- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Fast TV-PRO-seq: Accelerated and Streamlined Protocol for Timing RNA Polymerase Pausing
Fast TV-PRO-seq:RNA聚合酶停滞时间测定的加速与简化流程
(§Technical contact: zhangjie_gdas@foxmail.com) 发布: 2025年07月20日第15卷第14期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5395 浏览次数: 2424
评审: Andrea GramaticaAnonymous reviewer(s)

相关实验方案

用于全面分析细胞、细胞外囊泡和血浆 RNA 中编码和非编码 RNA 生物型的 TGIRT-seq 方法
Hengyi Xu [...] Alan M. Lambowitz
2021年12月05日 7299 阅读
Abstract
Transcriptional pausing dynamically regulates spatiotemporal gene expression during cellular differentiation, development, and environmental adaptation. Precise measurement of pausing duration, a critical parameter in transcriptional control, has been challenging due to limitations in resolution and confounding factors. We introduce Fast TV-PRO-seq, an optimized protocol built on time-variant precision run-on sequencing (TV-PRO-seq), which enables genome-wide, single-base resolution mapping of RNA polymerase II pausing times. Unlike standard PRO-seq, Fast TV-PRO-seq employs sarkosyl-free biotin-NTP run-on with time gradients and integrates on-bead enzymatic reactions to streamline workflows. Key improvements include (1) reducing experimental time from 4 to 2 days, (2) reducing cell input requirements, and (3) improved process efficiency and simplified command-line operations through the use of bash scripts.
Key features
• Reduces experimental duration from 4 to 2 days via on-bead enzymatic reactions and streamlined workflows.
• Enables single-nucleotide resolution pausing time mapping using time-variant biotin-NTP run-on with saturation kinetics.
• Compatible with reduced cell input (106–108 cells) and sarkosyl-free conditions for improved experimental feasibility.
• Integrates bash scripts and simplified commands for enhanced reproducibility and reduced computational complexity.
Keywords: RNA polymerase pausing (RNA聚合酶停滞)Graphical overview
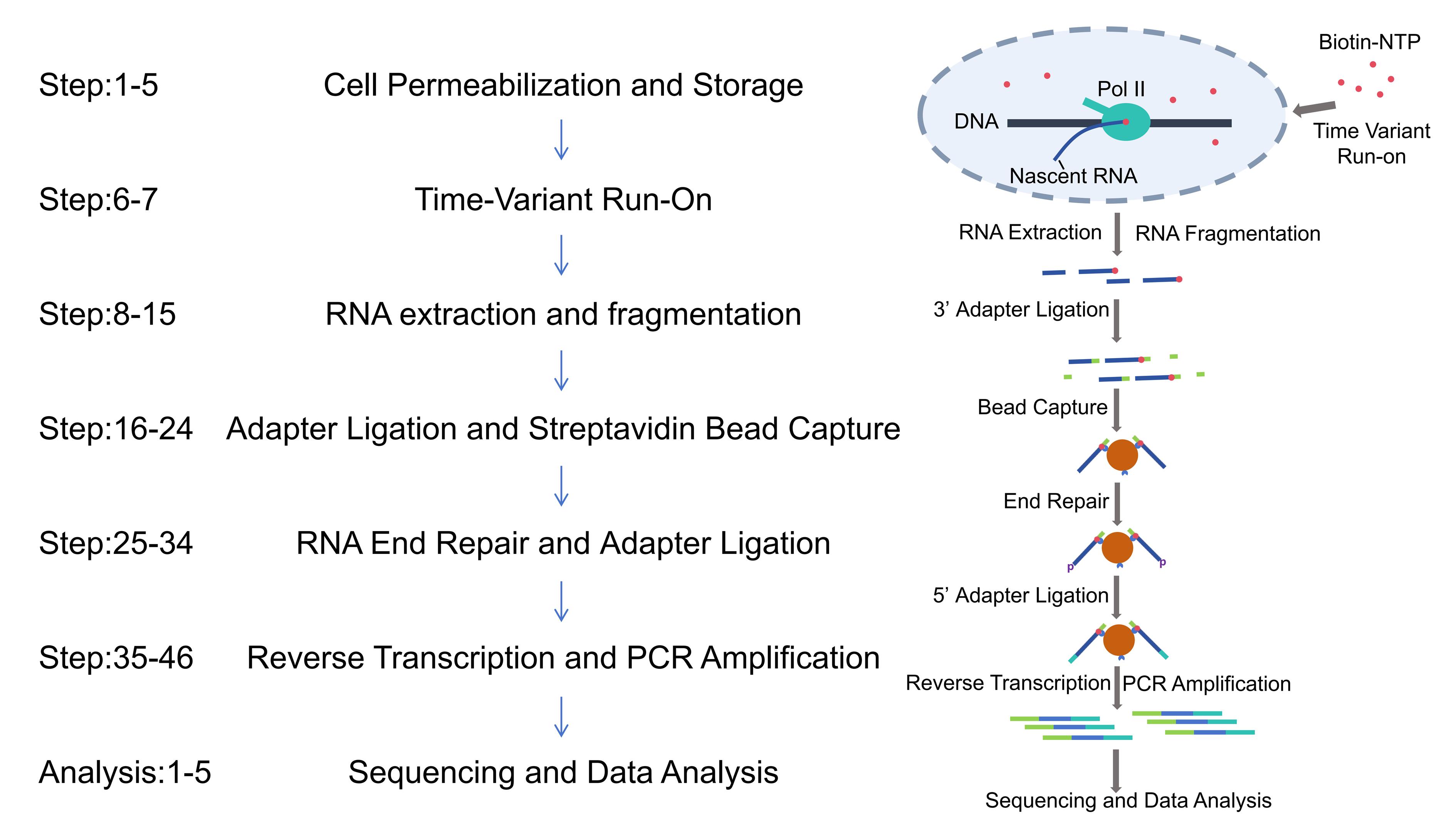
Background
RNA polymerase II (Pol II) pausing during transcription elongation is a widespread regulatory mechanism in metazoans, particularly in promoter-proximal regions (PPRs) [1,2]. This transient stalling of transcriptionally engaged polymerases influences gene expression dynamics, chromatin states, and transcriptional noise [3,4]. Traditional methods such as Pol II ChIP-seq [5], GRO-seq (global run-on sequencing) [2], NET-seq (native elongating transcript sequencing) [6], mNET-seq [7] (native elongating transcript sequencing technology for mammalian chromatin), and PRO-seq (precision run-on sequencing) have advanced our understanding of polymerase occupancy patterns. However, these approaches primarily measure polymerase occupancy, which conflates pausing time with confounding factors like transcription initiation rates, ratio of pausing, and abortive transcription [8,9]. The widely used triptolide (Trp) treatment method, which inhibits transcription initiation to estimate pause durations in PPRs [3,10], suffers from slow drug uptake and limited resolution [11]. Additionally, newly generated methods highlight that promoter-proximal Pol II accumulation may predominantly arise from high abortive transcription rates, further complicating interpretation [9,12,13].
