Advanced Search
Construct design
Last updated date: Mar 20, 2024 Views: 913 Forks: 0
Protocol title
Guidance for the expression & purification of trimeric ENaC in HEK cells in suspension.
Author information
Arpita Bharadwaj and Isabelle Baconguis
Materials and reagents
Biological Materials
- pUC57_hENaC_alpha (4742bp, synthesized by Biobasic)
- pUC57_hENaC_beta (4652 bp, synthesized by Biobasic)
- pUC57_hENaC_gamma (4682 bp, synthesized by Biobasic)
- pEG_Bacmam (Kind gift from Eric Gouaux)
- HEK293S GnTI- cells (ATCC, catalog number: CRL-3022)
- Max EfficiencyÔ DH10Bac competent cells (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 10361012)
- Sf9 cells (ATCC catalog number: CRL-1711)
- Sf9 Easy titer cells (Sf9-ET cells, ATCC, catalog number: 3357)
Reagents
- FreestyleÔ 293 expression medium (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 12338026)
- DMEM with 4.5 g/l glucose, L-glutamine, and sodium pyruvate (Corning|CellgroÔ, catalog number: 10-013)
- FBS (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 10082147)
- PolyjetÔ (SignaGen, catalog number: SL100688)
- Sodium butyrate (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: 303410)
- Phenamil Mesylate (Tocris Bioscience, catalog number: 3379)
- n-dodecyl-β-D-maltopyranoside (DDM, Anatrace, catalog number: D310HA)
- Cholesteryl hemisuccinate (CHS, Anatrace, catalog number: CH210)
- HALT protease inhibitor (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: PI78425)
- Pierce Protease inhibitors (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: A32965)
- Nuclease (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 88702)
- Kanamycin (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP9065)
- Gentamycin (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP9181)
- Tetracycline (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: MT61242RG)
- Bluo-Gal (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 15519028)
- IPTG (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 15529019)
- Bacmid prep kit (PureLink™ HiPure Plasmid Miniprep Kit, ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: K210003)
- Sf-900 III Serum free media (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 12658027)
- Cellfectin II (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 10362100)
- Hyclone SFX-insect cell culture medium (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: SH3027802)
- G418 Sulfate (Gibco™ Geneticin™ Selective Antibiotic Powder, Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 11811023)
- Asolectin (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: 11145)
- Cholesterol (Avanti Polar lipids, catalog number: 700100)
- Lipid A (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: L6895)
- Brain polar lipid extract (BPLE) (Avanti Polar lipids, catalog number: 141101)
- PD-10 desalting columns (Cytiva Lifesciences, catalog number: 17085101)
- Goat anti-mouse IRDye 680RD (Licor, catalog number: 926-68070)
- Papain (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: P3125)
- HiTrap Q column (Cytiva Lifesciences, catalog number: 17115301)
- Protein A slurry (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: 16125)
- Pierce protease inhibitor tablets (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: A32965)
- Desthiobiotin (IBA Lifesciences, catalog number: 21000005)
