- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Ribozyme-Mediated Knockdown of lncRNA Gene Expression in Drosophila
利用核酶介导的方式降低果蝇中lncRNA基因的表达水平
发布: 2025年10月20日第15卷第20期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5477 浏览次数: 2128
评审: Jibin SadasivanAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are increasingly understood to play important roles in cell biology, development, and disease, though the vast majority of annotated lncRNAs have yet to be functionally characterized. Disrupting lncRNAs is often challenging owing to their tolerance for mutations (e.g., single-nucleotide polymorphisms and short indels) along with the limitations of other genetic knockdown strategies such as RNA interference (RNAi). Here, we describe a protocol to achieve robust knockdown of lncRNAs in the fruit fly Drosophila using a self-cleaving ribozyme. The 111-bp ribozyme cassette, which consists of the N79 hammerhead ribozyme flanked by flexible linker sequences, is inserted into transcript regions of lncRNA genes using CRISPR/Cas9-mediated homology-directed repair (HDR). The fluorescent eye transformation marker is then removed using a piggyBac transposase, leaving no other modifications at the lncRNA locus save the ribozyme cassette insertion. When transcribed as part of the lncRNA, the ribozyme folds and catalyzes its own self-cleavage, resulting in two RNA cleavage fragments. The efficacy of lncRNA knockdown is then evaluated using reverse transcription quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) and single-molecule RNA fluorescence in situ hybridization (smFISH). This approach has resulted in efficient knockdown of both nuclear and cytoplasmic lncRNAs in Drosophila, with knockdown of steady-state RNA levels in 3' cleavage fragments typically exceeding 90% and no evidence of off-target effects. The method can also be applied to protein-coding genes in order to knock down specific mRNA isoforms. Thus, self-cleaving ribozymes are a valuable addition to the genetic toolkit in Drosophila.
Key features
• The ribozyme has the potential to knock down any RNA but is particularly useful for long noncoding RNAs, which can be resistant to mutations.
• The ribozyme is useful for the knockdown of nuclear-localized RNAs as well as RNAs that overlap with other genes in the genome.
• Ribozyme knockdown is typically stronger than RNAi and occurs in every cell.
• Insertion of the ribozyme cassette in the 5' region of a transcript ensures that most of the transcript is degraded.
Keywords: Long noncoding RNA (长非编码RNA)Graphical overview
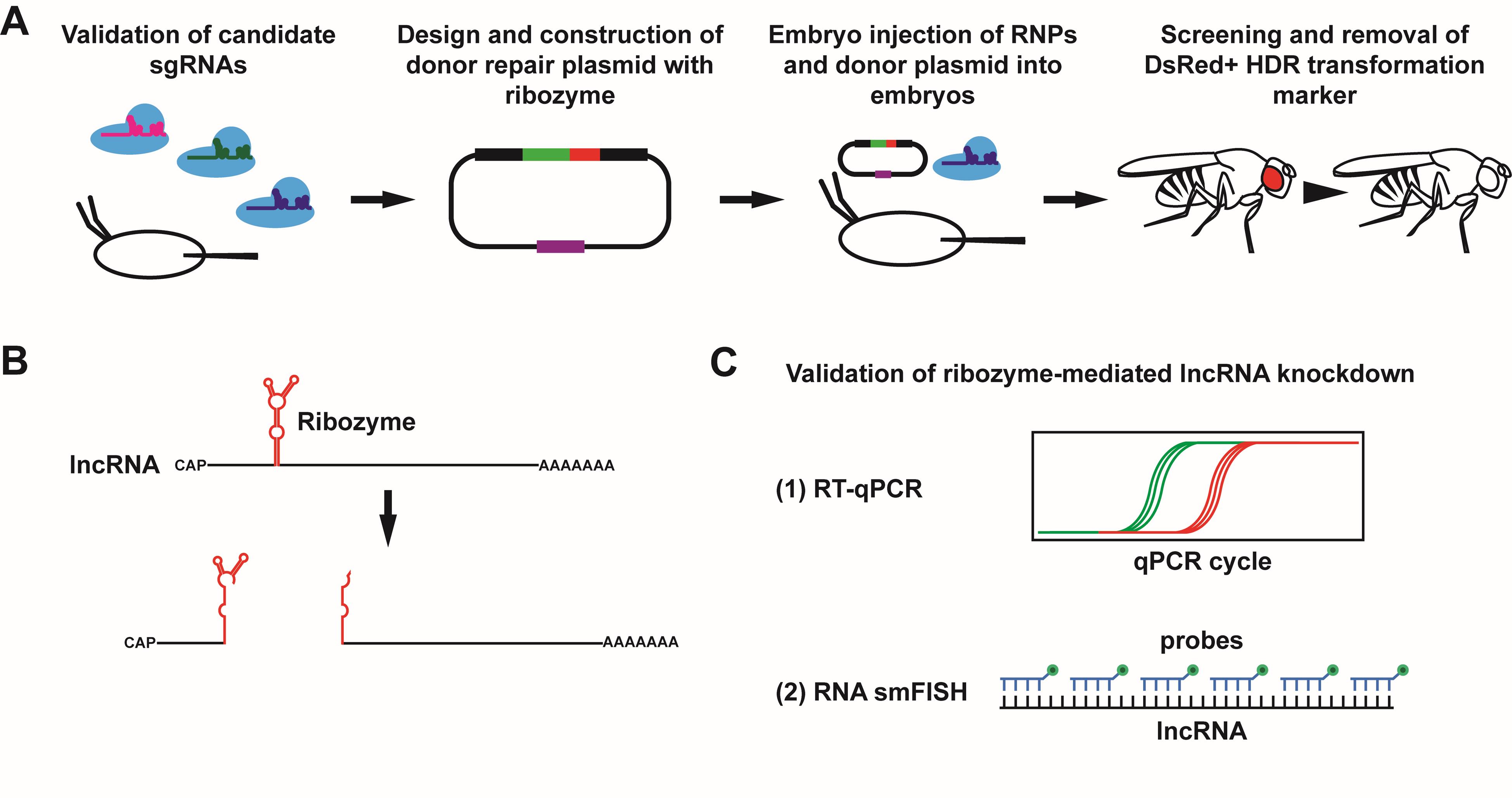
Overview of protocol to achieve and validate ribozyme-mediated knockdown of lncRNA gene expression in Drosophila. (A) To achieve knockdown of a target long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) using a self-cleaving ribozyme, the ribozyme cassette is integrated into the target lncRNA gene. Multiple candidate single-guide RNAs (sgRNAs) are first tested for cleavage efficiency in Drosophila embryos. Once a suitable sgRNA is identified, a donor repair plasmid is designed and constructed containing the ribozyme cassette, a selectable DsRed cassette, and two homology arms. See Figure 5 for a more detailed schematic of the donor repair plasmid. The Cas9/sgRNA RNPs and donor repair plasmid are then injected into Drosophila embryos to integrate the ribozyme cassette via homology-directed repair (HDR), and the progeny of injected flies are screened for the DsRed+ transformation marker. Once identified, the DsRed cassette is removed using a piggyBac transposase, resulting in the scarless insertion of the ribozyme cassette. (B) Upon transcription of the lncRNA, the ribozyme folds and cleaves itself, resulting in two RNA fragments with unprotected ends. (C) Successful knockdown of the lncRNA target can be validated using reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) and single-molecule RNA fluorescent in situ hybridization (RNA smFISH).
Background
