- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Effective Gene Silencing in Plants by Synthetic Trans-Acting siRNAs Derived From Minimal Precursors
利用来源于最小前体的合成反式siRNA实现植物中高效的基因沉默
发布: 2025年10月20日第15卷第20期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5475 浏览次数: 1813
评审: Diarmuid Seosamh Ó’MaoiléidighAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Synthetic trans-acting small interfering RNAs (syn-tasiRNAs) are 21-nucleotide small RNAs designed to induce highly specific and efficient gene silencing in plants. Traditional approaches rely on the transgenic expression of ~1 kb TAS precursors, which limits their use in non-model species, under strict GMO regulations, and in size-constrained expression or delivery systems. This protocol describes a rapid workflow for the design, assembly, and delivery of syn-tasiRNAs derived from much shorter precursors, referred to as minimal precursors. The pipeline includes in silico design of highly specific syn-tasiRNA sequences, cloning of minimal precursors into plant expression or potato virus X (PVX)-based viral vectors through Golden Gate or Gibson assembly, and delivery to plants through Agrobacterium-mediated expression or by spraying crude extracts containing recombinant PVX expressing the minimal precursors. These methodologies make syn-tasiRNA-based tools more accessible and broadly applicable for plant research and biotechnology across diverse species and experimental contexts.
Key features
• Syn-tasiRNAs allow the simultaneous silencing of multiple genes with high specificity, as they are computationally designed to avoid off-target effects.
• This protocol describes the design and obtention of syn-tasiRNAs for the simultaneous silencing of one or several endogenous genes in any plant species.
• This protocol also describes a non-transgenic alternative for applying syn-tasiRNAs to plants using a viral vector to induce whole-plant gene silencing.
• This protocol can also be applied to induce antiviral protection against pathogenic viruses, reducing viral mutational escapes when expressing multiple syn-tasiRNAs targeting different viral sites.
Keywords: Plant gene silencing (植物基因沉默)Graphical overview
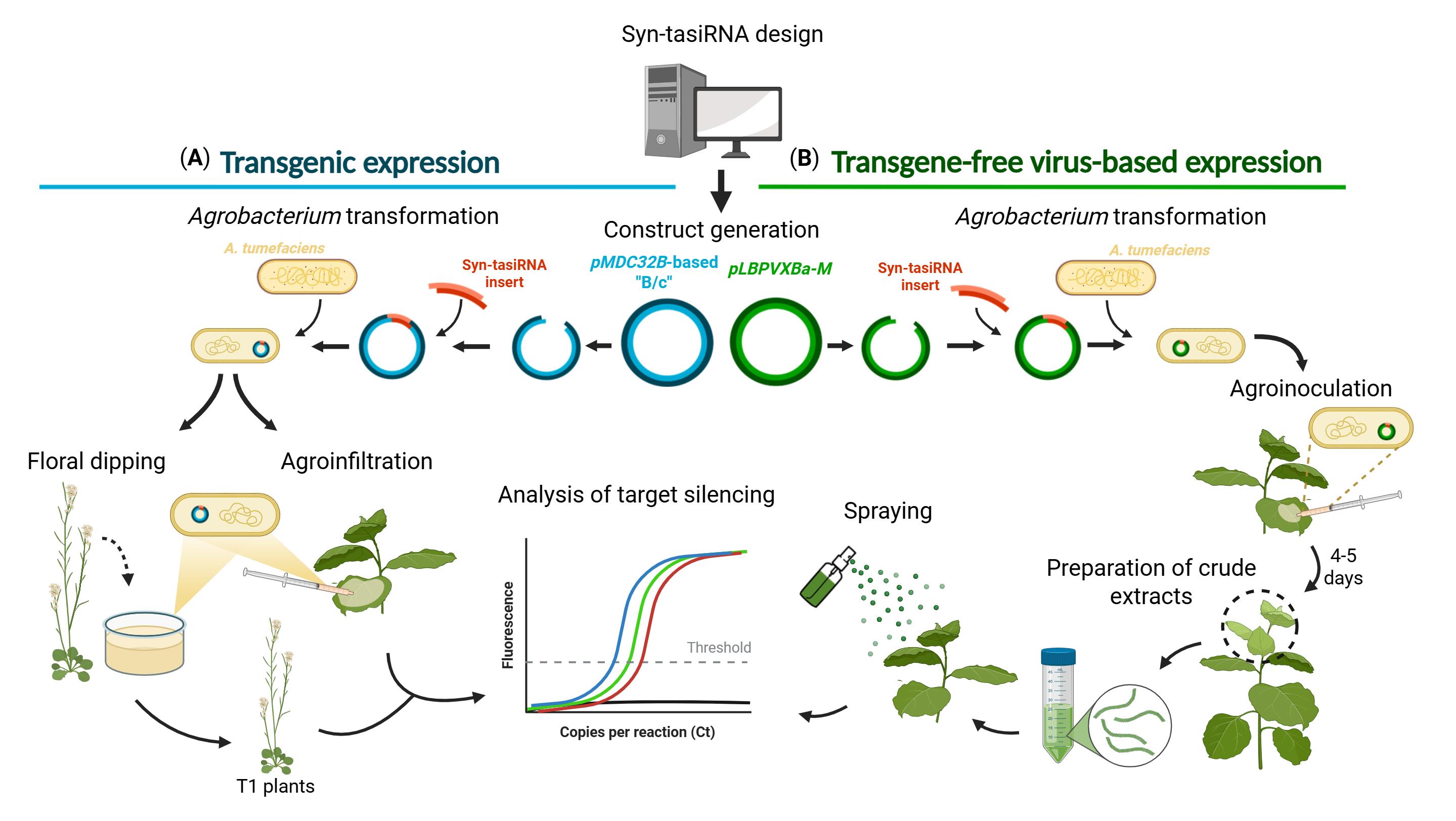
Steps to generate and apply synthetic trans-acting small interfering RNA (syn-tasiRNA) minimal precursors for either transgenic or transgene-free virus-based expression in plants. The protocol begins with the computational design of syn-tasiRNAs, followed by the generation of the corresponding expression constructs, and concludes with the evaluation of silencing efficacy by real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) quantification of target mRNA levels. (A) For transgenic expression, the syn-tasiRNA insert is cloned into a pMDC32B-B/c-based vector and transformed into Agrobacterium tumefaciens for either stable or transient expression. (B) For transgene-free, virus-based expression, the syn-tasiRNA insert is cloned into a Potato virus X (PVX)-based vector and transformed into A. tumefaciens for leaf agroinoculation. Once systemic PVX infection is established, upper leaves are collected and homogenized to produce a crude extract, which is then sprayed into a new set of plants to induce whole-plant gene silencing.
