Advanced Search
Creating Arabidopsis mutants with CRISPR/Cas9 by using the plasmid pHEE401E
Last updated date: May 8, 2023 Views: 563 Forks: 0
1. Selection of the gRNA (thereby selecting the target site within the gene of interest)
Use an online tool (i.e. CHOPCHOP https://chopchop.rc.fas.harvard.edu/ (Labun et al. 2016) or CCTop http://crispr.cos.uni-heidelberg.de/ (Stemmer et al. 2015)).
With CHOPCHOP:
1.1 Type in ATG and select A. thaliana and CRISPR/Cas9 then “Find Target Sites”.
1.2 Select a target sequence (by considering advantages and disadvantages of targeting a certain position within the gene of interest. Minimize off-targets.)
Additionally, maybe consider availability of proposed restriction enzymes for the genotyping test digest which can be done with T1 plants. In this case also consider the vicinity of the enzyme recognition sequence to the Cas9 cleavage site.
2. Designing primers compatible with the Green Gate cloning system (Lampropoulos et al. 2013)
2.1 To enter one gRNA between Green Gate sites use:
Fwd oligonucleotide: 5’-ATTG-N19 (ATT followed by the 20 nucleotides of the protospacer of the gRNA, whereby the first of the 20 nucleotides is changed to “G”→ G + N19).
Rev oligonucleotide: 5’-AAAC-N19 reverse complement of the 19 nucleotides of the protospacer of the gRNA.
5’- ATTGNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNCAAA -5’
Annealing of the gRNA oligo duplex
Prepare Annealing Buffer:
10 ml 5x Annealing Buffer:
2.5 ml of 5 M NaCl
0.5 ml of 0.5 M EDTA
2.5 ml of 1 M Tris-HCl pH 7.5
Reaction for annealing of the oligo duplex:
