- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Isolation of Neutralizing Antibody
Published: Vol 3, Iss 24, Dec 20, 2013 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1005 Views: 10700
Reviewed by: Anonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Quantification of Trypanosoma cruzi in Tissue and Trypanosoma cruzi Killing Assay
Hisako Kayama [...] Kiyoshi Takeda
Nov 20, 2017 8170 Views

A Refined Protocol for Identifying Citrulline-specific Monoclonal Antibodies from Single Human B Cells from Rheumatoid Arthritis Patient Material
Khaled Amara [...] Caroline Grönwall
Sep 5, 2019 6991 Views

Multiplication and Growth Inhibition Activity Assays for the Zoonotic Malaria Parasite, Plasmodium knowlesi
Franziska Mohring [...] Robert W. Moon
Sep 5, 2020 5891 Views
Abstract
Use of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) is an established laboratory strategy for characterization of specific pathogens and their antigenicity. Especially, Human MAbs (HuMAbs) with neutralizing activity against specific virus could have potential therapeutic application, and provide significant information on human epitopes that could be important for developing the next generation of universal vaccines against the virus. In addition to the classical method for murine MAb preparation, several methods for the preparation of HuMAbs have been developed. Here, we describe the development of neutralizing HuMAbs against specific virus. HuMAbs are established by fusion of the peripheral blood mononuclear cells of vaccinated volunteers or patients with the fusion partner cell line, named SPYMEG. Then each of prepared HuMAbs is confirmed whether it can neutralize the specific virus by in vitro neutralization assay.
Keywords: InfluenzaMaterials and Reagents
- Human blood immunized by vaccination or natural infection against specific pathogen
- Human fusion partner SPYMEG cells (product of the Medical & Biological Laboratories Corporation, Ltd, Nagoya, Japan)
- Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells provided from RIKEN cell bank
- MDCK-propagated Influenza B viruses (B/Florida/06/2004 and B/Malaysia/2506/2006) by the National Institute for Infectious Diseases, Japan
- Phosphate-buffered saline without Ca2+ and Mg2+ (PBS)
- HetaSep (STEMCELL Technologies, catalog number: 07906 )
- Ficoll-Paque PLUS (GE, catalog number: 17-1440-03 )
- Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM) (Life Technologies, catalog number: 11995 )
- Polyethylene glycol #1500 (PEG) (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 00-783-641-00 )
- Fecal Bovine Serum (FBS) (MP Biomedicals, catalog number: 2917054 )
- HAT supplement (Life Technologies, catalog number: 21060 )
- Antibody against the specific pathogen
- HT supplement (Life Technologies, catalog number: 11067 )
- Minimal Essential Medium (MEM) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M4655 )
- Ethanol (Nacalai Tesque, catalog number: 14713-53 )
- Hybridoma SFM (Life Technologies, catalog number: 12045-084 )
- HiTrap Protein G HP (GE, catalog number: 17-0404-01 )
- BM condimed (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 10-663-573-001 )
- Heparin 5,000 units per 5 ml (Novo-Heparin, Mochida Phrrmaceutical)
- FITC-conjugated anti-human IgG (Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories, catalog number: 109-096-097 )
- DMEM-FBS medium (see Recipes)
- DMEM-HAT medium (see Recipes)
- DMEM-HT medium (see Recipes)
- PBS (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 75 cm2 cell culture flask (T-75 flask) (IWAKI PUMPS, catalog number: 3110-075 )
- 15- and 50-ml plastic tube (BD Biosciences,, catalog number: 352096 and 352070 )
- 6- and 10-cm culture dish (IWAKI PUMPS, catalog number: 3010-060 and 3020-100 )
- 6-, 12-, 24-, 48- and 96-well cell culture plate (IWAKI PUMPS, catalog number: 3810-006 , 3815-012 , 3820-024 , 3830-048 and 3860-096 )
- Light microscope
- Fluorescent microscope
- CO2 incubator (5% CO2, 37 °C)
- Incubator
- Peristaltic pump (Perista BioMini Pump; ATTO Corporation)
- Slide A Lyzer Dialysis Cassetes (MW = 10 K) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, model: 2160728 )
- Beaker
- Stirrer
- Stirrer bar
- Millex-HV Filter Unit 0.45 μm (EMD Millipore, model: SLHVJ13SL )
- 2.5-ml syringe
- Floater
- 21 G needle
- Centrifuge (TOMY DIGITAL BIOLOGY, model: LC-121 ; TS-7 rotor )
Procedure
Note: Every centrifugation step is performed at room temperature.
