Advanced Search
Tissue processing and staining
Last updated date: Jun 6, 2023 Views: 791 Forks: 0
(related to article with DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aba5003)
1- Deeply anesthetize the mouse using ketamine (100 mg/kg) plus xylazine (10 mg/kg). Anesthetics are dissolved together in 0.9% NaCl working solution, and injected at 10 mL/kg, i.p.
2- Transcardially perfuse mice for chemical fixation.
2.1. Preparing solutions.
- Make 4% formaldehyde solution in neutral 0.1M PB. For 1L of fixative, heat up 0.5 L of ultrapure water to 60ºC in a glass baker and bring into a fume hood. Continuously stir water with a magnet while slowly adding 40 g of paraformaldehyde powder (Sigma # 158127).
- Add 3 drops of 5N NaOH to facilitate alkaline hydrolysis. The solution will quickly turn colorless.
- Filter dissolved formaldehyde with high-quality filter paper (e.g. sheet grade 1602/N from Sartorius) through a funnel. Let the solution cool down to RT under the hood.
- Add phosphate buffer solution (PB; we use a concentrated mixture of monobasic dihydrogen phosphate and dibasic monohydrogen phosphate) for final 0.1M, and top with water to 1L. Check pH is ~7.4. Seal and store at 4ºC until use.
- Prepare saline (0.9% NaCl, Acros # 424290059, in miliQ water) on the side.
- If you wish to immunostain the brain with phospho-specific antibodies, add 1mM Na3VO4 (Sigma # S6508) * and 50 mM NaF (Merck #1064490250) to saline to inactivate phosphatases. Stir and cool down protected from light.
* Concentrated vanadate (200 mM stock) needs to be pHed to 10 and boiled repeatedly until it no longer turns yellow. Aliquots can be frozen and thawed the day of use.
2.2 Transcardial perfusion. Use protective googles and gear. Once the mouse is deeply anesthetized, use standard perfusion technique inside the fume hood. Insert and secure perfusion cannula into the left ventricle, and cut open the right atrium to allow circulated solution to flow out. We use a Minipuls 3 pump (from Gibson) to perfuse at about 5 mL/min. Start perfusing with saline until blood is cleared, and then switch to FA until mouse is stiff (about 100 mL).
2.3 Postfixation. Dissect out the brain and plunge into 50 mL of the same fixative as above in a falcon tube. Leave at least 4 h or overnight in the cold room.
3- Cryoprotection. Prepare 30% sucrose solution in PB 0.1M and cool it in ice before use. Safely dispose fixative, wash the brain once in PB, and refill the tube with sucrose solution (50-100 mL / brain). Leave in the cold room with gentle shaking until the brain sinks to the bottom, about 2 days.
4- Tissue freezing and sections.
- Take out the brain, drain it briefly on paper, and freeze it in dry ice powder in a thick bucket for 5 min.
- Store the brain at -80 ºC in a sealed tube until sectioning.
- Use a cryostat (e.g. Leica CM1860 or equivalent) to cut the brain into 25 um-thick serial slices. We usually cut it into 4-6 series of sections (i.e. two consecutive sections in a series will be 100-150 um apart) to maximize staining from each brain. Use disposable fine blades and replace them often to avoid tissue damage.
- Collect them in pre-chilled cryoprotector solution (e.g. 30% glycerol, 30% ethyleneglycol, 40% PB, v/v) or mount directly on adhesive glass slides (e.g. VWR # 631-0108). Store sealed at -20ºC until use.
5- Free-floating staining. We use a 12-well plate with 15 mm-Netwell inserts (Corning #3477) to rinse and incubate sections during immunostaining, 2-3 mL solution/well. To save precious reagents, some steps can be done in 24-wells, 0.5 mL/well.
5.1 Rinse out cryoprotector from slices by washing 4-5 x 10 min in PB.
5.2 Reduce excess aldehyde cross-linking by incubating in 0.5% NaBH4 (Sigma # 71320) in PB for 10 min. Prepare and use solution inside a fume hood, and beware it gives off pressure. Rinse slices extensively in PB until reaction bubbles are cleared.
5.3 For peroxidase-based signal amplification, incubate in 1% H2O2-10% methanol in PB for 30 min to inactivate endogenous activity. Rinse 4 x 5 min in PB, and 2 x 10 min in PBS (PB with 0.9% NaCl).
