- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Pea Aphid Survival Assays on Arabidopsis thaliana
Published: Vol 4, Iss 19, Oct 5, 2014 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1251 Views: 10024
Reviewed by: Tie LiuAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Rice Ragged Stunt Virus Propagation and Infection on Rice Plants
Chao Zhang [...] Jianguo Wu
Oct 20, 2018 6521 Views

Botrytis cinerea in vivo Inoculation Assays for Early-, Middle- and Late-stage Strawberries
Piao Yang [...] Ye Xia
Oct 20, 2023 2805 Views
Abstract
Aphids are phloem-feeding insects that successfully colonize specific host plant species. Aphid performance on a given plant is commonly measured by assessing fecundity of an aphid species that is adapted to the host. However, this approach may not reveal roles for plant genes in defense pathways that adapted aphids suppress. The host range of the pea aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum) is mostly restricted to plants of the legume family, and does not include Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana). Pea aphids die within a few days of being placed on Arabidopsis plants, and their survival therefore provides a sensitive measure of the status of the host plant defenses. This protocol describes how to measure the survival rate of the pea aphid on the non-host plant Arabidopsis. The protocol consists of two phases: first, obtaining a population of pea aphids of synchronized age; and secondly measuring their survival on Arabidopsis plants.
Materials and Reagents
- 3 to 4-week-old Vicia faba plants grown in 14 h light (18 °C)/10 h dark (15 °C)
- 7-week-old Arabidopsis plants grown in a short day condition (10 h light/14 h dark (22 °C)
- Pea Aphids (Acyrthosiphon pisum) maintained on Vicia faba plants grown in 14 h light (18 °C)/10 h dark (15 °C)
Equipment
- Plant growth facilities
- Insect-proof cage to contain Vicia faba plants (Note 1)
- Petri dish
- Moist artist’s paintbrush (size 2 or 4)
- Clip cages (Figure 1)
