Advanced Search
Glutaraldehyde Cross-linked Nun/TEC Preparation for CryoEM
Last updated date: Jul 6, 2020 Views: 1390 Forks: 0
Mild glutaraldehyde crosslinking for single-particle cryo-electron microscopy sample preparation
Structural basis of transcription arrest by coliphage HK022 Nun in an Escherichia coli RNA polymerase elongation complex
DOI: 10.7554/eLife.25478
Detailed protocol
I. Screening for optimal glutaraldehyde concentration
1. If your sample is in a buffer solution that contains primary amines (such as Tris), then the sample must be buffer exchanged to eliminate primary amines (this step can be skipped if the sample buffer does not contain any primary amines). If your sample is in a buffer such as Tris, then the concentration of primary amines from the buffer is usually orders of magnitude higher than primary amines from the sample, so buffer exchange must be complete. Therefore, our samples (for our case, Escherichia coli RNA polymerase elongation complex and coliphage HK022 Nun protein) were buffer exchanged by running over a Superose 6 INCREASE 10/300 GL gel filtration column (GE Healthcare Life Sciences). equilibrated with reaction buffer [RB; 20 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 150 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 5 mM dithiothreitol (DTT)]. This also removes any potential aggregates that could confound subsequent steps. Prepare the sample so the concentration of protein is high enough to be visualizedby SDS-PAGE with Coomassie staining, but low enough to avoid inter-molecular crosslinking and aggregation.
2. Make 5X glutaraldehyde solutions in RB. For example, for the final reactions we tested 0, 0.0025% (w/v), 0.005%, 0.01%, 0.025%, 0.05%, 0.1%, 0.25% glutaraldehyde concentrations, so the 5X solutions should contain 0, 0.0125%, 0.025%, 0.05%, 0.125%, 0.25%, 0.5%, and 1.25% glutaraldehyde. Glutaraldehyde should be high quality, we use catalog# 16019 from Electron Microscopy Sciences (https://www.emsdiasum.com/microscopy/products/chemicals/glutaraldehyde.aspx)
3. Add and mix 1/5 volume of glutaraldehyde 5X solutions to samples to achieve 0, 0.0025%, 0.005%, 0.01% 0.025%, 0.05%, 0.1%, and 0.25% final glutaraldehyde in test reactions that have the same concentrations of sample. Incubate for 5 minutes at room temperature (incubation time and temperature may need to be adjusted for each sample).
4. Quench the reactions by adding 1/10 volume of 1 M Tris-HCl, pH 8.0 (for a final Tris concentration of 0.1 M), then add 2X SDS-PAGE loading buffer and run SDS-PAGE to compare each reaction mixture. The type of polyacrylamide gel will depend on the sample. In our case, we use NuPAGE 4-12%, Bis-Tris, 1.0 mm thick, Mini Protein Gel, 10-well (Thermo Fisher Scientific/Invitrogen NP0321). The gels were stained with Coomassie blue.
At low glutaraldehyde concentrations, the sample should look like the sample with no glutaraldehyde (just the inidividual protein subunit bands). At very high glutaraldehyde concentrations, everything will shift to a very high MW (low mobility) band or smear, or could be stuck in the well of the gel. The optimal condition will be an intermediate glutaraldehyde concentration where there is about a 50:50 mixture of bands on the SDS gel that look like the uncrosslinked complex, but also a higher MW band (or bands) that indicate crosslinking, but no (or very little) sample stuck in the wells (see Figures 1, 2).
5. After determining optimal range of glutaraldehyde solution concentration, you can prepare cryo-EM grids.
II. Cryo-EM grid preparation with glutaraldehyde cross-linked sample
1. Run the protein sample(s) over a Superose 6 INCREASE column equilibrated with RB to exchange the buffer and remove aggregates before cross linking. In our case we assembled E. coli RNA polymerase elongation complexes (ECs) and ran over the column, and ran coliphage HK022 Nun separately over the same column
2. Collect the main peak(s) from the Superose 6 column, mix samples as desired, and react with the glutaraldehyde in the determined condition. Rock the reaction mixture gently during the incubation.