- Preparation of SPYMEG cells (SPYMEG cells, that are almost confluent in a T-75 flask, are needed per 10 ml blood sample)
- SPYMEG cells stored in freezed condition are thawed.
- Cells are transferred to a 15-ml tube and 10 ml DMEM-FBS are added.
- The cell suspension is centrifuged at 1,000 rpm for 5 min.
- The supernatants are aspirated and the cells in the precipitate are suspended with 20 ml DMEM-FBS.
- They are transferred to a T-75 flask.
- The cells are incubated in the CO2 incubator until the cells become confluent.
- Fresh 10 ml DMEM-FBS are added to the flask a day ahead of fusion.
- The cultured medium is aspirated and 10 ml DMEM is added in the flask.
- The cells are detached by tapping the flask strongly.
- The cells are transferred to a 50-ml tube.
- Tube is centrifuged at 1,000 rpm for 5 min.
- The supernatants are removed.
- The cell pellets are suspended with 10 ml DMEM.
- Tube is centrifuged at 1,000 rpm for 5 min.
- The supernatants are aspirated.
- The cell pellets are suspended with10 ml DMEM.
- SPYMEG cells stored in freezed condition are thawed.
- Isolation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs)
- Fresh 10 ml blood is drawn from vaccinated donors or patients.
- Blood is collected in 15-ml tube including 1 drop of heparin.
- Blood is centrifuged at 1,000 rpm for 5 min.
- Plasma layer is removed.
- PBS is added up to 10 ml in the total volume.
- 3 ml undiluted HetaSep is added.
- The blood cells are mixed gently and stood for 1 h at room temperature.
- The upper layer is collected carefully and overlaid on 5 ml undiluted Ficoll in a 15-ml tube.
- Tube is centrifuged at 1,700 rpm for 1 h. (The brake is off).
- The upper layer is removed and the turbid intermediate layer is transferred to a new 50-ml tube.
- DMEM is added up to 20 ml in the total volume.
- The cells are mixed gently and centrifuged at 1,700 rpm for 5 min.
- The supernatants are removed.
- 20 ml DMEM is added.
- The cells are mixed gently and centrifuged at 1,700 rpm for 5 min.
- The supernatants are removed.
- 10 ml DMEM is added and the cells are mixed gently.
- Fresh 10 ml blood is drawn from vaccinated donors or patients.
- Fusion
- 10 ml SPYMEG cells prepared in A16 and 10 ml PBMCs solution prepared in B17 are mixed gently in a 50-ml tube.
- The mixed cell suspension is centrifuged at 1,400 rpm for 5 min.
- The supernatants are removed.
- The 0.6 ml undiluted PEG is added gradually to the cell pellet and the cells are stirred gently (It should take 4 min).
- 10 ml DMEM is added gradually and the mixture is stirred gently (It should take 2 min).
- 10 ml DMEM-FBS is added (not need to mix).
- The tube is centrifuged at 1,400 rpm for 5 min.
- The supernatants are removed.
- 10 ml DMEM-FBS is added and the cells are mixed gently.
- Tube is centrifuged at 1,000 rpm for 5 min.
- The supernatants are removed.
- 10 ml DMEM-HAT is added and the cells are mixed gently.
- The cell solution is divided into 2 tubes.
- 45 ml DMEM-HAT is added to each of tube.
- 100 ml cell solution is seeded to 500 wells in 96-well plates (200 μl cell suspension per well).
- Plates are incubated in the CO2 incubator.
- 100 μl culture medium is changed to new DMEM-HAT every 3 to 4 days until fused cells grow up.
