Advanced Search
Ascorbate peroxidase activity (APX) for Stress amelioration response of glycine betaine and Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in sorghum under Cr toxicity
Last updated date: Dec 29, 2021 Views: 1063 Forks: 0
Title: Ascorbate peroxidase activity (APX) for Stress amelioration response of glycine betaine and Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in sorghum under Cr toxicity
Ascorbate peroxidase activity (APX) (EC 1.11.1.11):
The APX is a widely distributed antioxidant enzyme. It differs from that of catalase and other peroxidases in its action that it scavenges/reduces reactive oxygen species (ROS) such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to water using reduced ascorbate as the electron donor. It is advantageous over other similar antioxidant enzymes in scavenging ROS since ascorbate may react with superoxide, singlet oxygen and hydroxyl radical too, in addition to reacting with H2O2. The detailed protocol can be seen in the attached file.
Reagents required: Prepare 0.1 M potassium phosphate buffer (pH-7.0)
Fresh 10mM H2O2
Fresh 15mM L-ascorbate
Sample extraction: The complete extraction procedure must be carried out below 40C temperature. Completely homogenize the 2g of fresh and cleaned tissue sample in 10 ml of 0.1 M potassium phosphate buffer (pH-7.0) by using previously chilled mortar and pestle. Centrifuge the homogenate at 10,000 rpm for 15 minutes in a temperature controlled centrifuge machine below 40C. Collect the supernatant as crude extract and discard the pellet completely. Use this extract at same time for enzyme assay and preserve the remaining extract in refrigerator for total soluble protein estimation which is required for enzyme specific activity calculation.
Enzyme assay: APX is assayed by the method of Nakano and Asada (1981). Use freshly prepared reagents and extracts only, for estimating APX activity. A total of 3ml reaction mixture containing 2.7ml of 100mM potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.0), 0.1ml L-ascorbate, 0.15ml H2O2 and initiate the reaction by adding 50µl of enzyme extract at the end. Record the decrease in absorbance at 290 nm spectrophotometrically for 2 minutes against a suitable blank. The blank can be prepared for each sample, simultaneously by taking 50µl boiled enzyme extract instead of enzyme extract. The enzyme activity can be calculated by using the molar extinction coefficient (Absorbance of one molar solution) of 2.8 mM-1 cm-1 for ascorbate in the standard equation for absorbance given below. That will be in enzyme units and one enzyme unit corresponds to the amount of enzyme required to oxidize 1nmol of ascorbic acid min-1.
Standard equation for absorbance as A = ε × Ɩ × с
Where, A is the amount of light absorbed by the sample at a given wavelength, ε is the molar extinction coefficient, Ɩ is the distance that the light travels through the solution, and с is the concentration of the absorbing species.
Note: The calibration of L-ascorbate and H2O2 concentration with enzyme extract quantity is required, once in the starting of the procedure, according to your samples and instruments to get better and accurate results.
Flow chart of standardized or calibrated enzyme assay with leaf samples of sorghum:
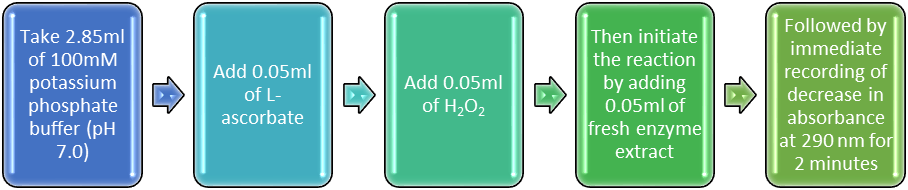
Calculations:
The enzyme activity and specific activity can be calculated by the procedure explained in the table below for a supposed sample size. The total protein content of the sample will be required to calculate the specific activity which can be determined by Lowry’s method.
Ascorbate peroxidase (APX) activity (units or nmol of ascorbate/minute) | |||||||||||
Supposed Sample used = extract was made from 2gm fresh leaves sample in 10 ml of potassium phosphate buffer from this 0.05 ml of extract was used for assay | |||||||||||
Absorbance at 290 nm | Enzyme activity and Specific activity | ||||||||||
| Replicates | Time 0 sec | 15 sec | 30 sec | 45 sec | 60 sec | Decrease in Absorbance | Average of Decrease in Absorbance | Enzyme activity/minute (units) = Activity/0.05ml | Dilution factor (activity/ml of extract) | Total Protein content of sample (mg/ml) | Specific activity (umol/min/mg) |
| 1st | a | b | c | d | e | a - e = F | (F + O + X) / 3 = Y | Y / 2.8 = Z | (Z / 0.05) × 1 = G | P | G / P = Q |
| 2nd | j | k | l | m | n | j - n = O | |||||
| 3rd | s | t | u | v | w | s - w = X | |||||
References:
Nakano, Y. and Asada, K., 1981. Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts.
Plant and cell physiology,22(5), pp.867-880.
Related files
 Bio-protocol.pdf
Bio-protocol.pdf - Kumar, P(2021). Ascorbate peroxidase activity (APX) for Stress amelioration response of glycine betaine and Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in sorghum under Cr toxicity. Bio-protocol Preprint. bio-protocol.org/prep1489.
- Kumar, P.(2021). Stress amelioration response of glycine betaine and Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in sorghum under Cr toxicity. PLoS ONE 16(7). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0253878
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link
