- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Targeted Occlusion of Individual Pial Vessels of Mouse Cortex
小鼠皮质个别软膜血管的靶标闭塞
发布: 2013年09月05日第3卷第17期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.897 浏览次数: 10710
评审: Xuecai Ge

相关实验方案
基于 rAAV-α-Syn 与 α-Syn 预成纤维共同构建的帕金森病一体化小鼠模型
Santhosh Kumar Subramanya [...] Poonam Thakur
2025年12月05日 1386 阅读
Abstract
Targeted photothrombosis is a method to occlude individual arterioles and venules that lie on the surface of the cerebral cortex. It has been used to study collateral flow patterns within the pial vascular network following occlusion of single surface vessels (Schaffer et al., 2006; Blinder et al., 2010; Nguyen et al., 2011), as well as to generate localized ischemic strokes following occlusion of single penetrating vessels (Nishimura et al., 2007; Drew et al., 2010; Shih et al., 2013). The intravascular clot is formed by irradiation of a target vessel with a focused green laser after injection of a circulating photosensitizing agent, Rose Bengal (Watson et al., 1985). We briefly describe modifications of custom-designed and commercial two-photon imaging systems required to introduce a green laser for photothrombosis. We further provide instructions on how to occlude a single penetrating arteriole within the somatosensory cortex of an anesthetized mouse.
Keywords: Two-photon imaging (双光子成像)Materials and Reagents
- Mouse with cranial window implant
- Buprenorphine hydrochloride (Buprenex®) (Butler Schein, catalog number: 031919 )
- Isoflurane (Butler Schein, catalog number: 029405 )
- Ophthalmic ointment (Butler Schein, catalog number: 039886 )
- Cover Glass (no. 0 thickness) (Thomas Scientific, catalog number: 6661B40 )
- Filter paper (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: S47573B )
- 60 mm Culture dish (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 130181 )
- Distilled water
- Glucose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G8270 )
- HEPES (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H7006 )
- Artificial cerebral spinal fluid (ACSF) (see Recipes)
- FITC-dextran (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: FD2000S ) solution (see Recipes)
- Rose Bengal (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 632-69-9 ) solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Insulin syringe, 0.3 ml volume with 29.5 gauge needle (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 309301 )
- Green laser, 532 nm (Beta Laser, catalog number: MGM20 )
- Heating pad with feedback regulation
- Temperature control system (FHC Inc., catalog number: 40-90-8 )
- Rectal thermistor (FHC Inc., catalog number: 40-90-5D-02 )
- Heat pad for mouse (FHC Inc., catalog number: 40-90-2-07 )
- Temperature control system (FHC Inc., catalog number: 40-90-8 )
- Isoflurane vaporizer (IsoTec4; Datex-Ohmeda) (GE Healthcare)
- Induction chamber (VetEquip, model: 941444 )
- Objective lens, 4x, 0.16-NA (UplanSApo) (Olympus, or equivalent for your system)
- Objective lens, 20x, 1.0-NA water immersion (XLUMPlanFI) (Olympus, or equivalent for your system)
- Two-Photon Microscope, adapted for targeted photothrombosis (custom-designed or commercial, i.e. Sutter Movable Objective Microscope)
Microscope setup
- With a custom-designed two-photon imaging system (Tsai et al., 2002), a green laser beam is introduced into the imaging beam path with dichroic mirror 1 (625 DRLP) (Figure 1) (Shih et al., 2011). The beam is adjusted to pass through a 3.5 mm diameter clearing etched in the dielectric coating of dichroic mirror 2 (700 DCXRU) (Figure 1). This allows transmission of the green laser to the back aperture of the objective lens, while still reflecting > 90% of emitted light from the sample toward the photomultiplier tubes (PMTs). The result is a fixed green laser beam, focused within the center of the imaging field. A shutter placed within the green laser path (LS3Z2 Uniblitz and VMM-D1 driver) will allow control over its on-off time. During occlusion of a vessel, irradiation can be periodically interrupted for brief epochs of imaging. Typically 1 frame (0.2 sec per frame) every 1 sec for an 80% duty cycle. This permits real time observation of the formation of the clot (Schaffer et al., 2006).
