Advanced Search
Dissection
Last updated date: Feb 2, 2021 Views: 929 Forks: 0
Surgical tools:
Iris scissors - 41/2" strait-sharp spring scissors, ROBOZ, catalog #: RS-5676SC.
Fine tip forceps FST-Fine Science Tools, Dumont 5SF, catalog# 11252-00
Standard sharp scissors
Extra fine forceps 1x2 teeth, FST, Graefe, catalog# 11153-10
Styrofoam lid or necropsy table and pins/needles or tape
Reagents:
Four to six, 10-12-week-old male FVB/NJ mice: JAX stock number 001800.
70% ethanol
10 cm petri-dishes
5 cm petri-dishes
Antibiotic and Anti-mycotic: 100X Anti-Anti (ThermoFisher 15240062 Antibiotic-Antimycotic (100X)).
Fetal bovine serum (FBS): ThermoFisher 10082-147.
KREBs Medium (see OBS at the end of this protocol):
-1 bottle Krebs buffer powder (Sigma Aldrich Product Number K3753)
-20mL 50X Amino Acid Solution (Gibco 1130-051)
-10mL 100X NEAA (Gibco 11140-050)
-10mL 100X glutaMAX (Gibco 35050-061)
-CaCl2 (0.14g)
-NaHCO3 (2.1g)
-0.14% BSA (14g)
- ~800mL ddH20 (fill to 1000mL after pH w/ 1M NaOH to pH 8.0)
1X RPMI-1640 Medium: Sigma R0883-6X500ml.
Complete RPMI Medium: RPMI-1640 supplemented with 10% FBS and 1X Antibiotic and Anti-mycotic.
Procedure:
Before you start make sure you have sterilized surgical instruments and a clean dissection area.
1) Euthanize mice, according to your institutions’ approved methods. We use isoflurane followed by cervical dislocation.
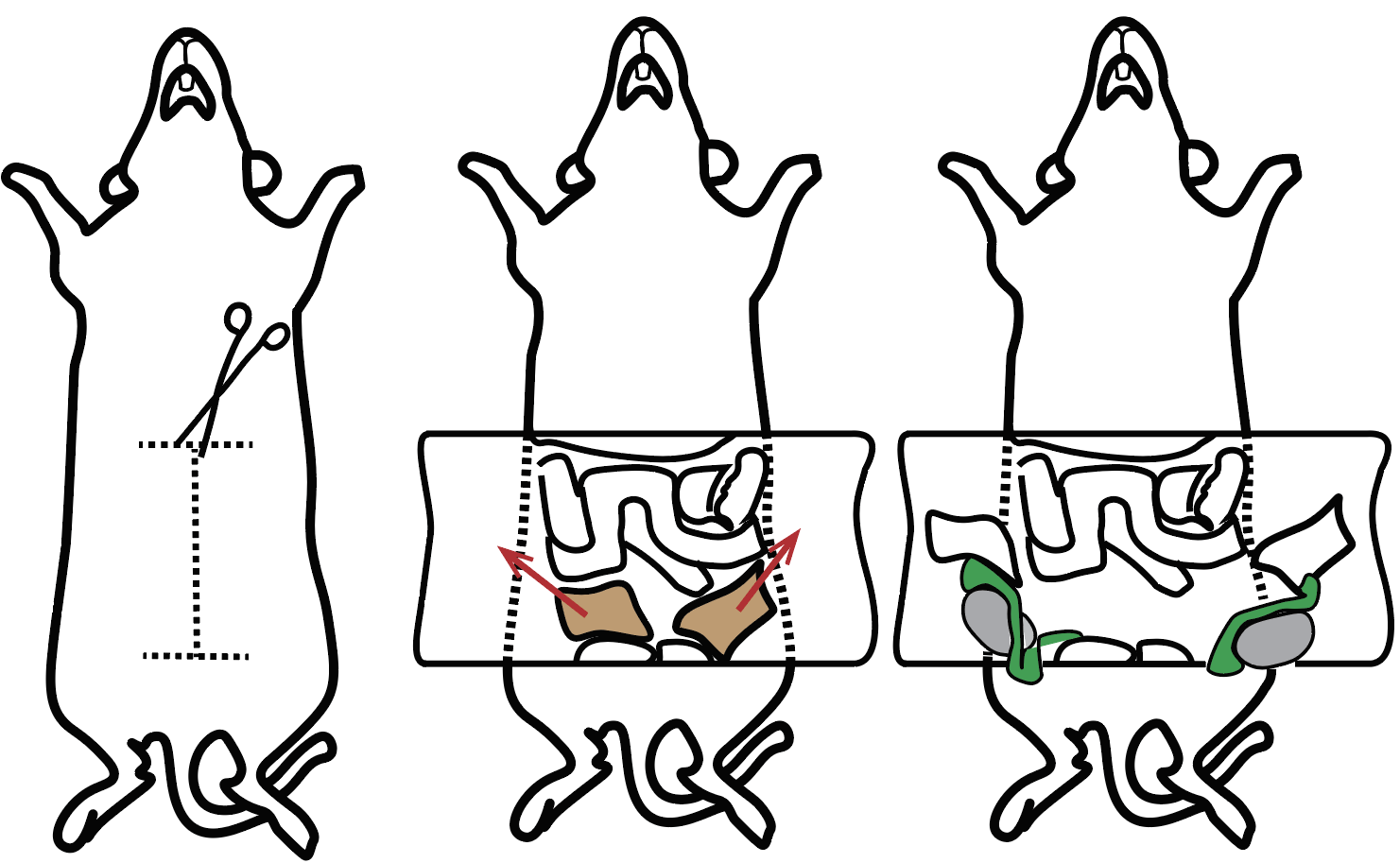
2) Once animal is dead, place it in dorsal recumbency and secure each limb to the Styrofoam with a pin/needle or tape the limbs to the necropsy table.
