- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Thermus thermophilus CRISPR Cas6 Heterologous Expression and Purification
嗜热栖热菌CRISPR Cas6的异源表达与纯化方法
(*Contributed equally to this work, §Technical contact: weijw@webmail.hzau.edu.cn) 发布: 2025年07月20日第15卷第14期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5382 浏览次数: 2171
评审: Alba BlesaLionel SchiavolinAnonymous reviewer(s)

相关实验方案

从蓝藻集胞藻sp. PCC 6803中分离类囊体膜并利用CN-PAGE非变性聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳分析光合色素蛋白复合物
Josef Komenda [...] Tomas Zakar
2019年01月05日 8591 阅读

通过制备连续聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳和凝胶酶谱分析法纯化来自梭状龋齿螺旋体的天然Dentilisin复合物及其功能分析
Pachiyappan Kamarajan [...] Yvonne L. Kapila
2024年04月05日 2095 阅读
Abstract
The CRISPR-Cas system of Thermus thermophilus has emerged as a potent biotechnological tool, particularly its Cas6 endonuclease, which plays a crucial role in CRISPR RNA (crRNA) maturation. This protocol details a robust and reproducible method for the high-level expression and purification of recombinant T. thermophilus Cas6 proteins (Cas6-1 and Cas6-2) in E. coli. We describe a streamlined approach encompassing plasmid construction using seamless assembly, optimized bacterial heterologous expression, and multi-step purification leveraging affinity and size-exclusion chromatography. The protocol outlines the generation of both His-tagged and GST-tagged Cas6 variants, enabling flexibility in downstream applications. Key steps, including primer design, PCR optimization, competent cell transformation, and chromatography strategies, are meticulously detailed with critical parameters and troubleshooting guidance to ensure experimental success and high yields of highly pure and active T. thermophilus Cas6 proteins. This protocol is useful for researchers requiring purified T. thermophilus Cas6 for structural studies, biochemical characterization, and the development of CRISPR-based biotechnological tools.
Key features
• Robust method for expressing and purifying Thermus thermophilus Cas6 proteins in E. coli.
