- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Agrobacterium-mediated Transformation of Mature Ginseng Embryos
Published: Vol 4, Iss 24, Dec 20, 2014 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1362 Views: 12283
Reviewed by: Tie Liu

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Bi-directional Dual-flow-RootChip for Physiological Analysis of Plant Primary Roots Under Asymmetric Perfusion of Stress Treatments
Claudia Allan [...] Claudia-Nicole Meisrimler
Aug 5, 2023 1941 Views

A Novel Gene Stacking Method in Plant Transformation Utilizing Split Selectable Markers
Guoliang Yuan [...] Xiaohan Yang
Feb 20, 2025 1968 Views

Enzymatic Starch Quantification in Developing Flower Primordia of Sweet Cherry
Nestor Santolaria [...] Afif Hedhly
Apr 5, 2025 1885 Views
Abstract
Ginseng refers to species within the genus Panax and is a slow-growing perennial herb from the Araliaceae family. The most widely used Panax species is Panax ginseng Meyer (Korean ginseng). Panax japonicus (Japanese ginseng), Panax notoginseng (Chinese ginseng), and Panax quinquefolium (American ginseng). Due to the various pharmaceutical importance of ginsenosides, ginseng plant has been cultivated for its highly valued root over 2,000 years as a medicinal plant in East Asian countries particularly in China, Korea, and Japan and North America. Korean ginseng (Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer) consists of nine cultivars from three Jakyung, Chungkyung, and Hwangsook lines. Cultivar “Yunpoong” has characteristics to have more axillary shoots and lateral roots compared to other cultivars. Thus “Yunpoong”: Ginseng seeds are relatively more feasible for regeneration of adventitious roots during gene transformation. Here, we describe how to prepare and treat ginseng seeds after harvest till the ginseng immature embryos are ready for the germination, and to be used in Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated gene transformation.
Keywords: Panax ginsengMaterials and Reagents
- Ginseng seeds, in which zygotic embryos were in a mature state (4 mm in length)
- Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58C1 (pMP90) strain
- Binary (pCAMBIA1390) vector
- MS powder (Duchefa Biochemie, catalog number: M0222 )
- Sucrose (Duchefa Biochemie, catalog number: S0809 )
- 2-(N-morpholino) ethanesulfonic acid (MES) monohydrate (MB cell, catalog number: MB-M4837 )
- Phytoagar (Duchefa Biochemie, catalog number: P1003) or Gelrite (Duchefa Biochemie, catalog number: G1101)
- Yeast extract (Duchefa Biochemie, catalog number: Y1333 )
- Peptone (Duchefa Biochemie, catalog number: P1328 )
- NaCl (Affymetrix, catalog number: 4171746 )
- Bactoagar (BD, catalog number: 214010 )
- Hygromycin (Duchefa Biochemie, catalog number: H0192 )
- Kanamycin (Duchefa Biochemie, catalog number: K0126 )
- Cefotaxime (Duchefa Biochemie, catalog number: C0111 )
- 6-benzylaminopurine (BAP) (Duchefa Biochemie, catalog number: B0904 )
- 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) (Duchefa Biochemie, catalog number: D0911 )
- Indole-3-butyric acid (IBA) (Duchefa Biochemie, catalog number: I0902 )
- Sucrose
- Phyto agar
- 70% ethyl alcohol (EtOH)
- 2% (v/v) sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 425044-1L )
- B5 medium (Duchefa Biochemie, catalog number: G0209 )
- MS (Murashige & Skoog) medium (see Recipes)
- YEP medium (see Recipes)
- Antibiotics stock solution (in ddH2O) (see Recipes)
- Plant growth regulators stock solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Laminar flow cabinet (HEPA filter 99.99% efficient on particle of 0.3 μ and vertical type)
- Shaking incubator (100~200 rpm on a gyratory shaker)
- Centrifuge (3,000 x g) (Labnet International, catalog number: C2500-R-230V )
- Micropipette
- Forceps (Phoenix Technologies, catalog number: ESD-16 )
- Erlenmeyer flask (50/100 ml) or autoclavable plastic tube for seed sterilization
- Autoclave machine
- Growth chamber (23 °C ± 2 °C)
- Sterile filter paper
- Petri dish
Procedure
- Korean ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer cv. “Yunpoong”) (Lee et al., 2011) seeds were stratified in humidified sand at 15 °C for 4 months (Figure 1) since the zygotic embryo right after the harvest were in an immature globular stage (about 200 μm in length).
