Advanced Search
Social Interaction Test
Last updated date: Jun 17, 2021 Views: 1473 Forks: 0
Summary
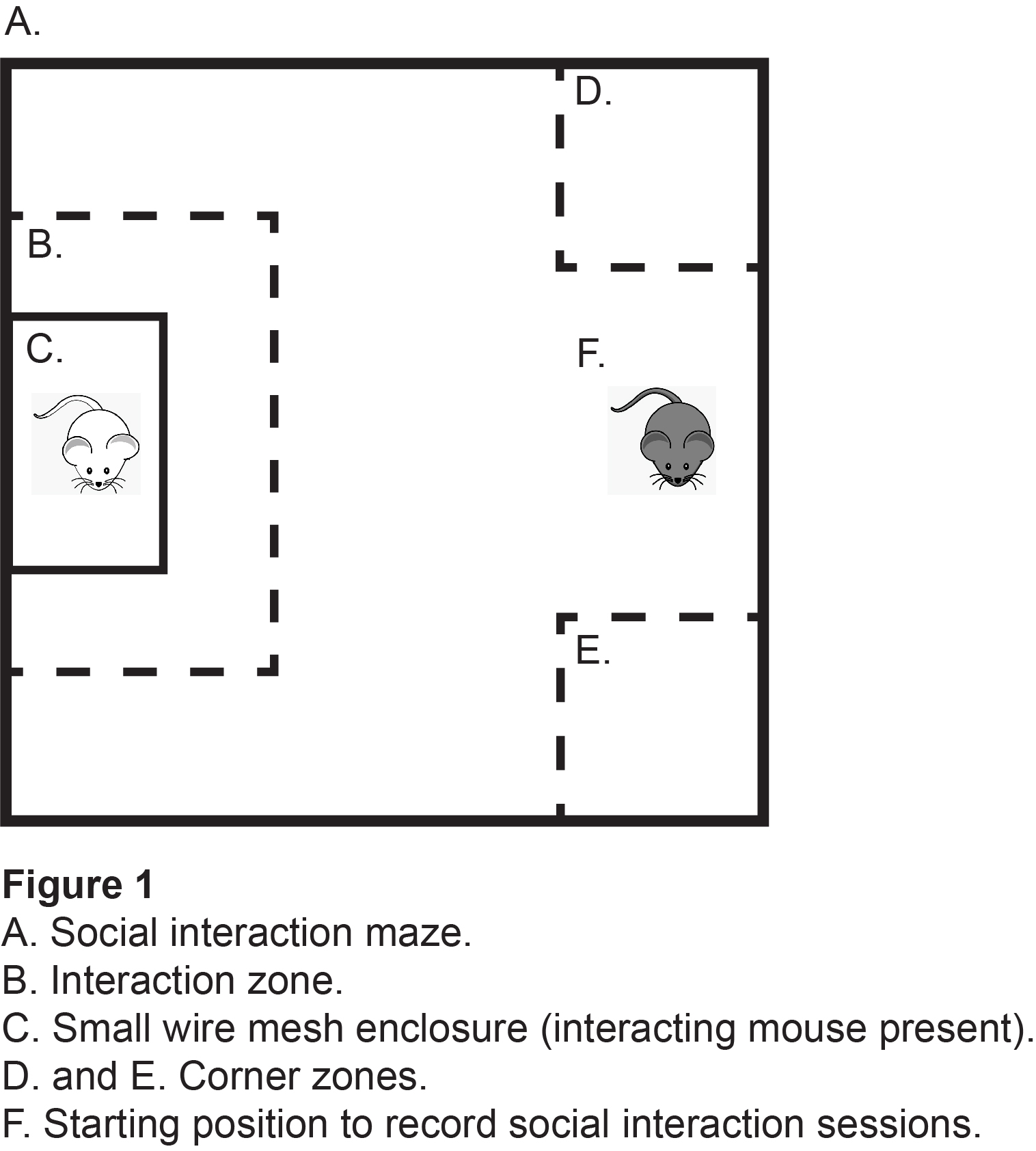
The social interaction test is utilized to assess pro-social behavior. An open field chamber (40 cm wide, 40 cm long, 30 cm walls; Noldus Information Technology, Leesburg, VA, USA) is outfitted with a small wire mesh enclosure (6.5 cm wide, 10 cm long, 30 cm height; Noldus Information Technology, Leesburg, VA, USA) on one side of the open field chamber (Figures 1, 2, 3). Experimental mice are introduced into the open field and allowed to explore their environment with an empty mesh enclosure for 2.5 min. Runs are performed with one experimental mouse at a time, and the chamber is thoroughly cleaned using water followed by 70% ethanol (allowing time for evaporation) to eliminate olfactory variables before the next experimental mouse is tested. After all experimental mice are assessed with an empty mesh enclosure, a different mesh enclosure (same dimensions and design as the first) is introduced into the open field containing a novel interacting mouse. This interacting mouse may be of any strain or sex desired for experimental purposes. Experimental mice are run in the aforementioned manner in the presence of the enclosed interacting mouse for 2.5 min. Sessions are recorded, tracked, and analyzed using specific motion tracking software (many commercial options are available). Social interaction and corner zone ratios are calculated by the amount of time an experimental mouse spends in the respective zone with an interacting mouse present in the enclosure vs. absent. Tests may be performed during the light or dark phase of the circadian cycle but must be reported accordingly since results will vary between the two phases.