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are RNA transcripts longer than 200 nucleotides that do not code for proteins. They are extensively transcribed in eukaryotic genomes and increasingly understood to play important roles in cell biology, development, and disease [1,2]. For example, the lncRNAs Xist [3,4] and roX [5–7] have been shown to play important roles in sex chromosome dosage compensation in mammals and Drosophila, respectively. The lncRNA Malat1 [8–10] has been implicated in tumorigenesis in various types of cancers. Despite striking examples such as these, however, relatively few of the thousands of annotated lncRNAs have been functionally characterized. In part, this is due to the inherent challenges in disrupting lncRNAs [11,12]. lncRNAs tend to be more tolerant of the types of mutations (i.e., single-nucleotide polymorphisms and short indels) that are often used to disrupt open reading frames in protein-coding genes. While large deletions of lncRNA genes are feasible, doing so may also remove DNA regulatory elements, leaving the interpretation of any resulting phenotypes murky. Further, many lncRNAs overlap with other genes in the genome, precluding their complete removal. Although RNA interference (RNAi) knockdown is feasible, RNAi has variable knockdown efficiency [13], is known to produce off-target effects [14,15], and, since the RNAi machinery is primarily localized to the cytoplasm, it may have limited efficacy against nuclear-localized lncRNAs.
Self-cleaving ribozymes have been used to achieve RNA knockdown in cis in mammalian cells [16–19], zebrafish [20], the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans [21], and Drosophila melanogaster [22,23], including knockdown of lncRNAs [16,17,23]. When inserted into a transcription unit within the genome, the ribozyme is transcribed along with its target gene, folds, and then cleaves itself, thus resulting, at the very least, in two RNA cleavage fragments. These cleavage fragments may then be susceptible to degradation by the endogenous exonucleases that attack unprotected RNAs. Because these self-cleaving ribozymes operate in cis, off-target effects are expected to be rare.
Here, we detail the protocol we used to knock down several lncRNAs in Drosophila using a self-cleaving ribozyme, as previously published [23]. We used a 111-bp ribozyme cassette that consists of the N79 hammerhead ribozyme [18], a variant engineered from the naturally occurring Sm1 hammerhead ribozyme found in the parasitic fluke Schistosoma mansoni. The ribozyme sequence is surrounded by flexible linker sequences to insulate it from surrounding RNA sequences when folding [24] (Figure 1). The N79 ribozyme cassette was then inserted into lncRNA transcription units within the Drosophila genome using CRISPR/Cas9-mediated homology-directed repair (HDR) from donor DNA as previously described [25–28]. In addition to the N79 ribozyme cassette, the donor DNA contains a selection marker (DsRed) for detection of integration events and a counterselection marker (eya RNAi) for detection of homologous integration events [27]. The selection marker is then precisely excised by PiggyBac transposition to yield a genome with only the N79 cassette inserted [25,28]. Using this method, we were able to achieve a strong knockdown in four lncRNAs, as verified with reverse transcription quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) and single-molecule RNA fluorescence in situ hybridization (RNA smFISH). These lncRNAs included both cytoplasmic and nuclear lncRNAs. RNA levels after ribozyme-mediated knockdown were typically diminished by 90% or more for the 3' cleavage fragments, higher than the knockdown typically achieved by RNAi [13]. However, knockdown of the 5' cleavage fragment was more variable. Further, we did not detect any off-target effects using ribozyme-mediated knockdown, even when inserted near essential protein-coding genes. Thus, self-cleaving ribozymes offer great potential for characterization of lncRNAs in eukaryotes and are a valuable addition to the genetic toolkit for Drosophila.