5.4 Permeabilize with 0.3% Triton X-100 or 0.1% Tween-20 in PBS for 15 min.
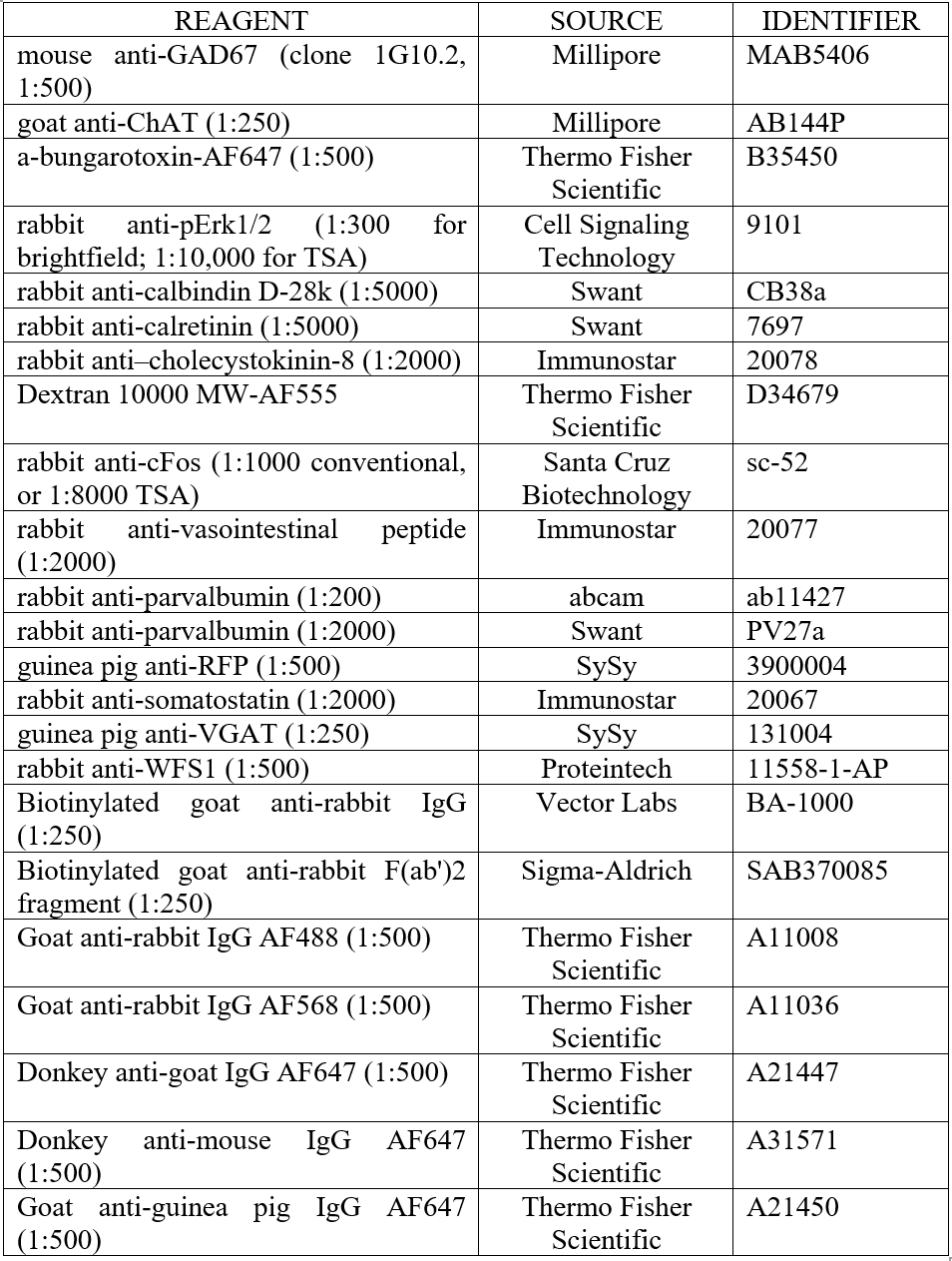
5.5 Prepare blocking solution: add 10% serum (FBS or NGS; culture-grade) and 2% bovine serum albumin (Sigma # A7906) to PBS, and dilute the primary antibodies in blocking solution accordingly. See Table 1 for antibody information. Incubate slices with antibodies ON at 4°C on a shaker. For immunodetection of GAD-67, we found that avoiding TritonX-100 improves staining. The next day, wash slices in PBS 4x10 min.
5.6 Incubate for 2 hours at RT in species-specific secondary antibodies conjugated to Alexa Fluor (1:500, Thermo Fisher Scientific) or biotin (1:250, Vectorlabs), diluted in blocking solution. For co-detection of multiple antigens using antibodies raised in various species, check for cross-reactivity of secondary antibodies, and preferably use highly cross-adsorbed IgG or F(ab')2. Keep slices shaking and protected from light. Rinse 4x5 min.
