Advanced Search
RNA Immunoprecipitation (RIP) Sequencing of Pri-miRNAs Associated with the Dicing Complex in Arabidopsis
Published: Jul 5, 2018 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2909 Views: 6984
Edited by: Amey Redkar Reviewed by: Marisa Rosa
Abstract
RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) is an antibody-based technique used to map in vivo RNA-protein interactions. DBR1, an RNA debranching enzyme, is responsible for the debranching of lariat RNA, for the degradation and turnover of lariat RNAs. It is well known that primary miRNA (Pri-miRNA) is recognized and further processed into mature miRNA by the Dicing complex mainly composed of DCL1 and HYL1. Due to the low abundance of pri-miRNAs, RIP followed qRT-PCR has been widely used to evaluate the binding efficiency of the Dicing complex with pri-miRNAs in previous studies. Therefore, the genome-wide evaluation of the Dicing complex with pri-miRNAs is lacking. With the improvement of high-throughput sequencing technologies, we successfully used RIP-seq to compare the binding efficiency of the Dicing complex with pri-miRNAs between wild-type and the dbr1-2 mutant in our recent study. In this protocol, we provide a detailed description of RIP-seq using GFP-trap beads in HYL1-YFP and DCL1-YFP transgenic plants between two different genotypes. This method can be used to assess the binding of pri-miRNAs with the Dicing complex in Arabidopsis, and it can be applied to other RNA binding proteins in plants.
Keywords: DBR1Materials and Reagents
- RNase-free pipette tips
- RNase-free Eppendorf tubes (Safe-Lock Tubes, Eppendorf, catalog number: 0030120086 )
- 50 ml and 15 ml RNase-free Falcon tubes (Corning Company)
- Miracloth (Merck, catalog number: 475855-1R )
- Paper towels
- Fresh inflorescences including all buds and open flowers together (see Figure 1) of proHYL1::YFP-HYL1/Col-0, proHYL1::YFP-HYL1/dbr1-2, proDCL1::DCL1-YFP/Col-0, proDCL1::DCL1-YFP/dbr1-2 plants grown in 16 h/8 h light/dark condition, 22 °C
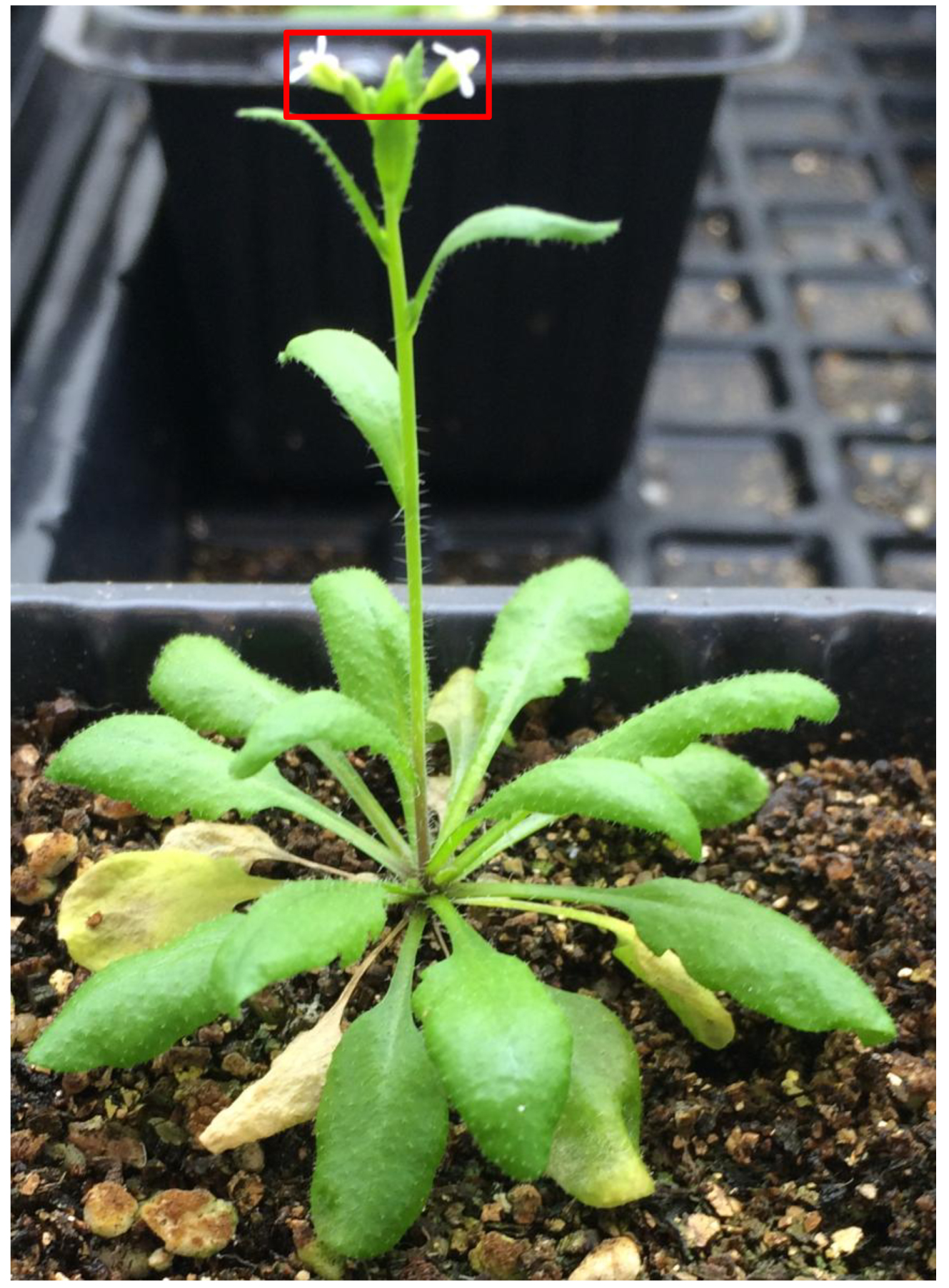

Figure 1. A mature plant with the position of the tissue used in this method indicated by a red rectangle. Inflorescences were collected freshly. In general, it is better to use the inflorescences from primary shoot for this experiment. - Liquid nitrogen
- Ice
- 37% formaldehyde (Sinopharm Chemical Regent, catalog number: 10010018 , store in the dark)
- Diethy pyrocarbonate (DEPC) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D5758 )
- GFP-Trap agarose beads (Chromotek, catalog number: gta-20 )
- Protein A agarose/Salmon Sperm DNA (Merck, Upstate, catalog number: 16-157 )
- RNase inhibitor (Promega, catalog number: N2611 )
- RQ1 DNase I (Promega, catalog number: M6101 )
- Glycogen (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: R0551 )
- Proteinase K (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: EO0491 )
- SuperScript IV (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 18090200 )
