- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Surface Plasmon Resonance Analysis of Antigen-Antibody Interaction
Published: Vol 3, Iss 24, Dec 20, 2013 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1006 Views: 13752
Reviewed by: Anonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Determination of Dissociation Constants for the Interaction of Myosin-5a with its Cargo Protein Using Microscale Thermophoresis (MST)
Rui Zhou [...] Xiang-Dong Li
Feb 5, 2025 1738 Views

Cell-Sonar, an Easy and Low-cost Method to Track a Target Protein by Expression Changes of Specific Protein Markers
Sabrina Brockmöller [...] Simone Rothmiller
Feb 5, 2025 1657 Views

SiMPull-POP: Quantification of Membrane Protein Assembly via Single Molecule Photobleaching
Ryan J. Schuck [...] Rajan Lamichhane
Jan 5, 2026 287 Views
Abstract
Molecular interaction between monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) and their recognized antigen is a fundamental event leading to the neutralization activity. Estimation of their binding affinity gives beneficial information to characterize the MAbs and to develop more effective MAbs. Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis is a powerful tool to analyze the molecular interaction, enabling rapid and repetitive estimation with relatively small amount of sample. Here we describe a general protocol about SPR analysis on the interaction between viral antigen and human MAb (HuMAb) IgG. Anti-human Fcγ is first covalently crosslinked on the sensor chip by amine coupling, and then HuMAb of interest is immobilized via anti-Fcγ MAb IgG interaction as ligand. Antigen injected on the sensor chip causes the SPR change in time course as the result of association and dissociation. By analyzing the kinetics, association rate, dissociation rate, and dissociation constant are obtained.
Keywords: Molecular interactionMaterials and Reagents
- Purified HuMAb (IgG)
- Purified antigen
- 2-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazinyl]ethanesulfonic acid (HEPES) (Nacalai tesque, catalog number: 17514-15 )
- Sodium hydroxide (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 198-13765 )
- 2 mol/L sodium hydroxide solution (Nacalai Tesque, catalog number: 37441-45 )
- Sodium acetate, anhydrous (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 192-01075 )
- Ethylenediamine-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid, disodium salt, dihydrate (EDTA.2Na) (Dojindo Molecular Technologies, catalog number: 345-01865 )
- Polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan monolaurate (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 167-11515 )
- Goat Anti-Human Fcγ (Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories INC., catalog number: 109-005-008 )
- 1-Ethyl-3-[3-dimethylaminopropyl]carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 22980 )
- N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide (NHS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 24500 )
- Acetic acid (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 017-00256 )
- 2-ethanolamine (Nacalai tesque, catalog number: 23405-42 )
- Hydrochloric acid (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 080-01066 )
- Magnesium chloride hexahydrate (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 135-00165 )
- Sodium Chloride (Nacalai tesque, catalog number: 321319-45 )
- Glycine (Nacalai tesque, catalog number: 17109-35 )
- EDC/NHS solution
- 0.5 M HEPES buffer (pH 7.4) (see Recipes)
- 0.5 M EDTA (pH 8.0) (see Recipes)
- 20% (v/v) polysorbate 20 (see Recipes)
- 10x HBS-E (see Recipes)
- 1x HBS-EP (see Recipes)
- 400 mM EDC (see Recipes)
- 100 mM NHS (see Recipes)
- 1 M 2-ethanolamine (pH 8.5) (see Recipes)
- 50 mM NaOH (see Recipes)
- 10 mM Acetate buffer (pH 4.0, 4.5, 5.0, 5.5) (see Recipes)
- Glycine buffer 10 mM (pH 1.8, 2.0 2.2, 2.4) (see Recipes)
- 1 M NaCl (see Recipes)
- 3 M MgCl2 (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Instrument for SPR analysis, e.g. Biacore T200 (GE) or ProteOn XPR36 (Bio-Rad Laboratories)
- Sensor chip (with carboxyl groups available for the amine coupling reaction), e.g. Series S Sensor Chip CM5 (GE, catalog number: BR-1005-30 ) for Biacore T200 or ProteOn GLM Sensor Chip (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 176-5012 ) for ProteOn XPR36
- Vacuum pump
- 0.22 μm PES PLUS bottom top filter (IWAKI PUMPS, catalog number: 8024-045 )
- 0.22 μm Millex-GV syringe filter unit (Millipore, catalog number: SLGV033RS )
- 20 ml syringe (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: SS-20ESZ )
- Centrifuge
- 1.5 ml centrifuge tube (Ina-optika corporation, catalog number: CF-0150 )
- Spectra/Por 3 Dialysis trial kit (SPECTRUM® LABORATORIES, catalog number: 132720T )
- Stir bar and stirrer
- UV spectrometer
- pH meter
Procedure
- Preparation of reagents and sample
- Prepare reagents (HBS-EP buffer, 400 mM EDC, 100 mM NHS, 50 mM NaOH, 1 M 2-ethanolamine-HCl, glycine buffers and acetate buffers).