Background
RNA interference (RNAi) is a regulatory mechanism involved in multiple plant biological processes such as stress responses, development, defense, or reproduction [1]. RNAi is characterized by the sequence-specific degradation of RNA molecules mediated by complementary small RNAs (sRNAs). These sRNAs are generated from double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) precursors processed by DICER-Like (DCL) ribonucleases into 20–24 base pair (bp) duplexes. One strand of the duplex is then loaded into an ARGONAUTE (AGO) protein, which guides the complex to sequence-complementary target RNAs, leading to their degradation or translational repression [2]. Initially, several classic RNAi-based tools using long dsRNAs were developed for targeted gene silencing in plants. Although widely used, these strategies lacked high specificity, as DCL-mediated processing of long dsRNAs generates a heterogeneous population of sRNAs that can unintentionally target nonspecific transcripts. To overcome this limitation, a second generation of more specific silencing tools based on 21-nucleotide (nt) artificial sRNAs (art-sRNAs) was developed. Current bioinformatic tools typically design multiple art-sRNA sequences based on the target region and off-target probability, increasing specificity over previous silencing techniques but without completely eliminating off-target risks [3].
Synthetic trans-acting small interfering RNAs (syn-tasiRNAs) are a class of art-sRNAs generated from modified TAS transcripts, in which the endogenous tasiRNA sequences are substituted by the designed syn-tasiRNAs. Upon transcription, the modified TAS transcript is recognized and cleaved by a miRNA-AGO complex containing a 22-nt endogenous microRNA (miRNA), a critical step that initiates the phase processing and release of the syn-tasiRNAs from the cleaved fragment (Figure 1). Importantly, a single modified TAS transcript can produce one or several syn-tasiRNAs, allowing for the simultaneous silencing of multiple genes. Syn-tasiRNAs are typically expressed in plants through Agrobacterium tumefaciens–mediated transformation, leading to the generation of transgenic plants, limiting their applications in non-model species or under strict GMO regulations. Furthermore, the considerable size of conventional TAS precursors (900–1,000 nt) greatly hampers the use of alternative expression systems like viral vectors.
