Advanced Search
2.7. Docking computation
Last updated date: Nov 28, 2022 Views: 805 Forks: 0
Docking computation protocol for protein and its ligand
Detailed protocol:
This protocol enables the evaluation of protein (Native KIT, PDB ID: 4U0I)-ligand (Compound 06) interactions and binding properties to predict the activity of the ligand molecule.
Software and Module: Discovery Studio 2016 (DS 3.0), Discovery Studio Client (DS CDOCKER).
File types: 4u0i.dsv for protein, Compound 06.mol2 for ligand.
Protein preparation:
1. Native KIT (PDB ID: 4U0I) (4u0i.dsv) as a protein was used in this protocol, the 3D structure of protein native KIT (4U0I.pdb) was searched and downloaded from www.rcsb.org;
2. In Files Explorer, opened Samples/Tutorials/Receptor-Ligand Interactions, opened the protein file (4U0I.pdb) downloaded from PDB database (www.rcsb.org) (Figure 1);
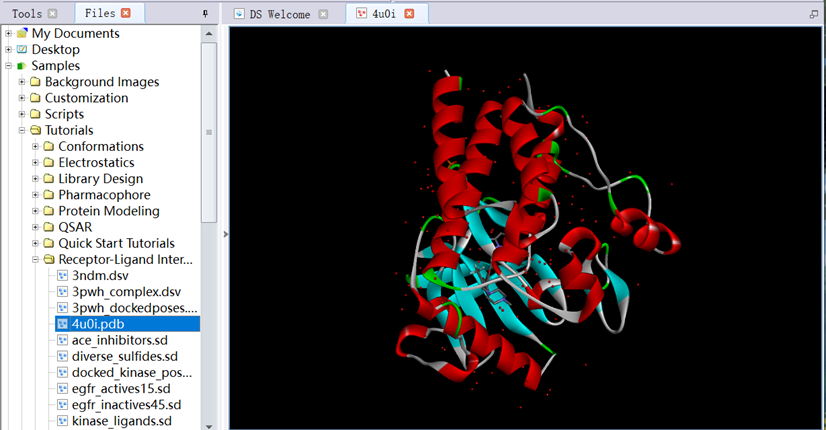
Figure 1 The three-dimensional structure of protein downloaded from PDB database
