- EN - English
- CN - 中文
CAPS-Based SNP Genotyping for Nitrogen-Response Phenotypes in Maize Hybrids
基于 CAPS 标记的玉米杂交种氮响应性状 SNP 基因分型方法
发布: 2025年12月20日第15卷第24期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5551 浏览次数: 550
评审: Samik BhattacharyaAthanas GuzhaAnonymous reviewer(s)

相关实验方案

利用Southern杂交技术研究植物中转座子DNA甲基化和拷贝数变异的情况
Vivek Hari Sundar G. and P. V. Shivaprasad
2022年06月05日 3412 阅读
Abstract
A simple and effective method to identify genetic markers of yield response to nitrogen (N) fertilizer among maize hybrids is urgently needed. In this article, we describe a detailed methodology to identify genetic markers and develop associated assays for the prediction of yield N-response in maize. We first outline an in silico workflow to identify high-priority single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers from genome-wide association studies (GWAS). We then describe a detailed methodology to develop cleaved amplified polymorphic sequences (CAPS) and derived CAPS (dCAPS)-based assays to quickly and effectively test genetic marker subsets. This protocol is expected to provide a robust approach to determine N-response type among maize germplasm, including elite commercial varieties, allowing more appropriate on-farm N application rates, minimizing N fertilizer waste.
Key features
• Leverages GWAS datasets to efficiently identify genetic markers.
• Employs basic molecular biology techniques.
• Can be adapted to any maize germplasm.
Keywords: SNP (单核苷酸多态性)Graphical overview
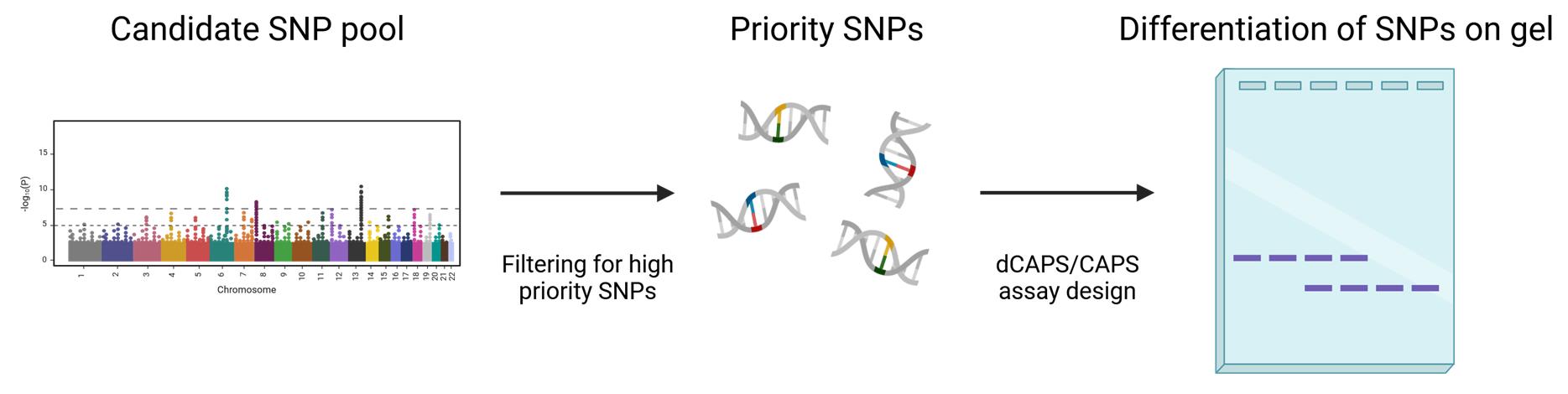
Visual description of the pipeline describing how to prioritize and visualize single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)
Background
Maize production systems are heavily reliant on the provision of N fertilizer to maximize growth and yield. However, the yield gain from N applications can vary widely depending on the underlying genetics. Certain hybrids, known as Type 3 hybrids, continue to increase yield even at very high N application rates, while others, known as Type 1 hybrids, hit a yield plateau at relatively low N application rates, meaning additional N is largely ineffective at increasing yield [1]. Knowledge of N-response type is highly valuable to a farmer, as it allows them to tailor their N application rates to match what the maize can utilize, thus minimizing financial and environmental costs. However, determination of N-response type currently requires time- and labor-intensive field tests spanning multiple years. A genetic marker–based approach to determine yield N-response of maize germplasm would be much faster and easily accessible for breeders and farmers.
Here, we describe a simple and effective protocol to identify candidate single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers associated with yield N-response type and to develop cleaved amplified polymorphic sequences (CAPS) assays to genotype these markers [2]. The following protocol begins with in silico filtering of SNP marker data that may have come from, for example, genome-wide association studies (GWAS). The filtering prioritizes candidate SNPs, essential to avoid repetitive or duplicated regions, which are less accessible to marker assays. A suitable CAPS assay is then developed to genotype candidate SNPs. The CAPS method relies on restriction enzyme cleavage that differentiates (i.e., cutting or not cutting) depending on the nucleotide at a particular SNP. As an alternative approach, when the SNPs do not present a suitable site for restriction digestion, the derived CAPS (dCAPS) approach can be employed [3]. In either case, a region encompassing the SNP is amplified and digested using a restriction enzyme before being separated by gel electrophoresis as a read-out of the SNP identity.
