Preparation and characterization of nanomedicine-shelled microbubbles
1. Disperse magnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4, iron oxide) in deionized water to form a 10 mg/mL stock solution.
2. Place the tube containing the Fe3O4 solution in an ultrasonic cleaning machine for 20 min. Obtain a uniformly dispersed Fe3O4 solution before use.
3. Add 150 μL of 0.2 mg/mL SiO2-tPA nanoparticles, 150 μL of 10 mM sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), and 400 μL of a stock solution of Fe3O4 nanoparticle from step 1 in 1.5 mL centrifuge tube.
4. Fix the homogenizer with a scaffold in an ice bath.
5. Place the tube of the mixture in an ice bath and position the homogenizer probe precisely to be immersed in the mixture solution.
6. Adjust the homogenizer speed to 20,000 rpm and turn on the homogenizer for 3 min.
7. Turn off the homogenizer and remove the tube from the ice bath.
8. Place the tube to the tube rack for 12 h stabilization at room temperature.
9. Adsorb the resulted nanomedicine-shelled microbubbles to the tube wall by a magnet and remove the supernatant. Then replenish with 1 mL of fresh deionized water.
10. Repeat the wash process for three times and re-suspend nanomedicine-shelled microbubbles in 1 mL of fresh distilled water.
11. Transfer 10 μL of nanoparticle-shelled microbubbles suspension to a clean glass slide after slightly shaking.
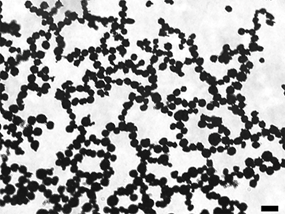
12. Use a microscope at 20x magnification to visualize nanoparticle-shelled microbubbles morphology. Ensure taking photos at random area
Nanoparticle
The iron oxide nanoparticle (Fe3O4) are hydrophobic and the iron oxide (Fe3O4 ) used in our experiment are superparamagnetic.
The surface of silica nanoparticles (SiO2) is exposed with Si-OH, which is negatively charged.
 .
.
Representative bright-field microscopy image of nanoparticle-shelled microbubbles. Scale bar: 20 μm.

 .
.