For the crosslinked EC, EC at ~0.5 mM protein was incubated with 0.005% (w/v) glutaraldehyde in RB for 7 min at room temperature.
For crosslinked EC + Nun, EC at ~0.5 mM (final) was incubated with ~15 mM Nun (final) and 0.005% (w/v) glutaraldehyde in RB for 7 min at room temperature.
3. The reactions were quenched by adding 1/10 volume of 1 M Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, for a final Tris concentration of 0.1 M.
4. The samples were centrigued on a microfuge for 10 min at 4°C to remove precipitate.
5. The supernatants from the centrifugation were concentrated by centrifugal filtration then run over the Superose 6 INCREASE column equilibrated with the cryo-EM grid buffer (in our case, 20 mM Tris, pH 8.0, 150 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 5 mM DTT). The desired complex, lightly crosslinked, will elute at about the same volume as the uncrosslinked complex whereas crosslinked oligomeric/aggregated proteins will elute earlier (these should be avoided).
6. The eluted complex was concentrated for cryo-EM grid preparation (in our case to ~3 mg/mL protein).
7. Cryo-EM grids can be prepared as usual.
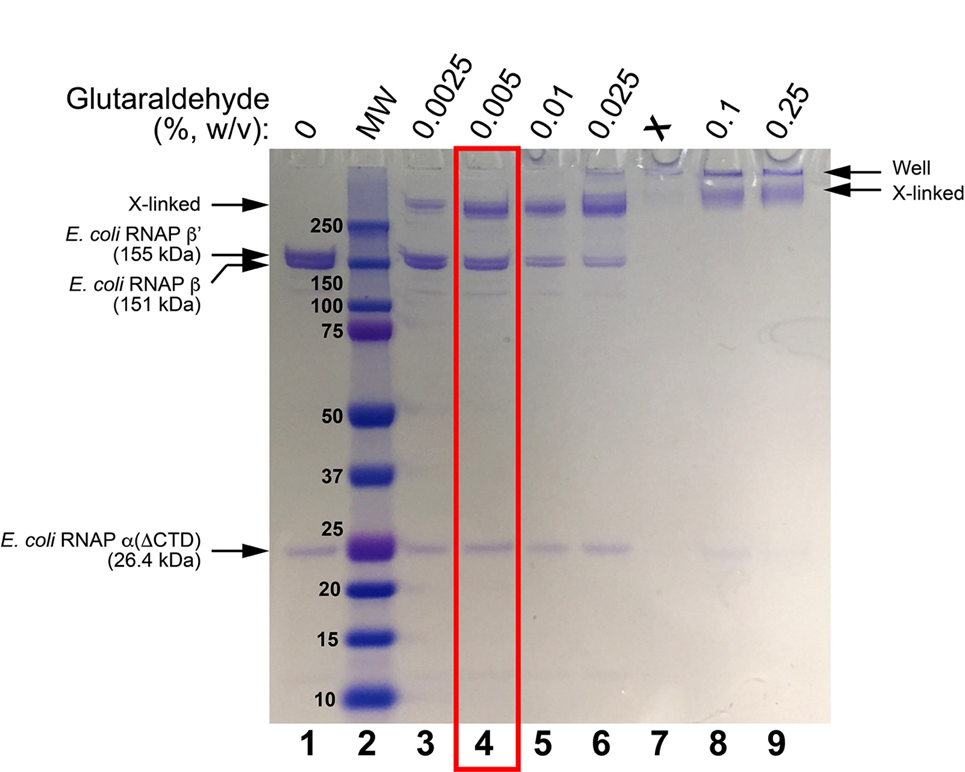
Figure 1. SDS-PAGE of glutaraldehyde screens for E. coli RNAP EC. Lane 1 shows the sample without glutaraldehyde crosslinking. Lane 2 shows Bio-Rad Precision Plus MW markers (MWs are shown). Lanes 3-6 and 8-9 show treatment of the sample with increasing concentrations of glutaraldehyde (incubation for 5 minutes, room temperature). The condition chosen for cryo-EM grid preparation is boxed in red.