- 10 ml SPYMEG cells prepared in A16 and 10 ml PBMCs solution prepared in B17 are mixed gently in a 50-ml tube.
- Screening for the hybridoma producing antigen-specific antibody
- The infected MDCK cells are prepared for screening.
- MDCK cells are passaged in 2 x 104 cells per well (100 μl per well) in 96-well plates using MEM including 10% FBS a day ahead of infection.
- MDCK cells are washed with 100 μl PBS once. After aspiration of PBS, MDCK cells are adsorbed 50 μl influenza B virus propagated with MDCK cells at an MOI of 0.1 for 1 h in the CO2 incubator.
- 100 μl MEM is added to the wells.
- The plates are incubated in the CO2 incubator for 12 h.
- The medium is removed.
- The cells are washed with 100 μl PBS once and fixed with 200 μl absolute ethanol for 2 min at room temperature.
- The plates are air-dried and stored at -20°C until screening.
- MDCK cells are passaged in 2 x 104 cells per well (100 μl per well) in 96-well plates using MEM including 10% FBS a day ahead of infection.
- The fixed MDCK cells prepared in D1 are adsorbed with the 75 μl cultured medium of fused cells prepared in C16 at 37 °C for 40 min.
- They are washed with 100 μl PBS three times with agitation for 5 min each.
- The plates are adsorbed with 75 μl FITC-conjugated anti-human IgG (1:500) and stood at 37 °C for 50 min.
- They are washed with 100 μl PBS three times with agitation for 5 min each.
- The fluorescent positive cells are observed under fluorescent microscope.
- The wells of hybridoma whose culture medium yield fluorescently positive cells are processed to cell cloning.
- The infected MDCK cells are prepared for screening.
- Cloning of the hybridoma
- Each of wells including fluorescent positive cells in D7 is pipetted until the cells are detached.
- Cell number is counted using counting chamber.
- The cell suspension is adjusted to 1 cell per well in 96-well plate with DMEM-HT (200 μl per well).
- They are seeded to a 96-well plate and incubated in the CO2 incubator.
- 100 μl medium is changed to new DMEM-HT every 3 to 4 days until the cells grow up (Cell proliferation is checked using light microscope).
- Screening is performed again to select the antigen-specific hybridoma clone as described in D1 to D7.
- The hybridoma clones producing antigen-specific antibody are passaged to the larger-well plates (96-, 48-, 24-, 12- and 6-well plates and 6-cm culture dish) and ultimately grown up in 10-cm culture dish.
- Each of wells including fluorescent positive cells in D7 is pipetted until the cells are detached.
- Purification of human monoclonal antibody
- Ten 10-cm dishes including confluent hybridoma in DMEM-HT are prepared.
- The medium is changed to Hybridoma SFM.
- The cells are incubated in the CO2 incubator until the half of hybridoma cells die.
- The cultured medium are collected and centrifuged at 5,000 rpm for 30 min.
- The monoclonal antibody is purified by IgG-affinity column (HiTrap Protein G HP) according to the manufacturer’s instructions using Peristaltic pump.
- The purified antibody is filled in the syringe with needle.
- The antibody is injected to the dialysis cassette.
- The cassette with a floater is immersed in a beaker filled with 1,000 ml PBS and stirred at 4 °C for 2 h.
- 1,000 ml PBS is changed and the cassette is stirred again at 4 °C for 2 h.
- 1,000 ml PBS is changed and the cassette is stirred again at 4 °C overnight.
- The antibody in the cassette is collected and filtrated with a 0.45 μm filter.
- The concentration of the antibody is measured.
- Ten 10-cm dishes including confluent hybridoma in DMEM-HT are prepared.
- Viral neutralization assay
- MDCK cells are prepared in a 96-well plate a day ahead of viral neutralization assay as described in D1.
- The antibody at a concentration of 100 μg/ml is serially 4-fold diluted with MEM.
- 30 μl diluted antibodies or MEM as a control are incubated with 30 μl 200 focus-forming units of virus in the CO2 incubator for 1 h.