5.7 Slices treated with biotinylated antibodies are further incubated with horseradish peroxidase–conjugates (1h at RT). We have used streptavidin-HRP (1:250, PerkinElmer #NEL750001EA) or ABC-HRP (1:250, Vector labs #PK-6100) with similar results. In the case of ABC, note that A and B solutions need to be pre-mixed in blocking solution 30 min before use. Rinse 4x5 min.
5.8 Tissue-bound HRP can either be visualized with deposition of a chromogenic (e.g. DAB) or fluorescent (e.g. conjugated tyramide) substrate. In both cases, rinse 2x10 min in 0.1M TBS (Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 0.9% NaCl), and once in 0.1 M TB.
5.9 (a) To visualize the immunoreaction with DAB, prepare a 2% DAB stock in water, 0.2 um-filtered and freeze in 1 mL aliquotes. Careful: DAB is a presumed carcinogen. When used, dilute stock DAB to 0.5% in 0.1M TB and incubate slices for 5 min. Optionally, one can add nickel (i.e. 50 uM Ni(NH4)2(SO4)2) and incubate for another 2 min to enhance final contrast. Slices should be virtually colorless until H2O2 is added. Incubate with 0.001% H2O2 in the dark. Optimal development time will vary with each primary antibody, anywhere from 4–20 min. We normally take one random slice and check the reaction intensity quickly under the microscope before terminating the reaction. When comparing between experimental groups, ensure all wells are incubated for identical times. Dispose DAB solution by pouring it into 10% bleach to inactivate it. Rinse sections in TB and transfer the well plate on ice to stop the reaction.
5.9 (b) For tyramide amplification, we use the TSA Plus system (PerkinElmer #NEL744001KT*) either conjugated to cyanine 3, 5 or fluorescein, depending on the combination of other secondary antibodies used. The tyramide conjugate is dissolved in a proprietary amplification solution (likely a buffer with H2O2) and applied to the tissue slices for 6-8' in the dark. Make sure they are completely covered in reaction solution. Rinse several times in cold TBS to stop the tyramide deposition.
*We note that PerkinElmer is now rebranded as Revvity, and it has repurposed the TSA technology for high-content screening. However, other companies continue to offer TSA reagents for IHC. We successfully tested the TSA system from Invitrogen (# B40912), which employs secondary antibodies directly conjugated with several HRP molecules (i.e. poly-HRP antibody), and AlexaFluor-conjugated Tyramide.
Note: the TSA system is extremely sensitive and it requires previous tittering of the primary antibody to obtain an optimal signal-to-noise. It also allows the experimenter to use multiple primary antibodies (even of the same species) to co-detect different antigens, as long as control experiments are carried out to confirm lack of cross-reactivity between secondary detection systems. Some specific examples from our published paper:
(i) We used TSA-FITC for pErk detection (primary rabbit antibody diluted 1:10,000) followed by conventional immunofluorescence against WFS-1 (primary rabbit antibody diluted 1:500) after establishing in control experiments that AlexaFluor568-conjugated anti-rabbit antibodies (1:250) fail to detect the very low concentration of anti-pErk that is used for TSA.
(ii) Similarly, we used TSA-Cy3 for cFos detection (primary rabbit antibody from Santa Cruz Biotech*, diluted 1:8,000) followed by conventional immunofluorescence against parvalbumin (antibody from abcam, diluted 1:200) and GAD-67 (antibody from Millipore, diluted 1:500).
*Since SCTB discontinued this product, we have also tried antibodies from other sources. We recommend rabbit anti-c-Fos (Merck #ABE457) as a good alternative. In contrast, guinea pig anti-c-Fos from Synaptic Systems (#226004) gave some undesired background.
6- Rinse 4 x 5 min in TBS.
7- Mount stained slices on adhesive glass slides, and let them dry in the dark protected from dust for about 2 h.
8-Apply mounting medium with nuclear counterstaining (EMS# 1798510) and carefully place a coverslip on top. Store in the dark at 4ºC until imaging.
Table 1. Antibodies and fluorescent reagents used.
- Sans-Dublanc, A and Sindreu, C(2023). Tissue processing and staining. Bio-protocol Preprint. bio-protocol.org/prep2329.
- Sans-Dublanc, A., Razzauti, A., Desikan, S., Pascual, M., Monyer, H. and Sindreu, C.(2020). Septal GABAergic inputs to CA1 govern contextual memory retrieval. Science Advances 6(44). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aba5003
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link
