Advanced Search
Lung tumor volume measurements from X-ray micro-computed tomography (μCT) scans
Last updated date: Jul 14, 2020 Views: 1220 Forks: 0
Lung tumor volume measurements from X-ray micro-computed tomography (μCT) scans
Contat Caroline1,2; Meylan Etienne1,2
1 Swiss Institute for Experimental Cancer Research (ISREC), School of Life Sciences, Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland; 2 Swiss Cancer Center Léman, Lausanne, Switzerland;
Abstract
In genetically-engineered mouse models of lung adenocarcinoma based on KrasLSL-G12D/WT; Trp53Flox/Flox (KP) genomic alterations, pulmonary tumors develop over several months. To non-invasively follow their growth throughout cancer development, an X-rays micro-computed tomography scanning method associated with a specific software analysis were used. This longitudinal study, allowing to monitor the evolution of the tumor volumes over time, also provides a careful care to comply with the animal ethics.
Keywords
Lung tumors; X-rays micro-computed tomography (μCT); non-invasive; volume measurements; longitudinal study;
Background
This is a non-invasive method to monitor tumor growth rates longitudinally, widely used for tumor growth analyses from this or from similar mouse models by multiple research groups.
Materials and Reagents
1. Lung tumor-bearing male and female mice
2. Isoflurane (Piramal, AP/DRUGS/220/96)
3. Eye ointment (Baush + Lomb, Viscotears Carbomerum 980, 2mg/g)
4. Heating pad
Equipment
1. Anaesthesia system (PerkinElmer)
2. O2 compressor (Kröber)
3. Induction chamber
4. X-rays micro-computed tomography (μCT; Quantum FX; PerkinElmer)
5. Computer
Software
1. Quantum FX (Perkin Elmer)
2. Analyze 12.0 software (PerkinElmer) OR OsiriX MD software (Pixmeo; RRID:SCR_013618)
3. Microsoft Excel (Microsoft)
4. Prism version 8 (GraphPad)
Procedure
X-rays micro-computed tomography
1. Anesthetize the mouse using isoflurane mixed with O2
! To induce deep anaesthesia, choose an isoflurane concentration of 3%, then adjust it to 2% when the mouse is anesthetized
! O2 flowmeter: 2 litres per minute (LPM); air flowmeter: 2 LPM
2. Apply eye ointment on the mouse eyes
3. Position the mouse into the X-rays micro-computed tomography device
4. Adjust anaesthesia mask to the mouse muzzle
5. Scan lung mouse with the X-rays micro-computed tomography using the following parameters:
| Voltage (kV) | Current (μA) | Scan Time | Voxel size (μm) |
| 90 | 160 | Respiratory gating 34 sec | 50 |
! Image reconstruction is automatically done by X-rays micro-computed tomography software (Quantum FX) after the scan
! Repeat the steps 1 to 4 at a certain frequency (determined by the scientist) during lung tumor development
6. Remove the mouse from the device, put it on a heating pad
7. Monitor the mouse awaking
Longitudinal tumor volume analysis
To follow tumor volumes, Analyze 12.0 and OsiriX MD are two possible softwares.
A. Analyze 12.0
1. Load VOX file in Analyze 12.0
2. Select the file and click on Region Of Interest (ROI)… to open it
3. Select Auto Trace
4. Click in the middle of the tumor (ROI) to analyse
5. Adjust the threshold with the cursor that appears to encircle the entire ROI
6. Click on Apply
7. In the Object To Define section, select x.Object (x being a digit) to define the tumor (ROI)
8. Click on Copy Current Region Forward or on Copy Current Region Backward to encircle the entire tumor volume.
! On each slice, adjust the ROI using Add Trace Limit to encircle the entire tumor
! Repeat the step 8 on each slice on which you detect the tumor to follow
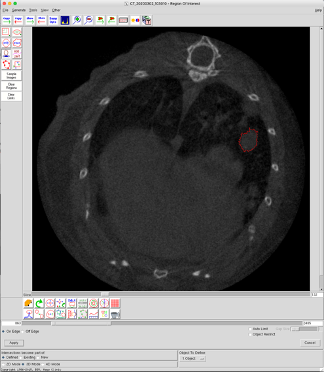
Figure A. Example of tumor volume analysis using Analyze 12.0.
