- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Extraction of Soluble and Insoluble Protein Fractions from Mouse Brains and Spinal Cords
小鼠脑和脊髓中可溶性和不溶性蛋白质组分的提取
发布: 2017年08月05日第7卷第15期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2422 浏览次数: 28846
评审: Fanny EhretAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
The current protocol details the preparation of soluble and insoluble protein lysates from mouse brain or spinal cord samples. In detail, tissue homogenization and sequential protein extraction are described. This procedure yields soluble and insoluble protein extracts that can be further processed in down-stream applications like ELISA or Western blotting.
Keywords: Protein extraction (蛋白质提取)Background
This simple and reproducible protocol of brain tissue protein fractionation details the initial separation of a total protein homogenate into a soluble and an insoluble fraction. It can also be applied also to other tissue samples and yields a soluble fraction containing hydrophilic proteins and an insoluble fraction consisting of more hydrophobic proteins. Following an initial homogenization in a lysis buffer containing no detergent, the supernatant including the soluble protein fraction is removed and the pellet containing the insoluble fraction can be further extracted using Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) as detergent to ensure entire cell lysis (see Figure 1). This approach can facilitate the analysis of low-abundance proteins by reducing the complexity of the sample. 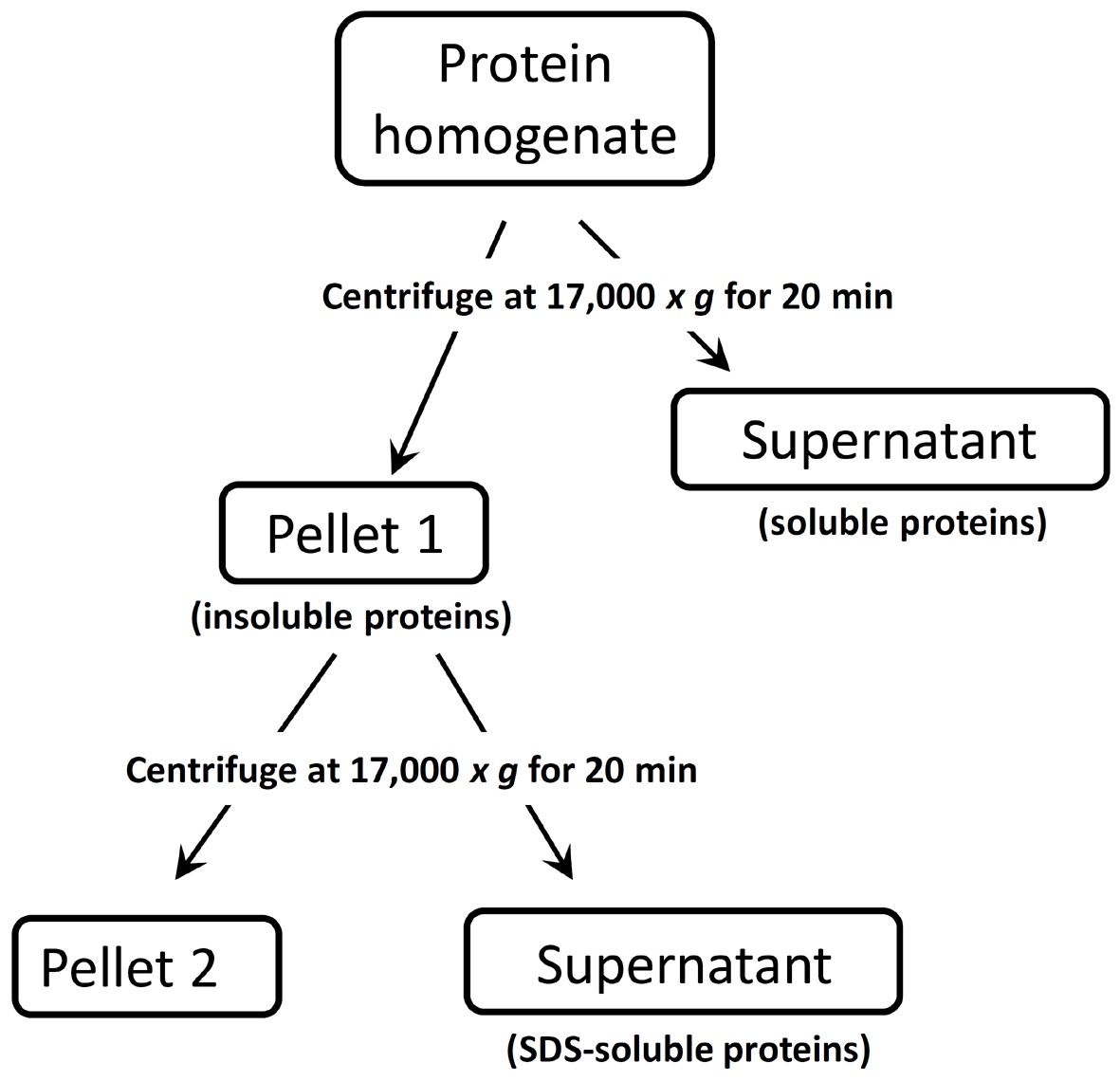
Figure 1. Flow-chart describing the sequential extraction procedure
Materials and Reagents
- Pipette tips
10 µl pipette tips (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 70.1130 )
200 µl pipette tips (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 70.760.002 )
1,000 µl pipette tips (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 70.762 ) - Reaction tubes
1.5 ml tubes (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 72.706 )
2 ml tubes (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 72.691 ) - Mice (protocol has been tested with male and female C57Bl/6 mice of 8-52 weeks)
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (≥ 99.5%) (Carl Roth, catalog number: 3957 )
- Tris (≥ 99.9%, p.a.) (Carl Roth, catalog number: 4855 )
- Protease inhibitor cocktail (cOmpleteTM Mini EDTA-free EasyPack) (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 04693159001 )
- Phosphatase inhibitor cocktail 3 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P0044 )
- Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) (≥ 99.5%) (Carl Roth, catalog number: 2326 )
- Benzonase (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: E1014 )
- Lysis buffer (see Recipes)
- 2% SDS (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Pipettes (Research 0.5-10 µl, 10-100 µl, 100-1,000 µl) (Eppendorf)
- Glass homogenizer (2 ml) (Carl Roth, catalog number: TT57.1 )
- Teflon pestle (Carl Roth, catalog number: TT63.1 )
- Stirring device (Ingenieurbüro CAT M. Zipperer, model: R 50D )
- Heraeus Biofuge Stratos (Rotor) (Heraeus Holding, catalog number: 3332 )
- Ultrasound sonicator (Emerson Electric, BRANSON, model: 150 )
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Wirths, O. (2017). Extraction of Soluble and Insoluble Protein Fractions from Mouse Brains and Spinal Cords. Bio-protocol 7(15): e2422. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2422.
分类
神经科学 > 细胞机理 > 蛋白质分离
分子生物学 > 蛋白质 > 分离
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
提问指南
+ 问题描述
写下详细的问题描述,包括所有有助于他人回答您问题的信息(例如实验过程、条件和相关图像等)。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link