Performing the Social Interaction Test
Important tip: Behavior testing of rodents is a very difficult task and must be stringently controlled and recorded. Before starting, it is recommended the investigators measure ambient noise, ultrasonics from equipment or lights, and ambient lighting in the room to understand potential variables that may affect their data. Furthermore, accurate recording of food, water, bedding, caging, and housing is also important to understand potential contributing aspects to rodent behavior. Any large noises or disruptions that occur during testing will void assessment of that specific animal, thus controlling these prior to starting enhances rigor and reproducibility of the data.
- Ensure mice are adequately acclimated to the behavior testing room. If testing in a different room than mice are housed, an acclimatization period of >1 hour is recommended prior to the initiation of testing.
- Place the small wire mesh enclosure that never houses an interacting mouse on one side of the open field chamber and secure it to the wall of the chamber with a clip (Figure 1C).
- Position the open field chamber with mesh enclosure directly under an arial mounted camera.
- Use additional arial mounted lights if needed to enhance lighting of the chamber.
- Prepare tracking software to record an experimental mouse for 2.5 minutes in the chamber in the absence of an interacting mouse.
- Introduce an experimental mouse into the chamber on the opposite side of the wire mesh enclosure (Figure 1F).
- Record the session for 2.5 minutes.
- Once the session is completed, remove the experimental mouse and return to their home cage.
- Clean the open field chamber with water and wipe clean. Then clean the chamber with 70% ethanol and wipe clean.
- Repeat steps 5 – 9, until all experimental mice have been recorded in the absence of an interacting mouse.
- Replace the small wire mesh enclosure with another identical enclosure that is used solely for interacting mice and secure it to the wall of the chamber with a clip (Figure 1C).
- Place a novel interacting mouse in the enclosure. Experimental mice should not have ever interacted with this mouse prior to testing.
- Prepare tracking software to record an experimental mouse for 2.5 minutes in the chamber in the presence of an interacting mouse
- Introduce an experimental mouse into the chamber on the opposite side of the wire mesh enclosure (Figure 1F).
- Record the session for 2.5 minutes.
- Once the session is completed, remove the experimental mouse and return to their home cage. Temporarily remove the interacting mouse as well for cleaning.
- Clean the open field chamber with water and wipe clean. Then clean the chamber with 70% ethanol and wipe clean.
- Repeat steps 11 – 17, until all experimental mice have been recorded in the presence of an interacting mouse.
- Return all mice back to their home cages, export data, and shut down system.
Analyzing the Social Interaction Test Data
Important tip: Every tracking software has unique capabilities and analysis parameters. The following analysis outlines one basic output of the social interaction test, but numerous others are possible depending on the specific system, setup, and software.
- Export the cumulative duration, in seconds, of the time spent in the corner zones (Figure 1D-E) and the interaction zone (Figure 1B), in the presence and in the absence of an interacting mouse. These zones are not present in the physical maze, but are created within the software based on the dimensions you choose. Exact dimensions will vary depending on your specific maze and setup.
- To calculate the corner zone ratio for each mouse, divide the cumulative duration in the corner zone in the presence of an interacting mouse by the cumulative duration in the corner zone in the absence of an interacting mouse.
- To calculate the social interaction ratio for each mouse, divide the cumulative duration in the interaction zone in the presence of an interacting mouse by the cumulative duration in the interaction zone in the absence of an interacting mouse.
- Moshfegh, C and Case, A J(2021). Social Interaction Test. Bio-protocol Preprint. bio-protocol.org/prep1172.
- Moshfegh, C. M., Elkhatib, S. K., Collins, C. W., Kohl, A. J. and Case, A. J.(2019). Autonomic and Redox Imbalance Correlates With T-Lymphocyte Inflammation in a Model of Chronic Social Defeat Stress. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience 13. DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2019.00103
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link
