- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Detection of Protein Oxidative Activity Using Reduced RNase A
Published: Vol 6, Iss 6, Mar 20, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1766 Views: 7385
Reviewed by: Valentine V TrotterKristin ShinglerAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

H2 Production from Methyl Viologen–Dependent Hydrogenase Activity Monitored by Gas Chromatography
Nuttavut Kosem
Dec 5, 2023 1763 Views

Monitoring Protein Stability In Vivo Using an Intein-Based Biosensor
John S. Smetana [...] Christopher W. Lennon
Apr 20, 2025 1579 Views

Endo-1,4-β-D-xylanase Assay Using Azo-Xylan and Variants Thereof
Luca Bombardi [...] Salvatore Fusco
Apr 20, 2025 1920 Views
Abstract
This assay allows to determine whether proteins possess oxidative activity-the ability to introduce disulfide bond in vitro. The substrate for potential oxidases is a ribonuclease A which, for its activity, needs 4 properly formed disulfide bonds (Raines, 1998).
RNase A activity can be detected by:
- Monitoring the digestion of RNA (Lambert and Freedman, 1983);
- Methylene Blue assay (Greiner-Stoeffele et al., 1996);
- Analyzing the cleavage of the cyclic CMP (Lyles and Gilbert, 1991; Lyles and Gilbert, 1991).
Oxidative activity will be tested by measuring spectrophotometrically RNase A cleavage of cyclic-2’, 3’-cytidinemonophosphate (cCMP) to 3’-cytidinemonophosphate (3’ CMP), which results in an increase in absorption at 296 nm.
The reaction equation: RNase A +2’ 3’-cCMP→RNase A + 3’ CMP.
Keywords: Thiol oxidoreductases
Materials and Reagents
- Flat-bottomed clear 96-well microplates (Optimum Line, catalog number: GP700 )
- Ribonuclease A from bovine pancreas (RNase A) (store -20 °C) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: R6513-10 mg )
- Desalting columns-Biorad Econo-Pac 10DG Desalting Columns, 30 units (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 7322010 )
- Bio-Scale Mini Profinity IMAC Cartridges (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 7324614 )
- ENrichTM SEC 70 size exclusion columns (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 7801070 )
- PierceTM Protein Concentrators, 9K MWCO (7 ml) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 89884A ) or Amicon Ultra-4 Centrifugal Filter Unit with Ultracel-10 membrane (EMD Millipore Corporation, catalog number: UFC801008 )
- Proteins of interest (purified to homogeneity proteins, concentration approx 7-8 mg/ml)
- Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P4417-50TAB )
- L-Glutathione oxidized disodium salt (GSSG) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G4626-100 mg )
- L-Glutathione reduced (GSH) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G6529-1 g )
- DL-Dithiothreitol (DTT) (AppliChem GmbH, catalog number: 3483-12-3 ; Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 43815-1 G )
- Guanidine hydrochloride (Gdn-HCl) (AppliChem GmbH, catalog number: A11061000 )
- 1 M Tris (pH 8.0) (Eurx, catalog number: E0273-01 )
- 0.5 M EDTA (pH 8.0) (Eurx, catalog number: E240-01 )
- DTNB (Ellman’s Reagent) (5, 5-dithio-bis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 22582 )
- Sodium phosphate dibasic (pH 8.0) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S3264-250 G )
- Cytidine 2’:3’-cyclic monophosphate monosodium salt (cCMP) (store -20 °C) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C9630-100 mg )
- 2x Reaction buffer (see Recipes)
- Reduction buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Plate reader (Tecan, Infinite®, model: 200 PRO series )
Procedure
- Preparation of proteins for assay (approx 1 week) (Chim et al., 2013)
- Purify proteins.
Note: We overexpressed proteins by autoinduction (Studier, 2005) and then purified by affinity chromatography using the NGC chromatography system (see Optional materials). - To obtain higher purity, load your proteins onto size exclusion columns and elute with PBS.
- Determine the amount of protein by nanodrop.
- Oxidize proteins with 50 mM oxidized glutathione (GSSG) and incubate for 1 h at RT (5-7 mg in 1 ml).