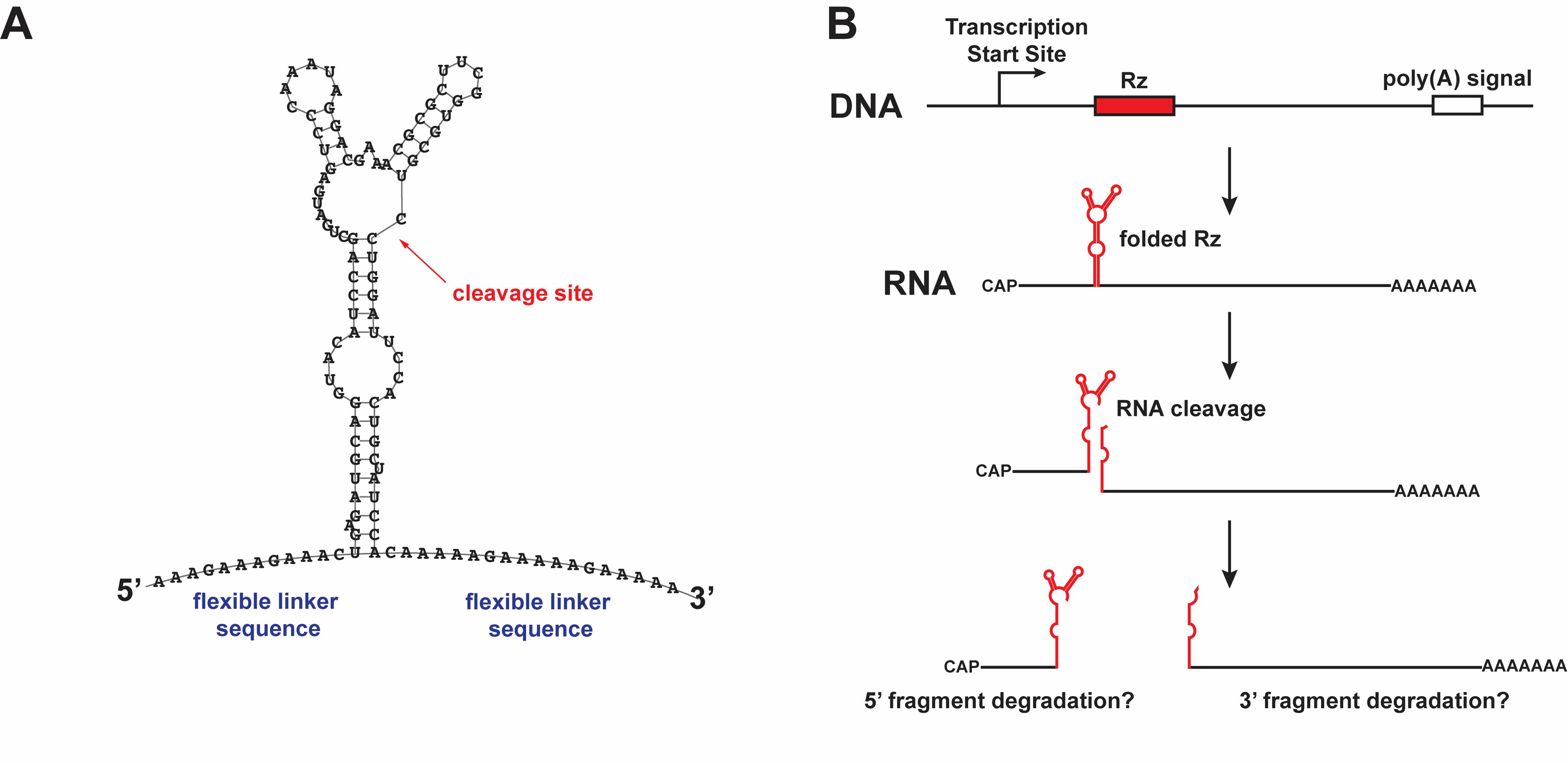
Figure 1. RNA knockdown using a self-cleaving ribozyme. (A) The sequence and predicted secondary structure of the N79 ribozyme cassette, as predicted by RNAfold [29], with the cleavage site indicated. (B) Model of ribozyme-mediated cleavage in cis, producing two cleavage fragments that may be susceptible to degradation by exonucleases. This figure is modified from Nyberg et al. [23] with permission from Oxford University Press (license 6070880155798).