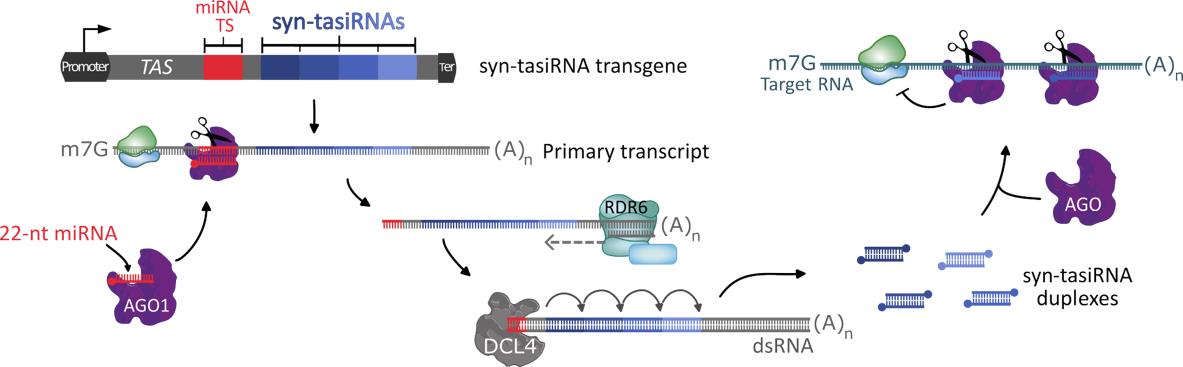
Figure 1. Synthetic trans-acting small interfering RNA (syn-tasiRNA) pathway. One or several syn-tasiRNAs are inserted in tandem, replacing the original tasiRNA sequences in a TAS precursor. After transcription, the primary transcript is targeted and cleaved by a 22 nucleotide (nt) microRNA (miRNA)–ARGONAUTE1 (AGO1) complex. The RNA-DEPENDENT RNA POLYMERASE 6 (RDR6) synthesizes a double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) from the sliced product, which is then cleaved every 21 nt by DICER LIKE 4 (DCL4), releasing syn-tasiRNA duplexes. Finally, one strand of the duplex is loaded into an AGO protein to silence target RNAs. Ter: terminator. miRNA TS: microRNA target site.
Very recently, a minimal syn-tasiRNA precursor of only 54 nt was developed and proved to be as efficient and accurately processed as canonical TAS precursors [4]. This minimal precursor consists of 22-nt from the miRNA target site (TS), an 11-nt spacer, and 21-nt of the syn-tasiRNA, with the possibility of multiplexing if desired (Figure 2). The initial version incorporated AtmiR137a TS for use in Arabidopsis thaliana (Arabidopsis), followed by a second variant containing the NbmiR482a TS for Nicotiana benthamiana applications (Figure 2). The minimal precursor design enhances cost-efficiency in both in vitro and in vivo production systems for topical delivery applications. Additionally, miRNA TS swapping facilitates adaptation across species, particularly in those expressing an abundant 22-nt miRNA trigger. Importantly, the compact size of the minimal precursor allows its expression from size-restricted systems, such as RNA-based viral vectors, which can only be applied in host species. Furthermore, this approach allows the non-transgenic systemic expression of syn-tasiRNAs following topical application [4]. This protocol describes the steps for the in silico design of highly specific syn-tasiRNAs, the generation of minimal syn-tasiRNA precursors containing either AtmiR137a or NbmiR482aTS, or a customizable TS. Two different application strategies are proposed: i) transgenic expression through genetic transformation, and ii) a transgene-free method based on the exogenous application of Potato virus X (PVX)-based vectors carrying the minimal precursor.
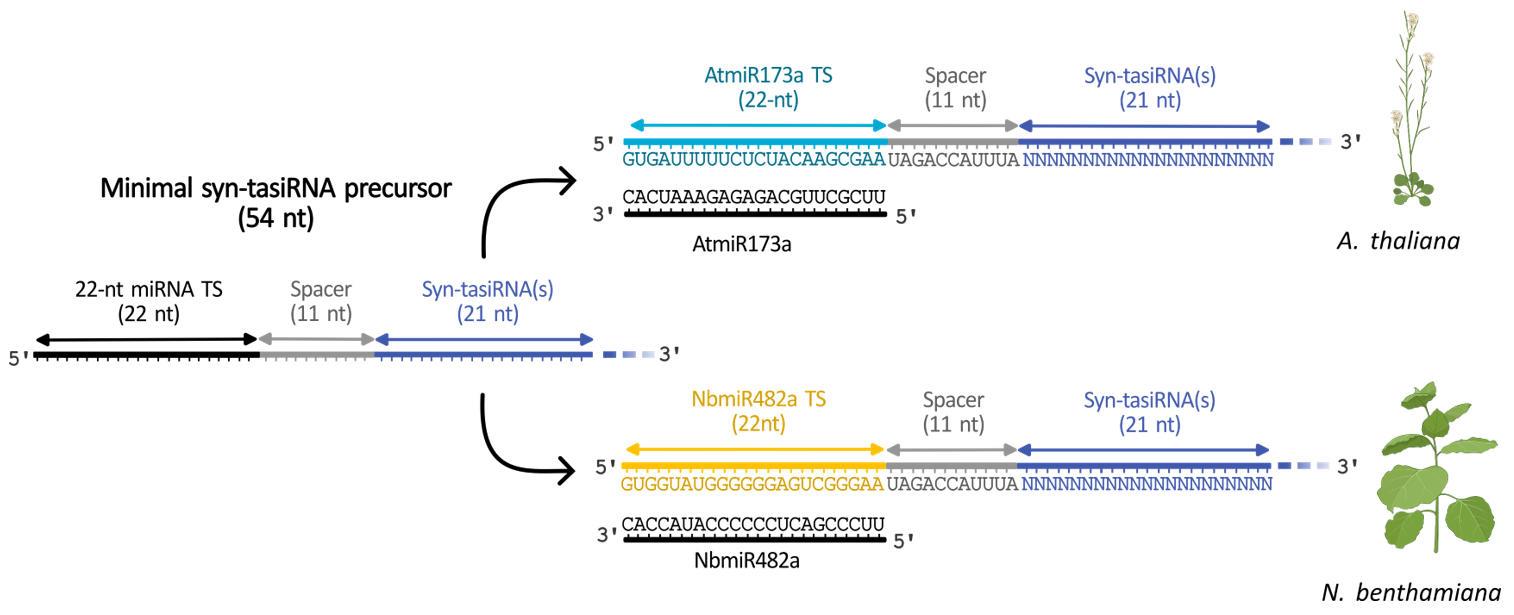