- Taq DNA polymerase (Takara Bio, catalog number: R500Z )
- dNTP (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: R0181 )
- Oligo dT (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: SO132 )
- DTT (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: R0861 )
- Acidic Phenol:Chloroform
- Ethanol (Acros Organics, catalog number: 397690010 )
- Agarose (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 16500100 )
- PMSF (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P7626 )
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 11873580001 )
- Illumina TruSeq Stranded Total RNA HT Sample Prep Kit (P/N15031048)
- MgCl2 (Sangon Biotech, catalog number: MB0331 )
- CaCl2 (Sangon Biotech, catalog number: CT1330 )
- Glycine (Sangon Biotech, catalog number: A610235 )
- EDTA (Sangon Biotech, catalog number: A100105 )
- NaAc (Sangon Biotech, catalog number: ST0827 )
- Sucrose (Sangon Biotech, catalog number: SB0498 )
- HEPES (Sangon Biotech, catalog number: H0511 )
- Tris (Sangon Biotech, catalog number: A600194 )
- SDS (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: L5750 )
- NaCl (Sangon Biotech, catalog number: A501218 )
- Ficoll (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F2637 )
- Dextran T40 (Sangon Biotech, catalog number: DB0374 )
- Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T8787 )
- Primers used in Figure 3:
Pri-miR156a-F: CAAGAGAAACGCAAAGAAACTGACAG
Pri-miR156a-R: AAAGAGATCAGCACCGGAATCTGACAG
Pri-miR158a-F: GTGATGACGCCATTGCTCTTT
Pri-miR158a-R: TGTGACTTTAGATGCCCTTGTTCA
Pri-miR159a-F: GGAGCTCTACTTCCATCGTCA
Pri-miR159a-R: CCACGTTCTCATCAAAACTTTC
Pri-miR166a-F: GACTCTGGCTCGCTCTATTCA
Pri-miR166a-R: TGGTCCGAAGACGCTAAAAC
Pri-miR167a-F: GAAGCTGCCAGCATGATCTA
Pri-miR167a-R: GGGTTTATAGAAGGGTGCGA
Pri-miR168aF: GCCTTGCATCAACTGAAT
Pri-miR168aR: CAAACAAAAGGAGACTAAAGA
Pri-miR169aF: TGGGTATAGCTAGTGAAACGCG
Pri-miR169aR: CCTTAGCTTGAGTTCTTGCGA
Pri-miR171aF: CCGCGCCAATATCTCAGTA
Pri-miR171aR: TGTCTCCATTTCAACACACACA
Pri-miR172aF: ATCTGTTGATGGACGGTGGT
Pri-miR172aR: AATAGTCGTTGATTGCCGATG
Pri-miR319aF: GAGATAGAGAGTTGAACAAATTCTTC
Pri-miR319aR: GTATCCATGATAGTTGAGAAATTTGC - Honda Buffer (see Recipes)
- Nuclei Lysis Buffer(see Recipes)
- ChIP Dilution Buffer (see Recipes)
- Binding/Washing Buffer (see Recipes)
- RIP Elution Buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Pipettes (Gilson Company)
- Fume hood
- Vacuum Pump (Shanghai SENCO Company, model: SHB-3 )
- Microcentrifuge (Thermo)
- Vortexer (VWR Company)
- Mortar and Pestle (Fisher)
- -80 °C Freezer (Thermo)
- Rotator (Haimen Kylin-Bell Lab Instruments, catalog number: KB-3-D )
- Mini Gel Electrophoresis Systems (Tanon Company)
- ChIP-grade Sonifier (Diagenode Bioruptor)
- Illumina HiSeq 2000 (Shanghai Genegy Company)
Procedure
Category
Plant Science > Plant molecular biology > RNA > RNA-protein interaction
Molecular Biology > RNA > RNA-protein interaction
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link