Materials and reagents
Biological materials
1. Drosophila stock for CRISPR/Cas9 injections, preferably a stock with the white allele w[1118] (Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center, catalog number: 6326)
2. X chromosome Drosophila balancer stock (e.g., l(1)*[*], w[1118]/FM7c, Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center, catalog number: 7756)
3. 2nd chromosome Drosophila balancer stock (e.g., y[1] w[*]; nub[2] Adc[b-1] sna[Sco] pr[1] cn[1]/CyO, Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center, catalog number: 3628)
4. 3rd chromosome Drosophila balancer stock (e.g., y[1] w[*];; TM3, Sb[1]/TM6B, Tb[+], Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center, catalog number: 3720)
5. piggyBac transposase Drosophila stock w[1118]; Herm[3xP3-eCFP, alphatub-piggyBacK10]M6 (Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center, catalog number: 32070)
6. Electrocompetent DH5α E. coli (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 11319019)
Reagents
Chemicals
1. Nuclease-free water (100 mL) (New England Biolabs, catalog number: B1500L)
2. Agarose (100 g) (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 16500-100)
3. GreenGlo Safe DNA Dye (500 μL at 20,000× in water) (Thomas Scientific, catalog number: C788T73)
4. Tris base (1 kg) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP152-1, product format: resuspend in double-distilled water to 1 M, adjust pH to 8.0 or 7.4, and sterilize by autoclave)
5. Glacial acetic acid (2.5 L) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: A490-212)
6. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt dihydrate (EDTA) (500 g) (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: E5134-500G, product format: resuspend in double-distilled water to 0.5 M, adjust pH to 8.0, and sterilize by autoclave)
7. Absolute ethanol (200 proof) molecular biology grade (500 mL) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP2818500)
8. Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) (500 g) [Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP166-500, product format: resuspend in double-distilled water to 0.5% (w/v) in a spray bottle]
9. Sodium chloride (NaCl) (10 kg) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP358-10, product format: resuspend in double-distilled water to 5 M and sterilize by autoclave)
10. Bacto yeast extract (500 g) (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 212750)
11. Tryptone (500 g) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP1421-500)
12. Agar (80–100 mesh) (500 g) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP2641-500)
13. Carbenicillin, disodium salt (5 g) (Research Products International, catalog number: C46000-5.0, product format: resuspend to 100 mg/mL in double-distilled water and sterilize using a 0.2 μm filter with syringe)
14. Potassium chloride (KCl) (500 g) (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: P3911-500G, product format: resuspend to 2 M in double-distilled water and filter-sterilize)
15. Halocarbon oil 700 (50 mL) (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: H8898-50ML)
16. Halocarbon oil 27 (100 mL) (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: H8773-100ML)
17. Boric acid (1 kg) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP168-1)
18. Ethidium bromide (10 mL at 10 mg/mL) (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 15585011)
19. Isopropanol (1 L) (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 327270010)
20. Sodium acetate (NaOAc) (500 g) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: S210-500)
21. Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (50 mL) (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: D2438-50ML)
22. TRIzol reagent (100 mL) (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 15596026)
23. Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) (500 g) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: S233-500, product format: resuspend in double-distilled water to 1 M and adjust pH to 8.3)
24. Atto 633 NHS ester (1 mg) (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: 01464-1MG-F, product format: resuspend in DMSO to 33.4 mM)
25. Amino-11-ddUTP (200 nmol) (Lumiprobe, catalog number: A5040, product format: resuspend in nuclease-free water to 10 mM)
26. Triethylammonium acetate buffer (TEAA buffer) (250 mL at 1 M) (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: 69372-250ML, product format: dilute to 100 mM in double-distilled water and sterilize by filtering using a 500 mL 0.2 μm filter unit)
27. Acetonitrile, HPLC grade (1 L) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: A998SK-1)
28. Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (1 L at 10×) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP399-1, product format: dilute to 1× in double-distilled water)
29. Tween 20 (50 mL) (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: P9416-50ML)
30. Paraformaldehyde (500 g) (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: P6148-500G)
31. Diethyl pyrocarbonate (DEPC) (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: D5758-25ML)
32. Methanol (4 L) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: A412SK-4)
33. Saline sodium citrate (SSC) (500 mL at 20×) (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: AM9770)
34. Bovine serum albumin (BSA) (10 g) (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: A2153-10G, product format: resuspend to 100 mg/mL in nuclease-free water and store at -20 °C)
35. Dextran sulfate sodium salt (100 g) (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 433241000)
36. Salmon sperm DNA solution (5 × 1 mL, 10 mg/mL) (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 15632011)
37. Vanadyl ribonucleoside complexes (10 mL at 200 mM) (New England Biolabs, catalog number: S1402S)
38. DAPI [4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride, 2-(4-Amidinophenyl)-6-indolecarbamidine dihydrochloride] (5 mg) (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: D9542-5MG, product format: resuspend to 5 mg/mL in nuclease-free water for stock solution)
39. Vectashield Plus antifade mounting medium (10 mL) (Vector Laboratories, catalog number: H-1900-10)
Enzymes and enzyme kits
1. Phusion High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase (100 units at 2,000 units/mL) (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0530S)
