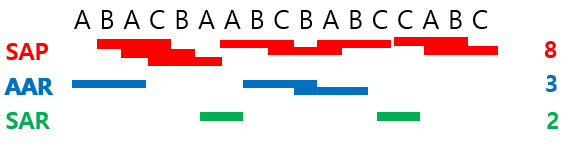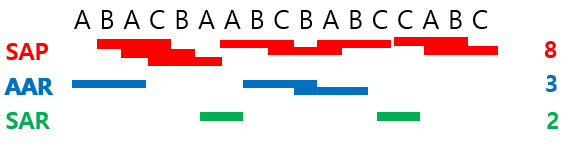A modified version of the Y-maze test
1. This take was conducted of black polypropylene walls with three arms (10 × 40 × 16 cm).
Note: Behavior was measured in a quiet and darkroom.
2. Before all experiments, rats underwent 2 days of habituation, during which they were allowed to freely visit all arms for 10 min.
3. In the sample phase trial, each animal was individually placed in the maze with one of the three arms closed. The animals were allowed to explore the other two arms freely for 10 min. 4. The test phase trial was conducted 24 h after the sample phase trial for 10 min.
5. The previously closed arm was opened in the test phase trial and defined as the “novel arm”.
6. Behavior was video-recorded for later analysis using a SMART v3.0 video tracking system (Panlab, S.L.U., Barcelona, Spain).

The spontaneous alternation Y-maze
1. This take was conducted of black polypropylene walls with three arms (10 × 40 × 16 cm).
2. Rat freely explored the three arms of a Y-shaped maze for 30 min to habituate in the maze.
3. After 1 day, the task began at the center of the maze after habituation for 10 min.
4. Each rat was visited at the end of one arm (labeled “A”, “B”, or “C”) and allowed to move freely through the maze for 8 min.
4. SAP (spontaneous alternation performance) was defined as visiting three different arms consecutively.
Note: ABC, ACB, BCA, BAC…
5. AAR (Alternate arm return) was defined as visiting other arms and return to the same arm.
Note: ABA, ACA, BAB, BCB, CAC, CBC…
6. SAR (Same arm return) was defined as visiting the same arm repeatedly.
Note: AA, BB, CC…
7. Percent spontaneous alternation was calculated as [(number of alternations) / (total arm entries − 2)] × 100.