- Plant labels
- Marker pen
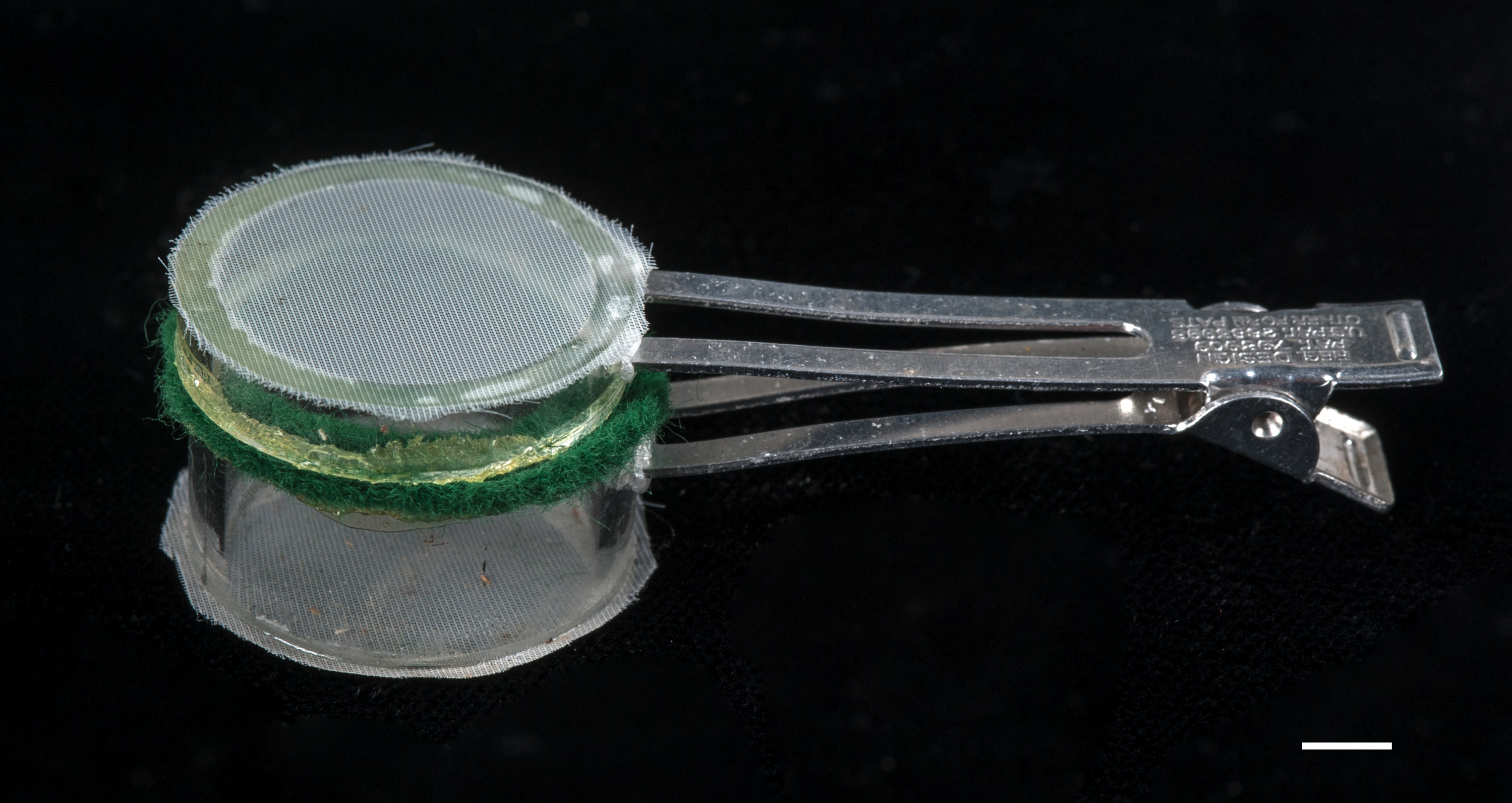
Figure 1. Clip cage. Composed of a metal double prong hair clip (50 mm long), two pieces of plastic tube (10 and 5 mm high, 2 mm thick, 25 mm diameter), two circles of felt (25 mm diameter, 4 mm across, 1 mm thick), and two pieces of fine gauze (25 mm diameter). The hair clip is heated and pushed into the plastic tubes. The felt and gauze are attached with superglue. Scale bar = 5 mm
Software
- Microsoft® Excel
Procedure
- Obtaining a cohort of aged pea aphids
- Collect adult pea aphids in a petri dish from a stock cage (Note 2).
- Use a moist paintbrush to transfer the aphids to a fresh cage containing several Vicia faba plants in pots.
- Place the cage, containing the aphids and plants, in long day growth conditions [14 h light (22 °C), 10 h night (15 °C)].
- After 24 h remove all the adult aphids, while the nymphs remain (Note 3).
- Allow the nymphs to reach the adult stage (Note 4).
- Collect adult pea aphids in a petri dish from a stock cage (Note 2).
- Setting up the experiment
- Use plastic plant labels to label 7-week-old Arabidopsis with their genotype and the plant number (e.g. Col-0, plant 1). Use at least five plants per genotype per replicate.
- Collect the cohort of aged pea aphids in a petri dish.
- Use a moist paintbrush to transfer 5 of the aphids to a clip cage.
- Gently clip the cage onto a fully developed leaf of the Arabidopsis plant.
- Repeat the previous two steps until all the plants have one clip cage each.
- Randomize the plants across the area that they are to be grown in (Note 5).
- Place the plants in short day conditions [8 h light (18 °C), 16 h night (16 °C)].
- Use plastic plant labels to label 7-week-old Arabidopsis with their genotype and the plant number (e.g. Col-0, plant 1). Use at least five plants per genotype per replicate.
- Collecting the results
- The day that the aphids are caged to the Arabidopsis plants is day 0.
- Count and record the number of live adults in the clip cages on days 2 to 7.