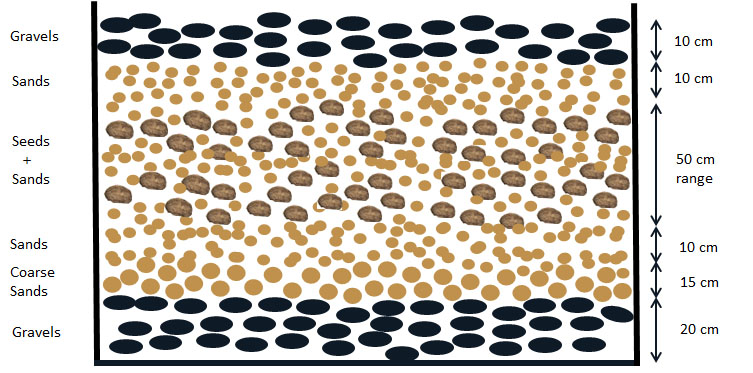
Figure 1. Diagram of ginseng seeds stratification. Ginseng seeds were stacked as depicted in the diagram inside of square cement pad or wooden square box. The seeds were mixed with river sand 1:3 (seed:sand) or often sandwiched in net bag with sand on top and down and kept at 15 ~20 °C, 10~15% moisture by watering once or twice a day. Sand within 2 mm size is good and coarse sand within 4 mm.
- Then the seeds were further stratified for 100 days at 2-4 °C to break seed dormancy. After stratification for about 6.5 -7 months, the zygotic embryos reach in mature stage (Figure 2C-D, about 4.0-4.5 mm in length), which means the seeds are ready to germinate.
- Once uncover the hard seed coat using fingers, the seeds were immersed in 70% (v/v) EtOH for 1 min, surface sterilized in 2% (v/v) NaOCl for 15 min, and washed three times with sterilized distilled water (Figure 2A-B) in the clean bench (Figure 2A). The zygotic embryos from the seed were carefully dissected using fingers and forceps, placed on MS (Murashige and Skoog, 1962) basal medium vertically containing 3% (w/v) sucrose and 0.8% (w/v) phytoagar, and grown for 5-10 days (Figure 3A).
- An Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58C1 (pMP90) (Bechtold and Pelletier, 1998) strain containing a plant binary vector (pCAMBIA1390) harboring gene of interest was cultured in 5 ml of YEP liquid medium overnight (170 rpm for 20 h) at 28 °C. The next day morning, 5 ml of A. tumefaciens cells was subcultured in 100 ml of erlenmeyer flask till the OD600 nm reach 0.6. Bacteria cells were washed with liquid MS medium containing 3% (w/v) sucrose twice and resuspended in the same media for the ginseng explants infection.
The cotyledon explants (Figures 2E and 3A, 4 mm) were used for A. tumefaciens transformation. A pCAMBIA1390 vector contains hptII and nptII genes under the cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) 35S promoter was used (Lee et al., 2010; Kim et al., 2014).
