- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
LC/MS-based Detection of Hydroxyproline O-galactosyltransferase Activity
Published: Vol 6, Iss 2, Jan 20, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1711 Views: 7715
Reviewed by: Renate WeizbauerHarrie van ErpAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

A Semi-throughput Procedure for Assaying Plant NADP-malate Dehydrogenase Activity Using a Plate Reader
Kevin Baudry and Emmanuelle Issakidis-Bourguet
Aug 20, 2023 1466 Views

An in vitro Assay to Probe the Formation of Biomolecular Condensates
Yu Zhang and Shen Lisha
Sep 5, 2023 3197 Views

Immunofluorescence for Detection of TOR Kinase Activity In Situ in Photosynthetic Organisms
Ana P. Lando [...] Giselle M. A. Martínez-Noël
Dec 20, 2024 1813 Views
Abstract
Arabinogalactan proteins (AGPs) are plant-specific extracellular glycoproteins regulating a variety of processes during growth and development. AGP biosynthesis involves O-galactosylation of hydroxyproline (Hyp) residues followed by a stepwise elongation of the complex sugar chains. The initial Hyp O-galactosylation is mediated by Hyp O-galactosyltransferase (HPGT) that catalyzes the transfer of a D-galactopyranosyl residue to the hydroxyl group of Hyp residues of peptides from the sugar donor UDP-α-D-galactose (Figure 1). Here we describe a LC/MS-based method for the detection of HPGT activity in vitro.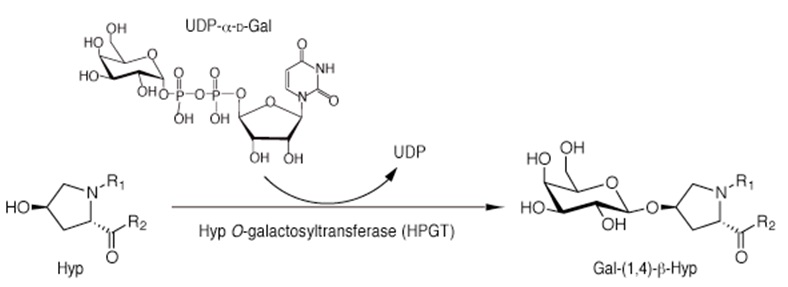
Figure 1. Reaction scheme for Hyp galactosylation by HPGT. HPGT catalyzes the addition of a D-galactopyranose from an UDP-α-D-Gal to the hydroxylgroup of Hyp residues.
Materials and Reagents
- 1-week-old Arabidopsis T-87 cells (50 g fresh weight)
- Bio-Rad Protein Assay (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 5000006JA )
- 2 mM synthesized substrate peptide [e.g., (OAOSOT)3S] [using standard Fmoc solid-phase synthesis chemistry on a 431A peptide synthesizer (Life Technologies)]
- 2 mM Uridine 5’-diphosphogalactose disodium salt (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: U4500 )
- 1 M MOPS-KOH (pH 7.0)
- 10 mM MnCl2
- 10% TX-100
- 1% Formic acid
- Acetonitrile (HPLC grade) containing 0.1% formic acid
- Water (HPLC grade) containing 0.1% formic acid
- Tris-HCl (pH 7.0)
- MgCl2
- Dithiothreitol
- Leupeptin
- Phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride
- Sucrose
- Extraction buffer (see Recipes)
- Suspension buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Waring blender
- Miracloth (Merck Millipore Corporation, catalog number: 475855 )
- Ultracentrifuge
- 30 °C incubator
- Micro centrifuge
- Semi-micro HPLC system (JASCO International Co., model: Micro21LC )
- LCQ Deca XP-plus ESI ion-trap mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific)
- TSK-gel Amide-80 (3 μm) column (2 x 150 mm) (Tosoh Bioscience LLC, catalog number: 21865 )
Procedure
- Preparation of Arabidopsis microsomal membranes
- Arabidopsis T-87 cells are maintained on a 1-week culture interval under continuous darkness at 22 °C with shaking at 120 rpm.
- Suspend 1-week-old Arabidopsis T-87 cell (50 g fresh weight) in 20 ml Extraction buffer.
- Cool off to 4 °C on ice.
- Homogenize at 20,000 rpm for 5 min at 4 °C in a Waring blender.
- Cool off to 4 °C on ice.
- Filter the slurry through two layers of Miracloth.
- Centrifuge the filtrate at 3,000 x g for 15 min at 4 °C.
- Centrifuge the supernatant at 100,000 x g for 30 min at 4 °C.
- Suspend the pellet (microsomal membranes: approximately 150 μg/μl) in 500 μl Suspension buffer by gentle pipetting.
- Determine the protein concentration by conventional Bradford assay according to the manufacturer’s protocol (Bio-Rad Protein Assay).
- Arabidopsis T-87 cells are maintained on a 1-week culture interval under continuous darkness at 22 °C with shaking at 120 rpm.
