- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Expression and Purification of the Human Voltage-Gated Proton Channel (hHv1)
人源电压门控质子通道(hHv1)的表达与纯化方法
发布: 2025年06月20日第15卷第12期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5344 浏览次数: 1993
评审: Alessandro DidonnaAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
The voltage-gated proton channel (Hv1) is a membrane protein that dissipates acute cell proton accumulations. To understand the molecular mechanisms explaining Hv1 function, methods for purifying the protein are needed. Previously, methods were developed for expressing and purifying human Hv1 (hHv1) in yeast and later in bacteria. However, these methodologies produced low protein yields and had high production costs, considerably limiting their usefulness. The protocol described in this work was developed to overcome those limitations. hHv1 is overexpressed in bacteria, solubilized with the detergent Anzergent 3–12, and purified by immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC) and size-exclusion chromatography (SEC). Our protocol produced higher protein yields at lower costs than previously published methodologies.
Key features
• hHv1, containing a poly-His tag followed by an enterokinase cutting site in its N-terminus, is overexpressed in E. coli by autoinduction.
• The detergent Anzergent 3–12 is used to solubilize and purify hHv1 using nickel-immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC).
• The entire procedure can be performed in 6 days.
Keywords: Voltage-gated proton channel (Hv1) (电压门控质子通道(Hv1))Graphical overview
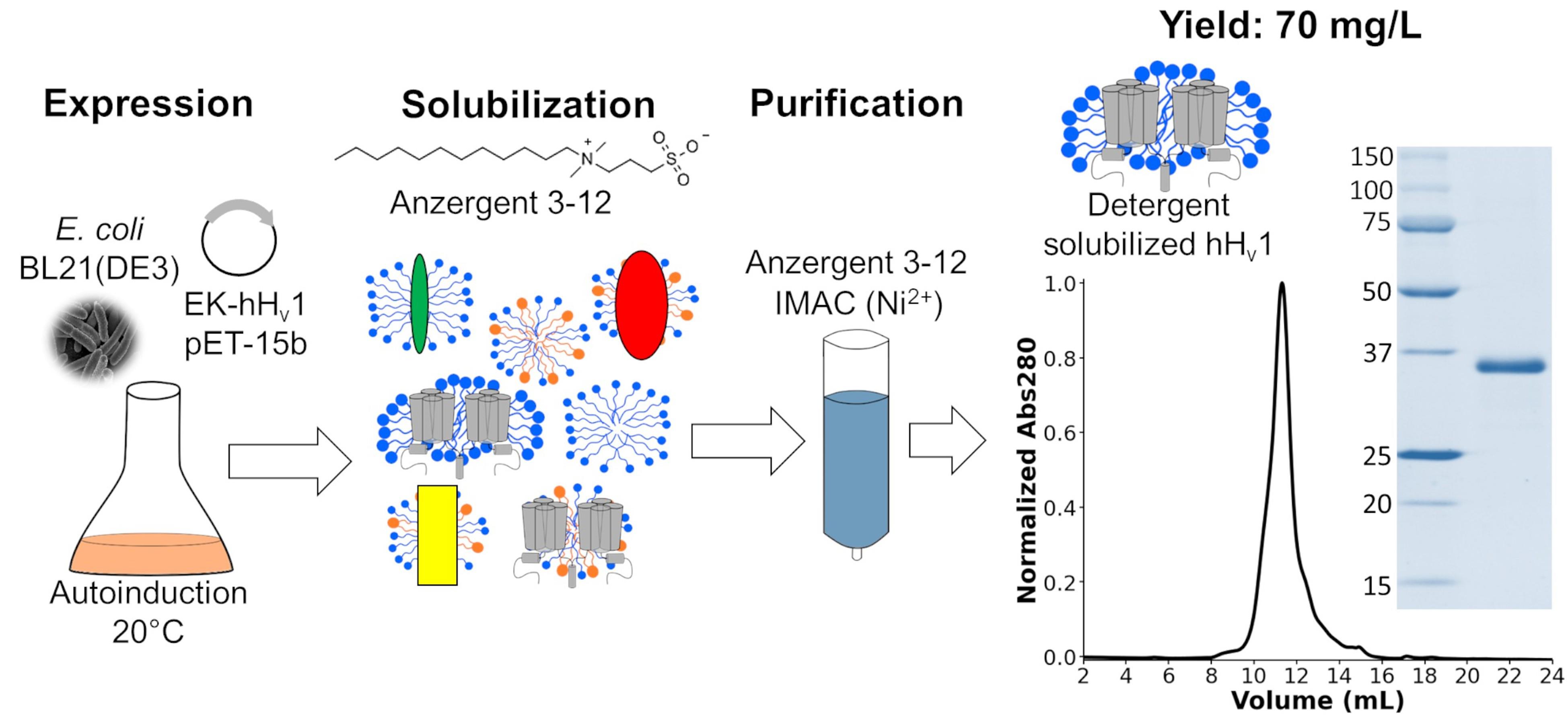
Background
The voltage-gated proton channel (Hv1) is a membrane protein that contains a highly selective permeation pathway for protons [1,2]. The opening of this proton permeation pathway is regulated by voltage [3,4], pH gradients [4,5], mechanical forces [6], and ligand binding [6–9]. The structural basis of these Hv1 biophysical properties is still poorly understood, including its permeation pathway location, sensitivity to pH gradients, mechanosensitivity, cooperativity of opening, and ligand binding sites. This missing knowledge is needed to use Hv1 as a therapeutic target for diseases such as immune disorders [10], diabetes [11], inflammatory pain [12], and cancer [13]. Most biophysical and structural studies require high quantities of stable and functional recombinant Hv1, which has been challenging to achieve. Initially, insect cells were used to express a chimeric recombinant mouse Hv1 to obtain its structure by X-ray crystallography [14]; later, the human Hv1 (hHv1) was expressed and purified using yeasts [15]. Finally, a new methodology was developed to produce hHv1 in E. coli for an electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) study [16]. Other authors have used this last protocol to study hHv1 using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) [17] and single-molecule Förster energy transfer (sm-FRET) [18]. Nevertheless, this protocol had two main limitations: i) the protein yield was low (0.7 mg per liter of culture), and ii) the expensive detergents Fos-choline 12 and 14 were used to purify the protein. Recognizing these limitations, we optimized each step of the protocol to produce a new method that increased the protein yield up to 70 mg per liter of culture and decreased costs using the more economical detergent Anzergent 3–12. The final purified hHv1 protein is stable and functional [19]. Here, we describe such a protocol in detail to accelerate hHv1 research.
Materials and reagents
Biological materials
1. BL21-Gold(DE3) competent cells (Agilent, catalog number: 200131)
2. pHis-EK-hHv1.pET15-b (source and sequence in Dataset S1)
3. Mouse α-penta-His antibody (Qiagen, catalog number: 34660)
4. StarBright Blue 700 goat α-mouse IgG (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 12004158)
Reagents
1. Tryptone (Fisher, catalog number: BP1421)
2. Yeast extract (Fisher, catalog number: BP1422)
3. NaCl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S9888)
4. PEG (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P3640)
5. MgSO4·7H2O (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M-9397)
6. MgCl2·6H2O (Fisher, catalog number: BP214)
7. Glycerol (Fisher, catalog number: G33-4)
8. Sterile-filtered DMSO (GoldBio, catalog number: D-361)
9. Ampicillin (sodium) (GoldBio, catalog number: A-301)
10. KCl (Fisher, catalog number: P217)
11. Glucose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G6152)
12. 1,000× trace metal mixture (Teknova, catalog number: T1001)
13. Na2HPO4·7H2O (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S9390)
14. KH2PO4 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P5655)
15. NH4Cl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 213330)
16. Na2SO4 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 239313)
17. Glycerol (Fisher, catalog number: G33-4)
18. α-lactose monohydrate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: L2643)
19. Tris buffer (Invitrogen, catalog number: 15504020)
20. Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1610302)
21. Bromophenol blue sodium salt (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: B7021)
22. 2-Mercaptoethanol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M3148)
23. 10% v/v antifoam 204 (Teknova, catalog number: A6427)
24. Phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P7626)
25. Isopropanol (Fisher, catalog number: A416)
26. Benzamidine hydrochloride hydrate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: B6506)
27. Lysozyme egg white (GoldBio, catalog number: L-040)
28. DNase I, bovine pancreas (GoldBio, catalog number: D-300)
29. 10× Tris/glycine/SDS running buffer (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1610772)
30. 12% Mini-PROTEAN® stain-freeTM protein gels (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 4568045)