Consummables
- Erlenmeyer flask, 125ml (VWR, catalog number: 89095262)
- 6-well plate (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 0720083)
- 96-well black plate (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 1256670)
- Deep-well 8-strip Corning cluster tube system (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 07200322)
- Erlenmeyer flask, 2L (VWR, catalog number: 10126408)
Solutions (see recipes)
- Tris buffered saline (TBS)
- Solubilization buffer 1 (SB1)
- SEC buffer
- TBST buffer
- Papain cleavage buffer
- Resuspension buffer
- Solubilization buffer 2 (SB2)
- SEC buffer (SEC2)
Recipes
Tris buffered saline (TBS)
Reagent
Final concentration
Volume (mL)
1 M Tris (pH 8.0)
20 mM
20
5 M NaCl
200 mM
40
ddH2O
940
Total
1000
Solubilization buffer 1 (SB1)
Reagent
Final concentration
Amount
n-dodecyl-β-D-maltopyranoside (DDM)
20 mM
102.1 mg
Cholesteryl hemisuccinate
3 mM
18 mg
HALT protease inhibitor
1:100
0.1 mL
1 M Tris (pH 8.0)
20 mM
0.2 mL
5 M NaCl
200 mM
0.4 mL
ddH2O
9.3 mL
Total
10 mL
SEC buffer (SEC1)
Reagent
Final concentration
Amount
n-dodecyl-β-D-maltopyranoside (DDM)
0.5 mM
255.5 mg
Cholesteryl hemisuccinate
75 uM
45 mg
1 M Tris (pH 8.0)
20 mM
20 mL
5 M NaCl
200 mM
40 mL
ddH2O
940 mL
Total
1000 mL
TBST buffer
Reagent
Final concentration
Volume (mL)
1 M Tris (pH 8.0)
20 mM
20
5 M NaCl
200 mM
40
Tween-20
0.1%
1
ddH2O
939
Total
1000
Papain cleavage buffer
Reagent
Final concentration
Volume (mL)
0.5 M Sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.0)
50 mM
1
0.5 M EDTA
1 mM
0.02
100 mM Cysteine
10 mM
1
1 mg/mL Papain
1:300 (w/w)
dependent on amount of mAb
dH2O
7.5-7.95
Total
10
Resuspension buffer
Reagent Final concentration Amount 1 M Tris (pH 8.0) 20 mM 4 mL 5 M NaCl 200 mM 8 mL 1 M MgCl2 5 mM 1 mL DNAse 25 ug/mL 5 mg Pierce Protease Inhibitors tablets 1 tab/50 mL 4 tabs ddH2O 187 mL Total 200 mL Solubilization buffer 2 (SB2)
Reagent
Final concentration
Amount
n-dodecyl-β-D-maltopyranoside (DDM
20 mM
1.53 g
Cholesteryl hemisuccinate
3 mM
270 mg
1 M Tris (pH 8.0)
20 mM
3 mL
5 M NaCl
200 mM
6 mL
ATP
2 mM
165 mg
1 M MgSO4
2 mM
0.3 mL
Pierce Protease inhibitors tablets
1 tab/50 mL
3 tabs
250 KU/mL Nuclease
25 U/mL
0.015 mL
ddH2O
140.685 mL
Total
150 mL
SEC buffer (SEC2)
Reagent
Final concentration
Amount
n-dodecyl-β-D-maltopyranoside (DDM
0.5 mM
255.5 mg
Cholesteryl hemisuccinate
75 uM
45 mg
1 M Tris (pH 8.0)
20 mM
20 mL
5 M NaCl
200 mM
40 mL
TCEP
1 mM
286.65 mg
ddH2O
940 mL
Total
1000 mL
Equipment
- HPLC system (Shimadzu)
- Superose 6 Increase 10/300 GL column (Cytiva Life Sciences, catalog number: 29091596)
- Bio-Dot apparatus (Biorad, catalog number: 1706545)
- Odyssey CLx infrared imaging system (LICOR)
Procedure
Cloning of full-length ENaC subunits
Purchase the cDNA encoding the full length α, β and γ subunits of human ENaC (hENaC) in pUC57 vector from Biobasic. Subsequently, clone the cDNA encoding α and β subunits into pEG BacMam expression vector and the γ subunit into pEG BacMam expression vector harboring an N-terminal eGFP (Goehring et al., 2014).
Generation of mutants
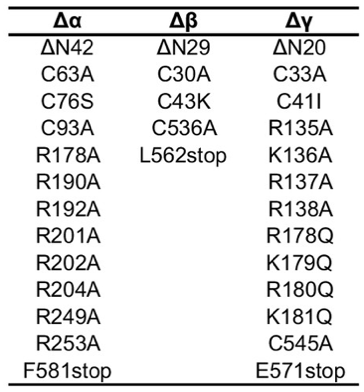 |
The summary of mutations is –
- Generate the Δα subunit by removing 42 amino acid residues in the N- terminal and 89 amino acid residues in the C-terminal. Also modify the furin sites [N-terminal RSRA (R178A) & C-terminal AAAA (R201A, R202A, R204A)].