3. Ctrl+H, entered the System View. Ctrl+T, entered the Table View. In the System View, checked box of Water, clicked Cut to delete it;
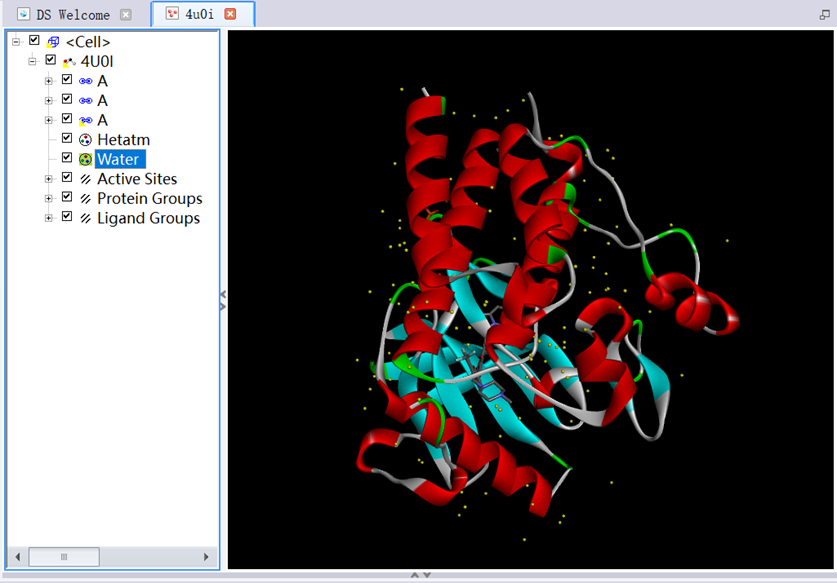
Figure 2 The three-dimensional structure of protein removed water molecules
4. In Tools Explorer, opened Macromolecules/Prepare Protein, clicked Clean Protein in Manual Preparation, clicked Prepare Protein in Automatic Preparation, clicked Run (Figure 3);
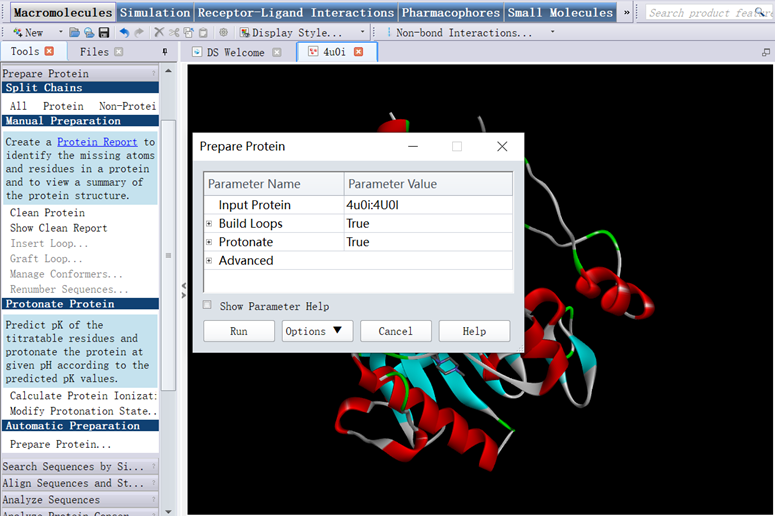
Figure 3 The three-dimensional structure of protein prepared for CDOCKER
5. In Tools Explorer, opened Receptor-Ligand Interactions/Define and Edit Binding Site/Define Receptor:4U0I, checked box of ligand Groups, Define Site/From Current Selection, checked box of ligand Groups clicked Cut to delete it saved as the protein file (4u0i.dsv) (Figure 4);
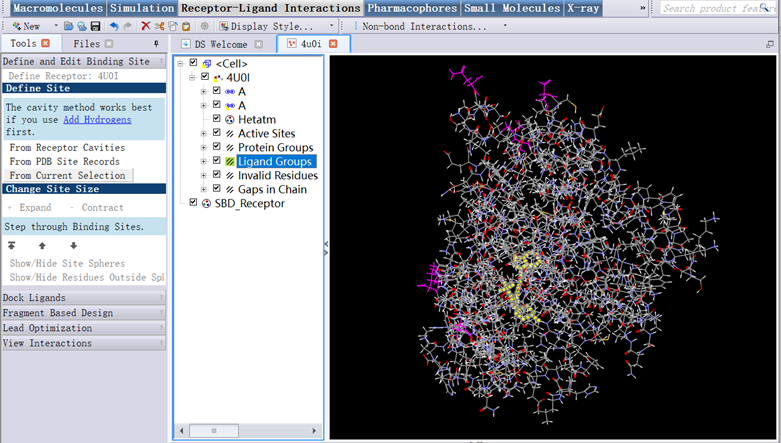
Figure 4 The three-dimensional structure of protein
Ligand preparation: Compound 06 (Compound 06.mol2) as a ligand was used in this protocol, the structure of ligand Compound 06 was prepared using ChemDraw 21.0.0 software (Figure 5).