By performing run-on reactions with varying durations, TV-PRO-seq generates saturation curves that reflect polymerase release kinetics, enabling genome-wide estimation of pausing times at single-nucleotide resolution [14]. This approach bypasses the influence of polymerase turnover and abortive transcription, providing unprecedented insights into the relationship between pausing dynamics, chromatin modifications (e.g., H3K36me3), and transcriptional noise. However, TV-PRO-seq requires the parallel execution of eight sarkosyl-free PRO-seq experiments, a process that is not only time-consuming but also demands substantial cell quantities, ultimately leading to high experimental failure rates that hinder the practical application of TV-PRO-seq. Based on the last version of PRO-seq [15], we present Fast TV-PRO-seq, an enhanced version featuring significantly reduced experimental duration and lower starting cell requirements.
Materials and reagents
Reagents
1. DEPC water (Invitrogen, catalog number: 10514065)
2. NaCl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S9888)
3. KCl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9333)
4. MgCl2·6H2O (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M2670)
5. 0.5 M EDTA (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 20-158)
6. EGTA (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: E3889)
7. Sucrose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S0389)
8. NaOH (Fisher Chemical, catalog number: 10396240)
9. DTT (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D0632)
10. Glycerol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G5516)
11. TWEEN-20 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9416)
12. Tris-HCl pH 6.8 1 M (AESAR, catalog number: J63831.K2)
13. Tris-HCl pH 7.4 1 M (AESAR, catalog number: J60202.K2)
14. Tris-HCl pH 8.0 1 M (AESAR, catalog number: J62726.K2)
15. 1× PBS pH 7.4 (Gibco, catalog number: 10728775)
16. Ethanol (Fisher Chemical, catalog number: BP2818)
17. Isopropanol (Fisher Chemical, catalog number: BP2816)
18. Chloroform (Fisher Chemical, catalog number: 10488400)
19. Biotin-11-CTP (PerkinElmer, catalog number: NEL542001EA)
20. Biotin-11-UTP (PerkinElmer, catalog number: NEL543001EA)
21. Biotin-11-ATP (PerkinElmer, catalog number: NEL544001EA)
22. Biotin-11-GTP (PerkinElmer, catalog number: NEL545001EA)
23. ATP (New England Biolabs, catalog number: P0756S)
24. GTP (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G3776)
25. Streptavidin Dynabeads C1 (Invitrogen, catalog number: 65002)
26. TRIzol (Invitrogen, catalog number: 15608948)
27. GlycoBlue (Invitrogen, catalog number: 10301575)
28. SUPERase RNase inhibitor (Invitrogen, catalog number: 10773267)
29. T4 RNA ligase I (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0204)
30. RppH and 10× ThermoPol buffer (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0356)
31. T4 polynucleotide kinase and 10× PNK buffer (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0201L)
32. BioZues® III reverse transcriptase (Bioligo, catalog number: SE0301)
33. Q5 master mix (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0544)
34. AMPure XP beads (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: A63880)
35. Sarkosyl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: L9150)
Oligos
3′ RNA adapter: p-GAUCGUCGGACUGUAGAACUCUGAAC -/inverted dT/