Figure 2. Structure of a minimal synthetic trans-acting small interfering RNA (syn-tasiRNA) precursor. The minimal syn-tasiRNA precursor consists of a 22-nucleotide (nt) microRNA target site (miRNA TS), an 11-nt spacer, and a 21-nt syn-tasiRNA sequence. In this example, the precursor expresses a single syn-tasiRNA, but it can be multiplexed to express several syn-tasiRNAs simultaneously. (Top) Minimal precursor containing AtmiR173a TS used to express syn-tasiRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana and closely related species. (Bottom) Minimal precursor containing NbmiR482a TS used to express syn-tasiRNAs in Nicotiana benthamiana.
Materials and reagents
Biological materials
1. pMDC32B-AtmiR173aTS-B/c (plasmid #227965 Addgene Watertown, MA, USA)
2. pMDC32B-NbmiR482aTS-B/c (plasmid #227967; Addgene Watertown, MA, USA)
3. pMDC32B-B/c (plasmid #227963; Addgene Watertown, MA, USA)
4. pLBPVXBa-M (plasmid #229079; Addgene Watertown, MA, USA)
5. Electrocompetent cells of Escherichia coli ccdB-sensitive strain DH5α (homemade, 1 × 106 CFU/μg DNA, see Protocol S1 for details)
6. Electrocompetent cells of Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain GV3101 (homemade, 6 × 106 CFU/μg DNA, see Protocol S2 for details)
Reagents
1. Liquid nitrogen
2. Sterile Milli-Q water
3. Peat (Kekkilä profesional)
4. Perlite (Projar)
5. GeneArtTM Gibson Assembly HiFi Master Mix (Invitrogen, catalog number: A46627)
Note: Store at -20 °C, shelf life 1.5 years.
6. T4 DNA ligase (5 U/μL) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: EL0011)
Note: Store at -20 °C, shelf life 2 years.
7. Zymo-Spin I columns (Zymo Research, catalog number: C1003-250)
8. GeneJET Plasmid Miniprep kit (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: K0481)
9. Kanamycin monosulfate (Duchefa Biochemie, catalog number: K0126.0005)
Note: Store at RT, shelf life 5 years.
10. Rifampicin (Duchefa Biochemie, catalog number: R0146.0005)
Note: Store at 2–8 °C, light-sensitive, shelf life 4 years.
11. Agarose (Pronadisa, catalog number: 8016)
12. Red Safe (iNtRON Biotechnology, catalog number: 21141)
13. Agar (INtRON biotechnology, catalog number: 25999)
14. Yeast extract (INtRON biotechnology, catalog number: 48045)
15. Tryptone (INtRON biotechnology, catalog number: 46046)
16. BsaI (10 U/μL, New England Biolabs, catalog number: R3733S)
Note: Store at -20 °C, shelf life 2 years.
17. MluI (10 U/μL) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: ER0561)
Note: Store at -20 °C, shelf life 2 years.
18. Dithiothreitol (DTT) (from SuperScriptTM IV kit, Invitrogen, catalog number: 18091050)
Note: Store at -20 °C, shelf life 2 years.