10 µL of 100 µM forward primer
10 µL of 100 µM reverse primer
5 µL of 5x Annealing Buffer
25 µL
Annealing:
95°C for 5 min. Then put tube on the bench and let it cool down.
(Alternatively: Ramp cool 0.1°/sec to 12°C. Hold at 12 °C.)
2.2 For two gRNAs:
To clone two gRNAs into the destination vector, we use the following approach as described by (Xing et al. 2014) with some modifications. Eco31I sites in bold.
Fwd oligonucleotide: 5’- ATATATGGTCTCGATTG-N19-GTTTTAGAGCTAGAAATAGC with N19 being 19 nucleotides of the protospacer of the first gRNA.
Rev oligonucleotide: 5’- ATTATTGGTCTCTAAAC-N19-CAATCTCTTAGTCGACTCTAC with N19 being the reverse complement of the 19 nucleotides of the protospacer of the second gRNA.
PCR is performed using plasmid pHEE2E-TRI (Wang et al. 2015) as a template.
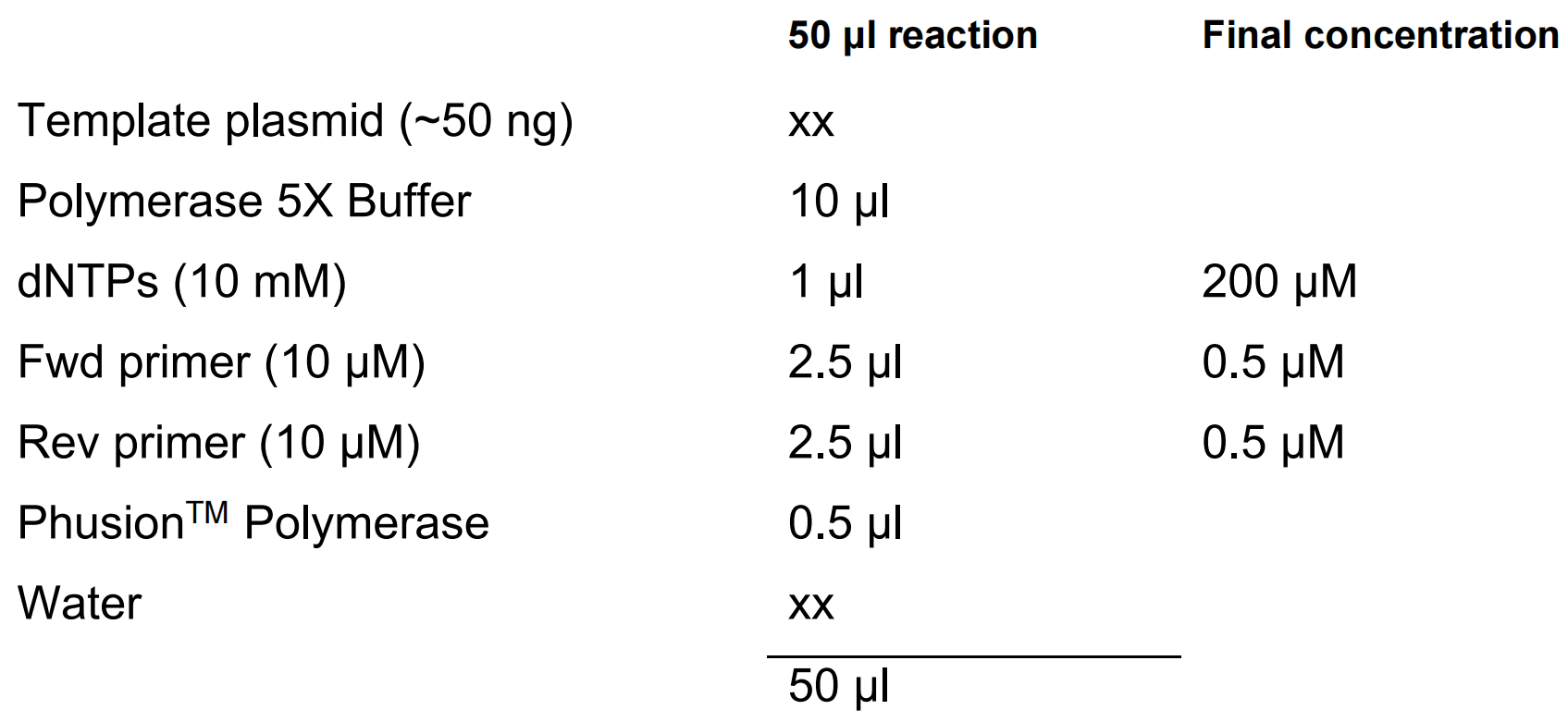
PCR is performed using an annealing temperature of 59°C, elongation time of 20 secs and with 35 cycles.
The PCR products are run on a 1% agarose gel and the 626 bp band is gel purified.
3. Ligation into the destination vector pHEE401E
The annealed oligos or PCR products are cloned into the destination vector via a Green Gate reaction. Dilute the oligo duplex 1:100.
Green Gate reaction:

Green Gate PCR program:
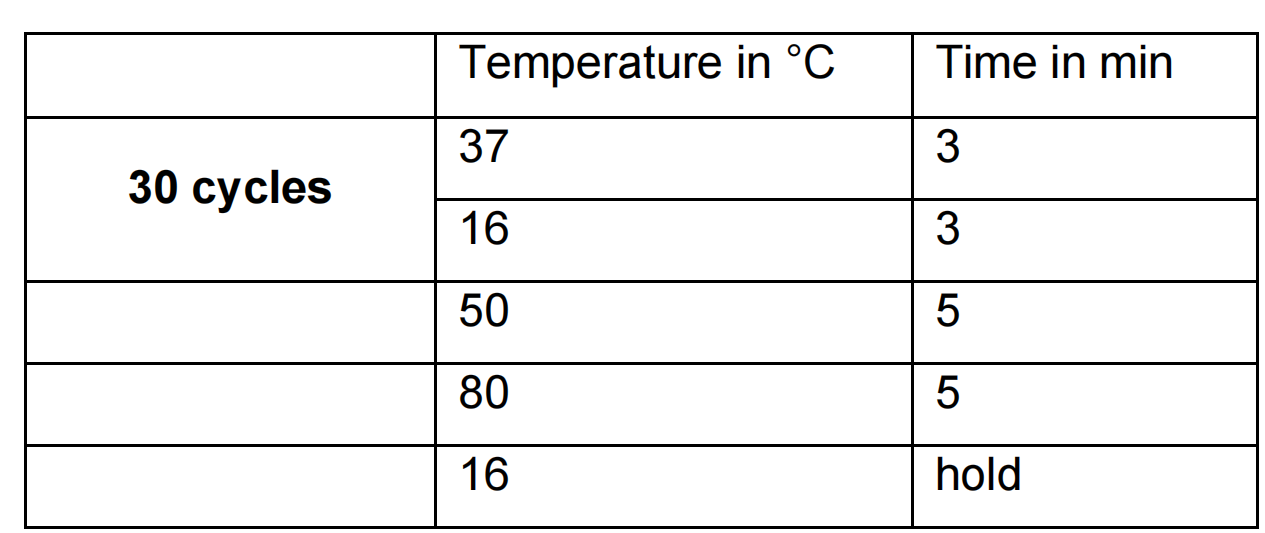
Use 5 µL of the reaction mixture to transform 50 μL of NEB® 5-alpha E. coli cells. The cells are then plated on LB medium containing 50 mg/mL kanamycin. Plasmids can be validated by restriction enzyme digestion with Bsu15I (ClaI) and the inserted fragment is further verified via Sanger sequencing using primer M13_uni_ (-43).