Wash dialysis membrane by 300 ml of dH2O and dialyze antigen in 1 L of HBS-EP buffer on stirrer at 4 °C for at least 8 h. The HBS-EP buffer should be changed to fresh one twice with at least 8 h interval.
Notes:- Imbalance in the refractive index between antigen solution and running buffer will cause high background signal (called bulk effect) and perturb the SPR analysis.
- The concentration of antigen is recommended to be 5 μM or higher, because the dissociation constant for weak antigen-antibody interaction sometimes reaches to 10-6 M range and in that case SPR experiment requires relatively high concentration of antigen, that is 5 μM or more.
- Imbalance in the refractive index between antigen solution and running buffer will cause high background signal (called bulk effect) and perturb the SPR analysis.
- Determine antigen concentration by ultraviolet UV spectroscopy or standard BCA analysis.
- Prepare reagents (HBS-EP buffer, 400 mM EDC, 100 mM NHS, 50 mM NaOH, 1 M 2-ethanolamine-HCl, glycine buffers and acetate buffers).
- Immobilization of anti-human Fcγ on sensor chip
- Set sensor chip into the SPR instrument.
Note: In all steps dealing with the instrument, you should follow the instrument’s manual. - Set the 1 L of HBS-EP buffer as running buffer.
- Prepare 300 μl l of ligand solutions: 100 μg/ml anti-human Fcγ solutions of four different pH values (4.0, 4.5, 5.0 and 5.5) by diluting with the 10 mM acetate buffer.
- Inject ligand solutions and determine the optimum pH condition in which the highest response level is observed (Figure 1a).
Note: When there is little or no difference, select higher pH in order to avoid ligand deterioration and to promote coupling reaction. Practically, pH 4.0 or 4.5 is selected for immobilization of anti-human Fcγ, though you should determine for your SPR system. - Initialize the chip surface by injecting 30 μl of 50 mM NaOH.
- Activate the chip surface by injecting 70 μl of 1:1 EDC/NHS mix.
- Inject anti-human Fcγ solution and check the baseline increment. Repeat injection until the increment becomes undetectable.
Note: In this step anti-human Fcγ should immobilize as much as possible. Usually, approx. 8,000 (Resonance Unit, RU) increment is obtained. - Inject 70 μl of 1 M 2-ethanolamine-HCl solution to block the active carboxyl groups remained on the sensor chip.
Note: If you want stop the experiment in this step, eject the sensor chip from the instrument and store at 4 °C in HBS-EP buffer to prevent drying out.
- Set sensor chip into the SPR instrument.
- Check the antigen-MAb interaction and design experiment.
- Prepare 1 ml of 1 μg/ml MAb solution by diluting with HBS-EP buffer.
Note: The original MAb solution should not include any reagents which perturb the interaction between MAb and anti-human Fcγ, for example, 100 mM glycine buffer of pH 2.4 or lower. - Inject target MAb and check the immobilization amount as the increment of baseline level.
Note: For SPR analysis, smaller immobilization amount is preferred as far as the response against antigen gives sufficient signal. - Inject 30 μl of 10 mM glycine solutions of different pH values 1.8, 2.0, 2.2, and 2.4. By checking the decrement of the baseline level, determine the MAb-stripping condition (pH, injection period, number of injections, period required for baseline stabilization).
Note: The baseline level should be close to the level before MAb immobilization. An example of practical condition is as follows: Inject 30 μl of 10 mM Glycine pH 2.0 thrice and wash by running buffer for 600 seconds as baseline stabilization period. - Prepare 1 ml of 1 μM antigen solution by diluting with HBS-EP buffer.
- Clarify the antigen solution by centrifugation at 15,000 x g for 5 min at room temperature.
- Inject 60 μl of the antigen solution and check the SPR response.