• Seamless assembly cloning and dual affinity tagging system: Offers options for both His-tag and GST-tag purification strategies for increased versatility.
• Applicable for diverse heterologous expression and purification of well-folding thermostable proteins in mesophilic host chassis cells [E. coli BL21(DE3)].
Keywords: CRISPR-Cas6 (CRISPR-Cas6)Graphical overview
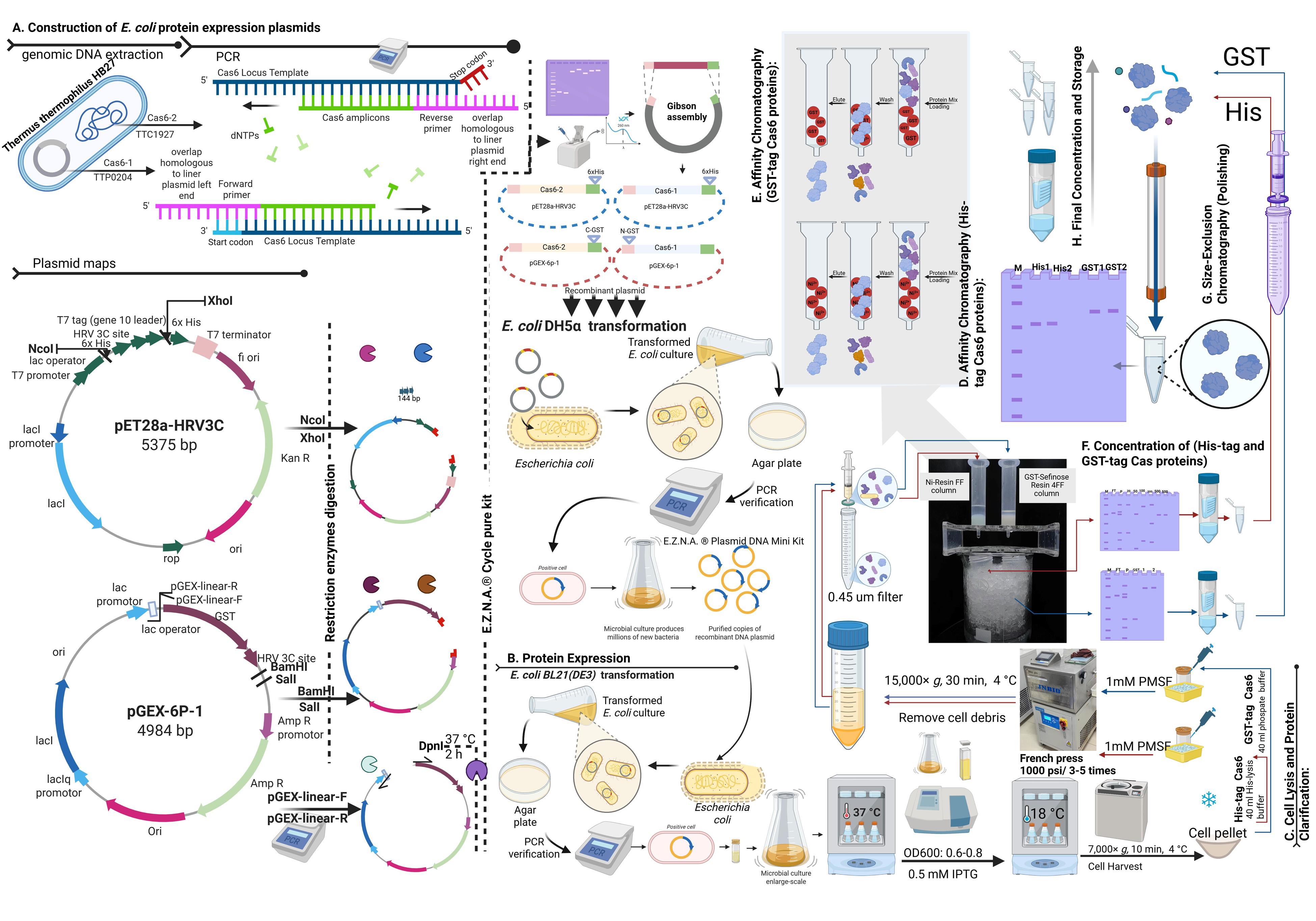
Flowchart outlining the steps in Cas6 heterologous expression and purification
Background
The CRISPR-Cas (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats–CRISPR-associated proteins) system, a cornerstone of bacterial and archaeal adaptive immunity, relies on CRISPR RNAs (crRNAs) that guide effector complexes to target foreign nucleic acids, such as plasmids and bacteriophages, through sequence-specific nucleic acid targeting [1–3]. This system has enabled precise genome editing and innovative applications in therapeutics and biotechnology [3,4]. The biogenesis of mature crRNAs involves the precise cleavage of precursor CRISPR RNAs (pre-crRNAs) by specialized endonucleases, such as Cas6, which recognize and process repeat sequences within the CRISPR array [5,6].
Thermus thermophilus HB27, a thermophilic bacterium thriving in high-temperature environments, harbors a remarkably thermostable CRISPR-Cas system that has garnered significant interest for its biotechnological potential [3]. Thermophilic CRISPR-Cas systems, including those of T. thermophilus, are of particular interest due to their stability and functionality at elevated temperatures, which enhances their utility in industrial bioprocessing and high-temperature biochemical assays [7]. T. thermophilus is a model organism for studying thermozymes—enzymes adapted to extreme thermal conditions—owing to its rich repertoire of thermostable proteins, including DNA polymerases and ligases widely used in molecular biology [3]. Among its diverse CRISPR-Cas arsenal, T. thermophilus encodes multiple CRISPR-Cas subtypes, including Type I and Type III systems, which exhibit extraordinary diversity in their defensive mechanisms, making it a valuable system for studying CRISPR evolution and function [8,9].