4. Transformation of Agrobacterium
Transform agrobacteria; GV3101:pMP90 with 1-2 µg of mini prep DNA.
Pick and select colonies (ONC -> Mini Prep -> transform NEB 5-alpha -> Mini prep-> Test Digest).
5. Transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana
E.g. by using a floral dip protocol.
6. Selection of transgenic T1 plants
Perform T1 selection on Hygromycin containing plates.
7. Selection of primers for genotyping T1 plants:
Chose a left and right primer shown by “CHOPCHOP” to amplify a region from genomic DNA which includes the CRISPR target site.
7.1 Use of restriction enzymes for genotyping T1 plants
You might order/use one of the enzymes shown by CHOPCHOP with recognition sites at the CRISPR target region or very close to it, in case you want to do pre-screening by test digest.
8. Identification of mutant T1 plants
Extract genomic DNA from transgenic T1 plants.
Perform PCR with the genotyping primers shown by CHOPCHOP to get a PCR product which includes the CRISPR target region. Perform agarose gel electrophoresis and purify the PCR product from the agarose gel.
(Possible pre-screening before sequencing: Digestion of the purified PCR product with a restriction enzyme which has its recognition sequence at or close to the CRISPR target region. A PCR product that is not digested indicates that there are mutations at the enzyme recognition site. Include an undigested control sample on the gel and keep a bit of purified PCR products for submission for sequencing.)
Submit purified PCR products for sequencing to unveil mutations. (More than one sequence in the sequencing chromatogram is indicative for bi-allelic plants or plants with several mutations.)
9. Selection of homozygous plants which do not contain Cas9 in T2
Extract gDNA from offspring of plants with mutated sequences.
Analyze for mutations at the CRISPR target region as described above. Test for the absence of Cas9 by PCR on gDNA with Cas9 specific primers. As control use gDNA of transgenic T1 plants and the plasmid pHEE4001E as templates.
(An option is to grow T2 plants on Hygromycin containing plates and select plants without the T-DNA by rescuing the non-resistant seedlings).
References:
Labun, Kornel et al. 2016. “CHOPCHOP v2: A Web Tool for the next Generation of CRISPR Genome Engineering.” Nucleic Acids Research 44(W1): W272–76. https://academic.oup.com/nar/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/nar/gkw398.
Lampropoulos, Athanasios et al. 2013. “GreenGate - A Novel, Versatile, and Efficient Cloning System for Plant Transgenesis” ed. Paul Jaak Janssen. PLoS ONE 8(12): e83043. https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0083043.
Stemmer, Manuel et al. 2015. “CCTop: An Intuitive, Flexible and Reliable CRISPR/Cas9 Target Prediction Tool.” PLoS ONE 10(4): 1–11.
Wang, Zhi Ping et al. 2015. “Egg Cell-Specific Promoter-Controlled CRISPR/Cas9 Efficiently Generates Homozygous Mutants for Multiple Target Genes in Arabidopsis in a Single Generation.” Genome Biology 16(1): 1–12. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13059-
015-0715-0.
Xing, Hui-Li et al. 2014. “A CRISPR/Cas9 Toolkit for Multiplex Genome Editing in Plants.” BMC Plant Biology 14(1): 327. https://bmcplantbiol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12870-014-0327-y.
- Lupanga, U and Schumacher, K(2023). Creating Arabidopsis mutants with CRISPR/Cas9 by using the plasmid pHEE401E. Bio-protocol Preprint. bio-protocol.org/prep2280.
- Lupanga, U., Röhrich, R., Askani, J., Hilmer, S., Kiefer, C., Krebs, M., Kanazawa, T., Ueda, T. and Schumacher, K.(2020). The Arabidopsis V-ATPase is localized to the TGN/EE via a seed plant-specific motif. eLife. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.60568
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link
