Advanced Search
In vivo single-cell mosaic labeling to visualize retinal neurons
Last updated date: Sep 9, 2022 Views: 765 Forks: 0
Preparatory steps:
- Prepare DNA plasmids to label specific cell types using a reporter protein (e.g. green fluorescent protein (GFP)) expressed under the control of cell-specific promotors. In this study, different constructs were utilized to label distinct retinal neurons in the developing zebrafish embryo (Ahmed et al., 2022).
Note: To obtain better results, purify DNA plasmids using a DNA purification kit like QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit (27104, QIAGEN) or by ethanol precipitation (Green and Sambrook, 2016). - Dilute the DNA plasmid in sterile water to a concentration of 10-20 ng/μL and store in -20°C.
- Set crosses of the desired genetic background one day before injection.
DNA injections:
- Backfill a pulled glass capillary needle with the diluted DNA construct and connect it to a microinjector apparatus (Narshige IM-300).
- Gently tap the tip of the needle with forceps to dispense the DNA solution. Set injection pressure to 30 psi and injection time between 50-100 msec. Ideally, the injected volume should not exceed 10% of the total egg volume (Rosen et al., 2009).
- Start the crosses and collect embryos in E3 embryo rearing medium (5 mM NaCl, 0.17 mM KCl, 0.33 mM CaCl2, 0.33 mM MgSO4) containing 0.01% methylene blue to prevent fungal growth.
- Align the embryos in silicone-molded dishes with a horizontal groove; the groove should have enough E3 medium to prevent drying.
- Inject the embryos into the cell of one-cell-stage embryos to obtain the best results.
Imaging:
- Allow embryos to develop till the desired developmental stage in E3 medium on a 14:10 hr light:dark cycle at 28°C. Add 1-phenyl-2-thiouera (PTU) after 10 hpf to a final concentration of 0.003% to prevent pigmentation.
Note: To image embryos younger than 2 dpf, dechlorinate embryos prior to imaging. - Select embryos with a strong fluorescent signal under the stereomicroscope. Then, transfer embryos to a dish containing E3 medium with 0.003% PTU and 0.02% tricaine (3-amino benzoic acid ethyl ester) to anesthetize the embryos.
Note: To visualize retinal landmarks, embryos can be incubated for 1 hour prior to imaging in a GFP-counterstain like CellTrace BODIPY TR Methyl Ester (C34556, Thermo Fisher Scientific). - To perform live imaging, use an upright confocal microscope (e.g.: Zeiss LSM 710) with a 20x or 40x water immersion objective. To mount the embryos with a positive signal, prepare a custom-made plastic stage with vertical grooves. Stick the plastic stage to the bottom of a 35 mm dish (see supplementary information, (Mochizuki et al., 2017)).
- Prepare 1% low-melting agarose, heat at 65°C for 30 min till it becomes liquid, then keep it incubated at 39°C for embryo mounting. To do that, place one drop of agarose on one groove, then transfer the embryo on the agarose drop and orient it laterally with the yolk sac inside the groove so that the eye faces the objective lens.
- After the agarose solidifies, cover the embryos with enough E3 medium containing PTU and tricaine to prevent drying throughout the imaging session.
Note: For overnight imaging, overlay the medium with a thin layer of mineral oil to prevent evaporation and minimize embryotoxicity. - Obtain confocal z-stack images under optimal conditions and perform 3D rendering of images using image analysis software like ImageJ (NIH, v2.1.0/1.53 C) or Imaris (Bitplane, v9.1.2).