19. NaCl (ITW Reagents, catalog number: 131659.1211)
20. MgCl2 (Vidra FOC, catalog number: 131396)
21. CaCl2 (PanReac, catalog number: 131232)
22. Na2HPO4 (PanReac, catalog number: 131678)
23. KH2PO4 (PanReac, catalog number: 121509)
24. NH4Cl (PanReac, catalog number: 131121)
25. MgSO4 (PanReac, catalog number: 127113)
26. KCl (PanReac, catalog number: A2939)
27. HCl (PanReac, catalog number: 131020)
28. KOH (PanReac, AppliChem, catalog number: 121515.1211)
29. NaOH (PanReac, catalog number: 131687.1211)
30. Acetosyringone (3’,5’-dimethoxy-4’-hydroxy-acetophenone) (Aldrich, catalog number: D13,440-6)
Note: Store at RT, shelf life 2 years.
31. Tris (ITW reagents, catalog number: A1086,1000)
32. EDTA (Sigma, catalog number: E5134-500)
33. Acetic acid glacial (PanReac, catalog number: 131008.1611)
34. Glucose (D-glucose) (Duchefa, catalog number: D0802)
35. Sucrose crystallized (Duchefa Biochemie, catalog number: S0809.1000)
36. 6-benzylaminopurine (BAP) (Duchefa Biochemie, catalog number: B0904.0001)
37. MES (Duchefa, catalog number: M1503)
38. Silwet L-77 (BioWorld, catalog number: 30630216-1)
39. Polyvinylpyrrolidone 10 (PVP) (PanReac AppliChem, catalog number: A2258,0250)
40. Polyethylene glycol 6000 (PEG) (Merck, catalog number: 81260-1KG)
41. 2-mercaptoethanol 14.3 M (BME) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M6250)
Note: Store at 2–8 °C, light-sensitive, shelf life 3 years.
42. Dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) (Sigma, catalog number: D8418-100 mL)
Note: Store at RT, shelf life 2 years.
43. Sodium acetate (3H2O) (PanReac AppliChem, catalog number: 131632.1211)
44. Guanidine thiocyanate (PanReac, catalog number: A4335,1000)
45. Ammonium thiocyanate (PanReac, catalog number: 131143.1210)
46. Glycerol 87% (PanReac AppliChem, catalog number: 122329.1211)
47. Phenol 90% (Scharlab, catalog number: FE04791000)
Note: Store at 4 °C; light-sensitive; shelf life 1 year.
48. Chloroform (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 10071970)
Note: Light-sensitive, shelf life 3 years.
49. Isopropanol (PanReac AppliChem, catalog number: 1.310.901.214)
50. Ethanol 96% (PanReac AppliChem, catalog number: 141085.1214)
51. TURBO DNA-Free kit (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: AM1907)
Note: Store at -20 °C.
52. PrimeScript RT Reagent kit (Takara, catalog number: RR037Q)
Note: Store at -20 °C.
53. TB Green Premix Ex Taq (TliRNaseH Plus) (Takara, catalog number: RR420A)
Note: Long-term storage at -20 °C. Once opened, store at 4 °C and use within 6 months; light-sensitive.
Solutions
1. Soil mix (see Recipes)
2. Liquid Luria Broth (LB) (see Recipes)
3. Solid LB (see Recipes)
4. Kanamycin 50 mg/mL (see Recipes)
5. Rifampicin 50 mg/mL (see Recipes)
6. 1 M KOH (see Recipes)
7. 10 M NaOH (see Recipes)
8. 1 M Tris-HCl pH 7.5 (see Recipes)
9. 1 M MgSO4 (see Recipes)
10. 1 M CaCl2 (see Recipes)
11. 1 M KCl (see Recipes)
12. 3 M NaCl (see Recipes)
13. 1 M MgCl2 (see Recipes)
14. 0.5 M KH2PO4 pH 8 (see Recipes)
15. Glucose 20% (see Recipes)
16. 3 M sodium acetate pH 5.5 (see Recipes)
17. 1 M MES buffer pH 5.2 (see Recipes)
18. 0.1 M acetosyringone (see Recipes)
19. 0.5 M EDTA pH 8 (see Recipes)
20. Super Optimal broth + catabolic repressor (SOC) (see Recipes)
21. Oligonucleotide annealing buffer (see Recipes)
22. TAE 10× (see Recipes)
23. M9 medium (see Recipes)
24. Vir induction medium (see Recipes)
25. Infiltration solution (see Recipes)
26. Sucrose solution (see Recipes)
27. Inoculation buffer (see Recipes)
28. Saturated phenol (see Recipes)
29. Phenol/guanidine-based extraction buffer (see Recipes)
30. Ethanol 75% (see Recipes)
Recipes
1. Soil mix
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| Peat | 80% | 8 kg |
| Perlite | 20% | 2 kg |
2. Liquid Luria Broth (LB)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| Tryptone | 10 g/L | 10 g |
| NaCl | 10 g/L | 10 g |
| Yeast extract | 5 g/L | 5 g |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | 1 L |
Divide the final volume into two 500 mL bottles and autoclave. Store at RT.
