Advanced Search
Fumigation- A disinfection process to decontaminate Tissue culture laboratory
Last updated date: Feb 1, 2023 Views: 6785 Forks: 0
Abstract
In plant and animal tissue/cell culture laboratories, microbial (Bacterial & Fungal) contamination is the primary challenge that hinders successful tissue culture procedures. To prevent contamination, in addition to regular sterilization procedures to decontaminate the explant and other equipment, it is essential to maintain an aseptic environment in the tissue culture room. Fumigation is the most common method used to decontaminate the tissue culture rooms by using the fumes of various toxic chemicals. In this protocol, we explain a simple and quick method of fumigation method using potassium permanganate (KMnO4) and formaldehyde. We also explain the sterility test to confirm the disinfection of the laboratory environment.
Keywords – Fumigation, Disinfection, Tissue/cell culture labs, Formaldehyde.
Background –
The most commonly used chemicals in fumigation are formaldehyde solution (Formalin) and potassium permanganate (KMnO4) because of their excellent disinfection efficacy and they are inexpensive (Connolly & Fletcher, 1981). The basic principle is that the addition of excess formaldehyde solution to potassium permanganate (KMnO4) generates fumes of formaldehyde (HCHO and methanol present in formaldehyde solution will oxidized by potassium permanganate (KMnO4) and leads to the generation of formaldehyde fumes.
Reaction-
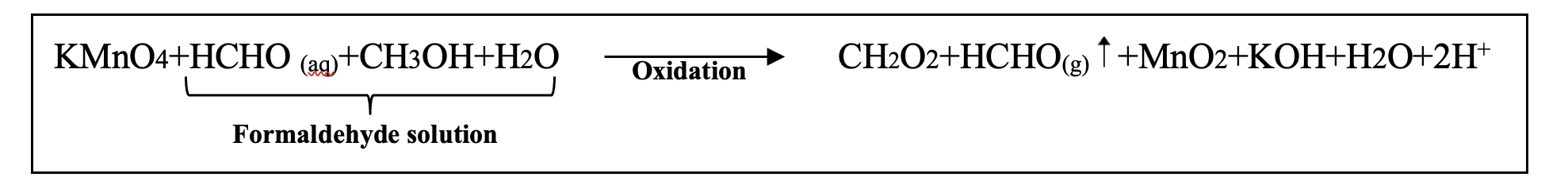
(Li et al., 2018)
Formaldehyde is a cytotoxic substance that inactivates cells or microorganisms by alkylating the amino groups and sulfhydryl groups of proteins. Therefore, the microorganisms present in the fumigated area become dysfunctional. To confirm the efficiency of fumigation and aseptic status of the disinfected room a sterility test is to be performed by counting the microorganisms present in the fumigated room(Mishra & Wadhai, 2016). As per WHO recommendations, in a clean room, the microbial limit for exposed plate is 10 CFU/m3 and the limit for contact plate is 5 CFU/plate (World Health Organization, 2011).
Materials and Reagents
- Potassium Permanganate ( Sisco Research Laboratories SRL, Catalogue Number: 36903- Part A)
- Formaldehyde solution (Formalin) 37-41%(W/V) Ar (Formalin Ar) (S D Fine Chem Limited, SDFCL, Catalogue Number: G18A/0318/2906/13
- Glass petri plate (Borosil)
- Absorbent Cotton Roll
- Ammonia Solution 10% (to be prepared from 25% Ammonia solution, ( Sisco Research Laboratories SRL, Catalogue number-78719)
- Sodium Hypochlorite (Oxford chemicals, Catalogue number – 28289019)
- Potato dextrose agar (PDA) (Himedia, Catalogue number MH096)
- Nutrient agar (NA) (Himedia, Catalogue number- M001)
- Ethanol, absolute (Changshu hongshong fine chemicals co.ltd UN No. 1170)
Before starting the fumigation process,
- Clean the room to be fumigated to remove any dust. Seal the windows to avoid the escape of fumes.
- Keep the laminar hood and incubator doors open to expose them to fumes.
Safety: The personnel performing fumigation should wear appropriate safety gear such as a protective face mask, apron, safety goggles, hand gloves etc.