2. MEGAscript T7 Transcription kit (40 reactions) (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: AM1334)
3. RiboLock RNase Inhibitor (2,500 units at 40 units/μL) (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: EO0381)
4. Alt-R S.p. Cas9 Nuclease V3 (500 μg at 10 μg/μL) (Integrated DNA Technologies, catalog number: 1081059)
5. Proteinase K (1 mL at 20 mg/mL) (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: EO0491)
6. Taq DNA polymerase (500 reactions) (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 10342020)
7. T7 Endonuclease I (1,250 units at 10,000 units/mL) (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0302L)
8. EcoRV-HF (4,000 units at 20,000 units/mL) (New England Biolabs, catalog number: R3195S)
8. NEBuilder HiFi DNA Assembly Master Mix (50 reactions) (New England Biolabs, catalog number: E2621L)
9. RQ1 RNase-free DNase (1,000 units at 1 unit/μL) (Promega, catalog number: M6101)
10. SuperScript III Reverse Transcriptase (50 reactions) (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 18080044)
11. RNaseOUT Ribonuclease Inhibitor (5,000 units at 40 units/μL) (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 10777019)
12. TB Green Premix Ex Taq II (Tli RNase H Plus), 1 × 5 mL (200 reactions) (Takara Bio USA, catalog number: RR820L)
13. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) (500 units at 20 units/μL) (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: EP0161)
Nucleic acids
1. Set of dATP, dCTP, dGTP, dTTP (40 μmol each at 100 mM) (Promega, catalog number: U1330)
2. pU6-BbsI-chiRNA plasmid (Addgene, catalog number: 45946)
3. Oligo primers for single-guide RNA (sgRNA) amplification (Integrated DNA Technologies, custom order, product format: resuspend to 100 μM in TE buffer for stock solution; dilute to 10 μM in nuclease-free water for working solution)
sgRNA_F: 5'-TTAATACGACTCACTATAGG[sgRNA_target_sequence_noPAM]GTTTTAGAGCTAGAAATAG-3'
sgRNA_R: 5'-AAAAGCACCGACTCGGTGCC-3'
4. 1 kb DNA ladder (200 gel lanes) (New England Biolabs, catalog number: N3232S)
5. 100 bp DNA ladder (100 gel lanes) (New England Biolabs, catalog number: N3231S)
6. pBS-GMR-eya(shRNA) plasmid (Addgene, catalog number: 157991)
7. pScarlessHD-DsRed plasmid (Addgene, catalog number: 64703)
8. Random oligo primers (Integrated DNA Technologies custom oligo 5’-N1-N1-N1-N1-N1-N1-N1-N1-N-3’ where N1 is hand-mixed ACGT at a ratio of 1:1:1:1 and where N is machine-mixed ACGT. Order 5 μmol and dissolve in double-distilled water to 500 μM. Dilute this stock to 50 μM and store as aliquots at -20 °C)
9. Anchored oligo(dT) primers (Integrated DNA Technologies custom oligo 5’-TTT TTT TTT TTT TTT TTT TTT TT-N2-N-3’ where N2 is hand-mixed ACGT at a ratio of 1:1:1:0 and where N is machine-mixed ACGT. Order 1 μmol and dissolve in double-distilled water to 50 μM. Store as aliquots at -20 °C)
Commercial clean-up kits
1. Monarch Spin PCR & DNA Cleanup kit (5 μg) (250 preps) (New England Biolabs, catalog number: T1130L)
2. Monarch Spin Plasmid Miniprep kit (250 preps) (New England Biolabs, catalog number: T1110L)
3. Monarch Spin RNA Cleanup kit (50 μg) (100 preps) (New England Biolabs, catalog number: T2040L)
4. Monarch Spin DNA Gel Extraction kit (50 preps) (New England Biolabs, catalog number: T1120S)
5. HiSpeed Plasmid Midi kit (25 preps) (Qiagen, catalog number: 12643)
6. EndoFree Plasmid Mega kit (5 preps) (Qiagen, catalog number: 12381)
7. Microspin G-25 columns (50 columns) (Cytiva, catalog number: 27532501)
Drosophila husbandry
1. Active dry yeast (2 lbs) (Genesee Scientific, catalog number: 62–103, product format: mix 7 g of yeast with 10 mL of deionized water in a 50 mL beaker and mix until it forms a paste with the consistency of peanut butter. Store covered with parafilm at 4 °C for up to a week, adding water or yeast as necessary to maintain consistency)
2. Molasses (1 gal) (Genesee Scientific, catalog number: 62-117)
3. Ethyl acetate (500 mL) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: E145-500)
4. Propionic acid (1 L) (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 149300010)
5. Tegosept (1 kg) [Genesee Scientific, catalog number: 20-258, product format: resuspend to 10.67% (w/v) by adding 16 g of Tegosept to 150 mL of 95% ethanol and store at room temperature]
Solutions
1. dNTP mix (see Recipes)
2. Tris-EDTA buffer (TE) (see Recipes)
3. 50× Tris-acetate-EDTA buffer (TAE) (see Recipes)
4. 5× Tris-borate-EDTA buffer (TBE) (see Recipes)
5. Luria broth (LB) (see Recipes)
6. Luria broth (LB) agar plates (see Recipes)
7. Embryo collection plates (see Recipes)
8. Halocarbon oil mix (see Recipes)
9. Squish buffer (see Recipes)
10. DEPC water (see Recipes)
11. PBT (see Recipes)
12. Paraformaldehyde (PFA) fixative (see Recipes)
13. RNA smFISH hybridization buffer (see Recipes)
14. RNA smFISH wash buffer (see Recipes)
Recipes
1. dNTP mix
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| dATP (100 mM) | 10 mM | 50 μL |
| dCTP (100 mM) | 10 mM | 50 μL |
| dGTP (100 mM) | 10 mM | 50 μL |
| dTTP (100 mM) | 10 mM | 50 μL |
| Nuclease-free water | 300 μL |
a. Thaw the individual dNTP stocks (100 mM each).
b. Briefly vortex them and spin them down.
c. Mix each dNTP as indicated below.
d. The dNTP mix can be stored at -20 °C.
2. Tris-EDTA buffer (TE)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| 1 M Tris pH 8.0 | 10 mM | 500 μL |
| 0.5 M EDTA | 1 mM | 100 μL |
| Double-distilled water | 49.4 mL |
a. Mix the individual stock solutions as indicated below.
b. Sterilize by filtering with a Steriflip vacuum filter unit.
c. Store at room temperature.
3. 50× Tris-acetate-EDTA buffer (TAE)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| Tris base (MW = 121.14 g/mol) | 2 M | 242 g |
| Glacial acetic acid | 1 M | 57.1 mL |
| 0.5 M EDTA | 50 mM | 100 mL |
| Double-distilled water | fill to 1,000 mL |
a. Mix the individual reagents as indicated below in ~650 mL of double-distilled water in a 1 L glass beaker with a stir bar until all reagents are in solution.
b. Bring volume up to 1,000 mL with double-distilled water and split between two 1 L glass bottles.
c. Sterilize by autoclave on a liquid cycle for at least 30 min.
d. Store at room temperature.
e. Dilute to 1× TAE in double-distilled water for standard agarose gel electrophoresis.