31. Precision plus protein unstained standards (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1610363)
32. Precision plus protein dual color standards (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1610374)
33. Ethanol (Fisher, catalog number: BP28184)
34. 5× Transfer buffer (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 10026938)
35. KCl (Fisher, catalog number: P217)
36. Tween 20 (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1706531)
37. Low-fat dry milk (Milkman)
38. TCEP HCl (GoldBio, catalog number: TCEP)
39. Anzergent 3–12 (Anatrace, catalog number: AZ312)
40. Imidazole (Thermo Scientific Chemicals, catalog number: 396745000)
41. HCl (Fisher, catalog number: AC423795000)
Solutions
1. Luria-Bertani broth (Miller) (LB) (see Recipes)
2. 1 M MgSO4 (see Recipes)
3. 1 M MgCl2 (see Recipes)
4. 50% glycerol (see Recipes)
5. Transforming and Storage Solution (TSS) (see Recipes)
6. 100 mg/mL ampicillin (see Recipes)
7. 3 M KCl (see Recipes)
8. 4 M NaCl (see Recipes)
9. 40% (w/v) glucose (see Recipes)
10. Super optimal broth with catabolite repression (SOC) (see Recipes)
11. Terrific broth (see Recipes)
12. 50× M solution (see Recipes)
13. 50 × 512 solution (see Recipes)
14. Complete autoinduction medium (AIM) (see Recipes)
15. 1 M Tris-HCl (see Recipes)
16. 4× SDS-PAGE sample buffer (see Recipes)
17. 10× buffer-H1 (see Recipes)
18. 26 mg/mL PMSF (see Recipes)
19. 200 mM benzamidine (see Recipes)
20. Lysozyme solution (see Recipes)
21. 2.5 mg/mL DNase I (see Recipes)
22. 10× Phosphate-Buffered Saline (PBS) (see Recipes)
23. PBS-Tween (PBS-T) (see Recipes)
24. Blocking solution (see Recipes)
25. 4 M NaCl (see Recipes)
26. 0.5 M TCEP (see Recipes)
27. 20% w/v Anzergent 3–12 (see Recipes)
28. Buffer-H2 (see Recipes)
29. 5 M imidazole (see Recipes)
30. Washing buffer (see Recipes)
31. Elution buffer (see Recipes)
Recipes
Note: Solutions listed below can be stored at room temperature unless indicated otherwise.
1. Luria-Bertani broth (Miller) (LB)
Prepare 500 mL of LB medium by adding the components listed below in an autoclavable bottle and dissolving them in 500 mL of ultra-pure (type 1) water. Sterilize by autoclaving at 121 °C for 30 min.
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Tryptone | 10 g/L | 5 g |
| NaCl | 10 g/L | 5 g |
| Yeast extract | 5 g/L | 2.5 g |
2. 1 M MgSO4
Dissolve 24.6 g of MgSO4·7H2O in 100 mL of ultra-pure (type 1) water. Sterilize by autoclaving at 121 °C for 30 min.
3. 1 M MgCl2
Dissolve 20.3 g of MgCl2·6H2O in 100 mL of ultra-pure (type 1) water. Sterilize by autoclaving at 121 °C for 30 min.
4. 50% glycerol
Dissolve 50 mL of glycerol in 100 mL of ultra-pure (type 1) water. Sterilize by autoclaving at 121 °C for 30 min.
5. Transforming and storage solution (TSS)
Prepare 50 mL of TSS medium by dissolving the components listed below in 47.5 mL of LB medium. Adjust the pH of the solution to 6.5. Sterilize by filtration. Finally, add 2.5 mL of filter-sterilized DMSO in sterile conditions (final concentration 5% v/v). Store at 4 °C.