Materials and reagents
Biological materials
1. B73, Zea mays L. subsp. mays (USDA National Plant Germplasm System, PI 550473 2024ncai01 SD)
2. LH195, Zea mays L. subsp. mays (USDA National Plant Germplasm System, PI 537097 13ncai01 SD)
3. PHN82, Zea mays L. subsp. mays (USDA National Plant Germplasm System, PI 601783 2022ncai01 SD)
4. PHB47, Zea mays L. subsp. mays (USDA National Plant Germplasm System, PI 601009 11ncai01 SD)
5. Mo17, Zea mays L. subsp. mays (USDA National Plant Germplasm System, PI 558532 08ncai02 SD)
6. PHK76, Zea mays L. subsp. mays (USDA National Plant Germplasm System, PI 601496 07ncai01 SD)
7. Additional maize germplasms of interest
Reagents
1. DNeasy Plant Mini kit (Qiagen, catalog number: 69104)
2. SYBR Safe DNA gel stain (Invitrogen, catalog number: S33102); store at room temperature or 4 °C away from light
3. Agarose LE (molecular biology grade) (GoldBio, catalog number: A201100)
4. Tris base (GoldBio, catalog number: T-400-500)
5. Disodium EDTA (Invitrogen, catalog number: 15576-028)
6. Acetic acid, glacial (Supelco, catalog number: AX0073-9)
7. Restriction enzymes, as necessary (New England Biolabs Inc., various catalog numbers); store at -20 °C
8. Restriction enzyme buffers, as necessary (New England Biolabs Inc., various catalog numbers); store at -20 °C
9. Nuclease-free water (Promega, catalog number: MC1191)
10. GoTaq Green Master Mix (Promega, catalog number: M7122); store at -20 °C
11. GoTaq Colorless Master Mix (Promega, catalog number: M7132); store at -20 °C
12. Milli-Q water
Solutions
1. 5× TAE buffer (see Recipes)
2. 0.5× TAE (see Recipes)
3. SYBR Safe incubation solution (see Recipes)
Recipes
1. 5× TAE buffer
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| Milli-Q water | n/a | ~800 mL |
| Tris base | 200 mM | 24.22 g |
| Disodium EDTA | 5.5 mM | 1.86 g |
| Glacial acetic acid | 0.6% v/v | 6.05 mL |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | Up to 1 L |
| Total | n/a | 1 L |
Adjust pH to 8.3 using KOH or NaOH. Store at room temperature. Stable for up to one month.
2. 0.5× TAE
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| 5× TAE buffer | 10% v/v | 1 L |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | 9 L |
| Total | n/a | 10 L |
Store at room temperature. Stable for up to one month.
3. SYBR Safe incubation solution
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| SYBR Safe | 0.1% v/v | 10 μL |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | 100 mL |
Store away from light at room temperature. Prepare no more than 2 h ahead of use.
Laboratory supplies
1. Olympus 0.2 mL 8-strip PCR tubes, V-seal caps (Genesee Scientific, catalog number: 27-426)
2. 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tubes (Dot Scientific, catalog number: 509-FTG)
3. Universal fit tips, 1,000 μL (VWR, catalog number: 89425-636)
4. Universal fit tips, 200 μL (VWR, catalog number: 89140-896)
5. Universal fit tips, 10 μL (VWR, catalog number: 89425-654)
Equipment
1. Horizontal mini gel electrophoresis system (Fisherbrand, catalog number: 14-955-170)
2. T100 thermal cycler (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1861096)
3. ChemiDoc imaging system (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 12003153)
4. Precision balance (Mettler Toledo, catalog number: 30133525)
5. Micropipettes
Software and datasets
1. indCAPS (indy-caps) (http://indcaps.kieber.cloudapps.unc.edu/, 5/16/25)
2. NCBI BLAST (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi, 7/10/25)
3. MEGA11 (Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis, version 11) (https://www.megasoftware.net/, 11/4/25)
4. Tm for Oligos Calculator (https://www.promega.com/resources/tools/biomath/tm-calculator/)
5. Ensembl Plants (https://plants.ensembl.org/index.html, 7/10/25)
6. Genome assembly Zm-B73-REFERENCE-NAM-5.0 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/datasets/genome/GCF_902167145.1/)
7. Genome assembly Zm-LH195-Draft-G2F-1.0 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/datasets/genome/GCA_963693415.1/, 7/10/25)
8. Genome assembly Zm-Mo17-REFERENCE-CAU-T2T-assembly (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/datasets/genome/GCA_022117705.1/, 7/10/25)
9. Genome assembly Zm-LH244-REFERENCE-BAYER-1.0 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/datasets/genome/GCA_905067065.1/, 7/10/25)
10. Genome assembly Zm-PHZ51-Draft-G2F-1.0 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/datasets/genome/GCA_963555735.1/, 7/10/25)
11. Genome assembly Zm-PHN11-Draft-G2F-1.0 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/datasets/genome/GCA_963859685.1/, 7/10/25)
12. Genome data in MaizeGDB (https://www.maizegdb.org/genome#!, 7/10/25)
13. All data and code have been deposited to GitHub: https://github.com/jannisjacobs/CAPS-based-SNP-genotyping
Procedure
文章信息
稿件历史记录
提交日期: Oct 9, 2025
接收日期: Nov 18, 2025
在线发布日期: Nov 27, 2025
出版日期: Dec 20, 2025
版权信息
© 2025 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
如何引用
Jacobs, J., Newton, L., Gardener, B. M., Webster, B., Thompson, A., Grotewold, E. and Lundquist, P. K. (2025). CAPS-Based SNP Genotyping for Nitrogen-Response Phenotypes in Maize Hybrids. Bio-protocol 15(24): e5551. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5551.
分类
植物科学 > 植物分子生物学 > DNA > 基因分型
分子生物学 > DNA > 基因分型
植物科学 > 植物生理学 > 营养
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