STP: CGACGAUCCCACGUUCCCGUGG
5′ RNA adapter: CCUUGGCACCCGAGAAUUCCA
RP1: AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACGTTCAGAGTTCTACAGTCCGA
RPI-n: CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATNNNNNNNNGTGACTGGAGTTCCTTGGCACCCGAGAATTCCA (replace NNNNNNNN according to the indexes of Illumina Tru-seq)
Solutions
1. Permeabilization buffer (see Recipes)
2. Storage buffer (see Recipes)
3. 1 N NaOH (see Recipes)
4. Washing solution A (see Recipes)
5. Washing solution B (see Recipes)
6. 2× Bead washing buffer (see Recipes)
7. 1× Bead washing buffer (see Recipes)
8. Pre-washed streptavidin beads (see Recipes)
Recipes
1. Permeabilization buffer
15 mL of 1 M Sucrose, 2.5 mL of 1% Tween-20, 500 µL of 1 M Tris-HCl pH 7.4, 500 µL of 0.1 M EGTA, 500 µL of 10% NP40, 250 µL of 2 M KCI, 250 µL of 1 M MgCl2, 25 µL of 1 M DTT, 5 µL of RNase inhibitor, and 1 tablet of protease inhibitors. Add DEPC water up to 50 mL. Make fresh before use.
2. Storage buffer
0.2 µL of 0.5 M EDTA, 10 µL of 1 M Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 5 µL of 1 M MgCl2, 5 µL of 1 M DTT, 250 µL of glycerol, 730 µL of DEPC water. Make fresh before use.
3. 1 N NaOH
2 g of NaOH in 50 mL of DEPC water.
4. Washing solution A
100 µL of 1 N NaOH, 10 µL of 5 M NaCl, and 890 µL of DEPC water. Store at 4 °C for 1 month.
5. Washing solution B
20 µL of 5 M NaCl and 980 µL of DEPC water. Store at 4 °C for 1 month.
6. 2× Bead washing buffer
20 mL of 5 M NaCl, 500 µL of 1 M Tris-HCl pH 7.4, and 5 mL of 1% Tween-20. Add DEPC water up to 50 mL. Store at 4 °C for 1 month.
7. 1× Bead washing buffer
25 mL of 2× Bead washing buffer and add DEPC water up to 50 mL. Store at 4 °C for 1 month.
8. Pre-washed streptavidin beads
Add 170 µL (20 µL for PRO-seq) Dynabeads MyOne Streptavidin C1 beads in a 1.5 mL tube. Place on a magnetic rack for 2 min and remove the supernatant. Wash beads with 500 µL of washing solution A twice. Wash beads with 500 µL of washing solution B once. Raise the beads in 425 µL (50 µL for PRO-seq) of 2× Bead washing buffer.
Laboratory supplies
1. Phase-lock gel tubes (Proandy, catalog number: 10447-1)
2. Low-bind, nuclease-free microcentrifuge tubes (GENEPLASTIX, catalog number: 243-MCT-C-1.5-L)
3. Low-bind, nuclease-free 1,000 µL filtered pipette tips (GENEPLASTIX, catalog number: 222-RF-C-1000S-L)
4. Low-bind, nuclease-free 200 µL filtered pipette tips (GENEPLASTIX, catalog number: 222-RF-C-200S-L)
5. Low-bind, nuclease-free 20 µL filtered pipette tips (GENEPLASTIX, catalog number: 222-RF-C-20S-L)
Equipment
1. Refrigerated centrifuge (Eppendorf, model: Centrifuge5424R)
2. PCR thermal cycler (LongGene, model: T30D)
3. Heat blocks (JOANLAB, model: MDB100/MDB100-C)
4. Magnetic separator (Invitrogen, model: DynaMagTM-2)
5. Rotating stand (BeyoEquip, model: yoVortexTM Basic Rotation Mixer E6800)
Procedure
文章信息
稿件历史记录
提交日期: May 1, 2025
接收日期: Jun 5, 2025
在线发布日期: Jul 10, 2025
出版日期: Jul 20, 2025
版权信息
© 2025 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
如何引用
Zhang, J., Liang, Z., Sun, M., Hebenstreit, D. and Zhang, S. (2025). Fast TV-PRO-seq: Accelerated and Streamlined Protocol for Timing RNA Polymerase Pausing. Bio-protocol 15(14): e5395. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5395.
分类
生物信息学与计算生物学
分子生物学 > RNA > 转录
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