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| PEG | 10% w/v | 5 g |
| 1 M MgSO4 | 20 mM | 1 mL |
| 1 M MgCl2 | 20 mM | 1 mL |
6. 100 mg/mL ampicillin
Dissolve 5 g of ampicillin in 50 mL of ultra-pure (type 1) water. Sterilize by filtration. Store at 4 °C.
7. 3 M KCl
Dissolve 22.36 g of KCl in 100 mL of ultra-pure (type 1) water.
8. 4 M NaCl
Dissolve 23.38 g of NaCl in 100 mL of ultra-pure (type 1) water.
9. 40% (w/v) glucose
Dissolve 20 g of glucose in 50 mL of ultra-pure (type 1) water. Sterilize by filtration.
10. Super optimal broth with catabolite repression (SOC)
Prepare 100 mL of SOC medium by dissolving the components listed below in ultra-pure (type 1) water. Adjust the pH of the solution to 7.0. Sterilize by filtration. Aliquot in 50 mL and store at 4 °C.
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Tryptone | 20 g/L | 2 g |
| Yeast extract | 5 g/L | 0.5 g |
| 4 M NaCl | 10 mM | 250 μL |
| 3 M KCl | 2.5 mM | 83.33 μL |
| 1 M MgCl2 | 10 mM | 1 mL |
| 1 M MgSO4 | 10 mM | 1 mL |
| 40% (w/v) glucose | 20 mM | 900.9 μL |
11. Terrific broth
Prepare 960 mL of terrific broth medium by dissolving the components listed below in ultra-pure (type 1) water. Sterilize by autoclaving at 121 °C for 30 min.
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Tryptone | 12 g/L | 12 g |
| Yeast extract | 24 g/L | 24 g |
12. 50× M solution
Prepare 1 L of solution by dissolving the components listed below in ultra-pure (type 1) water. Sterilize by autoclaving at 121 °C for 30 min. Filter the solution in sterile conditions to avoid crystal formation.
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Na2HPO4·7H2O | 1.25 M | 335.1 g |
| KH2PO4 | 1.25 M | 170 g |
| NH4Cl | 2.5 M | 134 g |
| Na2SO4 | 0.25 M | 35.5 g |
13. 50× 512 solution
Prepare 1 L of solution by dissolving the components listed below in ultra-pure (type 1) water. Sterilize by filtration.
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Glycerol | 25% w/v | 250 g |
| Glucose | 5% w/v | 50 g |
| α-lactose monohydrate | 10% w/v | 105.2 g |
14. Complete autoinduction medium (AIM)
Prepare 1 L of AIM by adding the components listed below to 960 mL of sterile terrific broth medium under sterile conditions.
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| 1 M MgSO4 | 2 mM | 2 mL |
| 1,000× trace metal mixture | 0.2× | 200 μL |
| 50× 512 solution | 1× | 20 mL |
| 50× M solution | 1× | 20 mL |
| 100 mg/mL ampicillin | 0.4 mg/mL | 4 mL |
15. 1 M Tris-HCl
Dissolve 12.1 g of Tris buffer in 70 mL ultra-pure (type 1) water. Adjust to the desired pH with HCl. Complete to 100 mL with ultra-pure (type 1) water. Sterilize by autoclaving at 121 °C for 30 min.
16. 4× SDS-PAGE sample buffer
Prepare 50 mL of solution by adding the components listed below and complete the final volume with ultra-pure (type 1) water. Aliquot 1 mL in 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tubes and store at -20 °C. This recipe is for preparing a reducing buffer. Replace the 2-mercaptoethanol with ultra-pure (type 1) water for a non-reducing buffer.
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| 1 M Tris pH 6.8 | 250 mM | 12.5 mL |
| SDS | 8% w/v | 4 g |
| Glycerol | 40% v/v | 20 mL |
| Bromophenol blue sodium salt | 0.4% w/v | 200 mg |
| 2-Mercaptoethanol | 20% v/v | 10 mL |
17. 10× buffer-H1
Prepare 1 L of solution by dissolving the components listed below in ultra-pure (type 1) water. Adjust the pH of the solution to 8.0. To prepare 1× solution, dilute 10 times with ultra-pure (type 1) water and adjust the pH to 8.0 if necessary.