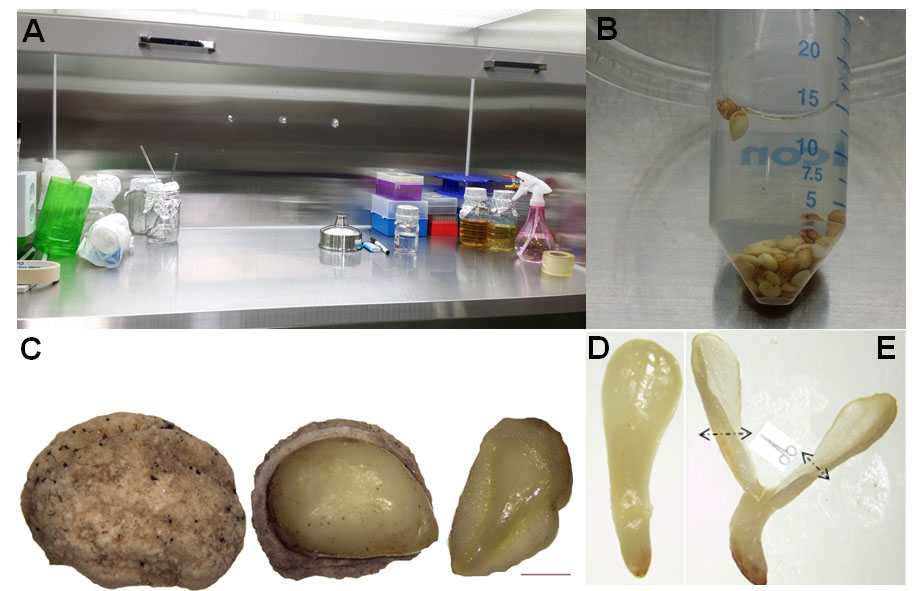
Figure 2. Ready-to-go ginseng seeds for transformation and sterilization. A. Clean Bench. B. Ginseng seeds for sterilization. C. Ginseng seed with and without hard seed coat, then ginseng embryo covered with endosperm. D. Ginseng embryo. E. Ginseng cotyledons ready for the Agrobacterium co-cultivation.
- The explants were dipped in the bacterial solution for 15 min, subsequently blotted with sterile filter paper, and co-cultivated on MS medium containing 3% (w/v) sucrose and 1 µg/ml 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2, 4-D) for 2 days (Figure 3B).
- Thereafter, the explants were cultured on MS selection medium (called callus induction medium) with 3% (w/v) sucrose, 1 µg/ml 2, 4-D, 0.5 µg/ml 6-benzylaminopurine (BAP), 250 µg/ml cefotaxime, and 50 µg/ml hygromycin (Figure 3C). After subculturing three to four times every two weeks on selection medium, the surviving cotyledons producing calli were cultured on the same medium without antibiotics (Figure 3D), and adventitious roots were induced from calli on B5 medium with 3% (w/v) sucrose and 3 mg/L indole-3-butyric acid (IBA) (Figure 3E).
- Adventitious roots were excised from the maternal explants prior to sub-culturing in liquid B5 medium with 3% sucrose and 2 mg/L IBA, which was replaced every 5 weeks (Figure 3F).
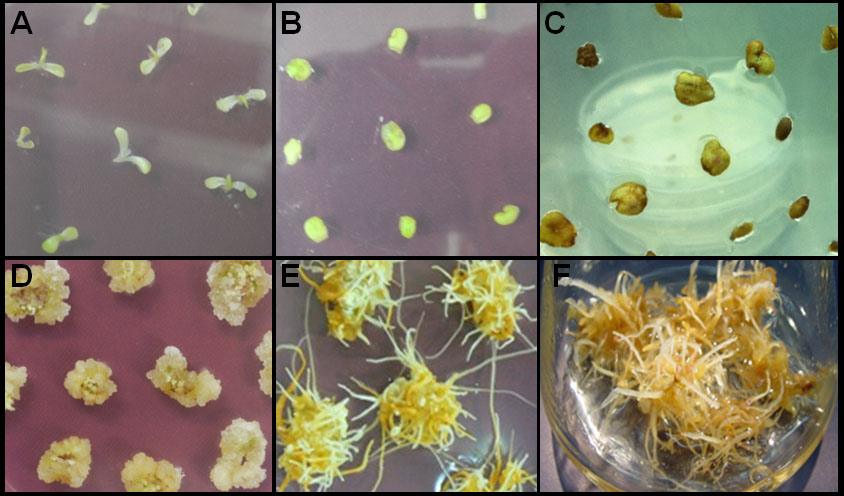
Figure 3. Ginseng transformation by Agrobacterium tumefaciens for the transgenic adventitious root induction. A. Five days further grown cotyledons. B. Cotyledon explants dipped in the bacterial solution for 15 min, subsequently blotted with sterile filter paper, and co-cultivated on MS medium containing 3% (w/v) sucrose and 1 µg/ml 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2, 4-D) for 2 days. C. Transgenic calli selection on MS selection medium, 1 µg/ml 2,4-D, 0.5 µg/ml BAP, 250 µg/ml cefotaxime, and 50 µg/ml hygromycin containing 3% (w/v) sucrose. D. Survived calli were cultured on the same medium without antibiotics. E. Adventitious roots on B5 medium containing 3% (w/v) sucrose and 3 mg/L IBA. F. Subculture in liquid B5 medium containing 3% sucrose and 2 mg/L IBA.
