- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Luminescence-based Antiviral Assay for Hepatitis E Virus
Published: Vol 4, Iss 15, Aug 5, 2014 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1196 Views: 10287
Reviewed by: Kanika GeraAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

General Maintenance and Reactivation of iSLK Cell Lines
Ariana C. Calderón-Zavala [...] Ekaterina E. Heldwein
Jun 5, 2025 1919 Views

Inducible HIV-1 Reservoir Reduction Assay (HIVRRA), a Fast and Sensitive Assay to Test Cytotoxicity and Potency of Cure Strategies to Reduce the Replication-Competent HIV-1 Reservoir in Ex Vivo PBMCs
Jade Jansen [...] Neeltje A. Kootstra
Jul 20, 2025 2473 Views

Assembly and Mutagenesis of Human Coronavirus OC43 Genomes in Yeast via Transformation-Associated Recombination
Brett A. Duguay and Craig McCormick
Aug 20, 2025 3055 Views
Abstract
Hepatitis E virus (HEV) is one of the main causes of acute hepatitis worldwide. Infections are particularly severe in pregnant women and chronic hepatitis E is known to occur in immunocompromised patients. Current therapy (ribavirin or pegylated alpha interferon) has severe side effects and cannot be employed in all patients. In order to evaluate potential new inhibitors of HEV replication, a luminescence-based replicon assay is particularly useful since it offers a rapid read-out and does not pose any biosafety risks (Debing et al., 2014).
Keywords: Hepatitis E virusMaterials and Reagents
- HEV Kernow-C1 p6/luc plasmid (genotype 3 subgenomic replicon expressing Gaussia luciferase; a kind gift from Suzanne Emerson, NIH) (Shukla et al., 2012)
- MluI restriction endonuclease with accompanying 10x buffer D (Promega Corporation, catalog number: R6381 )
- pT7-IRES-FFLuc-YFsfRNA plasmid (constructed in-house; IRES, internal ribosome entry site; FFLuc, firefly luciferase; YFsfRNA, yellow fever virus small flaviviral RNA) (Debing et al., 2014)
- Primers #1 (5’-CATATGTCGACTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGATCCGCCCCTCTCCC-3’) and #2 (5’-AGTGGTTTTGTGTTTGTCATCC-3’) (custom order) (Integrated DNA Technologies) (dissolved to a final concentration of 10 µM in buffer TE)
- Kapa HiFi HotStart ReadyMix master mix (Kapa Biosystems, catalog number: KK2601 )
- SeaKem LE agarose for gel electrophoresis (Lonza, catalog number: 50001 )
- QIAquick gel extraction kit (QIAGEN, catalog number: 28704 )
- T7 RiboMAX large scale RNA production system (Promega Corporation, catalog number: P1300 )
- RNeasy mini kit (QIAGEN, catalog number: 74104 )
- ScriptCap m7G capping system (CELLSCRIPTTM, catalog number: C-SCCE0610 )
- Huh7 human hepatoma cell line (Japanese Collection of Research Bioresources, catalog number: JCRB0403)
- Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium with high glucose (DMEM) (Life Technologies, catalog number: 41965-039 )
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (not heat-inactivated) (Life Technologies, catalog number: 10270-106 )
- Opti-MEM I reduced serum medium (Life Technologies, catalog number: 31985-062 )
- Lipofectin transfection reagent (Life Technologies, catalog number: 18292-011 )
- Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) without Ca2+ and Mg2+ (Life Technologies, catalog number: 14190-094 )
- Renilla luciferase assay system (Promega Corporation, catalog number: E2810 )
- 5x passive lysis buffer (Promega Corporation, catalog number: E1941 ) and demineralized H2O for dilution
- Luciferase assay system (Promega Corporation, catalog number: E1501 )
- CellTiter 96 AQueous MTS reagent powder [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium] (Promega Corporation, catalog number: G1111 )
- Phenazine methosulphate (PMS) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9625 )
- Minimum essential medium (MEM) (no glutamine, no phenol red) (Life Technologies, catalog number: 51200-046 )
- Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane powder (Trizma base) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T1503 ) (dissolved to 1 M and pH 8.0 in H2O)
- Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt solution (EDTA, 0.5 M) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: E7889 )
- MTS/PMS solution (see Recipes)
- Buffer TE (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Spectrophotometer to determine RNA concentrations (e.g. Thermo Fischer Scientific, NanoDrop, model: ND-1000 )
- Falcon transparent 96-well plate (Corning Incorporated, catalog number: 353072 )
- CulturPlate white 96-well plate (PerkinElmer, catalog number: 6005680 )
- 37 °C and 35 °C 5% CO2 cell culture incubators
- Plate shaker
- Saphire² microplate reader for both luminescence and absorbance (Tecan Trading AG)
Procedure
- 5 µg of the Kernow-C1 p6/luc plasmid is linearized in a 100 µl reaction containing 10 µl of 10x buffer D and 2.5 µl of MluI (10 units/µl) which is incubated at 37 °C for 2 h.
- The digested DNA is purified using the Qiaquick gel extraction kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions with final elution in 30 µl of buffer EB.