3. Solid LB
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| Tryptone | 10 g/L | 10 g |
| NaCl | 10 g/L | 10 g |
| Yeast extract | 5 g/L | 5 g |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | 1 L |
| Agar | 15 g/L | 15 g |
Divide the final volume into two 500 mL bottles, add 7.5 g of agar and a stir bar to each, and autoclave. Right after sterilizing, add the appropriate amount of antibiotic, mix with a magnetic stirrer, and pour 20–25 mL into each Petri dish, under sterile conditions. Store Petri dishes upside down, covered in plastic film, at 4 °C for up to 2–3 weeks.
4. Kanamycin 50 mg/mL
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| Kanamycin | 50 mg/mL | 1 g |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | 20 mL |
Dissolve and sterilize by filtration in a laminar flow cabinet. Store in 1 mL aliquots at -20 °C.
5. Rifampicin 50 mg/mL
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| Rifampicin | 50 mg/mL | 1 g |
| DMSO | n/a | 20 mL |
Dissolve and sterilize by filtration in a laminar flow cabinet. Distribute in 1 mL aliquots, cover the tubes in aluminum foil, and store at -20 °C.
6. 1 M KOH
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| KOH | 1 M | 5.6 g |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | 100 mL |
Autoclave and store at room temperature (RT).
7. 10 M NaOH
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| NaOH | 10 M | 39.99 g |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | 100 mL |
Autoclave and store at RT.
8. 1 M Tris-HCl pH 7.5
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| Tris | 1 M | 12 g |
| HCl | n/a | 6 mL |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | Up to 100 mL |
Dissolve in 80 mL of Milli-Q water and adjust the final pH to 7.5 with HCl. Add Milli-Q water up to the final volume and autoclave. Store at RT.
9. 1 M MgSO4
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| MgSO4 | 1 M | 12 g |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | 100 mL |
Autoclave and store at RT.
10. 1 M CaCl2
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| CaCl2 | 1 M | 14.7 g |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | 100 mL |
Autoclave and store at RT.
11. 1 M KCl
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| KCl | 1 M | 7.4 g |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | 100 mL |
Autoclave and store at RT.
12. 3 M NaCl
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| NaCl | 3 M | 17.5 g |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | 100 mL |
Autoclave and store at RT.
13. 1 M MgCl2
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| MgCl2 | 1 M | 50.8 g |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | 250 mL |
Autoclave and store at RT.
14. 0.5 M KH2PO4 pH 8
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| KH2PO4 | 0.5 M | 6.8 g |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | Up to 100 mL |
Dissolve in 80 mL of water, set pH to 8 with 1 M KOH, and add water to the final volume. Autoclave and store at RT.
15. Glucose 20%
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| Glucose | 20% | 20 g |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | 100 mL |
Sterilize by filtration and store at RT.
16. 3 M sodium acetate pH 5.5
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium acetate | 3 M | 40.8 g |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | Up to 100 mL |
Dissolve in 60 mL of Milli-Q water and adjust pH with acetic acid. Add Milli-Q water up to the final volume, autoclave, and store at RT.
17. 1 M MES buffer pH 5.2
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| MES | 1 M | 19.5 g |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | Up to 100 mL |
Add the MES to 50 mL of water and warm up to 37 °C to dissolve. Set the pH to 5.2 with 1 M KOH and add the rest of the water. Sterilize by filtration and store at RT.
18. 0.1 M acetosyringone
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| Acetosyringone | 0.1 M | 0.49 g |
| DMSO | n/a | 25 mL |
Sterilize by filtration and store in 1 mL aliquots at -20 °C until use.
19. 0.5 M EDTA pH 8
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| EDTA | 0.5 M | 93 g |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | Up to 500 mL |
Dissolve the EDTA in 200 mL of Milli-Q water and adjust the pH with 10 M NaOH. Heat the solution to completely dissolve EDTA and add Milli-Q water up to the final volume. Autoclave and store at RT.
20. Super Optimal broth + catabolic repressor (SOC)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| Tryptone | 20 g/L | 20 g |
| Yeast extract | 5 g/L | 5 g |
| NaCl | 0.5 g/L | 0.5 g |
| 1 M KCl | 2.5 mM | 2.5 mL |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | 972 mL |
| Autoclave | ||
| Glucose 20% | 0.09% | 4.5 mL |
| 1 M MgCl2 | 2.5 mM | 2.5 mL |
Adjust pH to 7 with 10 M NaOH and add Milli-Q water to the final volume. Distribute into four 250 mL bottles and autoclave. After sterilizing, add the remaining reagents under sterile conditions, distribute in 8 mL aliquots, and store at RT.