Representative images:
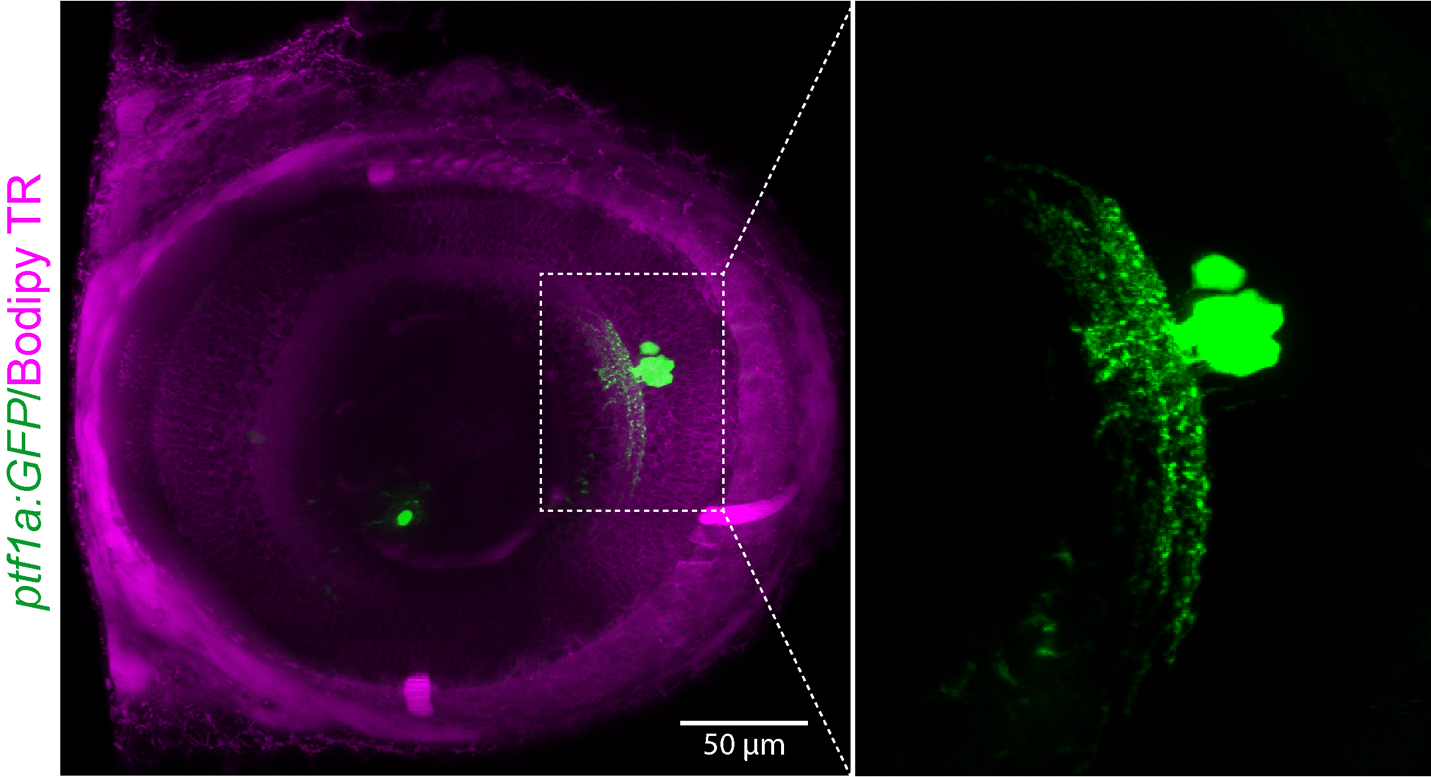
References:
AHMED, M., KOJIMA, Y. & MASAI, I. 2022. Strip1 regulates retinal ganglion cell survival by suppressing Jun-mediated apoptosis to promote retinal neural circuit formation. eLife, 11, e74650.
GREEN, M. R. & SAMBROOK, J. 2016. Precipitation of DNA with Ethanol. Cold Spring Harb Protoc, 2016.
MOCHIZUKI, T., LUO, Y. J., TSAI, H. F., HAGIWARA, A. & MASAI, I. 2017. Cell division and cadherin-mediated adhesion regulate lens epithelial cell movement in zebrafish. Development, 144, 708-719.
ROSEN, J. N., SWEENEY, M. F. & MABLY, J. D. 2009. Microinjection of zebrafish embryos to analyze gene function. J Vis Exp.
- Ahmed, M and Masai, I(2022). In vivo single-cell mosaic labeling to visualize retinal neurons. Bio-protocol Preprint. bio-protocol.org/prep1919.
- Ahmed, M., Kojima, Y. and Masai, I.(2022). Strip1 regulates retinal ganglion cell survival by suppressing Jun-mediated apoptosis to promote retinal neural circuit formation. eLife. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.74650
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link