- Exchange buffer on desalting columns according to manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Determine the amount of protein by nanodrop.
- Follow the Ellman assay to confirm proper redox state.
- Concentrate if necessary (using protein concentration columns). For this assay you need approx 3 mg/ml.
- Use fresh or in the next couple of days.
- Purify proteins.
- Reduction and denaturation of RNase A (2 days) (Daniels et al., 2010)
- Resuspend 10 mg of RNase A in 1 ml of reduction buffer (in 1.5 ml tube).
Note: 10 mg of RNase A permit to perform approx. 20 assays. - Incubate overnight at RT without shaking.
- Desalinate on columns and elute with PBS (according to manufacturer’s guidelines).
- Determine the amount of protein by nanodrop.
- If necessary, concentrate (for Ellman assay you need 2.5 mg/ml of RNase A).
- Follow the Ellman assay to confirm proper redox state.
- Use the same day.
- Resuspend 10 mg of RNase A in 1 ml of reduction buffer (in 1.5 ml tube).
- Oxidative folding of reduced RNase A (1 day) (Daniels et al., 2010)
- Prepare 2x reaction buffer.
- Prepare mixture of protein and reduced RNase A in a volume of 100 μl (add PBS if necessary) in a 96-well plate (40 μM protein and 20 μM RNase A).
Note: With concentration of 2.5 mg/ml you need to add 11 μl to the well to achieve 20 μM of RNase A. - Add 100 μl of 2x reaction buffer to the mixture of protein and RNase A; mix gently by pipetting up and down.
- Insert plate into the plate reader and start program.
- Prepare 2x reaction buffer.
Representative data
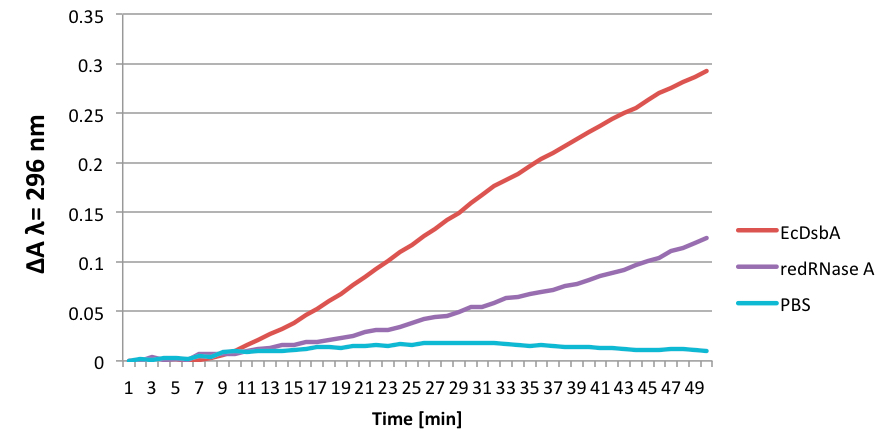
Figure 1. The results from one representative experiment. EcDsbA stands for main oxidase in E. coli.
Notes
- Notes about microplate reader settings (Table 1).
Table 1. Universal settings for microplate reader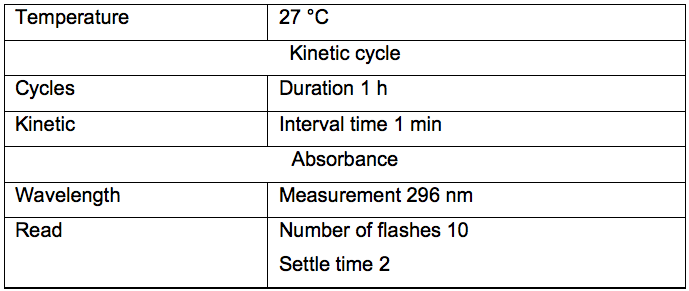
Recipes
- 2x reaction buffer
200 mM Tris/HCl (pH 8.0)
4 mM EDTA
0.4 mM GSSG
2 mM GSH
9 mM cCMP - Reduction buffer
100 mM Tris/HCl (pH 8.0)
6 M Gdn-HCl
140 mM DTT
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the National Science Centre (grant No. 2012/05/B/NZ1/00039).
References
- Chim, N., Harmston, C. A., Guzman, D. J. and Goulding, C. W. (2013). Structural and biochemical characterization of the essential DsbA-like disulfide bond forming protein from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. BMC Struct Biol 13: 23.
- Daniels, R., Mellroth, P., Bernsel, A., Neiers, F., Normark, S., von Heijne, G. and Henriques-Normark, B. (2010). Disulfide bond formation and cysteine exclusion in gram-positive bacteria. J Biol Chem 285(5): 3300-3309.
- Greiner-Stoeffele, T., Grunow, M. and Hahn, U. (1996). A general ribonuclease assay using methylene blue. Anal Biochem 240(1): 24-28.
- Lambert, N. and Freedman, R. B. (1983). Kinetics and specificity of homogeneous protein disulphide-isomerase in protein disulphide isomerization and in thiol-protein-disulphide oxidoreduction. Biochem J 213(1): 235-243.
- Lyles, M. M. and Gilbert, H. F. (1991). Catalysis of the oxidative folding of ribonuclease A by protein disulfide isomerase: dependence of the rate on the composition of the redox buffer. Biochemistry 30(3): 613-619.
- Lyles, M. M. and Gilbert, H. F. (1991). Catalysis of the oxidative folding of ribonuclease A by protein disulfide isomerase: pre-steady-state kinetics and the utilization of the oxidizing equivalents of the isomerase. Biochemistry 30(3): 619-625.
- Raines, R. T. (1998). Ribonuclease A. Chem Rev 98(3): 1045-1066.
- Studier, F. W. (2005). Protein production by auto-induction in high density shaking cultures. Protein Expr Purif 41(1): 207-234.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Grzeszczuk, M., Bocian-Ostrzycka, K., Lasica, A. and Jagusztyn-Krynicka, E. K. (2016). Detection of Protein Oxidative Activity Using Reduced RNase A. Bio-protocol 6(6): e1766. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1766.
Category
Microbiology > Microbial biochemistry > Protein > Activity
Biochemistry > Protein > Activity
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