21. Oligonucleotide annealing buffer
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) | 60 mM | 60 μL |
| 3 M NaCl | 500 mM | 166.6 μL |
| 1 M MgCl2 | 60 mM | 60 μL |
| 0.1 M DTT | 10 mM | 100 μL |
| Sterile Milli-Q water | n/a | Up to 1 mL |
Prepare under sterile conditions, distribute in 200 μL aliquots, and store at -20 °C until use.
22. TAE 10×
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| Tris | 400 mM | 48.46 g |
| 0.5 M EDTA (pH 8) | 10 mM | 20 mL |
| Acetic acid glacial | 200 mM | 11.44 mL |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | Up to 1 L |
No need to adjust pH as it should be ~8.5. Autoclave and store at RT. Dilute to 1× prior to use. Store the diluted TAE at RT.
23. M9 medium
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| Na2HPO4 | 6 g/L | 6 g |
| KH2PO4 | 3 g/L | 3 g |
| NaCl | 0.5 g/L | 0.5 g |
| NH4Cl | 1 g/L | 1 g |
| Milli-Q Water | n/a | Up to 1 L |
Adjust pH to 5.2 using HCl and add Milli-Q water to the final volume. Autoclave and store at RT.
24. Vir induction medium
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| Glucose 20% | 11.1 mM | 5 mL |
| 1 M MES buffer (pH 5.2) | 10 mM | 5 mL |
| 0.1 M acetosyringone | 0.1 mM | 500 μL |
| 1 M CaCl2 | 0.1 mM | 50 μL |
| 1 M MgSO4 | 0.5 mM | 1 mL |
| Sterile M9 solution (see Recipe 23) | n/a | 500 mL |
Prepare under sterile conditions.
Critical: Prepare right before use and do not store the leftover solution.
25. Infiltration solution
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| 1 M MgCl2 | 10 mM | 5 mL |
| 1 M MES (pH 5.2) | 10 mM | 5 mM |
| 0.1 M Acetosyringone | 0.15 mM | 750 μL |
| Sterile Milli-Q water | n/a | 500 mL |
Prepare under sterile conditions.
Critical: Prepare right before use and do not store the leftover solution.
26. Sucrose solution
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| 1 M MgCl2 | 10 mM | 10 mL |
| Sucrose | 5% | 50 g |
| BAP | 44 mM | 10 μL |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | Up to 1 L |
Mix reagents until fully dissolved.
Critical: Prepare right before use and do not store the leftover solution.
27. Inoculation buffer
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5 M KH2PO4 (pH 8) | 50 mM | 10 mL |
| PVP | 1% | 1 g |
| PEG | 1% | 1 g |
| Sterile Milli-Q water | n/a | Up to 100 mL |
| Autoclave | ||
| BME | 10 M | 0.7 μL/mL inoculation buffer |
Autoclave and store at RT.
Critical: Add the BME right before use. Do not store the leftover solution after adding BME.
28. Saturated phenol
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| Phenol 90% | 69.1% | 384 mL |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | 116 mL |
Mix thoroughly and store at 4 °C in a topaz bottle.
Caution: Phenol is toxic if swallowed, in contact with skin, or if inhaled. Prepare the mix with gloves, glasses, and a mask inside a fume hood.
29. Phenol/guanidine-based extraction buffer
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| Guanidine thiocyanate | 118 g/L | 59 g |
| Ammonium thiocyanate | 76 g/L | 38 g |
| 3 M Sodium acetate pH 5.5 | 99.9 mM | 16.66 mL |
| Glycerol 87% | 4.9% | 28.6 mL |
| Saturated phenol (Recipe 28) | n/a | 190 mL |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | Up to 500 mL |
Dissolve the guanidine thiocyanate and the ammonium thiocyanate in 200 mL of Milli-Q water. Add the rest of the reagents until fully dissolved. Add Milli-Q water up to volume and store at 4 °C in a topaz bottle.
Caution: Phenol is toxic if swallowed, in contact with skin, or if inhaled. Prepare the mix with gloves, glasses, and mask inside a fume hood.
30. Ethanol 75%
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or volume |
|---|---|---|
| Ethanol 96% | 75% | 78 mL |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | 22 mL |
Store at RT.