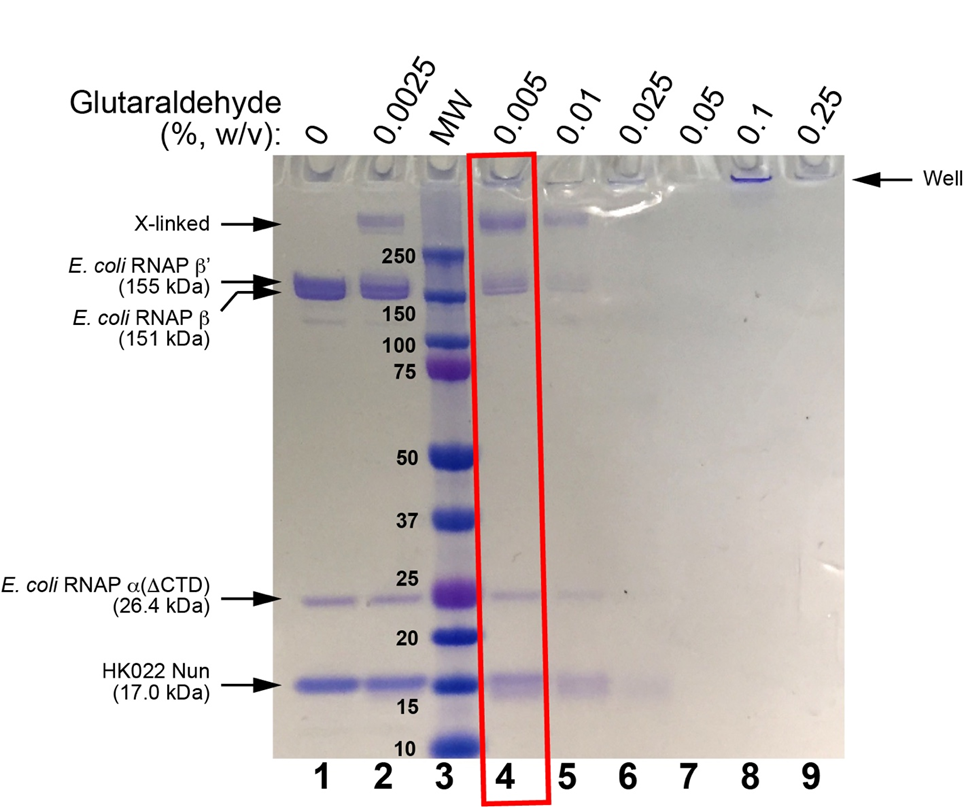
Figure 2. SDS-PAGE of glutaraldehyde screens for E. coli RNAP EC + HK022 Nun. Lane 1 shows the sample without glutaraldehyde crosslinking. Lane 2 shows incubation with 0.0025% glutaraldehyde (7 min, room temperature). Lane 3 shows Bio-Rad Precision Plus MW markers (MWs are shown). Lanes 4-9 show treatment of the sample with increasing concentrations of glutaraldehyde (incubation for 5 minutes, room temperature). The condition chosen for cryo-EM grid preparation is boxed in red.
- Kang, J and Darst, S(2020). Glutaraldehyde Cross-linked Nun/TEC Preparation for CryoEM. Bio-protocol Preprint. bio-protocol.org/prep373.
- Kang, J. Y., Olinares, P. D. B., Chen, J., Campbell, E. A., Mustaev, A., Chait, B. T., Gottesman, M. E. and Darst, S. A.(2017). Structural basis of transcription arrest by coliphage HK022 Nun in an Escherichia coli RNA polymerase elongation complex. eLife. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.25478
Category
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link
