- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Sandwich Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Analysis of Plant Cell Wall Glycan Connections
Published: Vol 4, Iss 8, Apr 20, 2014 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1106 Views: 18093
Reviewed by: Renate Weizbauer

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Protocol for RYMV Inoculation and Resistance Evaluation in Rice Seedlings
Agnès Pinel-Galzi [...] Laurence Albar
Jun 5, 2018 8090 Views

A Highly Sensitive, Reproducible Assay for Determining 4-hydroxynonenal Protein Adducts in Biological Material
T. Blake Monroe and Ethan J. Anderson
Oct 5, 2019 3967 Views

An Optimised Indirect ELISA Protocol for Detection and Quantification of Anti-viral Antibodies in Human Plasma or Serum: A Case Study Using SARS-CoV-2
Claire Baine [...] Jennifer Serwanga
Dec 20, 2023 3684 Views
Abstract
Sandwich ELISA is a highly sensitive method that can be used to determine if two epitopes are part of the same macromolecule or supramolecular complex. In the case of plant cell wall glycans, it can reveal the existence of inter-polymers linkages, leading to better understanding of overall cell wall architectures. This development of a conventional sandwich ELISA protocol uses a carbohydrate-binding module (CBM), a small protein domain found in some carbohydrate catalysing or activating enzymes, and rat monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) which can be combined in the same ELISA plate without risk of cross reaction; the secondary anti-rat HRP antibody being only able to bind to the rat mAb and not the CBM. This protocol was developed and modified in the Prof. J. Paul Knox lab at the University of Leeds.
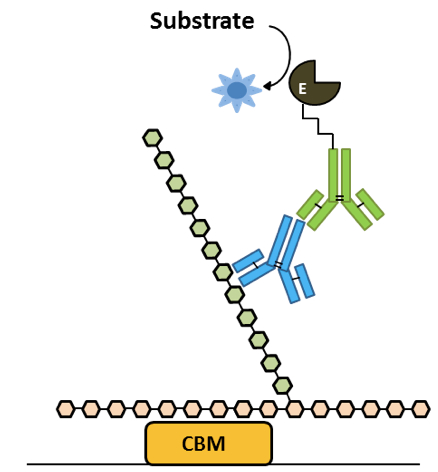
Figure 1. Sandwich ELISA analysis of complex glycans
Materials and Reagents
- Cell wall extracts [50 mM cyclohexanediamine tetraacetic acid (CDTA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D1383 ) or 4 M KOH/1% (w/v) NaBH4 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 452882 ) or purified cell wall polymers]
Notes:- Reagents for cell wall extracts are 50 mM cyclohexanediamine tetraacetic acid (CDTA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D1383) or 4 M KOH/1% (w/v) NaBH4 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 452882)
- Cell wall extraction protocol using 4 M KOH/1% (w/v) NaBH4 is described in Cid et al. (2010). This extraction will disrupt and release most cell wall glycans.
- CDTA is a chelating agent which is used to specifically extract the pectin fraction from cell walls. The same protocol can be followed using 50 mM CDTA instead of 4 M KOH (no neutralizing step necessary).
- Reagents for cell wall extracts are 50 mM cyclohexanediamine tetraacetic acid (CDTA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D1383) or 4 M KOH/1% (w/v) NaBH4 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 452882)
- Skimmed milk powder (Marvel Original) [used at 5% (w/v) in 1x PBS]
- Purified recombinant carbohydrate-binding module (CBM)
Note: A protocol for CBM expression and purification can be found in Lee et al. (2013). - Primary monoclonal antibody (PlantProbes, www.plantprobes.net)
- Secondary antibody (depending on the origin of the primary antibody used)
- 10 mg/ml tetramethyl benzidine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T2885 )
- 1 M sodium acetate buffer (pH 6)
- 6% H2O2 (VWR International, catalog number: 2858175C )
- 2.5 M H2SO4 (VWR International, catalog number: 191675A )
- Tween 20 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P2287 ) (optional)
- 1x phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (pH 7) (see Recipes)
- HRP developing solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 96-well surface treated ELISA microtitre plates (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Nunc-Immnuno Maxisorp, catalog number: 442404 )
- Microtitre plate reader (450 nm absorbance) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, MultiskanTM FC Microplate Photometer)
- Multi-channel pipette (if available, not critical)
- pH meter
Procedure
- Coat the microtitre plate using 0.5 to 1 µg/ml CBM in 1x PBS, 100 µl per well at 4 °C overnight.
Note: The amount of CBM necessary to obtain a good signal will vary depending of its affinity to the substrate. Trials may be necessary to find the appropriate dilution. - Wash the plate 3 times using tap water or 1x PBS 0.1 % (v/v) Tween 20. Shake the plate dry.
Note: We routinely used tap water but one might prefer using 1x PBS 0.1 % (v/v) Tween 20. The drying step is critical as any remaining water/buffer would dilute the next reagent. Make sure the plates are fully dried after each washing step. - Block the plate for 2 h using 5% (w/v) milk powder in 1x PBS, 200 µl per well at room temperature.