Note: To increase the yield, add the recommended amount of isopropanol to the mixture of the reaction and buffer QG. Other methods of DNA purification should be suitable as well. - The T7-IRES-FFLuc-YFsfRNA fragment (2.6 kb) is amplified from the pT7-IRES-FFLuc-YFsfRNA plasmid with primers #1 and #2:
- 12.5 µl 2x Kapa HiFi HotStart Readymix
- 0.75 µl of both primers (dissolved at 10 µM)
- < 0.5 µl of plasmid (1-10 ng of DNA)
- Ad 25 µl nuclease-free H2O
Using following temperature scheme:
- 5 min 95 °C
- 20” 98 °C |
- 15” 65 °C | x25
- 3 min 72 °C|
- 5 min 72 °C
- 4 °C - The resulting DNA fragment is purified on a 1% agarose gel and extracted with the Qiaquick gel extraction kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions with final elution in 30 µl of buffer EB.
- In vitro transcription reactions are prepared for both DNA fragments with the T7 RiboMAX large scale RNA production system:
- 10 µl of 5x T7 transcription buffer
- 15 µl of NTPs (ATP, GTP, CTP, UTP; all at 25 mM)
- 20 µl of DNA template
- 5 µl of enzyme mix
Reactions are incubated at 37 °C for 5 h. Afterwards, 5 µl of the supplied RQ1 RNase-free DNase solution is added and incubated at 37 °C for 15 min. - The produced RNA is purified with the RNeasy mini kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions with elution in 60 µl of RNase-free H2O (in 2 elution of 30 µl each). RNA concentration is determined by spectroscopy (absorbance at 260 nm).
- Sixty µg of HEV Kernow-C1 p6/luc RNA is capped with the ScriptCap m7G capping system according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- The produced RNA is purified with the RNeasy mini kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions with elution in 60 µl of RNase-free H2O (in 2 elution of 30 µl each). RNA concentration is determined by spectroscopy (absorbance at 260 nm).
- Huh7 cells are seeded into a transparent 96-well plate at 104 cells per well in 100 µl of DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS.
- Plate is incubated in a 5% CO2 incubator at 37 °C for 24 h.
- To transfect one well, 36.5 ng of capped viral RNA and 36.5 ng of FFLuc transfection control RNA are added to 3.65 µl of Opti-MEM. In another tube, 0.365 µl of Lipofectin transfection reagent is added to 3.65 µl Opti-MEM. Both tubes are incubated at room temperature for 30 min. Then, the contents of both tubes are combined and incubated for another 10 min at room temperature. An additional 29.2 µl of Opti-MEM is added and the resulting solution is mixed well.
Note: Multiply the indicated amounts and volumes by the number of wells to transfect and prepare an additional 10% extra. For cell control (CC) wells without replicon, viral RNA is omitted. - The culture medium is removed from cells seeded earlier and each well is washed with 100 µl of DMEM.
Note: Huh7 cells may easily detach from the culture plate, so medium is removed carefully using a pipette instead of a vacuum system. - To each well, 36.5 µl of transfection mixture is added.
- Plate is incubated in a 5% CO2 incubator at 37 °C for 5 h.
- Transfection medium is removed from each well and cell layers are washed once with 100 µl of PBS.
- One hundred microliters of DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS is added to each well. At this step, the compound to be tested is added and an appropriate dilution series is made.
Note: No compound is added to virus control (VC) and CC wells. - Plate is incubated in a 5% CO2 incubator at 35 °C for 72 h.
Note: Incubation can also be performed at 37 °C if no incubator would be available at 35 °C. - From each well, 20 µl is transferred to a white CulturPlate.
- Renilla luciferase substrate is diluted 1: 100 in assay buffer and 50 µl is added to each well of the CulturPlate containing the transferred culture medium.
- The plate is shaken vigorously on a plate shaker for a few seconds and luminescence read-out is performed (integration time: 100 ms).
Note: The time between substrate addition and read-out has to be kept to a minimum, since background signal will increase over time during the first few minutes. Later on, the overall signal will decline. - The remaining medium is removed from each well of the transfected 96-well plate.
- Passive lysis buffer is diluted 1: 5 in demineralized H2O and 20 µl is added to each well.
- Plate is shaken at room temperature for 10 min at 500 rpm for proper cell lysis.
- One hundred microliters of reconstituted Firefly luciferase substrate solution is added to the wells of a new white CulturPlate.
- All of the cell lysate solution is transferred into the luciferase substrate solution in the CulturPlate.
- The plate is shaken vigorously on a plate shaker for a few seconds and luminescence read-out is performed as described above.
- In order to assess compound toxicity, the following assay can be performed:
- Huh7 cells are seeded as described and incubated in a 5% CO2 incubator at 37 °C for 24 h.
- Culture medium is replaced by a compound dilution series in fresh DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS (100 µl per well). Plate is incubated in a 5% CO2 incubator at 35 °C for 72 h.
- Medium is removed and replaced with 100 µl of a 1: 20 dilution of MTS/PMS solution in colorless MEM per well. Plate is incubated in a 5% CO2 incubator at 37 °C until a brownish color develops (usually this requires incubation for 1-2 h).