Note: The minimum response level is 1 RU or less as far as the response curve is recognizable, though it apparently depends on the baseline stability, in other words, stability of the SPR system. - Determine antigen-stripping condition by injecting 60 μl of 1 M NaCl or 3 M MgCl2.
Note: As other option, you can remove the whole antigen-MAb with glycine buffer and retry from the MAb immobilization step. Antigen-stripping condition is not necessarily required depending on the experimental design. - Prepare 1 ml of antigen solutions of at least 5 different concentrations by 1:1 serial dilution with HBS-EP buffer.
- Determine the experimental design considering the following points.
- MAb immobilization condition.
- Injection period for the antigen solution and washing period.
Notes:- They are corresponding to the lengths of association and dissociation phases, respectively. Set appropriate values to obtain significant signal level and sufficient curvature.
- In some cases antigen dissociates very slowly from MAb, and then we need to set very long washing period. When no dissociation is observed, try reducing the immobilizing level of MAb.
- They are corresponding to the lengths of association and dissociation phases, respectively. Set appropriate values to obtain significant signal level and sufficient curvature.
- Antigen-stripping condition.
- Design of blank experiment: without MAb immobilization and/or injecting HBS-EP buffer in replace of antigen solution.
- Setting for individual flow paths.
Note: Usually, SPR system has multiple flow paths useful for blank experiment and for examination of multiple MAbs at once.
- MAb immobilization condition.
- Prepare 1 ml of 1 μg/ml MAb solution by diluting with HBS-EP buffer.
- Curve analysis
- Collected experimental data is analyzed according to the fitting algorism supplied by vendor of the SPR system (For example, see Figure 1c). Usually, 1:1 Langmuir fitting model is employed.
Note: Check the chi-square value and quality index supplied by the software.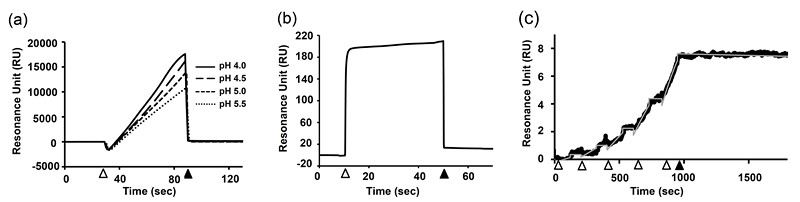
Figure 1. Practical example of the SPR experiment.- Determination of the pH value for amine-coupling immobilization of anti-human Fcγ. pH 4.0 showed the highest response, however, it also showed signs of leveling off. Then, we have chosen pH 4.5 in this case. Open arrowhead and closed arrowhead indicate the start and end points of the injection of anti-human Fcγ solution, respectively.
- Immobilization of MAb on the sensor chip via the interaction between anti-human Fcγ and human MAb. Open arrowhead and closed arrowhead indicate the start and end points of the injection of human MAb solution, respectively. The increment of baseline level (in this case, approx. 10 RU) represents the immobilized amount of MAb.
- Representative SPR response for the interaction between influenza B hemagglutinin (HA) and a human anti-HA antibody. Open arrowheads indicate the injection of HA solution and correspond to the association phase. Closed arrowhead indicates the end of the final injection and corresponds to the start of the dissociation phase. Fitting curve obtained by the 1:1 Langmuir fitting model was also shown by gray line.
- Determination of the pH value for amine-coupling immobilization of anti-human Fcγ. pH 4.0 showed the highest response, however, it also showed signs of leveling off. Then, we have chosen pH 4.5 in this case. Open arrowhead and closed arrowhead indicate the start and end points of the injection of anti-human Fcγ solution, respectively.
- Collected experimental data is analyzed according to the fitting algorism supplied by vendor of the SPR system (For example, see Figure 1c). Usually, 1:1 Langmuir fitting model is employed.
Notes
- Usually SPR analysis is performed under an integrated system in which equipment (sensor chip, buffer bottle, sample tube, etc), experimental design, analysis algorism and even in reagents are all supplied for using that instrument. We just described here a general procedure of SPR experiment for antigen-MAb interaction analysis. Please follow the manual of your instrument and/or contact the vendor for more detailed protocol.