A lung tumor-bearing slice with a Region of Interest (ROI) (=tumor) encircled in red.
Once the entire tumor is encircled
9. Compute the tumor volume (Generate → Sample Options… → adjust the parameters (see Figure 2) → Sample Images)
10. Copy the given volume in the Excel software (see Data Analysis, Figure D)
11. Repeat the steps 1 to 8 for several tumors of the same animal AND for the same tumor at different time points corresponding to the time-windows between two μCT scans (longitudinal study).
! Sometimes tumors can fuse between them during their development. Thus, it is recommended to observe all the scans coming from the same mouse before starting to follow a tumor to be sure that tumors could be followed all along the study.
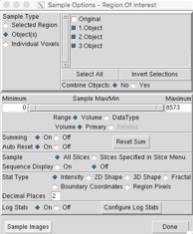
Figure B. Sample option parameters to compute tumor volume.
B. OsiriX MD
1. Convert VOX file to DICOM files using Analyze 12.0 software (File → Import/Export…)
2. Open DICOM files in OsiriX MD
3. Define a region of interest (ROI) corresponding to the tumor to follow (ROI → Set default ROI name)
4. Encircle the tumor (ROI) on several image slices (OsiriX MD) with the pencil tool to consider the entire tumor volume
5. Compute the tumor volume (ROI → ROI Volume → Compute volume)
6. Copy the given volume in the Excel software (see Data Analysis, Figure D)
7. Repeat the steps 1 to 6 for several tumors of the same animal AND for the same tumor at different time points corresponding to the time-windows between two μCT scans (longitudinal study).
! Sometimes tumors can fuse between them during their development. Thus, it is recommended to observe all the scans coming from the same mouse before starting to follow a tumor to be sure that tumors could be followed all along the study.
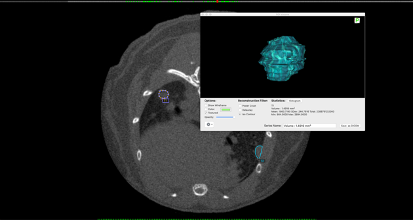
Figure C. Example of tumor volume analysis using OsiriX MD.
(Background) A lung tumor-bearing slice with two ROIs (=tumor) encircled in purple (T1) and in blue (T2). (Foreground) T1 tumor volume calculation and representation.
Data analysis
For each tumor:
1. In the Excel software, compute the relative tumor volume to the volume of the first time point (see Figure D)
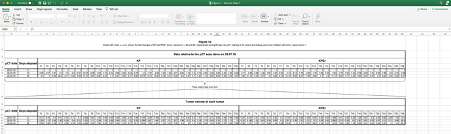
Figure D. Example of tumor volume analysis coming from Contat et al. _ Figure 1 - Source data 1.
(upper table) Relative lung tumor volumes to the first time point (27.07.19) for each tumor. (lower table) Raw lung tumor volumes for each tumor at each time point.
Once each tumor has been processed:
2. Copy all the data in the Prism software in a Table format XY
3. Generate a graph
4. Copy the data you want to statistically compare in the software Prism in a Table format Column
5. Apply a Mann-Whitney test
6. Repeat the steps 4 and 5 to make all the statistical comparisons required
Acknowledgments
Funding: Swiss Cancer Research Foundation (KFS-3681-08-2015-R); Swiss National Science Foundation (PP00P3_133661 and PP00P3_157527); Anna Fuller Fund; Emma Muschamp Foundation
No competing interests declared
Ethics
All mouse experiments were performed with the permission of the Veterinary Authority of Canton de Vaud, Switzerland (license numbers: VD2391 and VD2663).
- Contat, C and Meylan, E(2020). Lung tumor volume measurements from X-ray micro-computed tomography (μCT) scans. Bio-protocol Preprint. bio-protocol.org/prep390.
- Contat, C., Ancey, P., Zangger, N., Sabatino, S., Pascual, J., Escrig, S., Jensen, L., Goepfert, C., Lanz, B., Lepore, M., Gruetter, R., Rossier, A., Berezowska, S., Neppl, C., Zlobec, I., Clerc-Rosset, S., Knott, G. W., Rathmell, J. C., Abel, E. D., Meibom, A. and Meylan, E.(2020). Combined deletion of Glut1 and Glut3 impairs lung adenocarcinoma growth. eLife. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.53618
Category
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link
