- EN - English
- CN - 中文
PI(4,5)P2 Imaging Using a GFP Reporter in Living Cells
利用GFP报告蛋白在活细胞中成像PI(4,5)P₂
发布: 2025年06月05日第15卷第11期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5336 浏览次数: 1904
评审: Thirupugal GovindarajanAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate [PI(4,5)P2] is a phospholipid enriched on the cytoplasmic leaflet of the plasma membrane, where it plays important roles in membrane trafficking and cytoskeletal dynamics through proteins that directly bind to it. PI(4,5)P2 can be metabolized to other phosphorylated forms of phosphatidylinositol to regulate numerous processes such as cell growth and development. PI(4,5)P2 can also be hydrolyzed to generate the second messengers diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol triphosphate (IP3). Altered metabolism or mislocalization of PI(4,5)P2 can perturb one or more of its functions and contribute to disease states. Here, we present a protocol to visualize and quantify the localization of PI(4,5)P2 in live cells. The protocol uses a highly specific PI(4,5)P2 protein binding domain coupled to enhanced green fluorescence protein (PH-PLCD1-GFP), enabling localization and quantification of cytosol-facing PI(4,5)P2 to be determined. Localization and quantification of the PH-PLCD1-GFP, PI(4,5)P2 specific probe, is enabled by fluorescence imaging and confocal microscopy. This approach can be used to study the dynamics of PI(4,5)P2 localization temporally in live cells under both physiological and pathological conditions.
Key features
• Protocol for the quantification of PI(4,5)P2 membrane localization in live cells.
• Uses the expression of the highly specific PH-PLCD1-GFP, PI(4,5)P2 probe, in cells, followed by fluorescence image acquisition using confocal microscopy and subsequent image processing.
• Adaptable to various cell types and experimental conditions.
• Presents detailed instructions for reagent preparation, fluorescence measurement, and quantification.
Keywords: PI(4,5)P2 (PI(4,5)P2)Graphical overview
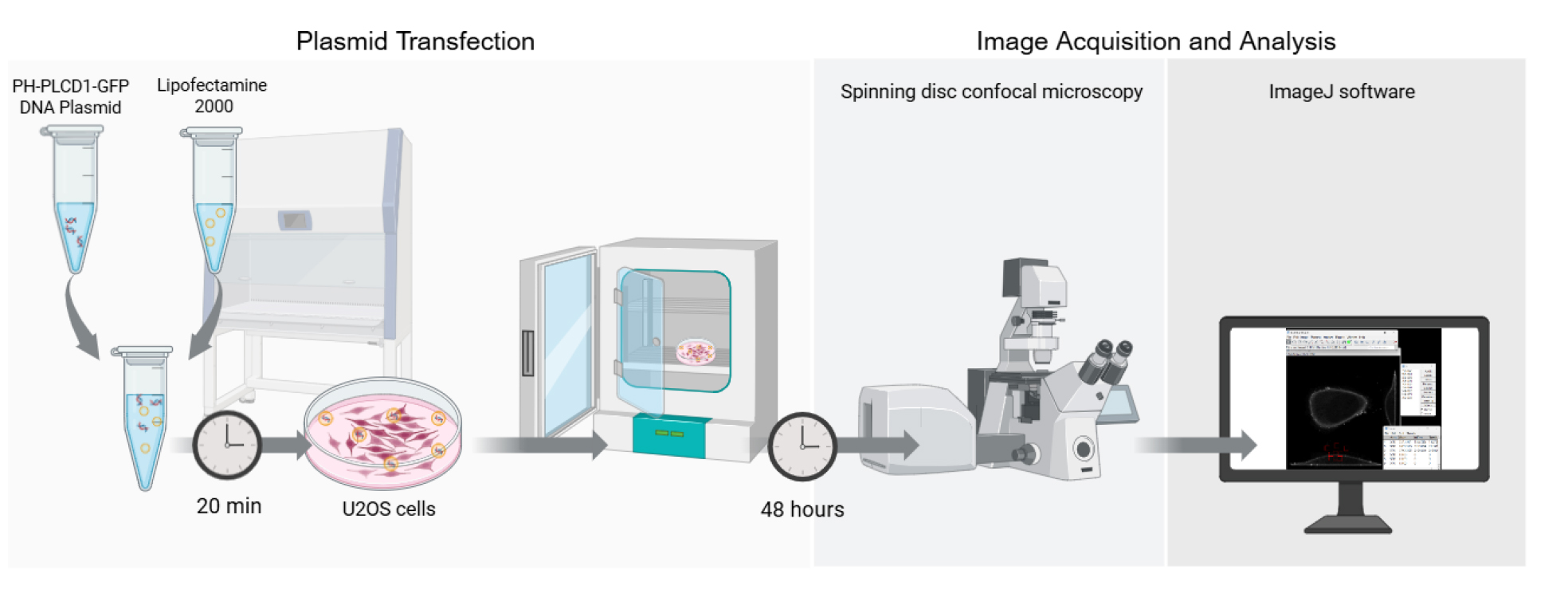
Graphical overview of the key steps for quantifying PI(4,5)P2 localization in living cells
Background
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate [PI(4,5)P2] is a phospholipid that belongs to the phosphoinositide family. Phosphoinositides are phosphorylated derivatives of phosphatidylinositol that can be further phosphorylated at different positions on the inositol ring to generate a variety of distinct lipid signaling molecules [1,2]. PI(4,5)P2 is a phosphoinositide that is preferentially localized to the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane [3–5]. PI(4,5)P2 can bind to numerous proteins, often through a distinct PI(4,5)P2 binding domain, with exemplars including Pleckstrin homology (PH) domain, Phox (PX) homology domain, Postsynaptic Density-95 (PSD-95)/Discs Large (Dlg)/Zonula Occludens-1 (PDZ), Protein Kinase C conserved Region 2 (C2), Src Homology 2 (SH2), Plant Homeodomain (PHD), and Myristoylated Alanine-Rich C-Kinase Substrate (MARCKS) domains [2,6–10]. This binding often aids in the localization of a protein to the plasma membrane, where they regulate numerous processes such as membrane trafficking and cytoskeletal dynamics [1,5,7–11]. PI(4,5)P2 also serves as a substrate for phospholipase Cs that convert PI(4,5)P2 to diacylglycerol and inositol triphosphate (IP3). Diacylglycerol can itself recruit proteins to membranes, including members of the protein kinase C family, while IP3 releases Ca2+ from the endoplasmic reticulum [12,13]. Perturbation of the level or localization of PI(4,5)P2 can have profound effects on cell dynamics and cell signaling and contribute to disease states [14–16].