Within this context, T. thermophilus Cas6 endonucleases, specifically Cas6-1 and Cas6-2, are critical for pre-crRNA processing, cleaving repeat sequences to generate mature crRNAs that integrate into CRISPR-Cas effector complexes for targeted nucleic acid recognition [3]. The thermostability of these enzymes, coupled with their precise RNA cleavage activity, positions them as promising tools for RNA manipulation, including in vitro RNA processing and diagnostic platforms requiring robust performance under stringent conditions [3]. However, structural and functional studies of T. thermophilus Cas6, as well as their biotechnological applications, have been hindered by the lack of efficient, high-yield recombinant production protocols.
This protocol addresses this gap by providing a comprehensive, optimized, and adaptable method for the expression and purification of recombinant T. thermophilus Cas6 proteins, including both His-tagged and GST-tagged variants. By enabling high-purity production, this procedure facilitates biochemical, structural, and applied research into these thermostable endonucleases, advancing their utility in CRISPR-based technologies and RNA manipulation tools.
Materials and reagents
Biological materials
1. Thermus thermophilus HB27 (ATCC, catalog number: BAA-163; extract gDNA according to Wei et al. [3])
2. Escherichia coli DH5α (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 18265017, stored at -80 °C)
3. Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: EC0114, stored at -80 °C)
Reagents
1. pET28a-HRV3C (Addgene ID: 241018, store at -20 °C)
2. pGEX-6p-1 (Addgene ID: 241019, store at -20 °C)
3. NcoI (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: FD0574, store at -20 °C)
4. XhoI (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: FD0694, store at -20 °C)
5. BamHI (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: FD0054, store at -20 °C)
6. SalI (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: FD0644, store at -20 °C)
7. Phanta Max Super-Fidelity DNA polymerase (Vazyme, catalog number: P505-d3-AA, store at -20 °C)
8. DpnI (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: FD1404, store at -20 °C)
9. ABclonal MultiF Seamless Assembly Mix (ABclonal, catalog number: RK21020, store at -20 °C)
10. Nuclease-free water (Sigma-Aldrich, CAS number: 7732-18-5)
11. 2× Phanta Max buffer (Vazyme, catalog number: P505-d3-Ab, store at -20 °C)
12. dNTP mix (10 mM each) (Vazyme, catalog number: P505-d3-Ac, store at -20 °C)
13. Tryptone (OXOID, catalog number: LP0042B)
14. Yeast extract (OXOID, catalog number: LP0021B)
15. Agar (BioFroxx, catalog number: 8211GR500)
16. Isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: I6758-5G)
17. Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, CAS number: 7558-79-4)
18. HEPES (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H3375)
19. Glycerol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G5516)
20. Imidazole (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: I2399)
21. Reduced glutathione (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G4251)
22. Potassium chloride (KCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9541)
23. Dibasic sodium phosphate (Na2HPO4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S3225)
24. Monobasic potassium phosphate (KH2PO4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9791)
25. Kanamycin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: K1377)
26. Ampicillin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A5354-10ML)
27. Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P7626)
28. Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) (BioFRoxx, catalog number: 3250GR500)
29. Tris base (2-Amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)-propane-1,3-diol,Tris base) (BioFRoxx, CAS number: 77-86-1)
