ratio (X). Signal from the native gel hybridization was first corrected for DNA loading (Y) and signal from T4 treated samples was subtracted from not treated samples (Z). A fold change in G-overhang was calculated to the wt sample with the highest value of Z (A); B. Relative quantification of the G-overhang signal; The relative G-overhang signal (calculated ratio) is represented as average fold changes in G-overhang signal relative to wild type with highest signal.
- EtBr gel (loading control)
Recipes
- 1x TAE
40 mM Tris
20 mM acetic acid
1 mM EDTA (pH 8) - 20x SSC
3.0 M NaCl
0.3 M sodium citrate (pH 7.0)
Dilute accordingly - Hybridization buffer
7% SDS
0.25 M Na-phosphate buffer (pH 7.2)
0.1 g/L BSA - Wash solution-1
0.25 x SSC
0.01% SDS - Wash solution-2
0.25 x SSC - Denaturation solution
150 mM NaCl
0.5 M NaOH - Neutralization solution
150 mM NaCl
0.5 M Tris-Cl (pH 8)
Acknowledgments
This protocol was used to analyze G-overhang structure in Arabidopsis (Kazda et al., 2012; Derboven et al., 2014) and was adapted from the previously published studies Dionne et al. (1996), Wei et al. (2002) and Heacock et al. (2007). This work was supported by the EMBO installation grant (1304130933) and the program SoMoPro II (3SGA5833) co-financed by EU and the South Moravian Region. This publication reflects only the author's views and the Union is not liable for any use that may be made of the information contained therein.
References
- Borevitz, J. O., Liang, D., Plouffe, D., Chang, H. S., Zhu, T., Weigel, D., Berry, C. C., Winzeler, E. and Chory, J. (2003). Large-scale identification of single-feature polymorphisms in complex genomes. Genome Res 13(3): 513-523.
- Derboven, E., Ekker, H., Kusenda, B., Bulankova, P. and Riha, K. (2014). Role of STN1 and DNA polymerase alpha in telomere stability and genome-wide replication in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet 10(10): e1004682.
- Dionne, I. and Wellinger, R. J. (1996). Cell cycle-regulated generation of single-stranded G-rich DNA in the absence of telomerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93(24): 13902-13907.
- Heacock, M. L., Idol, R. A., Friesner, J. D., Britt, A. B. and Shippen, D. E. (2007). Telomere dynamics and fusion of critically shortened telomeres in plants lacking DNA ligase IV. Nucleic Acids Res 35(19): 6490-6500.
- Kazda, A., Zellinger, B., Rossler, M., Derboven, E., Kusenda, B. and Riha, K. (2012). Chromosome end protection by blunt-ended telomeres. Genes Dev 26(15): 1703-1713.
- Wei, C., Skopp, R., Takata, M., Takeda, S. and Price, C. M. (2002). Effects of double-strand break repair proteins on vertebrate telomere structure. Nucleic Acids Res 30(13): 2862-2870.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Valuchova, S., Derboven, E. and Riha, K. (2016). Analysis of Telomeric G-overhangs by in-Gel Hybridization. Bio-protocol 6(7): e1775. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1775.
Category
Plant Science > Plant molecular biology > DNA
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link