- MDCK cells are washed with 100 μl PBS and adsorbed with 30 μl mixture prepared in VII-3 in the CO2 incubator for 1 h.
- MDCK cells are washed with 100 μl PBS three times and added 100 μl MEM.
- They are incubated in the CO2 incubator for 12 h.
- The cells are washed with 100 μl PBS and fixed with 200 μl absolute ethanol for 2 min at room temperature.
- The cells are air-dried.
- The fixed MDCK cells are adsorbed with 75 μl 1st antibody (mouse serum infected with influenza B virus, 1:500) for detecting viral antigen and incubated at 37 °C for 30 min.
- They are washed with 100 μl PBS three times.
- They are adsorbed with 75 μl FITC-conjugated antibody for IgG of the 1st antibody and incubated at 37 °C for 45 min.
- They are washed with 100 μl PBS three times.
- The antigen positive cells are counted in each of wells under observation by fluorescent microscope (Figure 1).
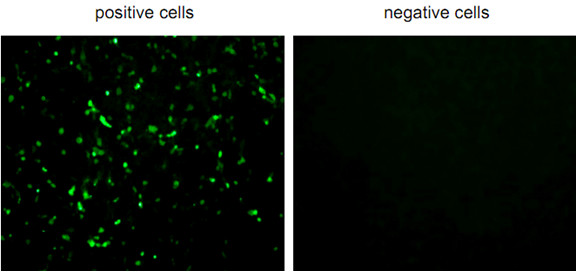
Figure 1. Fluorescent positive or negative cells observed by fluorescent microscope
- When the cell number is lower in the wells treated with antibody than in control (treated with PBS), the antibody is regarded as neutralizing monoclonal antibody. The lowest concentration of MAb that shows positive cell number to 50% compared with control is designated the VN50 titer. Low VN50 titer means that the MAb has strong neutralizing activity.
- MDCK cells are prepared in a 96-well plate a day ahead of viral neutralization assay as described in D1.
Recipes
- DMEM-FBS medium (500 ml)
DMEM
425 ml
FBS
75 ml
- DMEM-HAT medium (500 ml)
DMEM
401 ml
FBS
75 ml
HAT supplement
8 ml
HT supplement
1 ml
BM condimed
15 ml
- DMEM-HT medium (500 ml)
DMEM
405 ml
FBS
75 ml
HT supplement
5 ml
BM condimed
15 ml
- PBS (1,000 ml) pH is not adjusted.
NaCl
8 g
Na2HPO4.12H2O
2.9 g
KCl
0.2 g
KH2PO4
0.2 g
dH2O
1,000 ml
Autoclaved
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Japan Science and Technology Agency/Japan International Cooperation Agency, Science and Technology Research Partnership for Sustainable Development (JST/JICA, SATREPS) (http://www.jst.go.jp/global/kadai/h2011_thailand.html); and a Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (B) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science to MY (#23790660).
References
- Yasugi, M., Kubota-Koketsu, R., Yamashita, A., Kawashita, N., Du, A., Sasaki, T., Nishimura, M., Misaki, R., Kuhara, M., Boonsathorn, N., Fujiyama, K., Okuno, Y., Nakaya, T. and Ikuta, K. (2013). Human monoclonal antibodies broadly neutralizing against influenza B virus. PLoS Pathog 9(2): e1003150.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Yasugi, M. and Ikuta, K. (2013). Isolation of Neutralizing Antibody. Bio-protocol 3(24): e1005. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1005.
- Yasugi, M., Kubota-Koketsu, R., Yamashita, A., Kawashita, N., Du, A., Sasaki, T., Nishimura, M., Misaki, R., Kuhara, M., Boonsathorn, N., Fujiyama, K., Okuno, Y., Nakaya, T. and Ikuta, K. (2013). Human monoclonal antibodies broadly neutralizing against influenza B virus. PLoS Pathog 9(2): e1003150.
Category
Immunology > Antibody analysis > Antibody function
Microbiology > Antimicrobial assay > Killing assay
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link