30. Glycine (BioFRoxx, CAS number: 56-40-6)
31. Ammonium persulfate (APS) (SCR, CAS number: 7727-54-0)
32. Acryl/Bio 30% solution (37.5:1) (Sanggon Biotech, catalog number: B546018-0500, store at 2–8 °C)
33. TEMED (Sigma, CAS number: 110-12-9)
34. Disodium EDTA dihydrate (SCR, CAS number: 6381-92-6)
35. Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) (SCR, CAS number: 1310-73-2)
36. Glacial acetic acid (SCR, CAS number: 64-19-7)
37. Agarose (Singke, catalog number: TSJ001)
38. Goldview (GL Biotech, catalog number: H003-1)
Solutions
1. LB medium (LB) (see Recipes)
2. Kanamycin stock solution (30 mg/mL) (see Recipes)
3. IPTG stock solution (100 mM) (see Recipes)
4. His-lysis buffer (see Recipes)
5. 5 M Imidazole stock solution (see Recipes)
6. His-washing buffer (see Recipes)
7. 100 mM Imidazole His-elution buffer (see Recipes)
8. 200 mM Imidazole His-elution buffer (see Recipes)
9. 500 mM Imidazole His-elution buffer (see Recipes)
10. 1 M Imidazole His-elution buffer (see Recipes)
11. Phosphate buffer (see Recipes)
12. GST-elution buffer (see Recipes)
13. SEC buffer (see Recipes)
14. 10% SDS solution (see Recipes)
15. 1.5 M Tris-HCl (pH 8.8) stock solution (see Recipes)
16. 1.0 M Tris-HCl (pH 6.8) stock solution (see Recipes)
17. 2.5 M glycine stock solution (see Recipes)
18. 10% Ammonium persulfate (APS) (see Recipes)
19. SDS-PAGE running buffer (10× Tris-Glycine-SDS, pH 8.3) (see Recipes)
20. SDS-PAGE resolving gel (12% polyacrylamide) (see Recipes)
21. SDS-PAGE stacking gel (5% polyacrylamide) (see Recipes)
22. 0.5 M EDTA (pH 8.0) stock solution (see Recipes)
23. 50× TAE buffer (see Recipes)
24 1.5 % agarose gel (see Recipes)
Recipes
1. LB medium
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Tryptone | 10 g/L | 10 g |
| Yeast extract | 5 g/L | 5 g |
| NaCl | 10 g/L | 10 g |
| Water | n/a | to 1 L |
Dissolve reagents in approximately 900 mL of water. Adjust pH to 7.0 if necessary. Bring the volume to 1 L with water. For plate media, add agar to a final concentration of 1.5% (15 g/L). Sterilize by autoclaving at 121 °C for 20 min.
2. Kanamycin stock solution (30 mg/mL)
Dissolve 3 g of kanamycin in ddH2O to a final volume of 100 mL. Filter sterilize using a 0.22 μm filter. Store at -20 °C for long-term storage or 4 °C for short-term storage. This 1000-fold concentrated stock solution is designed to be added at 1 mL per 1 L of LB medium to achieve a final kanamycin concentration of 30 μg/mL.
Critical: Add kanamycin after the LB medium has cooled down to below 50 °C following autoclaving to prevent antibiotic degradation.
3. IPTG stock solution (100 mM)
Dissolve 2.383 g of IPTG in ddH2O to a final volume of 100 mL. Filter sterilize using a 0.22 μm filter. Store at -20 °C for long-term storage or 4 °C for short-term storage. This stock solution is designed to be added at 5 mL per 1 L of culture to achieve a final IPTG concentration of 0.5 mM.
4. His-lysis buffer (Base buffer)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| HEPES | 20 mM | 4.77 g |
| NaCl | 300 mM | 17.53 g |
| Glycerol (99%) | 5% (v/v) | 50 mL |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | to 1 L |
Dissolve HEPES in approximately 700 mL of Milli-Q water. HEPES dissolves best at neutral pH. Adjust the pH to 7.5 using a pH meter at room temperature. Then add the other components. Bring the final volume to 1 L with Milli-Q water. Filter using a 0.22 μm filter. Store at 4 °C for 1 week.
5. 5 M Imidazole stock solution
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Imidazole | 5 M | 34.02 g |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | to 100 mL |
Dissolve imidazole in Milli-Q water to a final volume of 100 mL. Adjust pH to 7.5 with HCl (imidazole dissolves best at neutral pH). Filter using a 0.22 μm filter. Store at -20 °C for long-term storage or 4 °C for short-term storage.
