Advanced Search
IIH6 Assays
Last updated date: Feb 10, 2022 Views: 842 Forks: 0
Immunoblotting with the mAb IIH6 (anti-matriglycan)
Introduction:
IIH6 is a mouse monoclonal antibody against matriglycan: a linear repeating disaccharide of alternating xylose and glucuronic acid that is synthesized uniquely by like-acetylglucosaminyltransferase-1 (LARGE1) on α-dystroglycan (α-DG) (Ervasti and Campbell, 1991; Inamori, et al., 2012; Yoshida-Moriguchi and Campbell, 2015). Defects in post-translational processing that reduce the size of matriglycan on α-DG result in various forms of muscular dystrophy (Ervasti, et al., 1990; Michele, et al., 2002; Walimbe et al., 2020).
Protocol:
- Separate proteins by electrophoresis on a 3–15% SDS–PAGE gel and transfer to a polyvinylidene fluoride (Immobilon-FL) membrane (Millipore Cat# IPFL00010).
- Stain membrane with Ponceau S solution (Millipore-Sigma Cat# P7170) for three to five minutes with gentle shaking on an orbital shaker.
- Rinse membrane in tap water. Membrane can be dried or blocked at this point.
- If membrane is dried, reactivate in 100% methanol.
Note: Be careful to handle the membrane by its edges and to avoid placing extra pressure on the blot, causing increased background.
- Block for one hour in blocking buffer at room temperature with gentle shaking on an orbital shaker.
- Incubate with the IIH6 antibody (RRID: AB_2617216) in blocking buffer at 1:100 overnight at 4oC on a gentle rocker.
Note: IIH6 activity is sensitive to ionic strength and 75mM NaCl works best. Use TBS not PBS in buffers. IIH6 is also very sensitive to multiple freeze-thaw cycles. We recommend storing IIH6 in 100 µL aliquots at -20oC. If stored in smaller aliquots, they should be no less than 10 µL.
- The next day, wash blot three times for 10 minutes each time, with gentle shaking on an orbital shaker at room temperature.
- Incubate the blot with secondary antibody IRDye 800CW Goat anti-mouse IgM (RRID:AB_2814919) in blocking buffer plus 0.075% SDS (1:400 of 30% SDS) at 1:2500 for 30 minutes at room temperature on a gentle rocker
Note: Keep blot protected from light.
- Wash blots again three times for 10 minutes each time with gentle shaking on an orbital shaker at room temperature.
Note: Keep blot protected from light.
- Image blots using the Odyssey Infrared Imaging System.
Note: Keep blot protected from light.
Solutions:
- Blocking buffer (Blotto): 2% non-fat dry milk in 50 mM Tris-HCl, 75 mM NaCl, 0.1% Tween-20, pH 7.6, make fresh weekly and store at 4oC.
- Wash Buffer: 50 mM Tris-HCl, 75 mM NaCl, 0.1% Tween-20, pH 7.6.
- 30% SDS (Crescent Chemical Company Inc. Cat# SE20765.03)
- Ponceau S solution (Millipore-Sigma Cat# P7170)
Antibodies:
Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
| Primary antibody | IIH6 mouse monoclonal IgM | DSHB Campbell Lab | Cat# IIH6 C4, RRID:AB_2617216 | WB (1:100) |
| Secondary antibody | IRDye 800CW goat anti-mouse IgM | LI-COR Biosciences | Cat# 926–32280, RRID:AB_2814919 | WB (1:2500) |
Primary Antibody (Ervasti and Campbell, 1991; Walimbe et al., 2020)
Results:
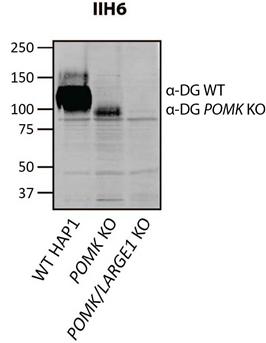
Figure 1. Immunoblotting of wild-type (WT) HAP1 cells or HAP1 cells lacking Protein O-Mannose Kinase (POMK KO) or both POMK and LARGE1 (POMK/LARGE1 KO) with IIH6 (anti-matriglycan), as described in Walimbe et al., 2020. Molecular weight standards in kilodaltons (kDa) are shown on the left.
References:
Ervasti, J. M., Ohlendieck, K., Kahl, S. D., Gaver, M. G., & Campbell, K. P. (1990). Deficiency of a glycoprotein component of the dystrophin complex in dystrophic muscle. Nature, 345(6273), 315–319. DOI: 10.1038/345315a0, PMID: 2188135
Ervasti, J. M., & Campbell, K. P. (1991). Membrane organization of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex. Cell, 66(6), 1121–1131. DOI: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90035-w, PMID: 1913804
Inamori, K. I., Yoshida-Moriguchi, T., Hara, Y., Anderson, M. E., Yu, L., & Campbell, K. P. (2012). Dystroglycan Function Requires Xylosyl- and Glucuronyltransferase Activities of LARGE. Science, 335(6064), 93–96. DOI: 10.1126/science.1214115, PMID: 22223806
Michele, D. E., Barresi, R., Kanagawa, M., Saito, F., Cohn, R. D., Satz, J. S., Dollar, J., Nishino, I., Kelley, R. I., Somer, H., Straub, V., Mathews, K. D., Moore, S. A., & Campbell, K. P. (2002). Post-translational disruption of dystroglycan–ligand interactions in congenital muscular dystrophies. Nature, 418(6896), 417–421. DOI: 10.1038/nature00837, PMID: 12140558
Walimbe AS, Okuma H, Joseph S, Yang T, Yonekawa T, Hord JM, Venzke D, Anderson ME, Torelli S, Manzur A, Devereaux M, Cuellar M, Prouty S, Ocampo Landa S, Yu L, Xiao J, Dixon JE, Muntoni F, Campbell KP. POMK regulates dystroglycan function via LARGE1-mediated elongation of matriglycan. eLife 2020; 9: e61388. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.61388, PMID: 32975514
Yoshida-Moriguchi, T., & Campbell, K. P. (2015). Matriglycan: a novel polysaccharide that links dystroglycan to the basement membrane. Glycobiology, 25(7), 702–713. DOI: 10.1093/glycob/cwv021, PMID: 25882296
Related files
 Elife Praissman Protocol FINAL.pdf
Elife Praissman Protocol FINAL.pdf - Walimbe, A and Campbell, K P(2022). IIH6 Assays. Bio-protocol Preprint. bio-protocol.org/prep1533.
- Praissman, J. L., Willer, T., Sheikh, M. O., Toi, A., Chitayat, D., Lin, Y., Lee, H., Stalnaker, S. H., Wang, S., Prabhakar, P. K., Nelson, S. F., Stemple, D. L., Moore, S. A., Moremen, K. W., Campbell, K. P. and Wells, L.(2016). The functional O-mannose glycan on α-dystroglycan contains a phospho-ribitol primed for matriglycan addition. eLife. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.14473
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link