Procedure –
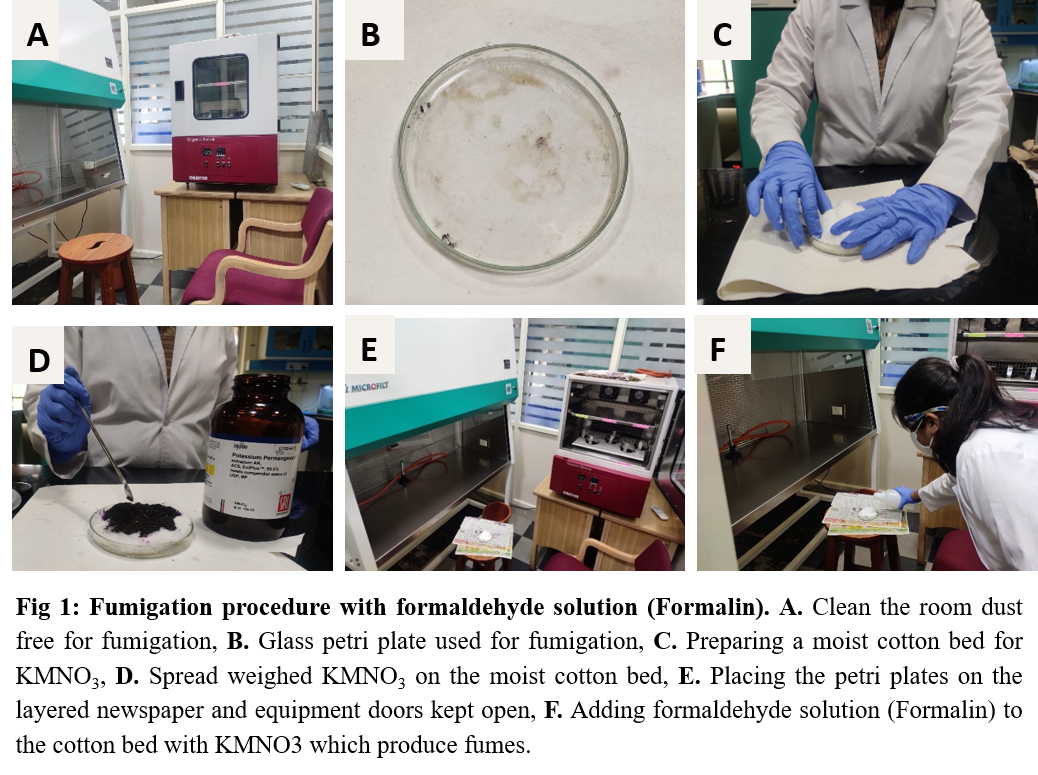
- In the room to be disinfected, place the glass Petri plates containing a thin layer of cotton and moisten the cotton using distilled water (Fig 1A, 1B, 1C). (For a 10x10x10 ft room, use 3 Petri plates in each room).
- Place 10gm of potassium permanganate (KMnO4) in each Petri plate and spread it evenly, place the cotton on it and make it wet with water as shown in the video. (Fig 1D)
- Place these plates in the appropriate position in the room. Keep the incubator doors and laminar airflow hoods open. (Fig 1E)
- Carefully pour 10ml of formaldehyde solution (Formalin) (37% - 41%) into each plates containing KMnO4.(Fig 1F)
- The moment black smoke starts to arise, immediately leave the room and seal the lab's main door using cellophane tape. Do not open the lab for 24- 36 hours.
- After 24-36 hours, wear a protective mask and goggles, open the sealed fumigated room and remove the plates by wrapping them with blotting paper.
- To neutralize the formaldehyde fumes, place the Petri plate inside the room and pour 15ml of 10% ammonium hydroxide solution. (1:2::ammonium hydroxide: formaldehyde solution (Formalin)) and keep the room closed for another 3- 6 hours for the complete neutralization of the formaldehyde gas.
- Open the lab again and clean the leftover residues of formaldehyde with sodium hypochlorite solution. Wipe the Incubator and Laminar Air Flow Hood with 70% ethanol.
- Perform the sterility test to validate the efficiency of the fumigation.