- Generate the Δβ subunit by removing 29 amino acid residues in the N- terminal and 79 amino acid residues in the C-terminal.
- Lastly, generate Δγ subunit by removing 20 and 79 residues at the N- and C-terminal domains, and modifying furin [RKRR (R135A, K136A, R137A, R138A)] and prostasin [RKRK (R178Q, K179Q, R180Q, K181Q)] sites. In addition include a Strep-tag II, an octa-histidine tag, and eGFP. A Thrombin cleavage site is located between eGFP and the γ subunit gene.
Testing expression of constructs
- Transfection
- Test the expression of all constructs by transfection of HEK293SGnTi- cells. Briefly, grow HEK293S GnTI- cells in suspension in FreestyleÔ 293 expression medium until they are in log phase. For transfection, plate 2ml of cells at a concentration of 1x106cells/well onto a 6-well plate and grow to confluence of about 70%. (The cells are able to quickly adapt from suspension to adherent in the absence of freestyle medium). Remove the old media and add freshly modified DMEM with 4.5 g/l glucose, L-glutamine, and sodium pyruvate with 5% FBS to the plate. Mix 900ng of DNA constructs with PolyjetÔ according to manufacturer’s instructions. Add the mixture to the cells drop by drop, swirl the plate and put back in the incubator at 37°C with 5% CO2. 5 hours later, add 5mM sodium butyrate and 500nM of phenamil mesylate to the wells of the plate and incubate for 48h at 30°C with 5% CO2.
- Solubilization
- Harvest cells by centrifugation and wash the pellet in Tris buffered saline (TBS). At this point, the pelleted cells can be snap frozen in liq. N2 & stored in -80°C until further use.
- Solubilize cells in SB1 (see recipes) (200ul/2ml cell pellet aliquot) for 1 hr at 4°C on a nutator. Isolate the solubilized fraction by ultracentrifugation using a TLA100 rotor at 100,000 xg for 1 hr.
- FSEC (Flourescence-detection size exclusion chromatography)
- For FSEC experiments, use the HPLC system by Shimadzu fitted with a RF-20A fluorescence detector. Inject the clarified lysate onto a Superose 6 Increase 10/300 GL column pre-equilibrated in SEC buffer to isolate the protein complex by size-exclusion chromatography.
After identifying a construct with high expression levels, proceed to the subsequent phase of virus production. Virus production allows for the infection of a large population of cells. Large scale expression of protein in suspended cells is essential for the purification process.
Virus Production
- Transform Max EfficiencyÔ DH10Bac competent cells with 15ng of optimally expressing DNA constructs as per standard protocol. After recovery of the DH10Bac cells, plate onto LB agar containing 50μg/ml kanamycin, 7μg/ml gentamicin, 10μg/ml tetracycline, 100μg/ml Bluo-gal, and 40 μg/ml IPTG. Incubate plates at 37°C for 48 hours to distinguish white and blue colonies.
- Pick & inoculate white colonies in LB broth containing 50μg/ml kanamycin, 7μg/ml gentamicin, 10μg/ml tetracycline as a bacterial starter culture for isolation of Bacmid. Perform Bacmid prep according to manufacturer’s instruction using the bacmid prep kit.
- Transfect Sf9 cells with 10ug of bacmid to produce first passage of virus particles (P1). Briefly, seed a 6 well plate with 1x106 Sf9 cells/well in 2ml of Sf-900 III Serum free media. Incubate the plate in the 37°C incubator until the cells attach. Mix Bacmid DNA with the transfection agent Cellfectin II according to manufacturer’s instruction. Add the cellfectin II & bacmid mix to the cells & incubate the cells for 5 days in 27°C incubator in a humid environment.
- After 5 days, harvest the supernatant containing the P1 virus particles filtration & add 2% FBS to the virus stock. Use P1 stock to generate the second passage (P2) virus particles. For generating P2, use Sf9 cells growing in log phase & infect with P1 virus at an MOI of 0.001 (titer determined by end point dilution assay).