Numerous phosphoinositide binding domains have varying affinities and specificities for each phosphoinositide [2,3,17]. The PH domain of phospholipase C delta (PH-PLCD1) has high affinity and specificity for PI(4,5)P2, and a chimeric PH-PLCD1-GFP fusion is an accurate reporter for PI(4,5)P2 localization [5,6,11,17,18]. This interaction has been validated in multiple species and cell types, including mammalian cells, Xenopus oocytes, Drosophila, and yeast, supporting its broad applicability [19–22]. Our optimized protocol allows for the visualization of PI(4,5)P2 and enables the quantification of the ratio of plasma membrane to intracellular PI(4,5)P2. Using the PH-PLCD1-GFP fusion allows for real-time high-resolution tracking of PI(4,5)P2 in live cells. This protocol serves as a comprehensive step-by-step guide providing a standardized approach to quantify PI(4,5)P2 plasma membrane localization.
Materials and reagents
Biological materials
1. U20S cells (ATCC, HTB-96)
2. PH-PLCD1-GFP plasmid (Addgene, plasmid #51407; map available at: https://www.addgene.org/51407)
Reagents
1. Lipofectamine 2000 (InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 11668019)
2. Opti-MEM (Gibco, catalog number: 31985070)
3. DMEM, high glucose (Gibco, catalog number: 11965092)
4. Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Gibco, catalog number: A3160502)
5. Antibiotic-antimycotic (AA) (100×) (Gibco, catalog number: 15240062)
Laboratory supplies
1. Two-chamber Lab-Tek® II chambered German coverslip system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 155379)
2. 1.5 mL Eppendorf tubes (Eppendorf, catalog number: 0540294)
3. Eppendorf Research® pipettes, 0.5–10 μL, 10–100 μL, 20–200 μL, 100–1,000 μL (Eppendorf, catalog number: 3123000942)
4. Biosphere® plus filter tip, 1000 μL, 200 μL, 100 μL, 10 μL (Sarstedt)
Equipment
1. Zeiss Axio Observer Z.1 spinning disk confocal microscope (Carl Zeiss AG)
2. Automated cell counter (Bio-Rad, model: 1450102)
3. Cell counting dual-chambered slides (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1450011)
4. Tissue culture incubator, 37 °C, 5% CO2 (Eppendorf, model: CellXpert® C170i)
5. Tissue culture hood, class II biosafety cabinet (Bio-Klone, model: BK-2-4)
Software and datasets
1. ZEISS ZEN (version 3.1; Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH, Jena, Germany)
2. Fiji (ImageJ-win64; version 1.54; https://imagej.net/software/fiji/downloads)
3. Microsoft Excel (version 2502; Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA)
4. GraphPad Prism (version 10; GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA)
Procedure
文章信息
稿件历史记录
提交日期: Mar 16, 2025
接收日期: May 8, 2025
在线发布日期: May 23, 2025
出版日期: Jun 5, 2025
版权信息
© 2025 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
如何引用
Alkandari, M., McMaster, C. R. and Tavasoli, M. (2025). PI(4,5)P2 Imaging Using a GFP Reporter in Living Cells. Bio-protocol 15(11): e5336. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5336.
分类
细胞生物学 > 细胞结构 > 细胞质膜
生物化学 > 脂质 > 膜脂
细胞生物学 > 细胞成像 > 荧光
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link