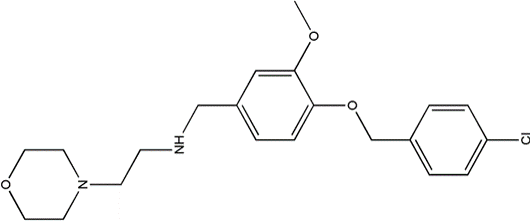
Figure 5 The structure of small molecule Compound 06
Preparation for CDOCKER:
1. In Files Explorer, opened Samples/Tutorials/Receptor-Ligand Interactions/4u0i.dsv (Figure 6);
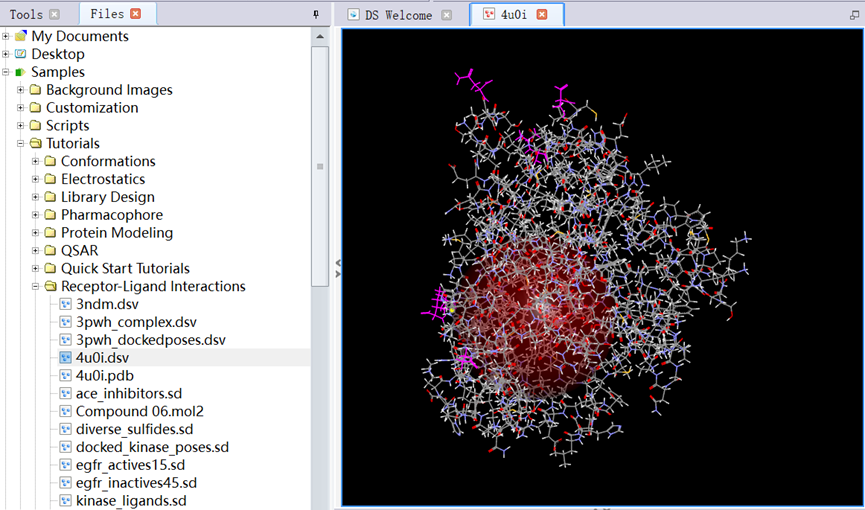
Figure 6 The three-dimensional structure of protein
2. In Tools Explorer, opened Receptor-Ligand Interactions/Define and Edit Binding Site, clicked Show/Hide Residues Outside Sphere and Show/Hide Sphere, opened View/Transform, clicked Fit to Screen (Figure 7);
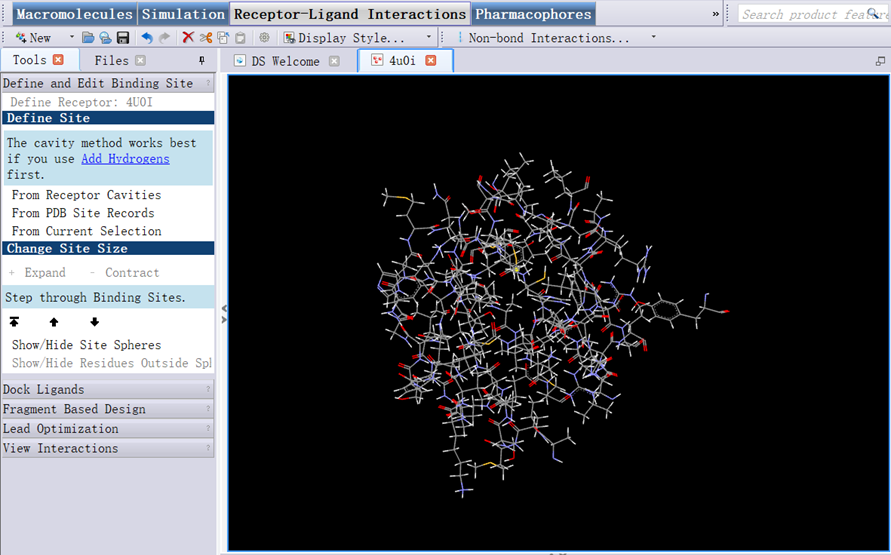
Figure 7 Amino acid in the active site of protein
3. In Files Explorer, opened Samples/Tutorials/Receptor-Ligand Interactions/ Compound 06.mol2 (Figure 8);
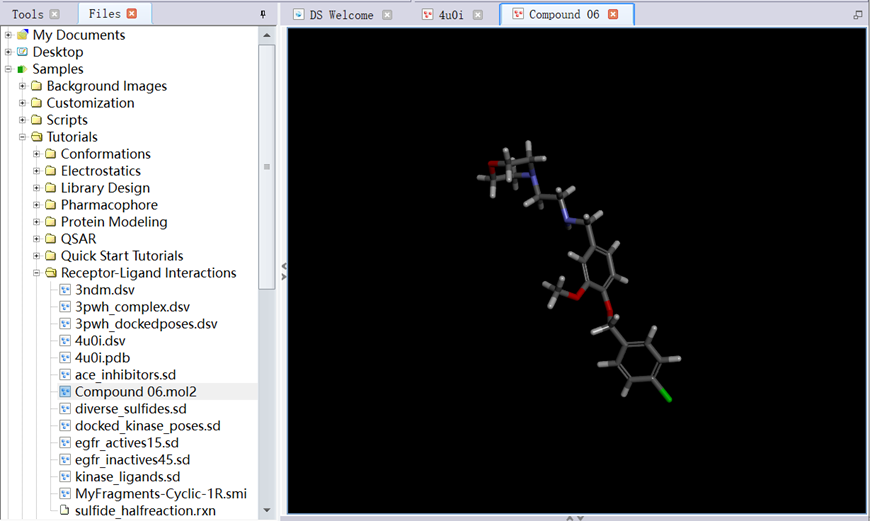
Figure 8 The structure of ligand
Running for CDOCKER:
1. In Tools Explorer, opened Receptor-Ligand Interactions/Dock Ligands, clicked Dock Ligands (CDOCKER);
2. Set parameters: Input Receptor (4u0i:4U0I), Input Ligands (Compound 06:All), Input Site Sphere (35.3194, 9.67323, 45.752, 12.5389);
3. Opened Top Hits, set parameters: Pose Cluster Radius (0.5), other parameters are shown in figure 9, including Random Conformations (10), Orientations to Refine (10), Simulated Annealing (True), then clicked run (Figure 9);
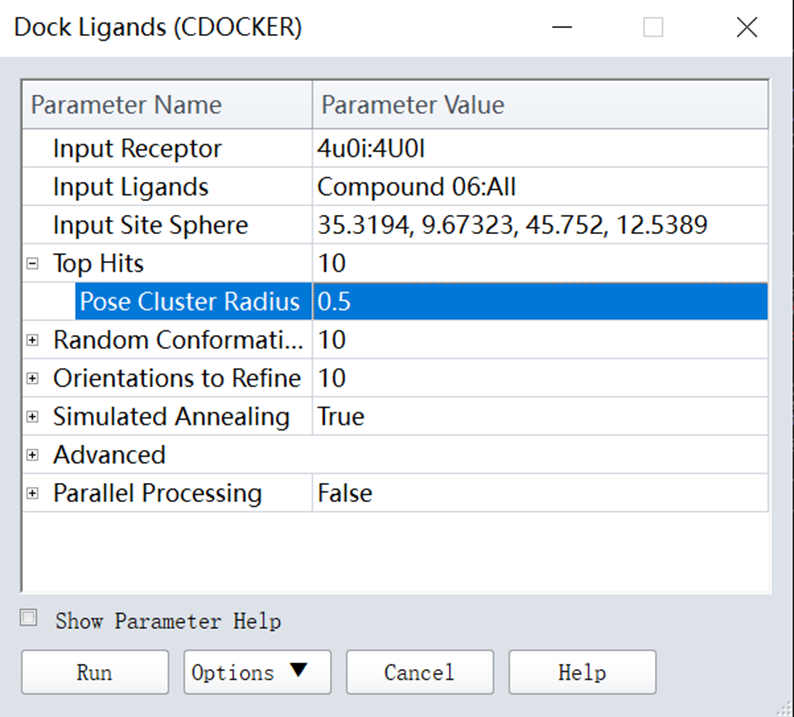
Figure 9 Parameters setting for CDOCKER
Results for CDOCKER:
1. In Tools Explorer, opened Receptor-Ligand Interactions/View Interactions, clicked Ligand Interactions (Figure 10);
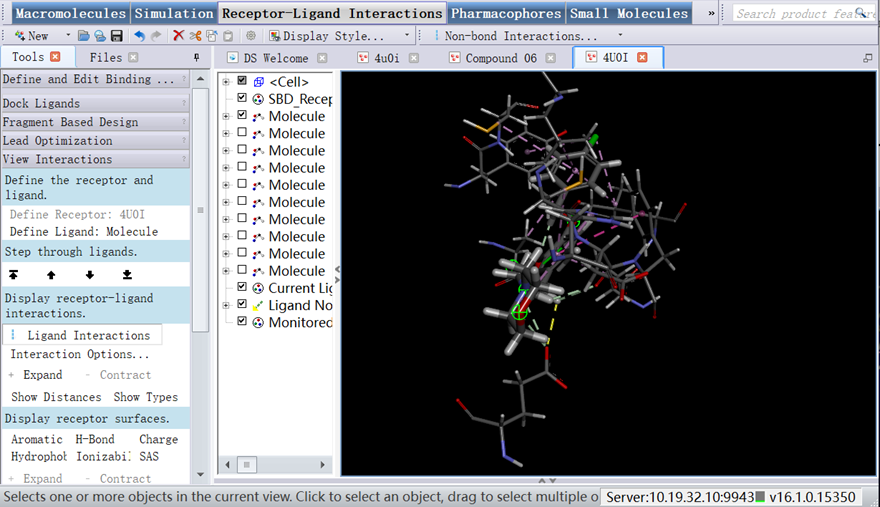
Figure 10 The interaction forces of protein-ligand
2. Clicked View Interaction/Interaction Options, as shown in figure 11;
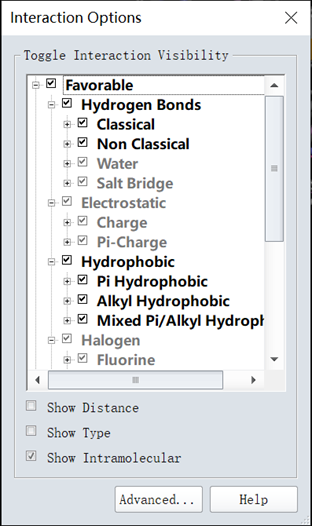