- Absorbance read-out is performed by determining the optical density (OD) at 498 nm (OD of CC should be above 0.6 but below 1 to stay in the linear range).
- Huh7 cells are seeded as described and incubated in a 5% CO2 incubator at 37 °C for 24 h.
Representative data
- A possible outline for a 96-well plate may be the following:
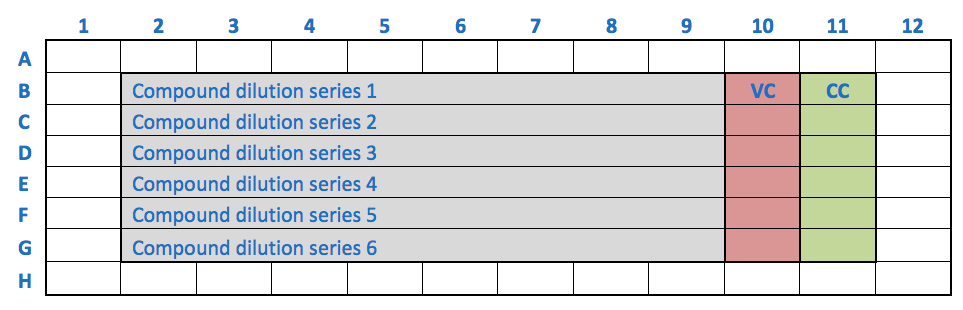
- A typical read-out for the luminescence-based assay would be the following:
p6/luc-transfected wells CC wells Relative luminescence units (RLU) 85264 759
The variability in Gaussia luminescence read-out between different replicates of the same experiment might be rather large. This is resolved by normalizing data to those obtained for untreated VC wells.
Notes
- The T7-IRES-FFLuc-YFsfRNA is used as a transfection control to normalize for transfection efficacy (see calculations below). Other FFluc-expressing RNA fragments can be used as well. The transfection control can be omitted, although this may impact the assay’s robustness.
- Following formulas are used to calculate the antiviral activity (%). First, Gaussia luciferase signals are normalized:
LucNormcompound = (GLucreplicon+compound – GlucCC)/FFLucreplicon+compound
LucNormVC = (GlucVC – GlucCC)/FFLucVC
Next, antiviral activity is calculated:
% Antiviral activity = 100 - (LucNormcompound/LucNormVC x 100)
For example, if the following luminescence data would have been obtained:Compound VC CC Gluc 18524 85264 759 FFLuc 10362 9254 8906
Antiviral activity is calculated as follows:
LucNormcompound = (18524 - 759)/10362 = 1.71
LucNormVC = (85264 - 759)/9254 = 9.13
% Antiviral activity = 100 - (1.71/9.13 x 100) = 81.3% - To calculate cell viability, the following formula can be employed:
% Viability = ODcompound/ODCC x 100 - The same protocol can be used with the Sar55/S17/luc construct, a genotype 1 subgenomic HEV replicon (Nguyen et al., 2014).
Recipes
- MTS/PMS solution
- Two grams of MTS powder is dissolved in 1 L of PBS and stirred for 15 min.
- Next, 46 mg of PMS powder is added (pH should be between 6-6.5).
- Solution is filtered, aliquoted and stored at -20 °C.
- Two grams of MTS powder is dissolved in 1 L of PBS and stirred for 15 min.
- Buffer TE
To 25 ml of nuclease-free H2O, add
250 µl of a 1 M Tris solution (pH 8.0) (final concentration: 10 mM)
50 µl of a 0.5 M EDTA solution (final concentration: 1 mM)
Acknowledgments
This protocol was adapted from Debing et al. (2014) and is partially based on earlier work by Shukla et al. (2012). Yannick Debing is a fellow of the Research Foundation-Flanders (FWO). This work was supported by KU Leuven Geconcerteerde Onderzoeksacties (GOA/10/014) and by EU FP7 project SILVER (260644).
References
- Debing, Y., Emerson, S. U., Wang, Y., Pan, Q., Balzarini, J., Dallmeier, K., Neyts, J. (2014). Ribavirin inhibits in vitro hepatitis E virus replication through depletion of cellular GTP pools and is moderately synergistic with alpha interferon. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58(1): 267-273.
- Nguyen, H.T., Shukla, P., Torian, U., Faulk, K., Emerson, S.U. (2014) Hepatitis E virus genotype 1 infection of swine kidney cells in vitro is inhibited at multiple levels. J Virol 88(2): 868-877.
- Shukla, P., Nguyen, H.T., Faulk, K., Mather, K., Torian, U., Engle, R.E., Emerson, S.U. (2012) Adaptation of a genotype 3 hepatitis E virus to efficient growth in cell culture depends on an inserted human gene segment acquired by recombination. J Virol 86(10): 5697-5707.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2014 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Debing, Y., Dallmeier, K. and Neyts, J. (2014). Luminescence-based Antiviral Assay for Hepatitis E Virus. Bio-protocol 4(15): e1196. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1196.
Category
Microbiology > Antimicrobial assay > Replicon assay
Microbiology > Microbe-host interactions > Virus
Immunology > Host defense > Human
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link