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Tris | 500 mM | 60.6 g |
| NaCl | 1.5 M | 87.7 g |
18. 26 mg/mL PMSF
Dissolve 1.3 g of PMSF in 50 mL of isopropanol. Store at room temperature, protected from light.
19. 200 mM benzamidine
Dissolve 1.64 g of benzamidine hydrochloride hydrate in 50 mL of cold ultra-pure (type 1) water. Aliquot and store at -20 °C.
20. Lysozyme solution
Prepare 50 mL of solution by supplementing cold 1× buffer-H1 with the components listed below. Prepare just before use and keep at 4 °C.
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| 200 mM benzamidine | 1 mM | 250 μL |
| 26 mg/mL PMSF | 0.17 mg/mL | 327 μL |
| 2-Mercaptoethanol | 2 mM | 7 μL |
| Lysozyme | 0.5 mg/mL | 25 mg |
21. 2.5 mg/mL DNase I
Prepare 20 mL of solution by dissolving the components listed below in cold, ultra-pure (type 1) water. Aliquot 1 mL in 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tubes and store at -20 °C.
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| 1 M Tris pH 7.5 | 20 mM | 0.8 mL |
| 1 M MgCl2 | 1 mM | 40 μL |
| DNase I | 2.5 mg/mL | 100 mg |
| Glycerol | 50% v/v | 20 mL |
22. 10× phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)
Prepare 1 L of solution by dissolving the components listed below in ultra-pure (type 1) water. Adjust the pH of the solution to 7.5. To prepare 1× solution, dilute 10 times with ultra-pure (type 1) water.
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Na2HPO4·7H2O | 100 mM | 26.8 g |
| NaCl | 1.37 M | 80 g |
| KCl | 27 mM | 2 g |
| KH2PO4 | 18 mM | 2.4 g |
23. PBS-Tween (PBS-T)
Add 0.5 mL of Tween 20 to 1 L of 1× PBS (0.05% Tween 20).
24. Blocking solution
Dissolve 2.5 g of low-fat dry milk in 50 mL of PBS-T.
25. 4 M NaCl
Dissolve 233.76 g of NaCl in 1 L of ultra-pure (type 1) water.
26. 0.5 M TCEP
Prepare 40 mL of solution by dissolving 5.733 g of TCEP-HCl in 25 mL of chilled ultra-pure (type 1) water. Bring the solution’s pH to 7.0 with a 10 M NaOH solution (around 7.5 mL). Complete the final volume to 40 mL, aliquot, and store at -20 °C.
27. 20% w/v Anzergent 3–12
Prepare 50 mL of solution by dissolving 10 g of Anzergent 3–12 in 50 mL of ultra-pure (type 1) water. Store at 4 °C.
28. Buffer-H2
Prepare 100 mL of solution by adding the components listed below in ultra-pure (type 1) water. Adjust the pH of the solution to 8.0. Since the 1× buffer-H1 contains 150 mM NaCl, adding 350 mM NaCl results in a final concentration of 500 mM NaCl.
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| 10× buffer-H1 | 1× | 10 mL |
| 4 M NaCl | 350 mM (500 mM total) | 8.75 mL |
| 20% w/v Anzergent 3–12 | 0.4% w/v | 2 mL |
29. 5 M imidazole
Prepare 200 mL of solution by dissolving 68.08 g of imidazole in 100 mL of ultra-pure (type 1) water. Adjust pH to 8.0. Complete volume to 200 mL with ultra-pure (type 1) water.
30. Washing buffer
Prepare 100 mL of solution by adding the components listed below in ultra-pure (type 1) water. Adjust the pH of the solution to 8.0. Since the 1× buffer-H1 contains 150 mM NaCl, adding 350 mM NaCl results in a final concentration of 500 mM NaCl. Supplement with 2 mM TCEP (400 μL of 0.5 M TCEP) and 0.17 mg/mL PMSF (654 μL of 26 mg/mL PMSF) just before use.