6. His-washing buffer
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity for 100 mL |
|---|---|---|
| His-lysis buffer | (Base buffer) | 99 mL |
| 5 M imidazole | 50 mM | 1 mL |
7. 100 mM Imidazole His-elution buffer
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity for 100 mL |
|---|---|---|
| His-lysis buffer | (Base buffer) | 98 mL |
| 5 M imidazole | 100 mM | 2 mL |
8. 200 mM Imidazole His-elution buffer
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity for 100 mL |
|---|---|---|
| His-lysis buffer | (Base buffer) | 96 mL |
| 5 M imidazole | 200 mM | 4 mL |
9. 500 mM Imidazole His-elution buffer
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity for 100 mL |
|---|---|---|
| His-lysis buffer | (Base buffer) | 90 mL |
| 5 M imidazole | 500 mM | 10 mL |
10. 1 M Imidazole His-elution buffer
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity for 100 mL |
|---|---|---|
| His-lysis buffer | (Base buffer) | 80 mL |
| 5 M imidazole | 1000 mM | 20 mL |
11. Phosphate buffer (pH 7.4)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| NaCl | 140 mM | 8.18 g |
| KCl | 2.7 mM | 0.20 g |
| Na2HPO4 | 10 mM | 1.42 g |
| KH2PO4 | 1.8 mM | 0.24 g |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | to 1 L |
Dissolve salts in approximately 800 mL of Milli-Q water and stir until fully dissolved. Adjust pH to 7.4. Bring the final volume to 1 L with Milli-Q water. Filter using a 0.22 μm filter. Store the buffer at 4 °C for up to 1 month.
Critical: Use anhydrous Na2HPO4 (141.96 g/mol) for accurate molarity. If using hydrated forms (Na2HPO4·7H2O, MW 268.07), adjust required mass = (10 mM × 268.07 g/mol) = 2.68 g/L.
12. GST-elution buffer (pH 8.0)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity for 50 mL |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced glutathione | 10 mM | 153.66 mg |
| Phosphate buffer | (Base buffer) | to 50 mL |
Dissolve in 40 mL of phosphate buffer.
Critical: GSH dissolves slowly; stir gently at room temperature for 10–15 min. Adjust pH to 8.0 with 1 M NaOH (typically requires ~1–2 mL).
Critical: GST elution is optimal at pH 8.0–8.5. Bring the final volume to 50 mL. Filter using a 0.22 μm filter. Store the buffer at 4 °C for up to 1 week (GSH oxidizes over time).
13. SEC buffer
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| HEPES | 20 mM | 4.77 g |
| NaCl | 150 mM | 8.77 g |
| Glycerol (99%) | 5% (v/v) | 50 mL |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | to 1 L |
14. 10% SDS Solution
Dissolve 50 g of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) in Milli-Q water to a final volume of 500 mL with stirring. Store at room temperature for up to 6 months.
Caution: Wear a mask and gloves when handling SDS powder to avoid dust inhalation.
15. 1.5 M Tris-HCl (pH 8.8) (500 mL) stock solution
Dissolve 90.85 g of Tris base (MW 121.14 g/mol) in 300 mL of Milli-Q water with stirring. Adjust pH to 8.8 using concentrated HCl (add slowly, as Tris buffering capacity is high). Top up the volume to 500 mL. Store at 4 °C for up to 1 month.
Critical: Allow the solution to cool to room temperature before final pH adjustment, as Tris pH is temperature-sensitive.
16. 1.0 M Tris-HCl (pH 6.8) (50 mL) stock solution
Dissolve 6 g of Tris base (MW 121.14 g/mol) in 40 mL of Milli-Q water with stirring. Adjust pH to 6.8 using concentrated HCl. Top up the volume to 50 mL. Store at 4 °C for up to 1 month.
Critical: Recheck pH after mixing, as small deviations can affect gel stacking.
17. 2.5 M glycine (1 L) stock solution
Dissolve 187.7 g of glycine (MW 75.07 g/mol) in Milli-Q water to a final volume of 1 L with stirring. Store at room temperature for up to 6 months.
Critical: Ensure complete dissolution, as glycine can take time to dissolve fully.
18. 10% Ammonium persulfate (APS ) (1 mL)
Dissolve 0.1 g of APS in 1 mL of Milli-Q water immediately before use.
Critical: Do not store, as APS degrades rapidly in solution. Prepare fresh each day to ensure effective polymerization.