3) Wet the ventral fur and skin with 70% alcohol.
4) Using the fine-toothed forceps and a standard scissors, make an incision at the lower abdomen, being careful not to cut the intestine or any visceral organs. Cut the abdominal wall forming and pinch the flaps in the Styrofoam/necropsy stage (see image bellow).
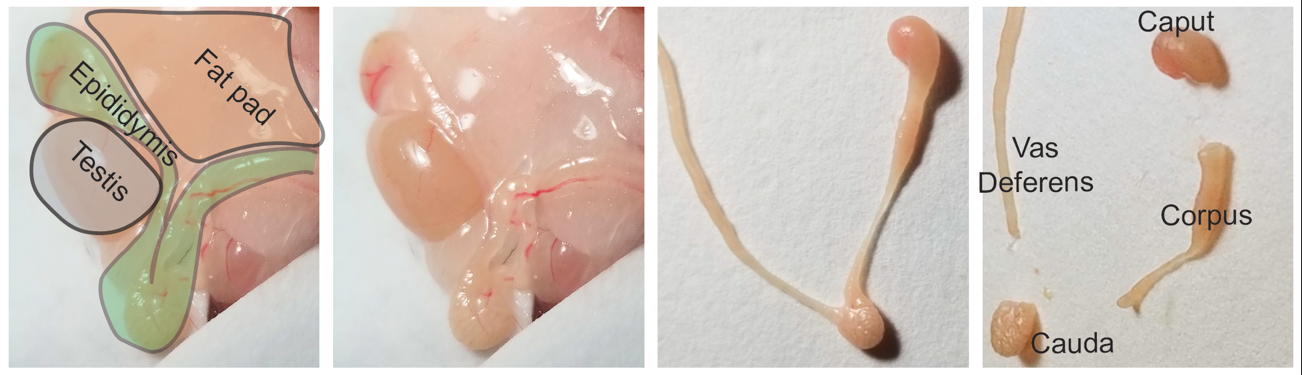
5) Locate the epididymal fat pad at the distal abdominal region there (represented in light brown in the schematic below). Locate both right and left fat pads and pull them until the testis and epididymis are visible and accessible (testis is represented in grey and epididymis in green).
6) Using a fine forceps and a spring scissor, excise the epididymis and place them in a 10cm dish with 10mL pre-warmed (35°C) complete RPMI media.
7) Clean the epididymis from excessive fat and connective tissue. For better precision remove the excessive tissue using a dissection microscope with warm stage set to 35°C. After cleared of fat and excessive connective tissue place organs in a new 10-cm dish containing fresh 10 mL of Krebs media.
8) Cut organs into four segments that roughly correspond to caput, corpus, cauda, and vas deferens (see below and Figure 1A of manuscript). Place each group of eight segments into a properly labeled 5-cm petri-dishe with about 2 mL of new Krebs media. Using a curved scissors cut samples into roughly 1–5 mm pieces.
9) Transfer samples to a properly labeled 15-mL conical tube and add new Krebs media to 10 mL. In order to get rid of as much sperm as possible washes with fresh media, followed by gravity decantation in an upright position should be performed at least two times. For a final wash transfer samples to a 50-mL conical tube containing 25 mL pre-warmed RPMI-1640 media. After ten minutes incubation at 35°C under mild agitation, allow samples to settle for 3–5 min, discard supernatant and proceed to tissue disaggregation.
Obs: The Rando lab has switched to using only IMDM (IMDM GlutaMAX, +25mM HEPES, +3.024g/L Sodium Bicarbonate (Gibco Cat# 31980030)) media in all steps instead of KREBS and RPMI and has been obtaining similar results.
- Rinaldi, V and Rando, O(2021). Dissection. Bio-protocol Preprint. bio-protocol.org/prep808.
- Rinaldi, V. D., Donnard, E., Gellatly, K., Rasmussen, M., Kucukural, A., Yukselen, O., Garber, M., Sharma, U. and Rando, O. J.(2020). An atlas of cell types in the mouse epididymis and vas deferens. eLife. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.55474
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link
