- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Bacterial Counts in Spleen
脾脏中的细菌菌落计数
发布: 2013年11月05日第3卷第21期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.954 浏览次数: 26594
评审: Anonymous reviewer(s)

相关实验方案
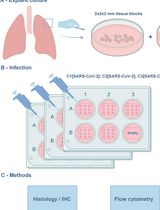
用于研究肺部感染与免疫反应的离体肺组织培养模型,以 SARS-CoV-2 为 RNA 病毒研究示例
Elena V. Maryukhnich [...] Elena J. Vasilieva
2025年12月20日 709 阅读
Abstract
Bacterial loads can be determined as colony forming units (CFU) at any point of the infection by culturing spleen homogenates on agar plates. This is a reliable method for comparing the kinetics of infection in various mouse strains, estimating the virulence of different bacterial mutants or isolates and for vaccine testing and vacine estandarization. Although this method has been designed to recover Brucella or Salmonella organisms from spleen, the procedure may be applicable for other bacteria such as Listeria and Mycobacterium as well as to count bacterial loads in other organs such as liver or lymph nodes.
Materials and Reagents
- Sterile plastic bags, 30 g capacity (~30 ml) (Whirl-Pak® Write-On Bags) (Nasco, catalog number: B01067WA )
- 70% Ethanol (Merck KgaA, Emsure®, catalog number: 1009834000 )
- Latex examination gloves (Dermagrip®, catalog number: D1402-14 )
- Pyrogen-free Type 1+ grade distilled water (Milli-Q Direct 8 and 16 Ultrapure Water System)
- Dulbecco′s Phosphate Buffered Saline (Gibco, catalog number: 21300-058 )
- Tween® 20 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P5927 )
- Tryptone Soya Agar (Oxoid Limited, catalog number: CM0131 ) (see Recipes), or other media according to culture bacterial requirements
- PBS 0.1% Tween 20 (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 24-well plates, low binding cell (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z721077 )
- Beaker (100 ml)
- Glass alcohol burner (WHEATON, catalog number: WHE-237070 )
- Surgical instruments for mice (Mouse Surgical Kit) (Kent Scientific, model: INSMOUSEKIT )
- Drigalski spatula (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: NC0242405 )
- Micropipettes (10-100 μl and 100-1,000 μl)
- Micropipette tips (100 μl and 1 ml)
- 1.5 ml eppendorf tubes (Eppendorf, catalog number: 0 22363204 )
- Tuberculin plastic syringe (1 ml) with 25-27 g needle gauge
- Plastic petri dishes (90 x 15 mm)
- Disposable medical plastic gloves (Lab Depot, catalog number: 266-P )
- Small sharp scissors and forceps
- Water purification system (Milli-Q Direct 8 and 16 Ultrapure Water System) (EMD Millipore, model: ZR0Q00800 )
- Bacterial incubator (Forma® Direct Heat CO2 Incubator) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, model: 310 )
- Autoclave (Yamato Scientific, model: SQ-500C )
- Analytical balance electronic digital (± 0.0001 g)
- Laminar flow cabinet (Esco Global, Labculture® Class II, Type A2, model: LA2-3A2 )
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Barquero-Calvo, E., Chacón-Díaz, C., Chaves-Olarte, E. and Moreno, E. (2013). Bacterial Counts in Spleen. Bio-protocol 3(21): e954. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.954.
分类
免疫学 > 动物模型 > 小鼠
细胞生物学 > 组织分析 > 组织分离
微生物学 > 微生物-宿主相互作用 > 离体模型
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link