Recipes
- 0.5 M HEPES buffer (pH 7.4) (500 ml)
Mix 59.6 g of HEPES powder with 400 ml dH2O
Adjust pH to 7.4 with NaOH
Add dH2O to 500 ml
Filtrate by 0.22 μm bottom top filter and vacuum pump - 0.5 M EDTA (pH 8.0) (500 ml)
Mix 93.1 g of EDTA.2Na with 400 ml dH2O
Adjust pH to 8.0 with NaOH
Add dH2O to 500 ml
Filtrate by 0.22 μm bottom top filter and store at room temperature - 20 % (v/v) polysorbate 20 (500 ml)
Add 400 ml dH2O to 100 ml polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan monolaurate - 10x HBS-E (500 ml)
Mix 100 ml 0.5 M HEPES buffer, pH 7.4
30 ml 0.5 M EDTA, pH 8.0
44 g NaCl
Add dH2O to 500 ml - 1x HBS-EP (4 L)
10x HBS-E buffer 400 ml
Add dH2O to 4 L
Filtrate by 0.22 μm bottom top filter and vacuum pump
Add 1 ml 20% (v/v) polysorbate 20 - 400 mM EDC (10 ml)
Dissolve 750 mg EDC in 10 ml dH2O
Dispense 200 μl into 1.5 ml tubes and store at -20 °C - 100 mM NHS (10 ml)
Dissolve 115 mg NHS in 10 ml dH2O
Dispense 200 μl into 1.5 ml tubes and store at -20 °C - 1 M 2-ethanolamine (pH 8.5) (50 ml)
Dilute 3.0 ml of 2-ethanolamine with dH2O to 40 ml
Adjust pH to 8.5 by HCl
Add dH2O to 50 ml
Dispense 1 ml into 1.5 ml tubes and store at 4 °C - 50 mM NaOH (10 ml)
Dilute 250 μl of 2 M NaOH solution with dH2O to 10 ml.
Dispense 1 ml into 1.5 ml tubes and stored at room temperature - 10 mM Acetate buffer (pH 4.0, 4.5, 5.0, 5.5) (50 ml each)
Mix 8.2 g sodium acetate with 100 ml dH2O to prepare 1 M acetate-Na
Dilute 5.7 ml of acetate with 100 ml dH2O to prepare 1 M acetate
Prepare 10 mM acetate-Na and 10 mM acetate by 100-fold dilution with dH2O
Adjust pH by mixing 10 mM acetate and 10 mM acetate-Na
Filtrate by 0.22 μm filter and syringe - Glycine buffer 10 mM (pH 1.8, 2.0 2.2, 2.4) (50 ml each)
Mix 0.30 g glycine with dH2O and add dH2O to 200 ml
Dispense 50 ml glycine solution into 100 ml beaker
Adjust pH by adding HCl
Add dH2O to 100 ml
Filtrate by 0.22 μm filter and syringe - 1 M NaCl
Mix 2.9 g NaCl with dH2O to 50 ml
Filtrate by 0.22 μm filter and syringe - 3 M MgCl2
Mix 30.5 g MgCl2.6H2O with dH2O and adjust volume to 50 ml
Filtrate by 0.22 μm filter and syringe
Acknowledgments
This protocol was established by reference to the product manuals of Biacore T200 (GE-Healthcare) and ProteOn XPR36 (BIO-RAD).
References
- Yasugi, M., Kubota-Koketsu, R., Yamashita, A., Kawashita, N., Du, A., Sasaki, T., Nishimura, M., Misaki, R., Kuhara, M., Boonsathorn, N., Fujiyama, K., Okuno, Y., Nakaya, T. and Ikuta, K. (2013). Human monoclonal antibodies broadly neutralizing against influenza B virus. PLoS Pathog 9(2): e1003150.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Nishimura, M. and Ikuta, K. (2013). Surface Plasmon Resonance Analysis of Antigen-Antibody Interaction. Bio-protocol 3(24): e1006. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1006.
- Yasugi, M., Kubota-Koketsu, R., Yamashita, A., Kawashita, N., Du, A., Sasaki, T., Nishimura, M., Misaki, R., Kuhara, M., Boonsathorn, N., Fujiyama, K., Okuno, Y., Nakaya, T. and Ikuta, K. (2013). Human monoclonal antibodies broadly neutralizing against influenza B virus. PLoS Pathog 9(2): e1003150.
Category
Immunology > Antibody analysis > Antibody-antigen interaction
Biochemistry > Protein > Interaction > Protein-protein interaction
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link











