- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Murine in vitro Memory T Cell Differentiation
Published: Vol 4, Iss 13, Jul 5, 2014 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1171 Views: 15311
Reviewed by: Omar AkilAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Isolation and Ex Vivo Testing of CD8+ T-Cell Division and Activation Using Mouse Splenocytes
Melissa Dolan [...] John M.L. Ebos
Aug 20, 2025 3975 Views

Novel Experimental Approach to Investigate Immune Control of Vascular Function: Co-culture of Murine Aortas With T Lymphocytes or Macrophages
Taylor C. Kress [...] Eric J. Belin de Chantemèle
Sep 5, 2025 3585 Views
Abstract
Upon pathogen encounter, naïve CD8+ T cells are primed and undergo massive clonal expansion. A fraction of effector CD8+ T cells remains during the contraction phase and differentiate into memory T cells critical for mounting robust recall responses in response to secondary infection. Low frequency of memory T cells in vivo is a major obstacle to investigate their functional aspects including migration capacity and genetic regulation. Here, we describe detailed protocol for memory T cell differentiation developed by von Andrian’s group to generate large number of CD44hiCD62Lhi antigen-specific memory T cells in vitro.
Keywords: Ag-specific memory CD8 T cellMaterials and Reagents
- Recombinant mouse IL-15 (rmIL15) (BioLegend, catalog number: 566302 )
- RPMI-1640 medium (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 11875-119 )
- Fetal bovine serum (Atlanta Biologicals, catalog number: S11055H )
- Penicillin/streptomycin (Gemini Bio-Products, catalog number: F52M00E )
- L-Glutamine (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 25030-081 )
- 100x 1 M Hepes (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 15630-080 )
- 100x MEM non-essential amino acids (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 11140-050 )
- 100x sodium pyruvate (100 mM) (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 11360-070 )
- 100x 2-mercaptoethanol (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 21985-023 )
- OVA257-264 synthetic peptide (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S7951 )
- Ficoll-PaqueTM Premium 1.084 (GE Healthcare, catalog number: 17-5446-02 )
- Antibodies:
- RBC lysis buffer (eBioscience, catalog number: 00-4333-57 )
- Bovine serum albumin (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP1605-100 )
- NaN3 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S8032 )
- T cell media (see Recipes)
- Staining buffer (in PBS) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Centrifuge (Thermo Fischer Scientific, SorvallTM Legend RT)
- 70 µm cell strainer (BD Biosciences, Falcon®, catalog number: 352350 )
- 15 ml and 50ml Falcon tubes
- 24 well plates (BD Biosciences, Falcon®, catalog number: 353226 )
- T75 culture flask (Corning, catalog number: 430641 )
- 37 °C, 5% CO2 cell culture incubator
Procedure
- CD44hiCD62Llo Memory T cell differentiation proceeds under sterile tissue culture conditions
- Euthanize a OT-1 CD8 TCR transgenic mouse and take spleen, and (optional) lymph nodes.
- Splenocytes are RBC lysed followed by washing with PBS twice.
- Euthanize a OT-1 CD8 TCR transgenic mouse and take spleen, and (optional) lymph nodes.
- OT-1 TCR stimulation with cognate peptide antigen
- Resuspend cells in 1 ml of T cell media and add OVA257-264 synthetic peptide to 1 µM.
- Incubate in the 5% CO2 at 37 °C for 1 h.
- Spin down cells at 1,500 rpm for 3 min at 4 °C and wash once with T cell media.
- Resuspend cells in 12 ml of T cell media and plate 1ml/well of a 24 well plate.
- Incubate in the 5% CO2 at 37 °C for 2 days.
- Harvest the cells by pipetting up and down, and pellet cells.
- Resuspend cells in 5 ml of T cell media, and load on to 2.5 ml of Ficoll.
- Spin down at 400 x g for 15 min at 4 °C.
- Transfer live cells on the interphase to a new 15 ml tube and fill up the tube with T cell media.
- Spin down cells at 1,500 rpm for 3 min at 4 °C.
- Resuspend cells in 1 ml of T cell media and add OVA257-264 synthetic peptide to 1 µM.
- Memory T cell culture in the presence of IL-15
- Resuspend cells in 24 ml of T cell media containing rmIL15 (20 ng/ml). Culture cells in T75 flask for four days.
- Harvest and pellet cells for Ficoll gradient (repeat steps 9-12).
- Resuspend cells in 40 ml of T cell media containing rmIL15 (20 ng/ml). Culture in T75 flask for two days.
- Staining cells with anti-CD44 and CD62L antibodies in staining buffer for 15 min on ice.
- Wash with staining buffer twice, then proceeds flow cytometry analysis.
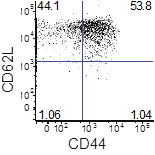
Figure 1. CD44 and CD62L expression of differentiated memory T cells
- Resuspend cells in 24 ml of T cell media containing rmIL15 (20 ng/ml). Culture cells in T75 flask for four days.
Recipes
- T cell media
RPMI-1640
10% fetal bovine serum
1% penicillin/streptomycin
1% L-Glutamine
1x 1 M Hepes
1x MEM non-essential amino acids
1x sodium pyruvate 100 mM
1x 2-mercaptoethanol
- Staining buffer (in PBS)
1% BSA
0.02% NaN3
Acknowledgments
The protocol was adapted from a previously described study (Manjunath et al., 2001). This work was supported by the Starr Cancer Consortium (13-A123 to M.O.L. and M.Q.Z.), the Rita Allen Foundation (M.O.L.), the NBRPC (2012CB316503 to M.Q.Z), and the NIH (HG001696 to M.Q.Z.).
References
- Kim, M. V., Ouyang, W., Liao, W., Zhang, M. Q. and Li, M. O. (2013). The transcription factor Foxo1 controls central-memory CD8+ T cell responses to infection. Immunity 39(2): 286-297.
- Manjunath, N., Shankar, P., Wan, J., Weninger, W., Crowley, M., Hieshima, K., Springer, T., Fan, X., Shen, H. and Lieberman, J. (2001). Effector differentiation is not prerequisite for generation of memory cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Clin Invest 108(6): 871-878.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2014 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Kim, M. V., Ouyang, W., Liao, W., Zhang, M. Q. and Li, M. O. (2014). Murine in vitro Memory T Cell Differentiation. Bio-protocol 4(13): e1171. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1171.
Category
Immunology > Immune cell function > Lymphocyte > Membrane protein detection
Immunology > Immune cell function > Antigen-specific response
Immunology > Immune cell isolation > Maintenance and differentiation
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link