4. 5× Tris-borate-EDTA buffer (TBE)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| Tris base (MW = 121.14 g/mol) | 450 mM | 54.51 g |
| Boric acid (MW = 61.83 g/mol) | 450 mM | 27.82 g |
| 0.5 M EDTA | 10 mM | 20 mL |
| Double-distilled water | fill to 1,000 mL |
a. Mix the individual reagents as indicated below in ~700 mL of double-distilled water in a 1 L glass beaker with a stir bar until all reagents are in solution.
b. Bring volume up to 1,000 mL with double-distilled water and split between two 1 L glass bottles.
c. Sterilize by autoclave in a liquid cycle for at least 30 min.
d. Store at room temperature.
e. Dilute to 0.5× TBE in double-distilled water for agarose gel electrophoresis of T7EI digestion products.
5. Luria broth (LB)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| NaCl | 5 g/L | 5 g |
| Tryptone | 10 g/L | 10 g |
| Bacto yeast extract | 5 g/L | 5 g |
| Double-distilled water | fill to 1,000 mL |
a. Mix the individual reagents as indicated below in ~700 mL of double-distilled water in a 1 L glass beaker with a stir bar until all reagents are in solution.
b. Bring volume up to 1,000 mL with double-distilled water and split between two 1 L glass bottles.
c. Sterilize by autoclave on a liquid cycle for at least 30 min.
d. Store LB without antibiotics at room temperature.
e. Add appropriate antibiotic (e.g., carbenicillin at a final concentration of 100 μg/mL) after LB is cooled down.
f. Store LB with antibiotics at 4 °C for up to 1 month.
6. Luria broth (LB) agar plates
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| NaCl | 5 g/L | 5 g |
| Tryptone | 10 g/L | 10 g |
| Bacto yeast extract | 5 g/L | 5 g |
| Double-distilled water | fill to 1,000 mL | |
| Agar | 15 g/L | 15 g |
a. Mix the individual reagents as indicated in ~700 mL of double-distilled water in a 2 L Erlenmeyer flask with a stir bar until all reagents are in solution.
b. Bring volume up to 1,000 mL with double-distilled water. Add agar, which will not go into solution until after autoclave sterilization.
c. Sterilize by autoclave on a liquid cycle for at least 30 min, leaving the stir bar in the flask.
d. Allow to cool to ~50 °C. Add appropriate antibiotics (e.g., carbenicillin at a final concentration of 100 μg/mL) and stir for 5 min.
e. Promptly pour the liquid mixture into 100 mm bacteriological Petri dishes with sterile technique and allow to cool at room temperature.
f. Once solidified, store LB agar plates with antibiotics at 4 °C for up to 1 month.
7. Embryo collection plates
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| Agar | 33.4 g/L | 22 g |
| Molasses | 13.7% (v/v) | 90 mL |
| Double-distilled water | 560 mL | |
| Ethyl acetate | 0.76% (v/v) | 5 mL |
| Propionic acid | 0.49% (v/v) | 3.2 mL |
| 10.67% (w/v) Tegosept solution | 0.20% (w/v) | 125 μL |
a. Mix agar, molasses, and water in a 2 L Erlenmeyer flask with a stir bar.
b. Agar will not go into solution until after autoclave sterilization.
c. Sterilize by autoclave on a liquid cycle for at least 30 min., leaving the stir bar in the flask.
d. After autoclaving, stir on a stir plate until the temperature cools to ~50 °C. Add the three inhibitors (ethyl acetate, propionic acid, and Tegosept) and stir for 5 min.
e. Promptly pour liquid mixture into 60 mm disposable Petri dishes. Do not flame the lip of the flask when pouring plates, as the mixture is flammable.
f. Allow plates to cool at room temperature overnight so that condensation evaporates.
g. Store embryo collection plates at 4 °C for up to 3 months.
8. Halocarbon oil mix
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| Halocarbon oil 700 | 75% (v/v) | 6 mL |
| Halocarbon oil 27 | 25% (v/v) | 2 mL |
a. Mix reagents as indicated below in a 15 mL conical tube.
b. Allow to mix thoroughly on a nutator.
c. Store at room temperature.
9. Squish buffer
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| 1 M Tris pH 8.0 | 10 mM | 500 μL |
| 5 M NaCl | 25 mM | 250 μL |
| 0.5 M EDTA | 1 mM | 100 μL |
| Double-distilled water | fill to 49.5 mL | |
| Proteinase K (20 mg/mL) | 0.2 mg/mL | 1 μL per 100 μL squish buffer |
a. Mix Tris, NaCl, EDTA, and water in a 50 mL conical tube.
b. Sterilize by filtering with a Steriflip vacuum filter unit.
c. Store this squish buffer without Proteinase K at room temperature.
d. Immediately before use, add 1 μL of Proteinase K (20 mg/mL) to 99 μL of squish buffer, scaling up or down as needed.
e. Add squish buffer (with Proteinase K) directly to samples.
10. DEPC water
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| Diethyl pyrocarbonate (DEPC) | 0.1% (v/v) | 1 mL |
| Double-distilled water | 1 L |
a. Add DEPC directly to double-distilled water.
b. Invert several times to mix and let it sit overnight.
c. Autoclave on a liquid cycle for at least 30 min to sterilize and decompose the DEPC.
d. Store at room temperature.