19. SDS-PAGE running buffer (10× Tris-Glycine-SDS, pH 8.3)
| Reagent | Final concentration (10×) | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| 1.5 M Tris-HCl (pH 8.8) | 250 mM | 166.7 mL |
| 2.5 M glycine | 1.92 M | 768 mL |
| 10% SDS | 1% (w/v) | 100 mL |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | to 1 L |
Bring the volume to 1 L with Milli-Q water and mix gently by stirring. Check pH (should be ⁓8.3). Store at room temperature for up to 6 months. To prepare 1× working buffer, dilute 100 mL of 10× with 900 mL of Milli-Q water within 1 week for optimal performance.
Critical: Do not adjust pH with NaOH, as sodium ions can interfere with electrophoresis.
20. SDS-PAGE resolving gel (12% polyacrylamide)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity for 10 mL |
|---|---|---|
| 30% Acrylamide/Bis (37.5:1) | 12% | 4.0 mL |
| 1.5 M Tris-HCl (pH 8.8) | 375 mM | 2.5 mL |
| 10% SDS | 0.1% | 100 μL |
| 10% APS | 0.1% | 100 μL |
| TEMED | 0.04% | 4 μL |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | to 10 mL (3.3 mL) |
In a 50 mL conical flask, combine 3.3 mL of Milli-Q water, 2.5 mL of 1.5 M Tris-HCl (pH 8.8), 4.0 mL of 30% acrylamide/Bis, and 0.1 mL of 10% SDS. Mix gently by inversion. Then, add 0.1 mL of 10% APS and 4 μL of TEMED immediately before pouring to initiate polymerization. Pour into the gel cassette with a 5 mL micropipette, leaving ~1 cm space for the stacking gel. Overlay with isopropanol or water to ensure a flat interface. Allow polymerization for 30–45 min at room temperature.
Caution/Critical: Acrylamide is neurotoxic; handle with gloves in a fume hood. Prepare APS fresh daily. Polymerization time may vary with ambient temperature.
21. SDS-PAGE stacking gel (5% polyacrylamide)
| Reagent | Final concentration (10×) | Quantity for 3 mL |
|---|---|---|
| 30% Acrylamide/Bis (37.5:1) | 5% | 500 μL |
| 1.0 M Tris-HCl (pH 6.8) | 125 mM | 375 μL |
| 10% SDS | 0.1% | 30 μL |
| 10% APS | 0.1% | 30 μL |
| TEMED | 0.1% | 3 μL |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | to 3 mL (2.062 mL) |
In a 15 mL centrifuge tube, combine 2,062 μL of Milli-Q water, 375 μL of 1.0 M Tris-HCl (pH 6.8), 500 μL of 30% acrylamide/bis, and 30 μL of 10% SDS. Mix gently by inversion. Then, add 30 μL of 10% APS and 3 μL of TEMED immediately before pouring to initiate polymerization. Remove the isopropanol/water overlay from the polymerized resolving gel. Pour the stacking gel mixture on top with a micropipette and insert the comb. Allow polymerization for 20–30 min at room temperature.
Critical: Ensure the resolving gel is fully polymerized before pouring the stacking gel. Use fresh APS for consistent polymerization. Measure volumes precisely using calibrated micropipettes.
22. 0.5 M EDTA (pH 8.0) stock solution
Dissolve 18.61 g of disodium EDTA dihydrate in 80 mL of Milli-Q water. Stir vigorously using a magnetic stir plate.
EDTA will not dissolve fully until the pH is ~8.0. Add NaOH (either pellets or a concentrated solution, e.g., 10 M) gradually while monitoring pH with a calibrated pH meter. Typically, ~0.5–1 g of NaOH pellets or ~0.5–1 mL of 10 M NaOH is sufficient. Continue stirring until the EDTA dissolves completely.
23. 50× TAE buffer
| Reagent | Final concentration (10×) | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Tris base | 2 M | 242 g |
| Glacial acetic acid | 1 M | 57.1 mL |
| 0.5 M EDTA (pH 8.0) | 50 mM | 100 mL |
| Milli-Q water | n/a | to 1 L |
Dissolve 242 g of Tris base in 700 mL of Milli-Q water with stirring until fully dissolved. Add 57.1 mL of glacial acetic acid and mix thoroughly. Add 100 mL of 0.5 M EDTA (pH 8.0) and mix. Bring the volume to 1 L with Milli-Q water. Stir gently. Verify the pH is ~8.0; adjust with acetic acid. Store at room temperature for up to 6 months. To prepare 1× TAE working buffer, dilute 20 mL of 10× with 980 mL of Milli-Q water.