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| 10× buffer-H1 | 1× | 10 mL |
| 4 M NaCl | 350 mM (500 mM total) | 8.75 mL |
| 5 M imidazole | 50 mM | 1 mL |
| 20% w/v Anzergent 3–12 | 0.4% w/v | 2 mL |
31. Elution buffer
Prepare 100 mL of solution by adding the components listed below in ultra-pure (type 1) water. Adjust the pH of the solution to 8.0. Since the 1× buffer-H1 contains 150 mM NaCl, adding 350 mM NaCl results in a final concentration of 500 mM NaCl. Supplement with 2 mM TCEP (400 μL of 0.5 M TCEP) just before use.
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| 10× buffer-H1 | 1× | 10 mL |
| 4 M NaCl | 350 mM (500 mM total) | 8.75 mL |
| 5 M imidazole | 500 mM | 10 mL |
| 20% w/v Anzergent 3–12 | 0.4% w/v | 2 mL |
Laboratory supplies
1. Pyrex® round media storage bottles and reusable screw caps (Corning, catalog number: CLS1395)
2. Pyrex® VistaTM test tubes 25 × 150 mm (Corning, catalog number: 70800)
3. Foam plugs for test tubes and laboratory flasks (Chemglass Life Sciences, catalog number: CGE-1490)
4. Pyrex® baffled shaker flasks (Corning, catalog number: 4444)
5. Sterile 15 mL and 50 mL conical polypropylene centrifuge tubes (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 339650)
6. Sterile 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tubes (Corning, catalog number: MCT-150-C)
7. Falcon® sterile polypropylene round-bottom tubes (Corning, catalog number: 352059)
8. PYREX® 2800 mL Fernbach-style culture flask with baffles (Corning, catalog number: 4423-2XL)
9. Glass beads, acid-washed (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G8772)
10. 0.6 mL microcentrifuge tubes (Corning, catalog number: MCT-060-C)
11. 1 L polycarbonate bottle assembly (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: C31600)
12. PVDF membrane (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1620264)
13. His-Pur Ni-NTA resin (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 88222)
14. Econo-Pac® chromatography column (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 7321010)
15. Vivaspin® Turbo 15 PES centrifugal concentrator (Sartorius, catalog number: VS15T32)
16. ENrich SEC 650 column (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 7801650)
17. Disposable polystyrene cuvettes (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 2239955)
Equipment
1. Synergy UV R water purification system (Millipore, model: SYNSVR000)
2. Incubator shaker (Infors HT, model: Multitron, SM100116-HC)
3. Refrigerated centrifuge (Beckman Coulter, model: Avanti J-26 XPI)
4. JS-5.3 AllSpin swinging-bucket rotor and buckets (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 368690)
5. Water bath (Fisher Scientific, model: 202S)
6. Spectrophotometer to measure OD600 (Implen, model: DiluPhotometer OD600)
7. Benchtop microcentrifuge (Fisher Scientific, model: accuSpin Micro 17R)
8. J-LITE JLA-8.1000 fixed-angle aluminum rotor (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 363688)
9. Digital sonifier (Branson, model: SFX 250)
10. Ultracentrifuge (Beckman, model: Optima XL-80K)
11. Type 45 Ti fixed-angle titanium rotor (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 339160)
12. Electrophoresis chamber (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1658004)
13. Power supply (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1645050)
14. Gel Doc EZ system (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1708270)
15. Stain-free sample tray (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1708274)
16. Trans-Blot® TurboTM transfer system (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1704150)
17. ChemiDoc MP imaging system (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 12003154)
18. NGC Quest 10 Plus chromatography system (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 7880003)
19. Spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, model: NanoDrop Lite)
20. Steam sterilizer autoclave (Market Forge, model: STM-E)
Procedure
文章信息
稿件历史记录
提交日期: Apr 8, 2025
接收日期: May 13, 2025
在线发布日期: May 30, 2025
出版日期: Jun 20, 2025
版权信息
© 2025 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
如何引用
Carmona, E. M., Cortes, D. M. and Cuello, L. G. (2025). Expression and Purification of the Human Voltage-Gated Proton Channel (hHv1). Bio-protocol 15(12): e5344. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5344.
分类
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 分离和纯化
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 表达
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link