Table 1. Example data from one repeat of an experiment with Col-0 Arabidopsis, with readings taken on days 3 to 7
Number of adult aphids alive
Day
Plant 1
Plant 2
Plant 3
Plant 4
Plant 5
3
4
5
4
5
5
4
4
2
3
1
3
5
0
2
1
0
0
6
0
0
0
0
0
7
0
0
0
0
0
- The day that the aphids are caged to the Arabidopsis plants is day 0.
- Repetition
- Repeat the whole experiment (steps 1-3) on at least 3 separate occasions.
- Analysing the results
- Calculate the time point at which survival on wild type Arabidopsis is 50% (Note 6). If this occurs between two of the days (e.g. between day 3 and 4) then average the number of adults alive on these two days.
- Use this time point to calculate the number of adults alive on each plant (Note 7).
- Analyze by classical linear regression analysis using a Poisson distribution within a generalized linear model.
- Calculate the time point at which survival on wild type Arabidopsis is 50% (Note 6). If this occurs between two of the days (e.g. between day 3 and 4) then average the number of adults alive on these two days.
Notes
- The cage should be large enough for the Vicia faba plants to grow, and allow sufficient light and ventilation while preventing the aphids from escaping. We use Perspex cages (47 cm high x 54 cm deep x 24 cm wide) with a fine mesh covering attached by magnetic strips at one end to serve as a door.
- 5 to 10 pea aphids per Arabidopsis plant in the experiment should be sufficient, as approximately one nymph is born per adult in 24 h at 22 °C. The aphids reproduce slower at lower temperatures and therefore more adults are needed to produce the same number of nymphs.
- Make sure to count the number of adults added to the cage, and remove the same number of adults at this stage.
- In the conditions stated, pea aphids should reach the adult stage by 8 or 9 days, having undergone four moults. Only adult aphids reproduce. It is recommended to use aphids 10 to 14 days old.
- For example, if you are placing the experimental plants in 3 trays for the experiment then randomly assign each plant a number of 1, 2 or 3, corresponding to trays 1, 2 and 3. This can be done using the RANDBETWEEN function in Microsoft® Excel.
- Average the number of adult pea aphids alive on each day across all your repeats of the wild type Arabidopsis. Then plot this data against the experiment day number on a line graph. See Reference 1 (Prince et al., 2014) Figure 6B for an example.
- For example, the data in Table 1 is part of a larger data set where 50% survival is between day 3 and 4. Therefore, the data would be calculated as: Plant 1 = 4, Plant 2 = 3.5, Plant 3 = 3.5, Plant 4 = 3, Plant 5 = 4.
Acknowledgments
We thank Andrew Davis for the photograph of the clip cage. This work was supported by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (grant no. BB/J004553/1 to S. A. H.), the John Innes Foundation (to S. A. H.), a Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council studentship (to D. C. P.) and a John Innes Foundation studentship (to T. R. V). This protocol is adapted from Reference 1 (Prince et al., 2014).
References
- Prince, D. C., Drurey, C., Zipfel, C. and Hogenhout, S. A. (2014). The leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase BRASSINOSTEROID INSENSITIVE1-ASSOCIATED KINASE1 and the cytochrome P450 PHYTOALEXIN DEFICIENT3 contribute to innate immunity to aphids in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 164(4): 2207-2219.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2014 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Prince, D. C., Mugford, S. T., Vincent, T. R. and Hogenhout, S. A. (2014). Pea Aphid Survival Assays on Arabidopsis thaliana. Bio-protocol 4(19): e1251. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1251.
- Prince, D. C., Drurey, C., Zipfel, C. and Hogenhout, S. A. (2014). The leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase BRASSINOSTEROID INSENSITIVE1-ASSOCIATED KINASE1 and the cytochrome P450 PHYTOALEXIN DEFICIENT3 contribute to innate immunity to aphids in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 164(4): 2207-2219.
Category
Plant Science > Plant immunity > Disease bioassay
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