11. PBT
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| PBS, 10× | 1× | 5 mL |
| Tween 20 | 0.1% (v/v) | 50 μL |
| DEPC water | 45 mL |
a. Add 10× PBS, DEPC water, and Tween 20 to a 50 mL conical tube.
b. Vortex briefly and rock on a nutator for at least 20 min.
c. Store at room temperature.
12. Paraformaldehyde (PFA) fixative
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| PBS, 10× | 1× | 1 mL |
| DEPC water | 9 mL | |
| Paraformaldehyde | 4% (w/v) | 0.4 g |
| Tween 20 | 0.1% (v/v) | 10 μL |
a. Add 10× PBS and DEPC water to a 50 mL glass beaker.
b. Swirl briefly and then microwave for 10 s.
c. Using gloves, add a stir bar and then stir on a heated stir plate (~70 °C) in a chemical fume hood.
d. Add paraformaldehyde and stir until it goes into solution.
e. Transfer to a 15 mL conical tube and replace any volume that has evaporated with fresh DEPC water to 10 mL.
f. Add Tween 20, vortex briefly, and rock on a nutator for 20 min.
g. Store at room temperature until use. Prepare fresh daily.
13. RNA smFISH hybridization buffer
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| Dextran sulfate | 10% (w/v) | 0.5 g |
| Nuclease-free water | 3.8 mL | |
| BSA (100 mg/mL) | 0.2 mg/mL | 10 μL |
| Salmon sperm DNA solution (10 mg/mL) | 0.1 mg/mL | 50 μL |
| Vanadyl ribonucleoside complexes (200 mM) | 2 mM | 50 μL |
| Tween 20 | 0.1% | 5 μL |
a. Add dextran sulfate to nuclease-free water in a 15 mL conical tube and vortex vigorously until dextran sulfate is in solution.
b. Add BSA, salmon sperm solution, vanadyl ribonucleoside complexes, and Tween 20, and vortex.
c. Store at 4 °C shielded from light for up to a year.
14. RNA smFISH wash buffer
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| Saline sodium citrate (SSC) (20×) | 4× | 10 mL |
| Tween 20 | 0.1% | 50 μL |
| DEPC water | 40 mL |
a. Add 20× SSC, DEPC water, and Tween 20 to a 50 mL conical tube.
b. Vortex briefly and rock on a nutator for at least 20 min.
c. Store at room temperature.
Laboratory supplies
1. 1.5 mL low retention microcentrifuge tubes (nuclease-free) (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 3451)
2. 0.2 mL PCR 8-tube strips (USA Scientific, catalog number: 1402-2900)
3. 1,250 μL low retention universal pipette tips (VWR, catalog number: 76323-456)
4. 200 μL low retention universal pipette tips (VWR, catalog number: 76323-390)
5. 10 μL low retention universal pipette tips (VWR, catalog number: 76323-394)
6. 1,250 μL SHARP low retention barrier pipette tips (nuclease-free) (Thomas Scientific, catalog number: 1159M42)
7. 200 μL SHARP low retention barrier pipette tips (nuclease-free) (Thomas Scientific, catalog number: 1159M40)
8. 20 μL SHARP low retention barrier pipette tips (nuclease-free) (Thomas Scientific, catalog number: 1159M43)
9. 10 μL SHARP low retention barrier pipette tips (nuclease-free) (Thomas Scientific, catalog number: 1159M41)
10. 5 mL disposable polystyrene serological pipettes (Corning, catalog number: 4487)
11. 10 mL disposable polystyrene serological pipettes (Corning, catalog number: 4488)
12. 25 mL disposable polystyrene serological pipettes (Corning, catalog number: 4489)
13. 50 mL disposable polystyrene serological pipettes (Greiner, catalog number: 768180)
14. 100 mm × 15 mm bacteriological Petri dishes (Falcon, catalog number: 351029)
15. 60 mm × 15 mm disposable Petri dishes (for embryo collection plates) (VWR, catalog number: 25384-328)
16. 100 mL Tri-Pour graduated disposable beakers (for embryo collection cages) (United States Plastic Corp., catalog number: 76076, product format: poke small holes in the top of the cage to allow air flow)
17. Microloader pipette tips (Eppendorf, catalog number: 930001007)
18. 18 mm × 18 mm micro cover glass (VWR, catalog number: 48366-045)
19. Frosted microscope slides, 75 mm × 25 mm (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 12-544-2)
20. Borosilicate capillary glass with filament (outer diameter = 1.0 mm, inner diameter = 0.5 mm, length = 10 cm, for microinjection needles) (Sutter Instrument, catalog number: BF100-50-10)
21. Masterstroke finest red sable paint brush, round, size 0 (Blick Art Materials, catalog number: 05457-1100)
22. Hypodermic needle, 26 gauge, 5/8 in. (Becton Dickinson, catalog number: 305115)
23. Razor blade, 0.22 mm (VWR, catalog number: 55411-050)
24. 50 mL polypropylene conical centrifuge tubes (Falcon, catalog number: 352098)
25. 15 mL polypropylene conical centrifuge tubes (Falcon, catalog number: 352099)
26. Kimwipes, 8.2 in. × 4.4 in. (Kimberly-Clark Professional, catalog number: 34120)
27. Saran wrap
28. RNase-free disposable pellet pestle (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 12-141-364)
29. MicroAmp EnduraPlate optical 96-well clear reaction plate (for qPCR) (Applied Biosystems, catalog number: A36924)
30. MicroAmp optical adhesive film (for qPCR) (Applied Biosystems, catalog number: 4311971)
31. High performance cover glass, No. 1.5H, 22 mm × 22 mm (Zeiss, catalog number: 474030-9020-000)
