Advanced Search
Coevolutionary analysis and coarse-grained simulations
Last updated date: Apr 25, 2022 Views: 642 Forks: 0
Use HHblits (1) to align multiple sequences from the clustered UniProtdatabase.
To measure residue-residue coevolution, use DCA (2, 3) with default parameters: x = 0:2; λ = 0:5 (for more info: http://dca.rice.edu/portal/dca/home). DCA outputs a directinformation (DI) score per pair of residues, rankingevolutionary correlation. Only coevolution pairs at a sequence distance ≥5 are considered.
Given a DI-ranked list of coevolution pairs, keep for further analysis only the first n pairs that maximize the Matthew's Correlation Coefficient (MCC) resulting from the prediction of contacts (<10 Å) in the initial structure. Given a list of n selected coevolution pairs, MCC is calculated as:
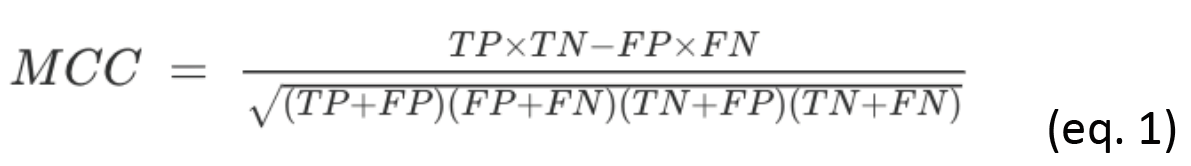
where TP is the number of contacts in the selected list, while FP corresponds to the selected pairs that are not in contact, TN to the non-selected pairs that are not in contact, and FN to contacts that have not been selected.
Coevolution pairs that are far apart in the initial structure are used to guide an initial, exploratory conformational sampling. Concretely, run a pulling trajectory for each distant coevolution pair i-j using discrete (d) MD. According to the standarddMD algorithm, the protein Hamiltonian is defined as a series of flat square wells (in this case Go-like single well, see (4)) and particles (Cα) move at constant velocity until a collision occurs, where momentum and energy conservation rules are enforced. To favor the formation of coevolutionary contacts (i-j) bias the trajectory by inverting velocities of particles i and j every 100 simulation steps if i and j arenot approaching each other, and keeping them unaltered otherwise. Maintain the trajectory for downstream analysis if i-j are in contact at some point of the trajectory.
To evaluate the coincidence between trajectories and coevolution maps, check whether contacts are spontaneously established along the pulling trajectory (k − l, where k,l ≠ i,j are indeed coevolution pairs). For this, compute receiver-operating characteristic curves (ROC; sensitivity versus 1 − specificity) to quantify the agreement between conformations generated inthe trajectory and the list of n coevolution pairs (filter out those contactsat ≤6.5 Å to exclude trivial trajectories). In this framework, the ROC space is defined as follows:
Sensitivity=TP/TP+FN;
Specificity=TN/FP+TN;
where TP counts contacts generated along the trajectory that are in turn selected coevolution pairs, FN is the number of coevolution pairs that are not in contact along the trajectory, TN are the pairs that are not in contact during the trajectory and, accordingly, are not coevolution pairs, and FP are the pairs that are in contact but do not coevolve.
Given the pulling trajectories described above, build a multiple SBM that would enable a single dMD trajectory to explore the nmodels ensemble. To this aim, shape particle-particle interactions to reflect the variability spanned by exploratory trajectories. Concretely, take the original PDB and the last snapshot of the accepted pulling trajectories, and describe the potential energyinteractions by meansof double-well squarepotentials when a pair of particles i-j distance change across the ensemble of structures, and single-well square potential otherwise. The wells are centered at
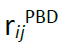 (the distance in the initial PDB structure), and, when needed, a second one centered at the coevolution interaction distance between residues i −j (
(the distance in the initial PDB structure), and, when needed, a second one centered at the coevolution interaction distance between residues i −j (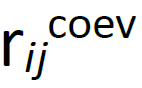 , which is set considering all nmodels i −j distances coming from the accepted pulling trajectories; eq.2); to increase the importance of short-distance contacts, which could be obscured by larger ones, introduce a weight factor in the averaging (
, which is set considering all nmodels i −j distances coming from the accepted pulling trajectories; eq.2); to increase the importance of short-distance contacts, which could be obscured by larger ones, introduce a weight factor in the averaging ( ; eq.3). If nmodels is the number of structures used to build the SBM, the center of the coevolution well is:
; eq.3). If nmodels is the number of structures used to build the SBM, the center of the coevolution well is: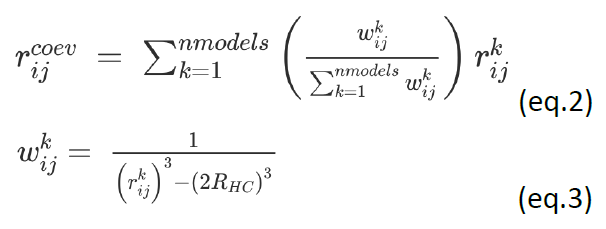
where
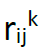 is the residues i − j distance in the kth model, and the hard-core radius of the particles RHC is 2 Å.
is the residues i − j distance in the kth model, and the hard-core radius of the particles RHC is 2 Å.For more details on the above protocol, the sampling strategy and the selection and evaluation of the sampled structures please refer to Sfriso et al. (5).
References
- M. Remmert, A. Biegert, A. Hauser, J. Söding, HHblits: Lightning-fast iterative protein sequence searching by HMM-HMM alignment. Nat. Methods. 9, 173–175 (2012).
- M. Weigt, R. A. White, H. Szurmant, J. A. Hoch, T. Hwa, Identification of direct residue contacts in protein-protein interaction by message passing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 106, 67–72 (2009).
- F. Morcos, A. Pagnani, B. Lunt, A. Bertolino, D. S. Marks, C. Sander, R. Zecchina, J. N. Onuchic, T. Hwa, M. Weigt, Direct-coupling analysis of residue coevolution captures native contacts across many protein families. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 108 (2011), doi:10.1073/pnas.1111471108.
- A. Emperador, O. Carrillo, M. Rueda, M. Orozco, Exploring the Suitability of Coarse- Grained Techniques for the Representation of Protein Dynamics. Biophys. J. 95, 2127– 2138 (2008).
- P. Sfriso, M. Duran-Frigola, R. Mosca, A. Emperador, P. Aloy, M. Orozco, Residues Coevolution Guides the Systematic Identification of Alternative Functional Conformations in Proteins. Structure. 24, 116–126 (2016).
- Colizzi, F and Orozco, M(2022). Coevolutionary analysis and coarse-grained simulations. Bio-protocol Preprint. bio-protocol.org/prep1637.
- Colizzi, F. and Orozco, M.(2021). Probing allosteric regulations with coevolution-driven molecular simulations. Science Advances 7(37). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abj0786
Category
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link
