- EN - English
- CN - 中文
MAPK Phosphorylation Assay with Leaf Disks of Arabidopsis
拟南芥叶片中MAPK的磷酸化检测
发布: 2013年10月05日第3卷第19期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.929 浏览次数: 13139
评审: Anonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Activation of mitogen activated protein kinases (MAPKs) is involved in many abiotic and biotic stress responses including plant defense. MAPK acitvation is based on the dual phosphorylation of threonine (T) and tyrosin (Y) residues (T-x-Y motif) in the activation loop of the MAPK protein. By determination of the phosphorylation status of a specific MAPK one can detect if the MAPK has been activated or not.
This protocol describes how to analyze the phosphorylation status of Arabidopsis MAPKs MPK3 and MPK6 by using leaf disks, western blotting and a specific antibody (Figure 1). It can also be used for the analysis of MAPKs in other plant systems although some alterations regarding protein extraction might be necessary.
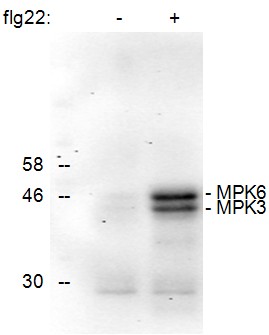
Figure 1. Detection of the phosphorylation of Arabidopsis thaliana MAPKs MPK6 and MPK3 upon treatment of seedlings for 15 min with the active epitope (flg22, 1 μM) of the bacterial elicitor flagellin (+). No phosphorylated MAPKs were detected in the control treated sample (-).
Materials and Reagents
- Arabidopsis thaliana adult plants
- Liquid nitrogen
- Phospho-p44/42 MAPK (Erk1/2) (Thr202/Tyr204) Rabbit mAb #4370 (Cell Signaling Technology) (http://www.cellsignal.com/products/4370.html)
- Anti-Rabbit secondary antibody
- Tris-HCl
- Glycerol
- SDS
- Dithiothreitol (DTT)
- Bromphenol blue
- Reagents for SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
- 6x Protein extraction/loading buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 1.5 ml Microcentrifuge tubes
- Small petri dishes (~ 5 cm diameter) or 6-well plates
- Cork borer (~ 10 mm diameter)
- Glass beads (~ 1-2 mm diameter)
- Silamat S6 (http://www.ivoclarvivadent.com/en/products/equipment/mixer/silamat-s6)
- Alternatively for 4. and 5. Mortar (~ 5 cm diameter) and pestle
- Vortexer
- Heating block
- Centrifuge
- Equipment for SDS-PAGE, Western Blotting and detection
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Flury, P., Klauser, D., Boller, T. and Bartels, S. (2013). MAPK Phosphorylation Assay with Leaf Disks of Arabidopsis. Bio-protocol 3(19): e929. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.929.
- Flury, P., Klauser, D., Schulze, B., Boller, T. and Bartels, S. (2013). The anticipation of danger: microbe-associated molecular pattern perception enhances AtPep-triggered oxidative burst. Plant Physiol 161(4): 2023-2035.
分类
植物科学 > 植物免疫 > 信号感知与传递
细胞生物学 > 细胞信号传导 > 磷酸化
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 免疫检测
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
提问指南
+ 问题描述
写下详细的问题描述,包括所有有助于他人回答您问题的信息(例如实验过程、条件和相关图像等)。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link