- After 4 days, collect the supernatant by centrifugation at 4790 xg for 15 min & filter (0.22um) sterilize to obtain P2 virus particles. Add 2% FBS to the virus stock. Use a small aliquot to determine the virus titer using the end point dilution assay.
- End point Dilution Assay
Seed Sf9 Easy titer cells at 100ul/well of a 96-well black plate (75,000 cells/well) and let attach.
Using a sterile, deep-well 8-strip Corning cluster tube system, make 10-1 to 10-8 stocks of viruses in Hyclone SFX-insect cell culture medium with 5% FBS & G418 by serial dilution (360ul medium + 40ul virus)
- 360ul medium + 40ul P1 virus = 10-1
- 360ul medium + 40ul 10-1 dilution = 10-2
- 360ul medium + 40ul 10-2 dilution = 10-3
- 360ul medium + 40ul 10-3 dilution = 10-4
- 360ul medium + 40ul 10-4 dilution = 10-5
- 360ul medium + 40ul 10-5 dilution = 10-6
- 360ul medium + 40ul 10-6 dilution = 10-7
- 360ul medium + 40ul 10-7 dilution = 10-8
Once the cells are attached to the 96-well plate, aspirate the medium by carefully tilting the plate and replace with 100ul serially diluted virus using the multi-channel pipet. Do the infection in triplicate.
After 72-hr post-infection, count the number of green foci in the dilution that gave <10 foci/well. To calculate viral titer, apply the following equation:
(Average # foci) x dilution factor x 10 = pfu/ml
To calculate the volume required for subsequent infection, use the following equation:
(desired MOI) x (number of cells) = Amount of virus stock (ml)
Virus titer
Generation and isolation of Fabs
Mouse monoclonal antibodies 7B1 and 10D4 were generated using standard procedure by Dan Cawley at the Vaccine and Gene Therapy Institute (OHSU).
- Immunization of mice
Prepare Liposomes containing asolectin:cholesterol:lipidA:brain polar lipid extract (BPLE) (16:4.6:1:5.3) in 20 mM Tris, 150 mM NaCl at pH 8.0 at a concentration of 40 mg/ml. Subject the mixture to repeated freeze-thaw cycles followed by extrusion through a 200-nm filter. Add purified ΔENaCASIC (Δα, ΔβASIC, Δγ) protein to the liposome mixture in the presence of 400 mM NaCl and 0.8% Na-cholate and pass through a PD-10 desalting column to remove excess salt and detergent. To generate hybridoma cell lines, immunize mice with approximately 30μg of the reconstituted ΔENaCASIC. Test supernatants of hybridoma cell cultures containing the monoclonal antibodies for recognition of the protein.
- Screening of monoclonal antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies were screened by FSEC and BioDot blot to identify clones that recognize tertiary or primary epitopes. The 7B1 and 10D4 mAbs were selected because they recognize tertiary epitopes of ENaC.
FSEC – Use affinity-purified ΔENaC with the GFP intact at a concentration of 25nM. Mix it with 50nM of the different mAbs. Clarify the samples by ultracentrifugation at 100,000g for 20 mins. Inject the supernatant containing the mAb & protein mix onto a Superose 6 column 10/300 GL preequilibrated with SEC buffer and run at a flow rate of 0.5ml/min. The eluent from the SEC column passes through a fluorescence detector to monitor GFP fluorescence. Repeat the same procedure but with 10 fold & 100 fold diluted mAb & protein mix.
BioDot blot – Carry out the procedure as per manufacturer’s recommendation. Amount of protein/well is 70ng. To determine western positive mAbs, denature the affinity-purified ΔENaC in the presence of 2% SDS and 100mM DTT. Determine the presence of western negative mAbs by using intact affinity-purified ΔENaC. Briefly, apply affinity-purified ΔENaC (either denatured or native) onto the nitrocellulose membrane, followed by blocking overnight. Incubate with the mAbs (the source of primary antibody) for 1.5h followed by multiple washes with TBST buffer. Incubate the samples with the secondary antibody, goat anti-mouse IRDye 680RD for 1h. Wash the nitrocellulose membrane twice in TBST and image using the Odyssey CLx infrared imaging system.