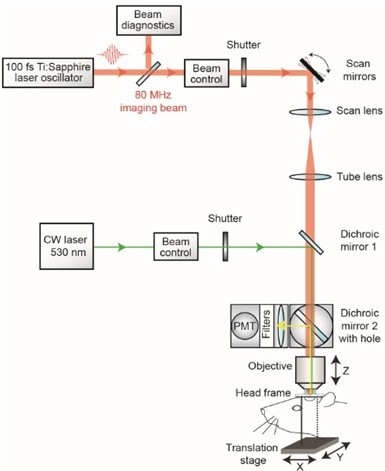
Figure 1. Schematic of custom-designed two-photon system modified to introduce a continuous wave green laser beam. (CW) continuous wave, (PMT) photomultiplier tube. The beam control module for the green laser refers to a neutral density filter to attenuate the laser intensity to a level suitable for photothrombosis. A ~ 3.5 mm diameter hole is etched in the coating of dichroic mirror 2 to allow the green laser to pass while the PMT assembly is in place, thereby allowing visualization of clot formation in real-time. Components and instructions to adapt a custom-designed two-photon system (Tsai et al., 2002) for targeted photothrombosis are provided in Shih et al. (2011). - For the enclosed design of commercial two-photon imaging systems, there is often limited space within the microscope for additional optomechanical components. Here we illustrate how the green laser may be introduced through the camera port of a Sutter Movable Objective Microscope (MOM), using a custom green laser module described by Sigler et al. 2008. The port is located above the ocular lenses, as is the case for most commercial microscope systems (Figure 2a). This path leads to a movable mirror (mirror 2) already located within the Ti-Sapphire imaging beam path between the scan and tube lenses. The green laser is then deflected toward the back aperture of the objective. When transitioning from two-photon to wide-field imaging mode with the MOM system, built-in servo-motors move mirror 2 into the beam path and move the primary dichroic above the objective out of the path synchronously (Figure 2a). This allows the green laser to pass to the objective. In this configuration, however, one will be not be able to visualize the formation of the clot in real-time. Rather, the extent of clot is monitored in between epochs of continuous irradiation (30 sec), by transitioning back to two-photon imaging mode when the green laser is off (Figure 2b). Finally, while not discussed here, another entry point for the green laser is through an epifluorescence filter slot, as described in detail by Sigler et al. (2008).
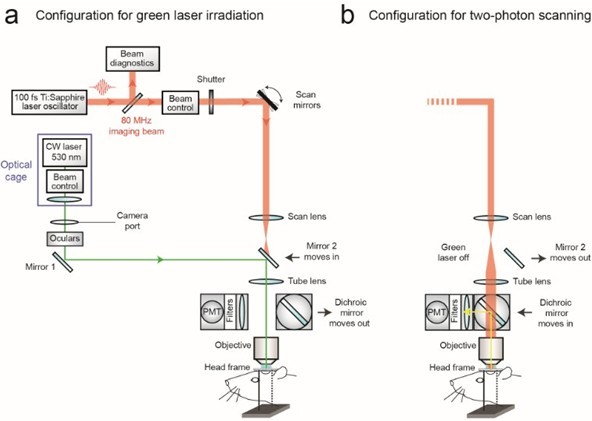
Figure 2. Schematic of commercial two-photon system (Sutter Movable Objective Microscope) modified to introduce a continuous wave green laser beam through the camera port. The beam control module refers to a neutral density filter to attenuate the laser intensity to a level suitable for photothrombosis, and a polarizing filter on a rotation mount for finer adjustments of intensity (see Sigler et al., 2008 for detailed instruction for green laser assembly for camera port). A single plano convex lens, rather than the lens doublet described by Sigler et al. 2008, is added to the optical cage assembly to ensure that the beam is collimated after it passes through the tube lens of the microscope. The beam control module and lens are housed in an optical cage generated from Newport parts, which is bolted to a C-mount adaptor that fits into the camera port. The PMT assembly is moved out of the imaging beam path to allow the green laser to pass. - With both custom and commercial two-photon imaging systems, additional optics may be necessary to adjust the power of the green laser and modify the diameter of the beam, depending upon the system. Power control is typically achieved by adding a neutral density filter and/or polarizer filter on a rotation mount (Sigler et al., 2008; Shih et al., 2011). The power of the green laser at its focus after the microscope objective should range between 0.5–1 mW. The green laser beam should under fill the back aperture of the microscope objective, in order to generate a relatively large 3 to 5 μm diameter region of photoactivation within the center of the imaging plane. The beam should also be collimated to ensure that the green laser is focused at the imaging plane. It may therefore be necessary to add lenses to alter the beam diameter and/or adjust for convergence/divergence of the green laser caused by other lenses within the beam path. For example, with the Sutter MOM system an additional plano convex lens (LA1978-A) was added to reduce convergence caused by the tube lens (Figure 2a; located within optical cage system). All necessary optics can be housed together with the green laser using cage systems available from ThorLabs or Newport, and then mounted on the camera port as a single unit, similar to that described by Sigler et al. (Figure 2a) (Sigler et al., 2008).
We now describe the procedures involved in occluding a single penetrating arteriole in mouse cortex using a green laser beam coupled through the camera port of a Sutter MOM.
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Taylor, Z. J. and Shih, A. Y. (2013). Targeted Occlusion of Individual Pial Vessels of Mouse Cortex. Bio-protocol 3(17): e897. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.897.
分类
神经科学 > 神经系统疾病 > 动物模型
细胞生物学 > 组织分析 > 组织分离
细胞生物学 > 细胞成像 > 固定组织成像
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link