Laboratory supplies
1. Nitrile gloves (StarGuard, catalog number: EcogenSG-N-M-200)
2. Protective coat (LabBox, catalog number: GOSW-00M-001)
3. Protective glasses (Epica S.L., catalog number: 1034)
4. Protective mask (LabBox, catalog number: MASK-002-010)
5. 20 μL pipette (Eppendorf, catalog number: 3123000039)
6. 200 μL pipette (Eppendorf, catalog number: 3123000055)
7. 1,000 μL pipette (Eppendorf, catalog number: 3123000063)
8. 200 μL tubes (UVAT, catalog number: F-0302-01)
9. 1.5 mL tube (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 72690001)
10. 2 mL tube (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 72.691)
11. 2 mL SafeSeal tube (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 72695500)
12. 13 mL tubes (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 60540500)
13. 15 mL conical tubes (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 62.554.502)
14. 50 mL conical tubes (LabBox, catalog number: CTGP-050-050)
15. 96-well PCR plate (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 72.1981)
16. 250 mL glass Erlenmeyer flasks (LabBox, catalog number: EFN3-250-012)
17. 1 L glass Erlenmeyer flasks (LabBox, catalog number: EFN3-1K0-006)
18. 250 mL plastic Beckman tube (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 356011)
19. Petri dish (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 821473)
20. Round container 20–20 cm wide
21. Mortar and pestle (Porcelaine, LabBox, catalog number: MORK-100-001)
22. Zirconia beads (Biospec Products, catalog number: 11079124zx)
23. Electroporation cuvette (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: 12338212 (5510-11))
24. Spectrophotometer cuvette (Kartell, catalog number: 425-001938)
25. 1 mL needle-less disposable syringes (Vidra FOC, catalog number: 875/01)
26. Miracloth (Millipore; Vidra FOC, catalog number: 475855)
27. 30 mL high-density polyethylene vaporizer (Yizhao)
28. 15 cm pots (Mena Agrícola, catalog number: 750103)
29. Filter 0.2 μm (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 83.1826.001)
30. 100 mL Pyrex bottle (LabBox, catalog number: SBG3-100-001)
31. 500 mL Pyrex bottle (LabBox, catalog number: SBG3-500-001)
32. 500 mL topaz bottle (LabBox, catalog number: SBGA-500-001)
33. Measuring cylinder (Vitlab)
34. Beaker (LabBox, catalog number: BKLP-1K0-006)
35. Spoon (LabBox, catalog number: SPSS-150-005)
Equipment
1. Millipore Milli-Q Direct 16 Water Purification System
2. Computer connected to the internet
3. Balance (Kern, catalog number: EG2200)
4. Stir bar (lbx, catalog number: MAGC-040-005)
5. Magnetic stirrer (VWR, catalog number: 442-0551)
6. Autoclave (P Selecta)
7. GeneExplorer thermal cycler (Bioer, catalog number: BYQ6617E)
8. Electroporator (Eppendorf, catalog number: 4309000019)
9. Mini Sub Cell GT System with 7 × 10 cm gel tray + mini gel caster + PowerPac supply (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 164-0300)
10. 37 °C walk-in growth chamber
11. 28 °C walk-in growth chamber
12. 37 °C dry bath (Fisher, catalog number: 15387928)
13. 1.5 mL tube centrifuge (Eppendorf, catalog number: 30215964) with rotor (Eppendorf, catalog number: FA-24x2)
14. 50 mL conical tube centrifuge (Eppendorf, catalog number: 5428000205) with rotor (Eppendorf, catalog number: F35-6-30)
15. 250 mL Beckman centrifuge (Avanti J-HC, catalog number: 367502) with rotor (JA-14 Fixed-Angle Aluminum Rotor, 339247)
16. Orbital shaker (VWR, catalog number: 444-0268)
17. Biowave cell density meter wavelength 600 nm (WPA, catalog number: CO8000)
18. Plant walk-in growth chamber
19. Laminar flow cabinet (Telstar Aeolus H6)
20. Fume hood (Flowtronic AFA 1000)
21. pH meter (ViciTac, HACH.LPV200.98.0002)
22. Transilluminator (Cleaver Scientific, model: EZEE geloue)
23. NanoDrop (Thermo Fisher Scientific, model: ND-2000)
24. QuantStudio 3 Real-Time PCR system, 96-well (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: A28567)
25. Bead beater mixer mill (Retsch, model: MM400)
Procedure
文章信息
稿件历史记录
提交日期: Jun 12, 2025
接收日期: Sep 9, 2025
在线发布日期: Sep 21, 2025
出版日期: Oct 20, 2025
版权信息
© 2025 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
如何引用
Cisneros, A. E., Alarcia, A., Juárez-Molina, M. and Carbonell, A. (2025). Effective Gene Silencing in Plants by Synthetic Trans-Acting siRNAs Derived From Minimal Precursors. Bio-protocol 15(20): e5475. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5475.
分类
植物科学 > 植物分子生物学 > RNA > RNA 干扰
分子生物学 > RNA > RNA 干扰
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link