- Generation of fabs from mAbs
Generate fabs by papain cleavage of mAbs. Briefly, incubate the mAbs with papain cleavage buffer (1:300::papain:mAb) for 2h at 37°C. Stop the reaction by incubating with 90mM iodoacetamide at room temperature for 10mins in the dark. Isolate fab 7B1 by anion exchange using HiTrap Q HP column according to standard protocol. Elute Fab 10D4 using Protein A column to remove Fc. After isolation, dialyze both Fabs in 200 mM NaCl and 20 mM Tris at pH 8.0. After overnight dialysis, test the fabs to determine whether they were able to bind to the protein.
Expression and purification of ΔENaC-Fab complexes
- Large Scale expression
Grow 800ml of human embryonic kidney cells lacking N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I (HEK293S GnTI- cells) in suspension on a shaker (130 rpm) at a density of 2−4 × 106 cells / ml in Freestyle medium with 2% FBS in large 2L polycarbonate Erlenmeyer flasks. Transduce cells in log phase with the virus (Δα, Δβ and Δγ) at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 1 and incubate at 37°C with 8% CO2 on a shaker (130 rpm). (It is crucial to be aware of the virus titer, ensuring that the volume of the virus does not surpass 10% of the total medium). Eight hours post-transduction, add 10mM sodium butyrate and 500nM phenamil mesylate and move the cells to an incubator maintained at 30°C with 8% CO2 on a shaker (130 rpm). After 36 hr, collect the cells by centrifugation at 4790 xg for 15 min.[IB1] Wash the pellet with 20 mM Tris, 200 mM NaCl and followed by a second round of centrifugation at 4790 xg for 15 min. At this stage the cell pellet can be snap-frozen in liquid N2 and stored at -80°C for use in the future or it could be used immediately.
- Purification
Homogenize cells with a dounce homogenizer and sonicate in resuspension buffer (see recipes) until a majority of cells are broken down (check the viability of cells by the trypan blue exclusion method). Centrifuge the lysed cells at 9715 xg for 20 min to remove cellular debris. Collect the supernatant containing the membrane fraction & centrifuge at 100,000 xg for 1 hr. Resuspend membrane pellets and solubilize in SB2 for 1 hr at 4°C. Resuspend one gram of membrane pellet in 15ml of the solubilization buffer. Isolate the solubilized fraction by ultracentrifugation 100,000 xg for 1 hr, and bind ΔENaC to streptactin resin packed into an XK-16 column. Wash the column with SEC buffer supplemented with 25 U/mL nuclease, followed by an additional wash of the same buffer containing 2 mM ATP. After the washes, elute with 2.5 mM desthiobiotin. Concetrate the eluted fractions and then incubate with either one Fab 10D4 (monoFab complex) or two Fabs 7B1 and 10D4 (diFab complex) in a 1:3 molar ratio of ENaC:Fab for 10 min, and clarify by ultracentrifugation 100,000 xg for 1 hr. Inject the supernatant onto a Superose 6 Increase 10/300 GL column equilibrated in SEC2 to isolate the protein complex by size-exclusion chromatography. Pool the monodispersed fractions and concentrate to 2.2 mg/mL.
Reference
Goehring A, Lee CH, Wang KH, Michel JC, Claxton DP, Baconguis I, Althoff T, Fischer S, Garcia KC, Gouaux E (2014). Screening and large-scale expression of membrane proteins in mammalian cells for structural studies Nature Protocols 9:2574–2585.
- Bharadwaj, A and Baconguis, I(2024). Construct design. Bio-protocol Preprint. bio-protocol.org/prep2607.
- Noreng, S., Bharadwaj, A., Posert, R., Yoshioka, C. and Baconguis, I.(2018). Structure of the human epithelial sodium channel by cryo-electron microscopy. eLife. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.39340
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link