Figure 11 The interaction force types
3. Clicked View/Tool panels, checked the box of View Interaction (Advanced), selected the ligand you want to describe. In Tools Explorer, opened Receptor-Ligand Interactions/View Interactions, clicked Define Ligand, opened Receptor-Ligand Interactions/View Interactions (Advanced), clicked Show 2D Diagram (Two-dimensional diagram) (Figure 12);
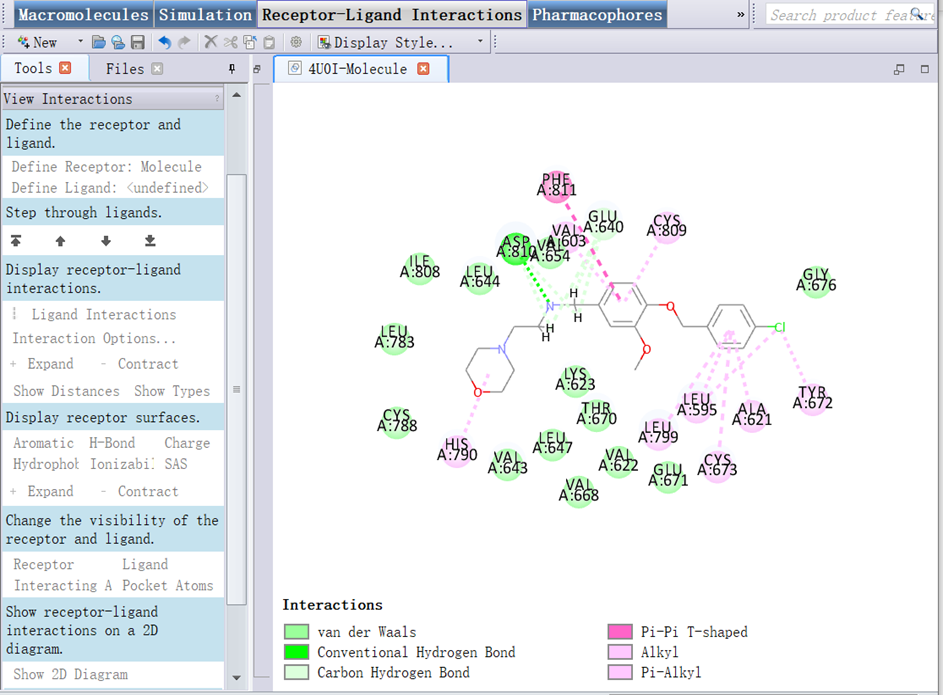
Figure 12 The 2D diagram interactions
- Jiang, L, Sun, J and Liu, Y(2022). 2.7. Docking computation. Bio-protocol Preprint. bio-protocol.org/prep2060.
- Jiang, L., Zhang, Z., Wang, Z. and Liu, Y.(2021). Discovery of novel potential KIT inhibitors for the treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Open Life Sci 16(1). DOI: 10.1515/biol-2021-0036
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link