32. Clear nail polish (Sally Hansen, catalog number: 45083)
33. Steriflip 0.22 μm vacuum filter unit, 50 mL (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: SCGP00525)
34. Disposable 0.2 μm filter unit, 500 mL (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: FB12566504)
35. Syringe filter, 0.2 μm (50 filters) (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 725-2520)
36. Syringe, 20 mL (50 syringes) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 14-817-111)
37. Magnetic stir bar kit (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 14-513-82)
Equipment
General molecular biology
1. Thermocycler (Bio-Rad, model: T100)
2. Pipetman 4-pipet kit (P2, P20, P200, P1000) (Gilson, catalog number: F167360)
3. Owl EasyCast B2 mini gel electrophoresis system (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: B2-BP)
4. Owl compact power supply (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: EC300XL)
5. Ultraviolet gel imaging system (Azure Biosystems, model: c600)
6. Vortex mixer (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 02-215-414)
7. Electronic controller for serological pipets (Gilson, catalog number: F110120)
8. MyFuge mini centrifuge (Braintree Scientific, catalog number: C1008)
9. Centrifuge with 24 × 2 mL rotor (Eppendorf, model: 5425, catalog number: 5405000441)
10. Refrigerated centrifuge with 24 × 2 mL rotor (Eppendorf, model: 5425R, catalog number: 5406000445)
11. NanoDrop Ultra UV-Vis spectrophotometer (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: NDULTRAGL)
12. Qubit 4 fluorometer (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: Q33238)
13. Heat block (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 88-860-022)
14. Gene Pulser Xcell Microbial System (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1652662)
15. Shaking incubator for microbiology (37 °C) (New Brunswick Scientific, model: Innova43)
16. Autoclave (Spire Integrated Solutions, model: PRIMUS)
17. Microwave (Sharp, model: SMC1441CW)
18. Magnetic hot/stir plate (VWR, catalog number: 76447-044)
19. Nalgene autoclave pan (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 6900-0020)
20. 1 L PYREX glass beaker (Corning, catalog number: 10031L)
21. 50 mL glass beaker (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: FB10050)
22. 2 L PYREX glass Erlenmeyer flask (Corning, catalog number: 49802L)
23. 1 L Wheaton glass bottle (DWK Life Sciences, catalog number: 219760)
24. Refrigerator (4 °C)
25. Freezer (-20 °C)
26. Ultra-low temperature freezer (-80 °C)
Drosophila husbandry
1. Stereomicroscope (Zeiss, model: Stemi 508)
2. Dual gooseneck fiber-optic illuminator (AmScope, catalog number: HL150-AY)
3. Drosophila anesthesia system (Genesee Scientific, catalog number: 59-122BC)
4. NightSea full system with royal blue illumination (Electron Microscopy Sciences, catalog number: SFA-RB)
5. NightSea add-on light and filter set, violet (Electron Microscopy Sciences, catalog number: SFA-LFS-VI)
6. NightSea add-on light and filter set, green (Electron Microscopy Sciences, catalog number: SFA-LFS-GR)
7. Drosophila incubator (Genesee Scientific, catalog number: 59-407L)
Embryo injections
1. Inverted phase contrast microscope (for microinjections) (Nikon, model: TMS)
2. Femtojet 4i microinjector (Calibre Scientific, catalog number: EPE-5252000021)
3. Mechanical micromanipulator (Leica, model: Micromanipulator)
4. Micropipette grinder (Narishige, model: EG-40)
5. Micropipette puller (Sutter Instrument, model: P-97)
RT-qPCR
1. Plate centrifuge (Eppendorf, model: 5810)
2. Real-time PCR system (Applied Biosystems, model: QuantStudio 3)
RNA smFISH
1. ZORBAX Eclipse Plus C18 Reverse Phase HPLC column (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: 959961-902)
2. High-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) system (Agilent Technologies, model: 1100)
3. Savant SpeedVac DNA 130 system (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: DNA130-115)
4. ProBlot 12 hybridization oven (Labnet, catalog number: H1200A)
5. Nutating mixer (Corning, catalog number: 6720)
6. Laser scanning confocal microscope (Leica Microsystems, model: SP8)
Software and datasets
1. FlyBase (https://flybase.org)
2. flyCRISPR Optimal Target Finder (https://flycrispr.org/target-finder/)
3. Benchling (https://www.benchling.com)
4. NEBuilder Assembly Tool (https://nebuilder.neb.com/)
5. Primer3Plus (https://www.primer3plus.com)
6. Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT) OligoAnalyzer Tool (https://www.idtdna.com/calc/analyzer)
Procedure
文章信息
稿件历史记录
提交日期: Jul 22, 2025
接收日期: Sep 9, 2025
在线发布日期: Sep 22, 2025
出版日期: Oct 20, 2025
版权信息
© 2025 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
如何引用
Nyberg, K. G. and Carthew, R. W. (2025). Ribozyme-Mediated Knockdown of lncRNA Gene Expression in Drosophila. Bio-protocol 15(20): e5477. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5477.
分类
分子生物学 > RNA > RNA 干扰
发育生物学 > 基因组编辑
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link