Sterility test
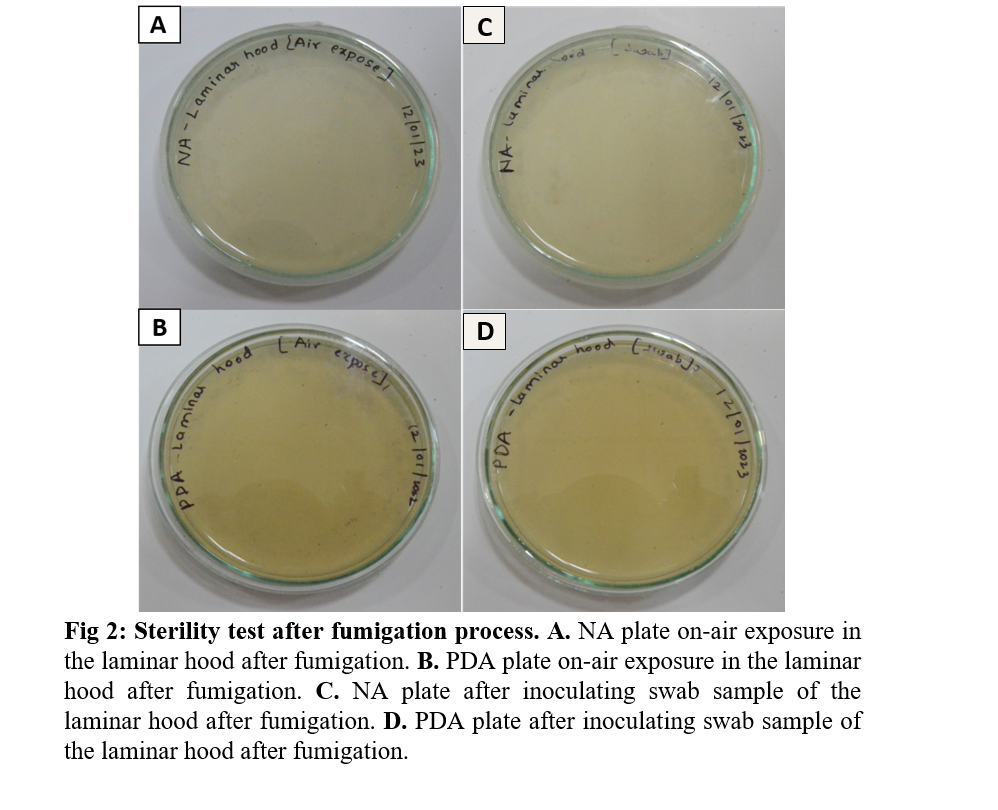
- Prepare Potato dextrose agar (PDA) and Nutrient agar (NA) plates as per the number of equipment present in the room. PDA is used to identify any fungal contamination and NA is used to identify bacterial contamination in the fumigated room.
- Prepare sterile cotton swabs for sample collection. Moist the cotton swab with sterile water and collect the sample from the surface of the equipment by swabbing and inoculating it onto PDA and NA plates.
- For the open plate method, expose the PDA and NA plates in the fumigated room for 10 seconds by waving method (Video 1 in attachment below).
- Incubate all the plates at 37°C for 24 hours for NA and 25°C ± 1 for 7 days for PDA to examine the bacterial and fungal growth respectively.
- After 24 hrs observe the plates for any growth of microorganisms. If the growth of any microorganisms persists, it is recommended to repeat the disinfection procedure.
Recipes -
Potato Dextrose agar (PDA)
Weigh 39gm of PDA (Himedia- MH096) and dissolve in 1000ml distilled water. Autoclave the media at 121°C under 15lbs pressure for 15mins. Pour the media into sterile Petri plates and allow it to solidify.
Nutrient Agar (NA)
Weigh 28gm of NA (Himedia-M001) and dissolve in 1000ml distilled water. Autoclave the media at 121°C under 15lbs pressure for 15mins. Pour the media into sterile Petri plates and allow it to solidify.
References
CONNOLLY, G. P., & FLETCHER, J. T. (1981). Procedures for the generation of formaldehyde vapour to fumigate structures. Plant Pathology, 30(4), 245–250.
Li, Y. S., Mo, L. M., & Gao, X. F. (2018). Direct automatic determination of the methanol content in red wines based on the temperature effect of the KMnO4/K2S2O5/fuchsin sodium sulfite reaction system. RSC Advances, 8(15), 8426–8434.
Mishra, A. K., & Wadhai, V. S. (2016). Sterility Testing of Operation Theatres in Hospitals. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, 5(5), 440–447.
Related files
 Fumigation video-3.mp4
Fumigation video-3.mp4 - Bhat, A R, Hegde, S, Kammar, S S, Mohan, T C and Rajulu, C(2023). Fumigation- A disinfection process to decontaminate Tissue culture laboratory. Bio-protocol Preprint. bio-protocol.org/prep2137.
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link