Critical: Tris and EDTA solutions are pH-sensitive; ensure EDTA stock is at pH 8.0.
24. 1.5% agarose gel
Prepare a flask that can hold 2–4 times the volume of agarose you are preparing. Add 100 mL of the diluted buffer (1× TAE) to the flask, followed by 1.5 g of agarose. Heat the flask in the microwave in bursts of 30 s. Swirl after each burst. Cool it down to 40 °C. Add 10 μL of goldview. Pour in the tray. Add the combs.
Laboratory supplies
1. E.Z.N.A® Cycle Pure Kit (omega BIO-TEK, catalog number: D6492-02)
2. E.Z.N.A.® Plasmid DNA Mini Kit I (omega BIO-TEK, catalog number: D6943-02)
3. Bradford Protein Assay kit (Tiangen, catalog number: PA102)
4. Ni-charged Resin FF columns (GenScript, catalog number: L00666)
5. GST-Sefinose Resin 4FF columns (Sangon, catalog number: C600031)
6. Superdex 200 Increase 10/300 GL column (Cytiva, catalog number: 28990944)
7. Amicon Ultra centrifugal filter devices 10,000 MWCO (Millipore, catalog number: UFC901024)
8. Volumetric flasks, beakers, Erlenmeyer flasks
9. Pipettes (various volumes, calibrated) and pipette tips
10. Microcentrifuge tubes and centrifuge tubes (50 mL)
11. Petri dishes
12. Spreader for plating bacteria
13. Inoculation loops
14. Toothpicks (sterile, wooden)
15. Syringes
16. Syringe filters (0.22 μm, 0.45 μm)
Equipment
1. Thermocycler for PCR (Monad, model: Arhat 96)
2. Microcentrifuge (refrigerated) (Hunan Kecheng Instrument Equipment Co., model: H1-16KR)
3. Benchtop centrifuge (refrigerated) (Hunan Kecheng Instrument Equipment Co., model: H3-16KR)
4. Ultracentrifuge (refrigerated) (Beckman Coulter, model: optima xpn-100)
5. French Press (JNBIO, model: JNBIO-minipro)
6. NanoDrop (YoMin, model: Unano-1000)
7. Gel electrophoresis apparatus HET (Yeasen, catalog number: 80230ES01)
8. Power supply for agarose and SDS-PAGE EpPlus (Yeasen, catalog number: 80311ES05)
9. SDS-PAGE electrophoresis apparatus PET2 (Yeasen, catalog number: 80212ES05)
10. Gel documentation system (Clinx, model: GenoSens 2000)
11. pH meter (calibrated)
12. Magnetic stirrer and stir bars (Yeasen, model: MS400)
13. Rotary shaker/incubator (37 °C and 18 °C temperature control) (BLabotery, ZQPL-200)
14. Chromatography system (ÄKTA pure, catalog number: 21906560)
15. Autoclave (HefeiME, model: LX-B75L)
16. Static incubator (37 °C) (BLabotery, SPL-250)
17. Water bath
Software and datasets
1. SnapGene version 3.2.1 software was used for sequence analysis, primer design, PCR, and cloning stimulation
Procedure
文章信息
稿件历史记录
提交日期: Apr 14, 2025
接收日期: Jun 16, 2025
在线发布日期: Jul 9, 2025
出版日期: Jul 20, 2025
版权信息
© 2025 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
如何引用
Wei, J., Motawaa, M. and Li, Y. (2025). Thermus thermophilus CRISPR Cas6 Heterologous Expression and Purification. Bio-protocol 15(14): e5382. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5382.
分类
微生物学 > 微生物生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 分离和纯化
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 分离和纯化
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