- Wash the plate 3 times using tap water or 1x PBS 0.1 % (v/v) Tween 20. Shake the plate dry.
- Incubate for 90 min with a cell wall extract or test glycan diluted in 5% (w/v) milk/1x PBS, 100 µl per well at room temperature.
Note: Normal ELISA analysis can be used to determine which dilution of the extract gives the best signal. However, the amount of CBM used will determine the amount of glycan that can be immobilised. Therefore it is better to use more concentrated sample rather than less. - Wash the plate 6 times using tap water or 1x PBS 0.1 % (v/v) Tween 20. Shake the plate dry.
- Incubate with a primary antibody appropriately diluted in 5% (w/v) milk/1x PBS, 100 µl per well for 1 h at room temperature.
Note: Use 10x dilution of hybridoma cell culture supernatants if working with PlantProbes monoclonal antibodies. - Wash the plate 6 times using tap water or 1x PBS 0.1 % (v/v) Tween 20. Shake the plate dry.
- Incubate with secondary HRP-conjugated antibody diluted 1:1,000 in 5% (w/v) milk/1x PBS, 100 µl per well for 1 h at room temperature.
- Wash the plate 9 times using tap water or 1x PBS 0.1 % (v/v) Tween 20. Shake the plate dry.
Note: Plates should be thoroughly washed at this step to ensure no false positive signals due to non-specifically bound secondary antibody/HRP. - Develop the plate using 150 µl of substrate solution per well to detect secondary antibody binding. Let the plates develop for 5 to 10 min. Stop the reaction by adding 50 µl of 2.5 M sulphuric acid.
Note: As developing the plate is a time dependent process it is important to ensure that all comparable samples are developed for the same time. - To collect the data, read the plates at 450 nm using the microtitre plate reader.
Notes
- Make sure all experimental combinations in the microtitre plate wells are assayed in triplicates.
- A control with no CBM (1x PBS) needs to be included in every experiment. This should remain blank if the plates are properly blocked. In case of a signal in no CBM wells increase the % of milk powder, block for longer or use >3% Bovine Serum Albumin in place of milk powder.
Recipes
- 1x phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (pH 7)
- To prepare this buffer you need to add NaH2PO4 to 0.6712 moles/L and Na2HPO4 to 0.3288 moles/L.
- The amount of acid and base is calculated using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation [pH= pKa + log (Base)/(Acid)].
- Prepare just under a litre of the solution using the correct amounts of NaH2PO4 and Na2HPO4 in dH2O.
- Check the pH using a pH meter and adjust slightly if necessary using phosphoric acid or sodium hydroxide.
- Once the pH is adjusted, bring the volume to 1 L.
- To prepare this buffer you need to add NaH2PO4 to 0.6712 moles/L and Na2HPO4 to 0.3288 moles/L.
- HRP developing solution (50 ml)
Mix 45 ml of dH2O with 5 ml of 1 M sodium acetate buffer (pH 6)
Add 500 µl of tetramethyl benzidine
At the last minute add 50 µl of 6% H2O2
Note: Adding hydrogen peroxide starts the reaction. It is therefore important to add it at the last minute to avoid high background signal.
Acknowledgments
The research leading to this protocol has received funding from the European Union Seventh Framework Programme (FP7 2007-2013) under the WallTraC project (Grant Agreement n 263916). This article reflects the author’s views only. The European Community is not liable for any use that may be made of the information contained herein.
References
- Cid, M., Pedersen, H. L., Kaneko, S., Coutinho, P. M., Henrissat, B., Willats, W. G. and Boraston, A. B. (2010). Recognition of the helical structure of beta-1,4-galactan by a new family of carbohydrate-binding modules. J Biol Chem 285(46): 35999-36009.
- Lee, K. J., Cornuault, V., Manfield, I. W., Ralet, M. C. and Knox, J. P. (2013). Multi-scale spatial heterogeneity of pectic rhamnogalacturonan I (RG-I) structural features in tobacco seed endosperm cell walls. Plant J 75(6): 1018-1027.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2014 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Cornuault, V. and Knox, J. P. (2014). Sandwich Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Analysis of Plant Cell Wall Glycan Connections. Bio-protocol 4(8): e1106. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1106.
Category
Plant Science > Plant biochemistry > Carbohydrate
Biochemistry > Carbohydrate > Polysaccharide
Biochemistry > Protein > Immunodetection > ELISA
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