Recipes
- MS (Murashige & Skoog) medium
2.2 g of MS powder
30 g of sucrose
0.5 g of 2-(N-morpholino) ethanesulfonic acid (MES) monohydrate
8 g of phytoagar or 0.25% of Gelrite
Adjust pH to 5.6 with 1 N KOH
Autoclave at 121 °C for 15 min
- YEP medium
10 g of yeast extract
10 g of peptone
5 g of NaCl and 15 g of Bactoagar
Adjust pH to 7.0 with 1 N HCl
Add to dH2O to 1,000 ml
Autoclave at 121 °C for 15 min
- Antibiotics stock solution (in ddH2O)
Hygromycin 50 mg/ml
Kanamycin 50 mg/ml
Cefotaxime 200 mg/ml
Filter sterilize (0.2 μm)
- Plant growth regulators stock solution
- 6-benzylaminopurine (BAP): 0.5 mg/ml in 1 N NaOH
Dissolve 50 mg of BAP in small amount of 1 N NaOH
Bring to volume 100 ml with ddH2O
Autoclave or filter sterilize (0.2 μm)
Freeze at -20 °C
- 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D): 1 mg/ml in 1 N NaOH
Dissolve 100 mg of 2, 4-D in small amount of 1 N NaOH
Bring to volume 100 ml with ddH2O
Autoclave or filter sterilize (0.2 μm)
Freeze at -20 °C
- Indole-3-butyric acid (IBA): 10 mg/ml in 1 N NaOH
Dissolve 1 g of IBA in small amount of 1 N NaOH
Bring to volume 100 ml with ddH2O
Autoclave or filter sterilize (0.2 μm)
Freeze at -20 °C
- 6-benzylaminopurine (BAP): 0.5 mg/ml in 1 N NaOH
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 Program (SSAC, grant#: PJ00952902), Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea to ORL.
References
- Bechtold, N. and Pelletier, G. (1998). In planta Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of adult Arabidopsis thaliana plants by vacuum infiltration. Methods Mol Biol 82: 259-266.
- Kim, Y. J., Lee, O. R., Oh, J. Y., Jang, M. G. and Yang, D. C. (2014). Functional analysis of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase encoding genes in triterpene saponin-producing ginseng. Plant Physiol 165(1): 373-387.
- Lee, O. R., Kim, S. J., Kim, H. J., Hong, J. K., Ryu, S. B., Lee, S. H., Ganguly, A. and Cho, H. T. (2010). Phospholipase A(2) is required for PIN-FORMED protein trafficking to the plasma membrane in the Arabidopsis root. Plant Cell 22(6): 1812-1825.
- Lee, O. R., Sathiyaraj, G., Kim, Y. J., In, J. G., Kwon, W. S., Kim, J. H. and Yang, D. C. (2011). Defense genes induced by pathogens and abiotic stresses in Panax ginseng CA Meyer. J Gins Res 35(1): 1-11.
- Murashige, T. and Skoog, F. (1962). A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plantarum 15(3): 473-497.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2014 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Lee, O. R., Han, J. H. and Kim, Y. (2014). Agrobacterium-mediated Transformation of Mature Ginseng Embryos. Bio-protocol 4(24): e1362. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1362.
- Kim, Y. J., Lee, O. R., Oh, J. Y., Jang, M. G. and Yang, D. C. (2014). Functional analysis of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase encoding genes in triterpene saponin-producing ginseng. Plant Physiol 165(1): 373-387.
Category
Plant Science > Plant transformation > Agrobacterium
Plant Science > Plant physiology > Plant growth
Molecular Biology > DNA > Transformation
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link