- Hyp O-galactosyltransferase activity assay
- Set up 20 μl HPGT assay reactions in 0.5 ml microcentrifuge tube as follows.
HPGT assay components Amount per reaction 1 M MOPS-KOH (pH 7.0) 2 μl 2 mM UDP-α-D-galactose 5 μl 10 mM MnCl2 2 μl 10% TX-100 2 μl 2 mM substrate peptide 1 μl Arabidopsis T-87 microsomal membranes 30 μg protein equivalent WaterTotal 20 μl - Incubate at 30 °C, 1 h.
- Add 2 μl 1% formic acid to stop reaction.
- Add 80 μl acetonitrile.
- Centrifuge at 20,000 x g for 5 min.
- Set up 20 μl HPGT assay reactions in 0.5 ml microcentrifuge tube as follows.
- LC/MS analysis
10 μl aliquots of the assay solution were analyzed by LC-MS using a micro HPLC (high pressure liquid chromatography) system connected to an LCQ Deca XP-plus ESI ion-trap mass spectrometer. Chromatographic separation is performed by normal-phase HPLC on a TSK-gel Amide-80 (3 μm) column (2 x 150 mm).- The mobile phase is composed of HPLC grade water containing 0.1% formic acid (eluent A) and HPLC grade acetonitrile containing 0.1% formic acid (eluent B). The column temperature is maintained at 25 °C.
- The HPLC flow rate is 100 μl/min, and the elution gradient was 60 to 30% B over 15 min.
- The HPLC eluate was introduced into an electrospray ionization (ESI) ion-trap mass spectrometer in the positive ionization mode.
- MS source parameters are as follows [e.g., (OAOSOT)3S peptide]:
- Capillary temperature: 200 °C
- Capillary voltage: 42 V
- Source voltage: 5 kV
- Source current: 8.5 μA
- Sheath gas flow: 50
- Aux gas flow: 0
- Sweep gas flow: 0
- The mass range: m/z 500-2,000
- Capillary temperature: 200 °C
- The mass spectra are obtained by selected ion monitoring. [e.g., (OAOSOT)3S: m/z 951.1, Galactosylated product: m/z 1032.2] (Figure 2).
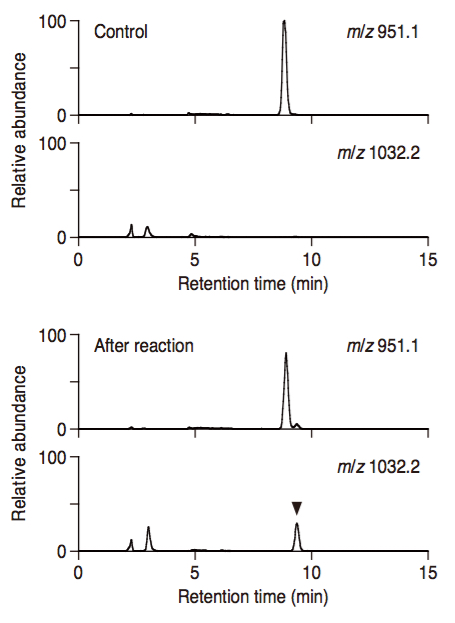
Figure 2. Selected ion chromatogram of substrate peptide and the galactosylated product. Substrate peptide was incubated with solubilized membrane fractions in the presence of UDP-α-D-galactose, then analyzed by LC-MS with selected ion monitoring of the substrate (m/z 951.1) and the galactosylated product (m/z 1032.2).
- The mobile phase is composed of HPLC grade water containing 0.1% formic acid (eluent A) and HPLC grade acetonitrile containing 0.1% formic acid (eluent B). The column temperature is maintained at 25 °C.
Recipes
- Extraction buffer (prepare freshly and keep on ice)
25 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.0)
10 mM MgCl2
2 mM dithiothreitol
2 μM leupeptin
2 mM phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride
250 mM sucrose - Suspension buffer
10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.0)
250 mM sucrose
Acknowledgments
This is the detailed protocol for the detection of HPGT activity described by Ogawa-Ohnishi and Matsubayashi (2015). This research was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (S) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (No. 25221105).
References
- Ogawa-Ohnishi, M. and Matsubayashi, Y. (2015). Identification of three potent hydroxyproline O-galactosyltransferases in Arabidopsis. Plant J 81(5): 736-746.
- Ogawa-Ohnishi, M., Matsushita, W. and Matsubayashi, Y. (2013). Identification of three hydroxyproline O-arabinosyltransferases in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Chem Biol 9(11): 726-730.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Ogawa-Ohnishi, M. and Matsubayashi, Y. (2016). LC/MS-based Detection of Hydroxyproline O-galactosyltransferase Activity. Bio-protocol 6(2): e1711. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1711.
Category
Plant Science > Plant biochemistry > Protein > Activity
Biochemistry > Carbohydrate > Glycoprotein
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









